Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: LaBoy C, Siziopikou KP. Fibromatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastfibromatosis.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Low grade infiltrative spindle cell neoplasm composed of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts
Essential features
- Rare low grade neoplasm with infiltrative pattern
- Bland spindle cells arranged in long intersecting fascicles within a collagenous stroma
- Characterized by alterations in WNT / beta catenin pathway
- Does not metastasize but can locally recur after surgical excision
Terminology
- Desmoid tumor, aggressive fibromatosis, desmoid type fibromatosis, extra-abdominal desmoid
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8821/1 - desmoid type fibromatosis
- ICD-11: 2F75 & XH13Z3 - neoplasms of uncertain behavior of breast & aggressive fibromatosis
Epidemiology
- < 0.2% of tumors of the breast
- F > M, third through fifth decades
- Reference: Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77
Sites
- May be primary to the breast or be secondary extension into the breast from the chest wall
Pathophysiology
- Up to 95% harbor CTNNB1 activating mutation (sporadic); APC gene inactivating mutation responsible for remainder of cases (hereditary) (Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:1851)
- Through the WNT / beta catenin pathway, these mutations motivate cells to proliferate while destabilizing beta catenin that then accumulates within the nucleus (J Clin Oncol 2018;36:202)
Etiology
- Can consequently occur after surgery, trauma or rarely, after breast implants (Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:1851)
- Estrogen thought to influence growth (Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77, Indian J Surg Oncol 2020;11:71)
- Can be associated with Gardner syndrome or familial adenomatous polyposis
Clinical features
- Slow growing, often self detected firm mass
Diagnosis
- May arise as palpable mass that appears as abnormality on mammography
- Rarely presents with breast pain, nipple discharge and skin retraction (Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77)
Radiology description
- Imaging may show well circumscribed mass or poorly defined / spiculated mass that can be mistaken for malignant process (Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Does not metastasize (Pathologica 2019;111:344)
- Locally aggressive, local recurrence rates reported in 29% to as high as 40 - 50% of cases after excision (Ann Surg Oncol 2008;15:274, J Clin Oncol 2018;36:202)
- Margin status not reliable risk factor for recurrence (J Clin Oncol 2018;36:202, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:1851)
Case reports
- 25 year old woman with indentation and pain in left inframammary fold (Radiol Case Rep 2018;13:1174)
- 31 year old woman with dimpling in the left breast (Int J Surg Case Rep 2017;41:392)
- 36 year old woman with rapidly growing lump in right breast (Oncol Lett 2017;14:1433)
- 42 year old woman with breast implants and palpable lump in left breast (Radiol Case Rep 2017;12:431)
- 60 year old man with 2 year history of right breast mass (Chirurgia (Bucur) 2019;114:664)
Treatment
- Surgical local excision
- Other options include active surveillance for asymptomatic patients and systemic therapy, such as adjuvant radiation for patients with multiple recurrences (Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77, Cancers (Basel) 2020;12:1851)
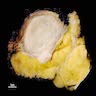
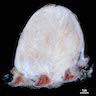
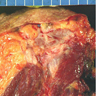
Gross description
- Well to poorly circumscribed mass of variable size (from < 1 cm to > 10 cm), with white-gray whorled or trabeculated cut surface
Frozen section description
- Bland spindle cells seen on intraoperative frozen section would prompt benign diagnosis
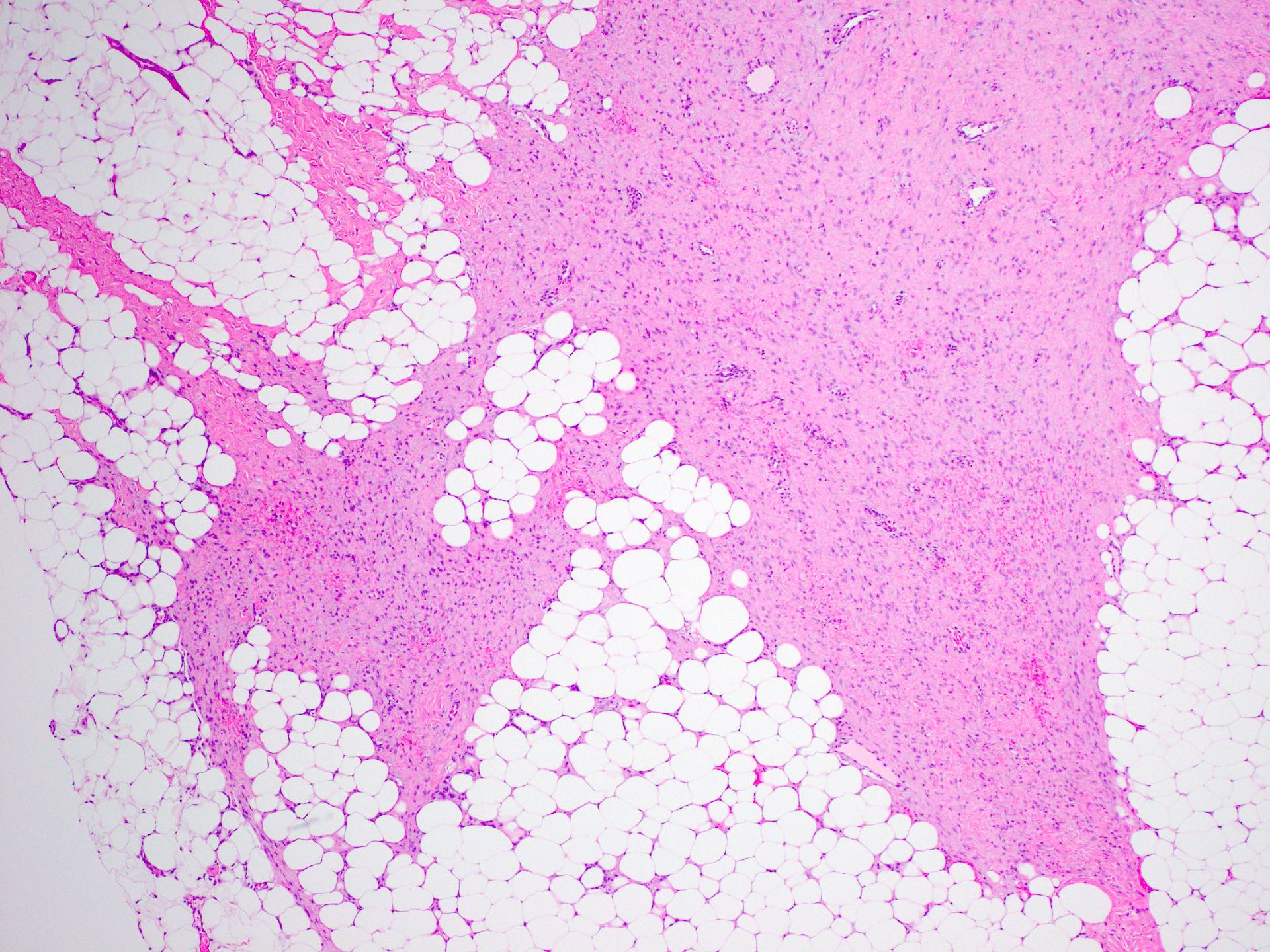
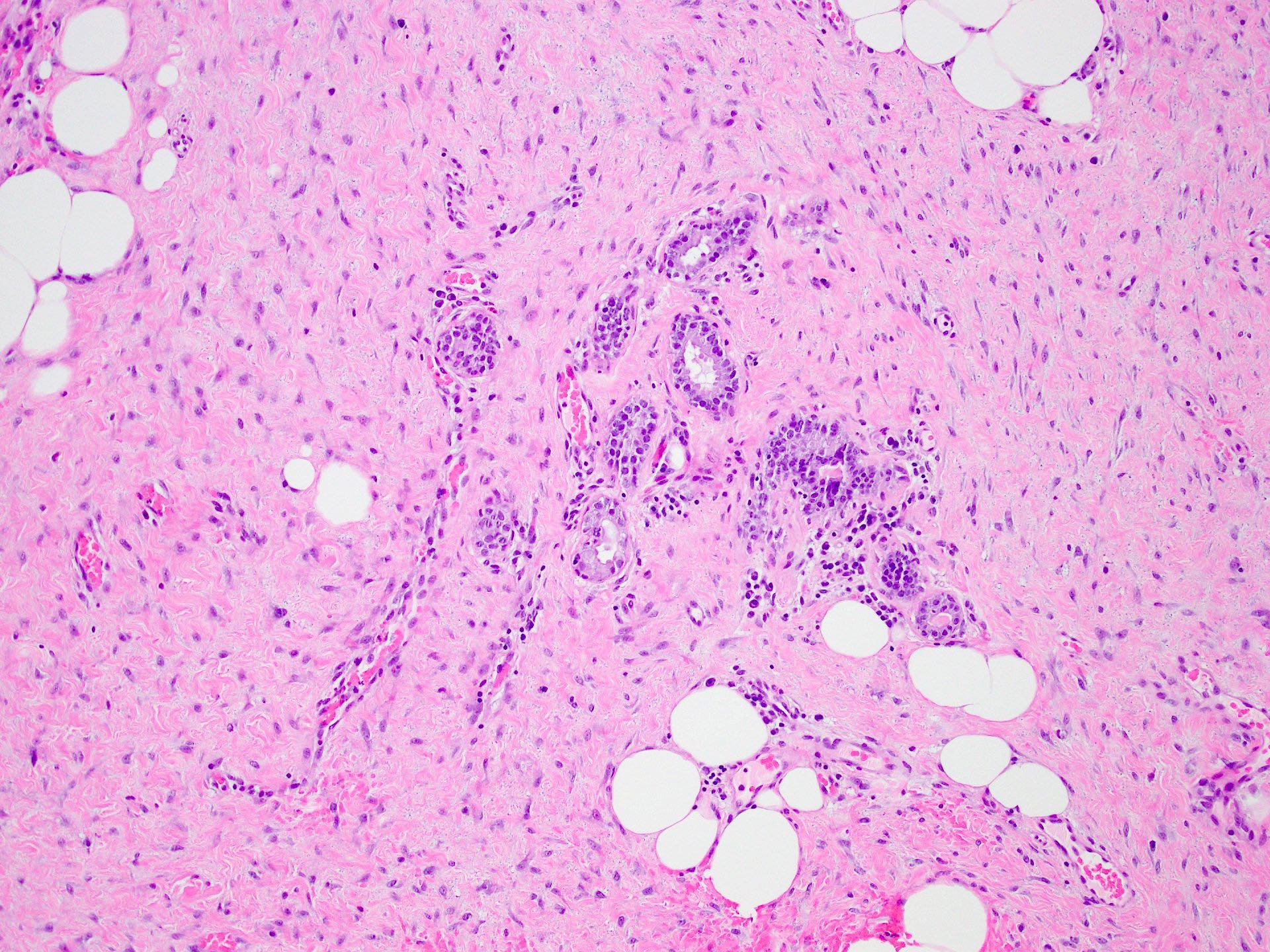
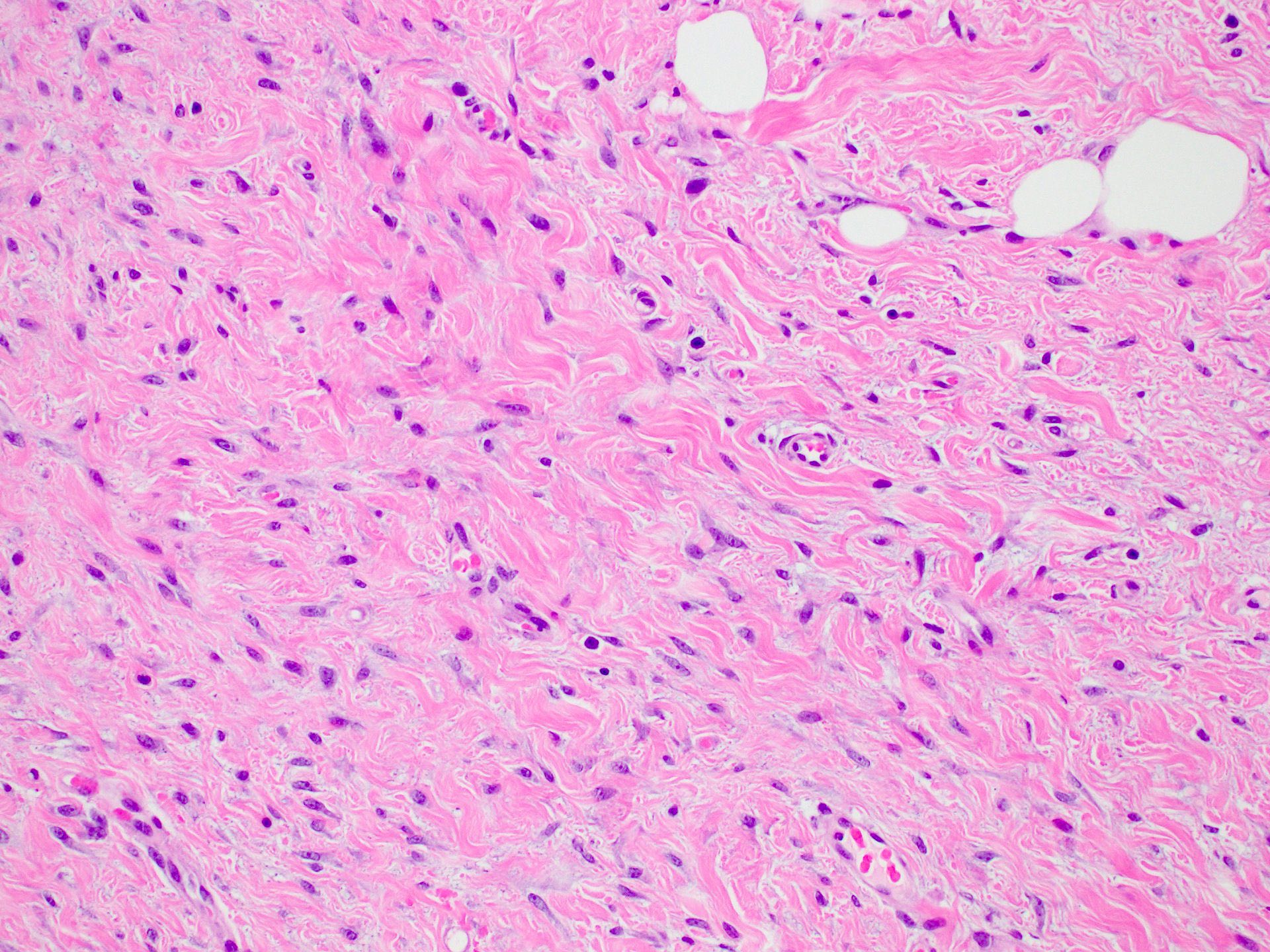
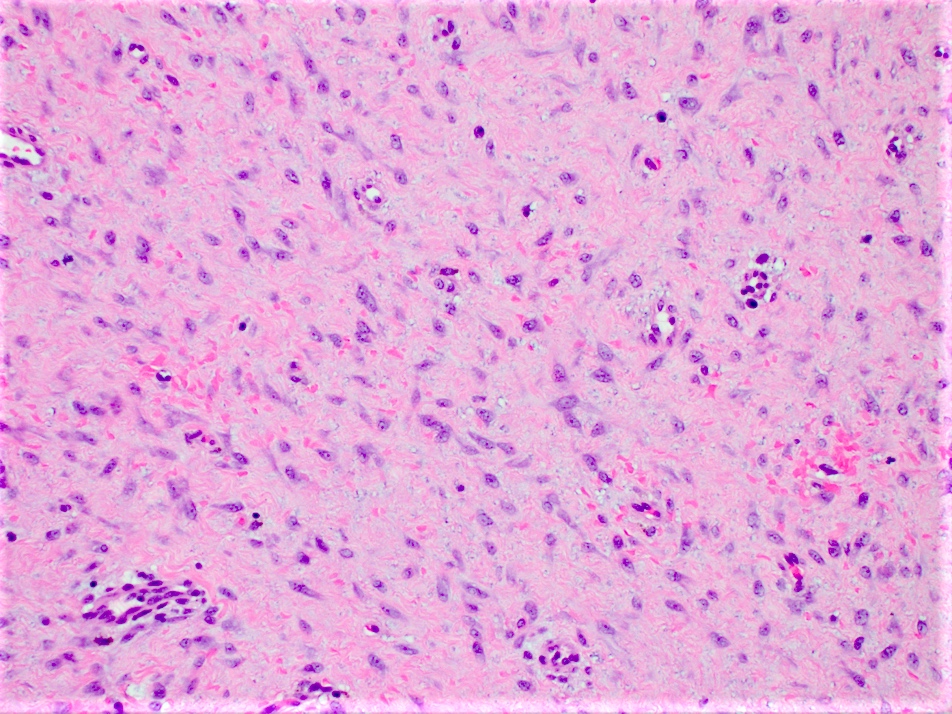
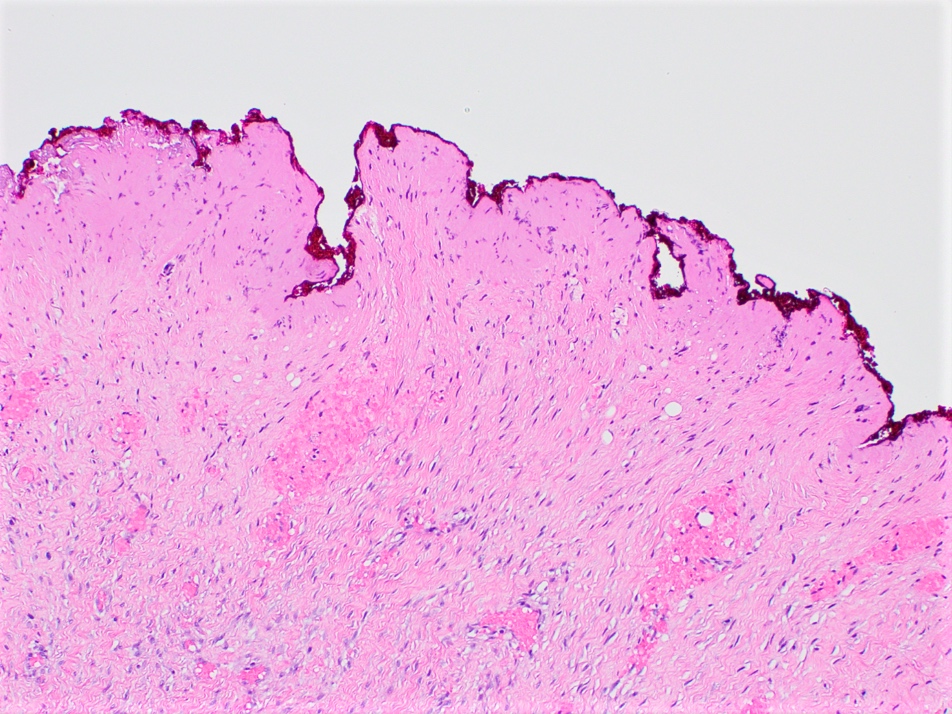
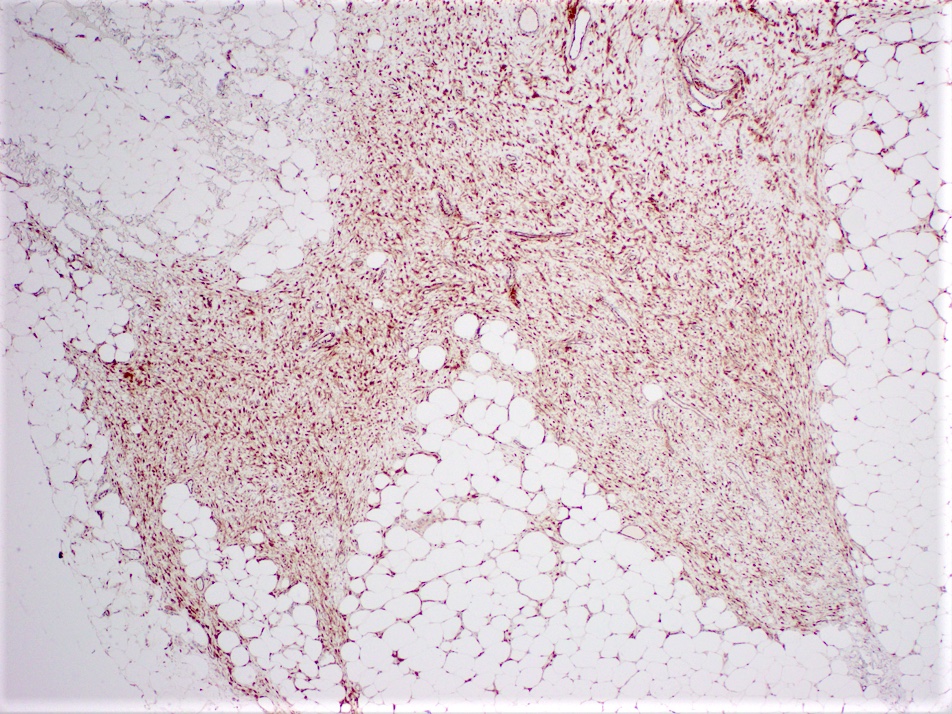
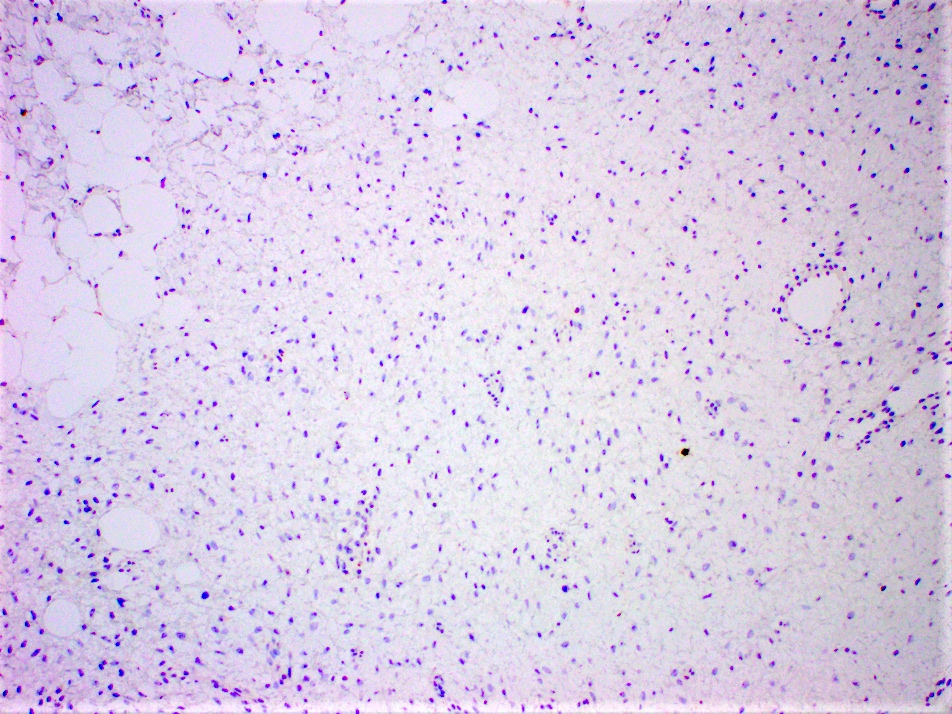
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Long intersecting fascicles composed of bland spindle cells with indistinct borders, hyperchromatic nuclei with occasional nucleoli and eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Cells infiltrate normal ducts and lobules, adipose tissue and skeletal muscle, thus mimicking invasive process
- Mitosis is rare
- Background stroma has thickened collagen resembling keloid
- Older lesions may calcify
- Lymphoid aggregates may be seen at the periphery of the lesion
- Reference: Pathologica 2019;111:344
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Fine needle aspiration is difficult and often yields fibrous nondiagnostic material
- When successful, fine needle aspiration shows bland spindle cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and wispy cytoplasm within abundant stroma (Cancer 2007;111:166)
Cytology images
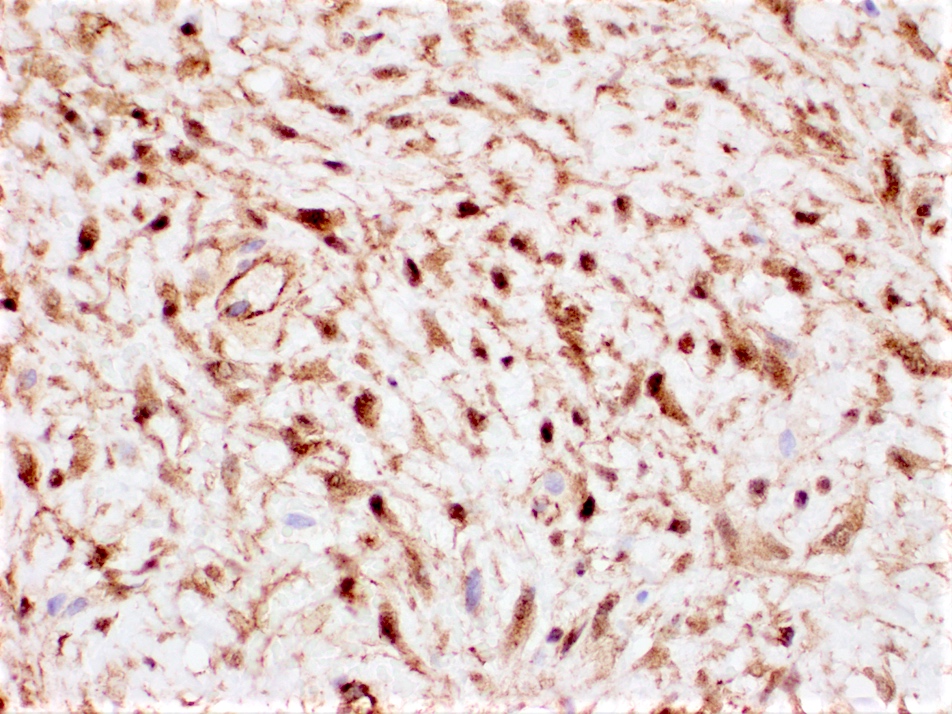
Positive stains
- Beta catenin (80% of cases) (Pathologica 2019;111:344)
- Not specific, can also be positive in spindle cell carcinomas, metaplastic breast carcinomas and benign phyllodes tumors (Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77)
- SMA
- Calponin
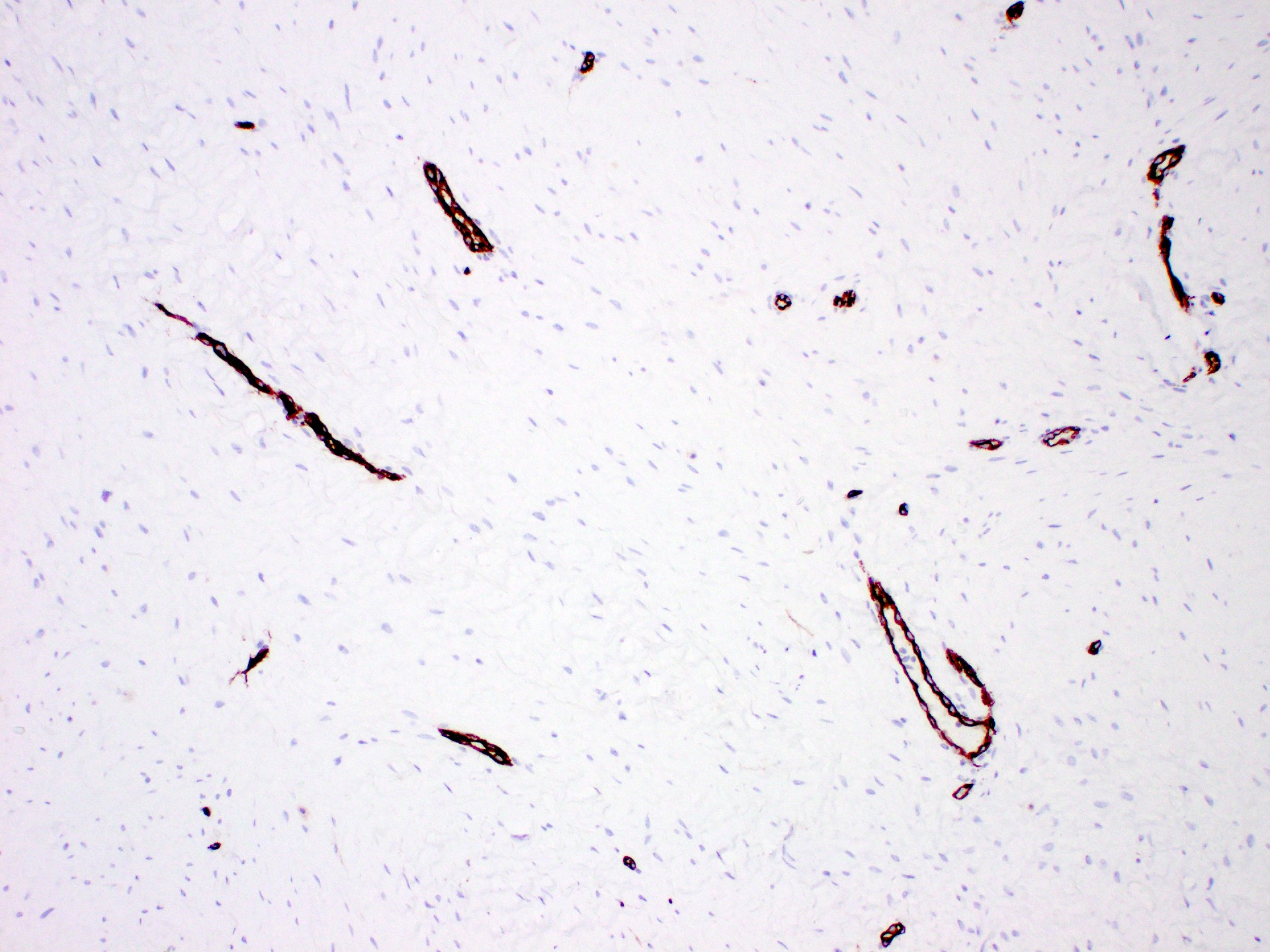
Negative stains
- Pancytokeratin
- p63
- CD34
- ER
- PR
- HER2
- Reference: Breast Care (Basel) 2021;16:77
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Sequencing can identify activating CTNNB1 mutation or inactivating APC mutation in 79% of cases (Hum Pathol 2002;33:39, Curr Opin Oncol 2017;29:268)
- Trisomies in chromosome 8 or 20 occur, significance is unknown (J Clin Oncol 2018;36:202)
Videos
Review of fibromatosis
Sample pathology report
- Left breast, needle localized lumpectomy:
- Fibromatosis, measuring 2.8 cm in greatest dimension
- Margins negative with tumor > 0.5 cm from all margins
Differential diagnosis
- Scar:
- Focally infiltrative lesion composed of bland spindle cells with associated histiocytes, foreign body giant cell reaction and lymphocytes
- History of prior procedure
- Nodular fasciitis:
- Focally infiltrative lesion composed of spindle cells forming short fascicles or storiform pattern with increased mitotic activity
- Does not display nuclear beta catenin staining
- Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans:
- Focally infiltrative lesion with spindle cells in storiform growth pattern and low mitotic activity
- Low grade fibromatosis-like metaplastic carcinoma:
- Infiltrative lesion composed of spindle to epithelioid cells arranged in small clusters with low mitotic activity
- Cytokeratin and p63 positive
- Low grade myofibroblastic sarcoma:
- Focally infiltrative lesion composed of spindle cells arranged in fascicles
- Mild to moderate nuclear pleomorphism and brisk mitosis
- Myofibroblastoma:
- Spindle cells arranged in short, disorganized fascicles with intersecting thick collagen bands resembling keloid; do not typically entrap normal ducts or lobules
- Benign phyllodes tumor:
- Well circumscribed mass with hyperplastic epithelium within a hypercellular stroma composed of spindle cells with mild atypia and low mitotic activity
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Nuclear. The pathophysiology of fibromatosis involves an activating CTNNB1 mutation in sporadic cases and an APC gene inactivating mutation in hereditary cases. Both types of mutations activate the WNT / beta catenin pathway, motivating cells to proliferate while degrading beta catenin, which then accumulates within the nucleus. This in turn yields a nuclear pattern of staining by immunohistochemistry.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is correct regarding the histologic features and clinical behavior of breast fibromatosis?
- Chemotherapy is the preferred treatment due to high mitotic activity
- Metastasis is a common feature of this tumor
- Necrosis and pleomorphism make this a high grade tumor
- Tumor has a high frequency of local recurrence
Board review style answer #2
D. Tumor has a high frequency of local recurrence. Breast fibromatosis is a low grade tumor consisting of bland spindle cells with rare or no mitotic activity and no metastatic potential. However, due to its infiltrative nature, this tumor has a tendency to locally recur after surgical excision.
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis
Comment Here
Reference: Fibromatosis