Table of Contents
Definition / general | Trade name | Indications | Pathophysiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical information | Uses by pathologists | Side effects | Drug administration | Molecular theory | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Yeh YA. Atezolizumab. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastatezolizumab.html. Accessed December 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- A humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody blocking programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1)
- Developed by Genentech, Inc.
- Synonyms: MPDL3280A, RG7446
Trade name
- Tecentriq®
Indications
- Urothelial carcinoma locally advanced or metastatic disease fulfilling 1 of the following criteria
- Not eligible for cisplatin based chemotherapy and tumor expresses PDL1 (PDL1 stained tumor infiltrating immune cells covering ≥ 5% of the tumor area) - FDA approved 2017
- Not eligible for platinum based chemotherapy with any PDL1 staining status - FDA approved 2017 (Oncologist 2019;24:563)
- Disease progression with platinum based chemotherapy - FDA approved 2016
- Non small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) fulfilling one of the following criteria
- First line treatment for metastatic NSCLC with high PDL1 expression (PDL1 staining ≥ 50% tumor cells or immune cells ≥ 10%) and no EGFR or ALK gene alterations - FDA approved 2020
- In combination with chemotherapy (paclitaxel protein bound; nab-paclitaxel and carboplatin) for metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK gene alterations - FDA approved 2019
- In combination with bevacizumab, paclitaxel and carboplatin for metastatic nonsquamous NSCLC with no EGFR or ALK gene alterations - FDA approved 2018
- Metastatic NSCLC with EGFR or ALK gene alterations and disease progression when treated with platinum based chemotherapy - FDA approved 2016 (Lancet 2017;389:255)
- Triple negative breast cancer locally advanced or metastatic with PDL1 expression of immune cells ≥ 1% of tumor area - FDA approved 2019 (N Engl J Med 2018;379:2108)
- Small cell lung cancer advanced stage in combination with carboplatin and etoposide - FDA approved 2019 (N Engl J Med 2018;379:2220)
- Hepatocellular carcinoma in combination with bevacizumab - FDA approved 2020 (N Engl J Med 2020;382:1894)
- Melanoma unresectable or metastatic with BRAF V600 mutation in combination with cobimetinib and vemurafenib - FDA approved 2020 (Nat Med 2019;25:929)
- Reference: Drugs.com: Tecentriq FDA Approval History [Accessed 18 December 2020]
Pathophysiology
- PD1 receptor expressed on activated T cells, B cells, macrophages and NK cells (Nat Rev Immunol 2018;18:153)
- PDL1 expressed on antigen presenting cells and many types of cancer cells (Nature 2016;534:402)
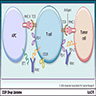
- Binding of PD1 to PDL1 or B7H1 can suppress T cell proliferation, cytokine production and cytolytic activity
- Aberrant expression of PDL1 on cancer cells through interaction with PD1 receptor blocks antitumor immunity and escape immune surveillance (Nature 2016;534:402)
- Atezolizumab, a PDL1 inhibitor, blocks the binding of PD1 with PDL1, resulting in prevention of inhibition of T cell immune response and reactivation of T cell mediated antitumor cytolytic activity (Clin Cancer Res 2017;23:1886)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical information
- Immune mediated diseases associated with treatment with atezolizumab
- Pneumonitis: withhold or discontinue based on severity (Chest 2017;152:271)
- Hepatitis: monitor liver function, withhold or discontinue
- Colitis: withhold or discontinue based on severity (JAMA Oncol 2018;4:1721)
- Endocrinopathies (JAMA Oncol 2018;4:173):
- Hypophysitis: withhold based on severity of hypophysitis
- Hyperthyroidism: monitor thyroid function
- Adrenal insufficiency: withhold based on severity
- Type 1 diabetes mellitus: withhold based on severity
- Infections: withhold for severe infection (Respir Med 2020;161:105853)
- Infusion related reactions: slow the rate of infusion or discontinue
- Embryo fetal toxicity: advise females of reproductive potential
- Pharmacokinetics (Clin Pharmacol Ther 2017;102:305):
- Dose range: 1 - 20 mg/kg, including a dose of 1,200 mg every 3 weeks
- Clearance: 0.20 L/day
- Volume of distribution: 6.91 L
- Terminal half life: 27 days
- Steady state: achieved after 6 - 9 weeks (2 - 3 cycles)
- Tecentriq treatment costs approximately $13,860 per month (Drugs.com: What Is the Cost of Tecentriq? [Accessed 17 December 2020])
Uses by pathologists
- VENTANA PDL1 SP142 Assay (Roche Diagnostics): FDA approved companion diagnostic to atezolizumab; not substitutable with other PDL1 assays (22C3, SP263) (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2019;27:92)
- Tumor cell (TC) staining: membranous, linear, partial to complete circumferential staining pattern at any intensity (Mod Pathol 2019;32:929, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:982)
- Immune cell (IC), including lymphocyte, neutrophil and macrophage staining: punctate, incomplete, membranous staining pattern at any intensity; exclude intravascular immune cells and cells in necrotic area (Mod Pathol 2019;32:929, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:982)
- Total tumor area: the area covered by tumor cells with intratumoral and peritumoral stroma
- Urothelial carcinoma: evaluate immune cells only and disregard tumor cells
- Positive: presence of staining at any intensity in immune cells ≥ 5% of tumor area
- Negative: absence of any staining in immune cells < 5% of tumor area (see PDL1 SP142) (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1059)
- NSCLC: evaluate tumor cells and then evaluate immune cells (if tumor cells negative)
- Positive: presence of staining at any intensity in tumor cells ≥ 50%
- Negative: staining at any intensity in tumor cells < 50% (proceed to immune cell count)
- Positive: presence of staining at any intensity in immune cells ≥ 10% of tumor area
- Negative: staining at any intensity in immune cells < 10% of tumor area (Histopathology 2018;72:449)
- Triple negative breast carcinoma: evaluate immune cells only and disregard tumor cells
- Positive: presence of staining at any intensity in immune cells ≥ 1% of tumor area
- Negative: staining at any intensity in immune cells < 1% of tumor area (see PDL1 SP142)
Side effects
- Tecentriq as a single agent (reported in > 20% of patients)
- Constipation, cough, decreased appetite, dyspnea, fatigue, nausea (N Engl J Med 2020;383:1328)
- Tecentriq in combination with bevacizumab, paclitaxel and carboplatin (reported in > 20% of patients)
- Arthralgia, asthenia, alopecia, constipation, decreased appetite, diarrhea, hypertension, nausea, peripheral neuropathy (N Engl J Med 2018;378:2288)
- Tecentriq in combination with paclitaxel protein bound (reported in > 20% of patients)
- Alopecia, anemia, constipation, cough, decreased appetite, diarrhea, fatigue, headache, nausea, neutropenia, peripheral neuropathies, vomiting (N Engl J Med 2018;379:2108)
- Others: hyponatremia, pneumonia, hyperkalemia, thrombocytopenia, death
- Reference: FDA: Tecentriq (atezolizumab) [Accessed 18 December 2020]
Drug administration
- For metastatic urothelial carcinoma:
- Tecentriq 1,200 mg IV over 60 min for 3 weeks
- For treatment of nonsquamous non small cell lung cancer:
- Tecentriq 1,200 mg IV over 60 minutes, followed by bevacizumab, paclitaxel and carboplatin every 3 weeks for a maximum of 4 - 6 cycles
- Following completion of chemotherapy, Tecentriq 1,200 mg IV, followed by bevacizumab every 3 weeks
- For metastatic triple negative breast cancer:
- Tecentriq 840 mg IV over 60 minutes, followed by 100 mg/m² paclitaxel
- Every 28 days, Tecentriq is administered on days 1 and 15 and paclitaxel is administered on days 1, 8 and 15
- Reference: PDR: Atezolizumab - Drug Summary [Accessed 17 December 2020]
Molecular theory
- PDL1 expressed on tumor cells, through binding to PD1, inhibits T cell immune response
- PDL1 may suppress IFN mediated cytotoxicity through a STAT3 / caspase 7 dependent signaling pathway (Sci Adv 2020;6:2712)
- The RMLDVEKC motif of PDL1 is essential to hinder interferon toxicity, while the DTSSK motif blocks this function (Sci Adv 2020;6:2712)
- PDL1 protects tumor cells from T cell dependent cytotoxicity
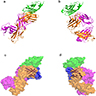
- Crystal structures of interaction of PDL1 with atezolizumab antigen binding fragment through the immunoglobulin superfamily V set domain of PDL1 (Sci Rep 2017;7:5532)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following proteins is blocked by atezolizumab?
- PD1
- PDE1
- PDGF
- PDL1
Board review style answer #1
D. PDL1. Atezolizumab is a humanized IgG1 monoclonal antibody that blocks programmed death ligand 1 (PDL1). Answers A - C are incorrect because PD1, PDGF and PDE1 are not blocked by atezolizumab.
Comment Here
Reference: Atezolizumab
Comment Here
Reference: Atezolizumab
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about the PDL1 SP142 assay?
- Evaluates percentage of tumor cells stained positive for PDL1 and disregards tumor infiltrating immune cells in non-small cell lung cancer
- Evaluates percentage of tumor cells stained positive for PDL1 and evaluates tumor infiltrating immune cells if tumor cells are negative in non-small cell lung cancer
- Evaluates percentage of tumor cells stained positive for PDL1 in triple negative breast carcinoma
- Evaluates percentage of tumor cells stained positive for PDL1 in urothelial carcinoma
Board review style answer #2
B. Evaluates percentage of tumor cells stained positive for PDL1 and evaluates tumor infiltrating immune cells if tumor cells are negative in non-small cell lung cancer. Answers C and D are incorrect because PDL1 SP142 evaluates immune cells only and disregards tumor cells in both urothelial carcinoma and triple negative breast carcinoma. Answer A is incorrect because in non-small cell lung cancer, PDL1 SP142 evaluates tumor cells and then evaluates immune cells if tumor cells are negative.
Comment Here
Reference: Atezolizumab
Comment Here
Reference: Atezolizumab