Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Sample pathology report | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Mohamed A, Geradts J. Ki67 breast. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/breastKi67.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Nuclear protein that is expressed during all active phases of the cell cycle (G1, S, G2 and M) but is absent in resting cells (G0) (Pathology 2017;49:166)
- Encoded by MKI67 gene on chromosome 10q25 (Pathology 2017;49:166)
- Ki67 expression level varies throughout the cell cycle (Pathology 2017;49:166)
Essential features
- Cellular proliferation marker that is reported as percentage of tumor cells with nuclear staining
- Low in benign tumors, luminal A carcinomas and low grade carcinomas (Breast Cancer Res 2016;18:104, Mod Pathol 2014;27:554, BMC Res Notes 2019;12:605)
- High in high grade carcinomas, triple negative breast carcinomas, HER2 positive carcinomas and luminal B carcinomas (Breast Cancer Res 2016;18:104, Mod Pathol 2014;27:554, BMC Res Notes 2019;12:605)
- Independent prognostic marker to predict disease free survival, overall survival and complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Pathology 2017;49:166, J Natl Cancer Inst 2021;113:808)
- Associated with low interlaboratory reproducibility and high interobserver variability (Breast Cancer Res 2016;18:104, J Natl Cancer Inst 2013;105:1897, Histopathology 2019;75:225)
Terminology
- MIB1 is not equivalent to Ki67; rather, it is a widely used monoclonal antibody against the Ki67 antigen (Breast Cancer 2020;27:1058)
Pathophysiology
- Anti-Ki67 antibody binds Ki67 protein in formalin fixed paraffin embedded tissue block and highlights nuclei of all cells in nonresting cell cycle phases (Pathology 2017;49:166)
- Increased expression in tumor cells is a marker of cell cycle activation and proliferative activity
- Ki67 often is heterogeneously expressed in breast carcinomas, with hot spots and inactive areas (J Natl Cancer Inst 2013;105:1897)
Clinical features
- Can be used to predict and monitor response to neoadjuvant endocrine or chemotherapy (Pathology 2017;49:166, J Natl Cancer Inst 2021;113:808)
- Used in distinguishing luminal A and luminal B breast carcinomas (Breast Cancer Res 2016;18:104, Mod Pathol 2014;27:554, BMC Res Notes 2019;12:605)
- Used by oncologists to guide adjuvant chemotherapy (Pathology 2017;49:166, J Natl Cancer Inst 2021;113:808)
- High Ki67 expression correlated with decreased survival (Pathology 2017;49:166, J Natl Cancer Inst 2021;113:808)
Interpretation
- Nuclear staining (any intensity)
- Number of tumor cells with positive staining divided by total number of tumor cells (hot spots [less reproducible] or average across tumor section [recommended]) (Pathology 2017;49:166)
- No consensus on number of tumor cells to be scored (J Natl Cancer Inst 2013;105:1897)
- Marked variability in published thresholds separating high and low scores (Pathology 2017;49:166)
- Due to significant interlaboratory and interobserver variability, thresholds ideally should be established in each laboratory (J Natl Cancer Inst 2021;113:808)
- In ER+ / HER2- T1-2, N0-1 patients Ki67 is prognostic, with Ki67 ≤ 5% considered low and Ki67 ≥ 30% considered high (J Natl Cancer Inst 2021;113:808)
- Several automated scoring algorithms for Ki67 quantitation have been developed which reduce interobserver variability (Mod Pathol 2019;32:59, Lab Invest 2019;99:107)
Uses by pathologists
- As an independent prognostic marker to predict disease free survival, overall survival and complete pathologic response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy
- Subtyping ER positive breast carcinomas into 2 prognostically distinct subtypes:
- Luminal A (low Ki67 index; better prognosis)
- Luminal B (high Ki67 index; worse prognosis) (Mod Pathol 2014;27:554)
- Ki67 IHC MIB1 pharmDx has been approved by the FDA as a companion diagnostic for detecting Ki67 expression in patients with high risk breast cancer who may be eligible for treatment with abemaciclib combined with endocrine therapy
- FDA approval of abemaciclib was restricted to patients at high risk of recurrence and with a Ki67 score ≥ 20%, as determined by an FDA approved test; however, restricting the approval to patients with a high Ki67 and the 20% cutoff is debated (Ann Oncol 2022;33:234)
Prognostic factors
- Prognostic factor in early stage, ER positive breast cancer (Breast Cancer Res 2016;18:104, Pathology 2017;49:166)
- High Ki67 expression in a breast carcinoma is associated with higher pathologic stage, higher grade, estrogen and progesterone receptor negativity, HER2 overexpression, extracapsular extension and lymphovascular invasion (Eur J Breast Health 2019;15:256)
- High Ki67 index is associated with shortened disease free survival and overall survival (Breast Cancer Res Treat 2013;139:539)
- High Ki67 proliferative index is a predictive marker for pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e9384)
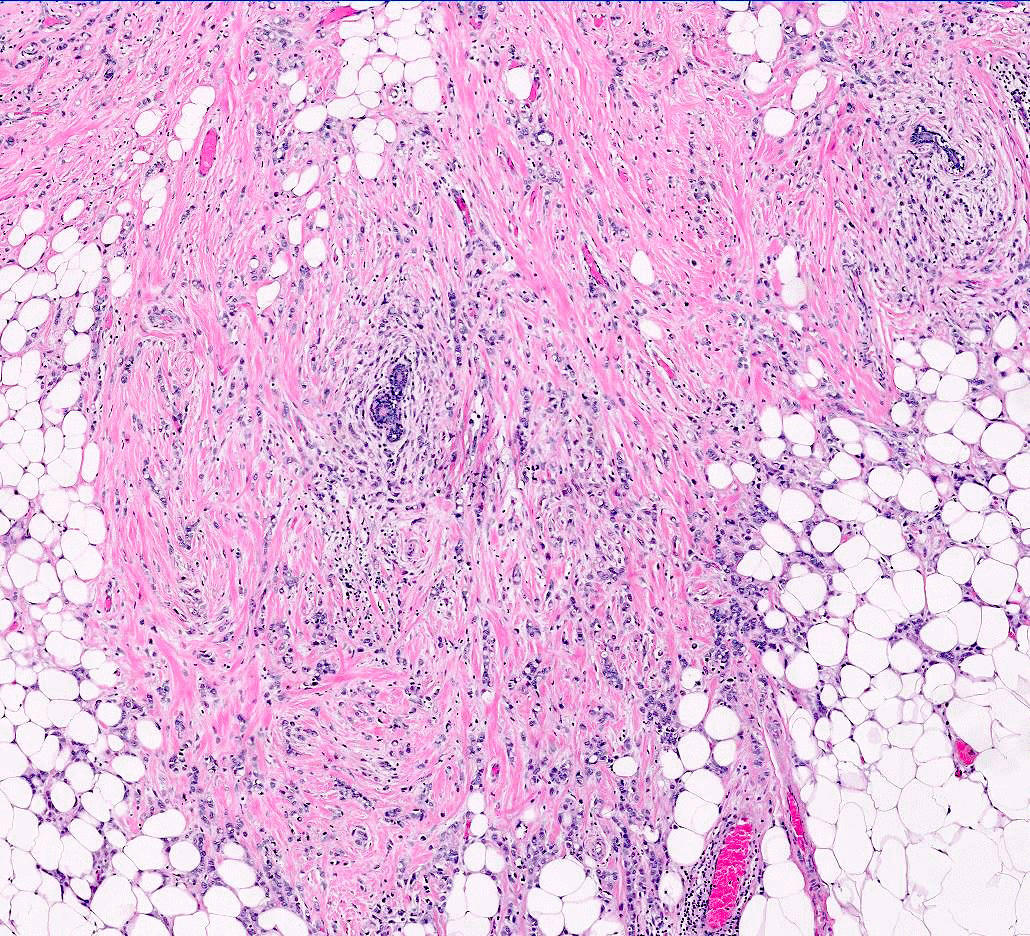
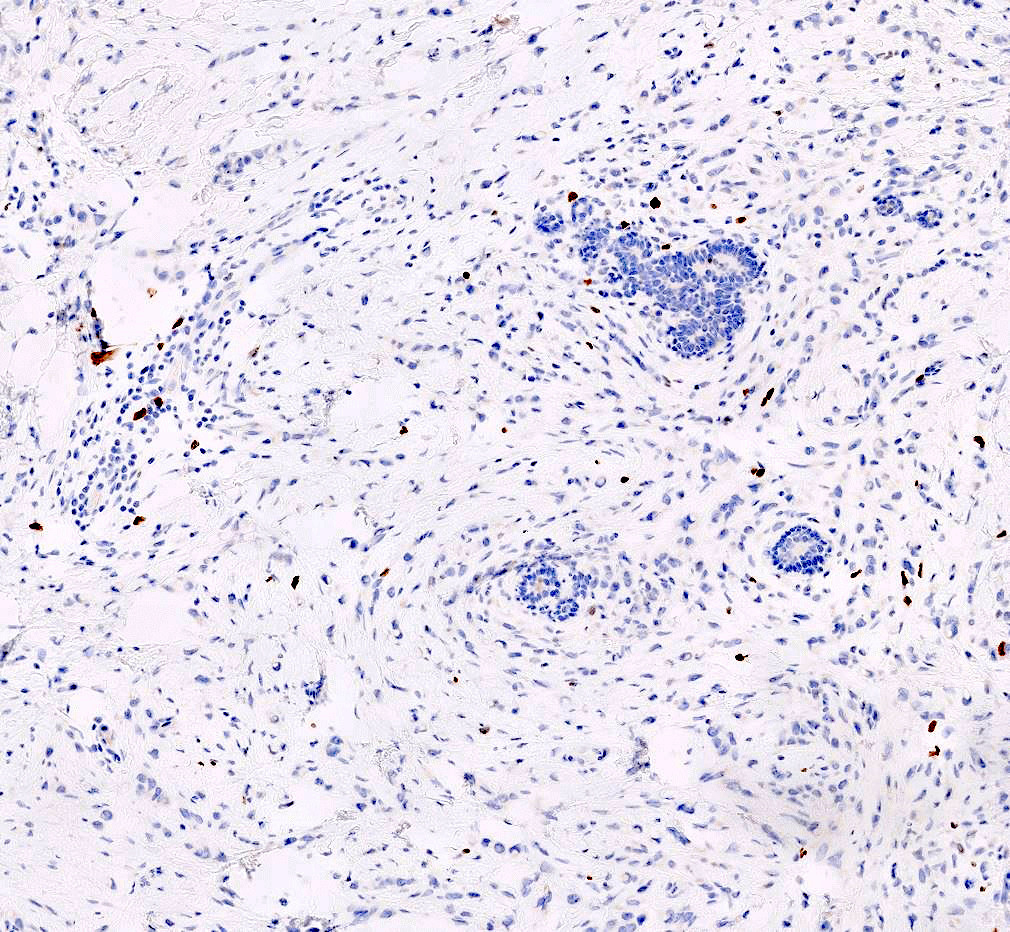
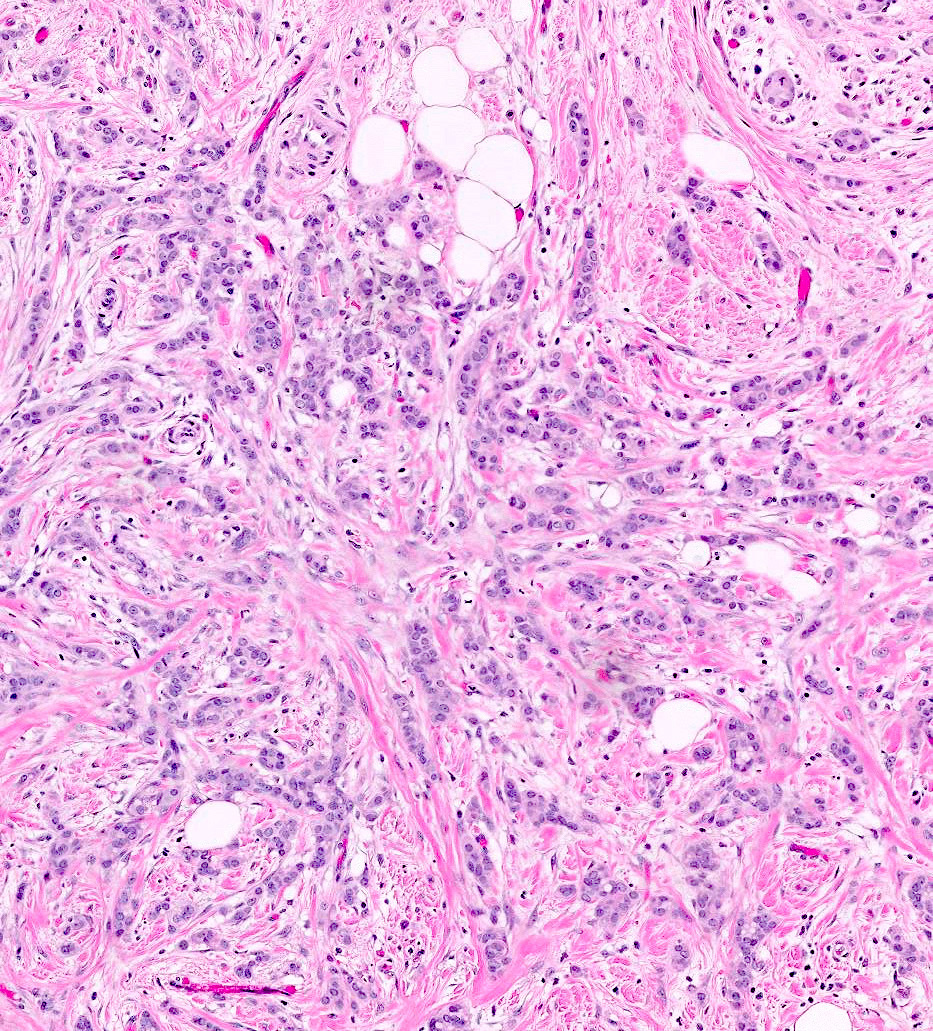
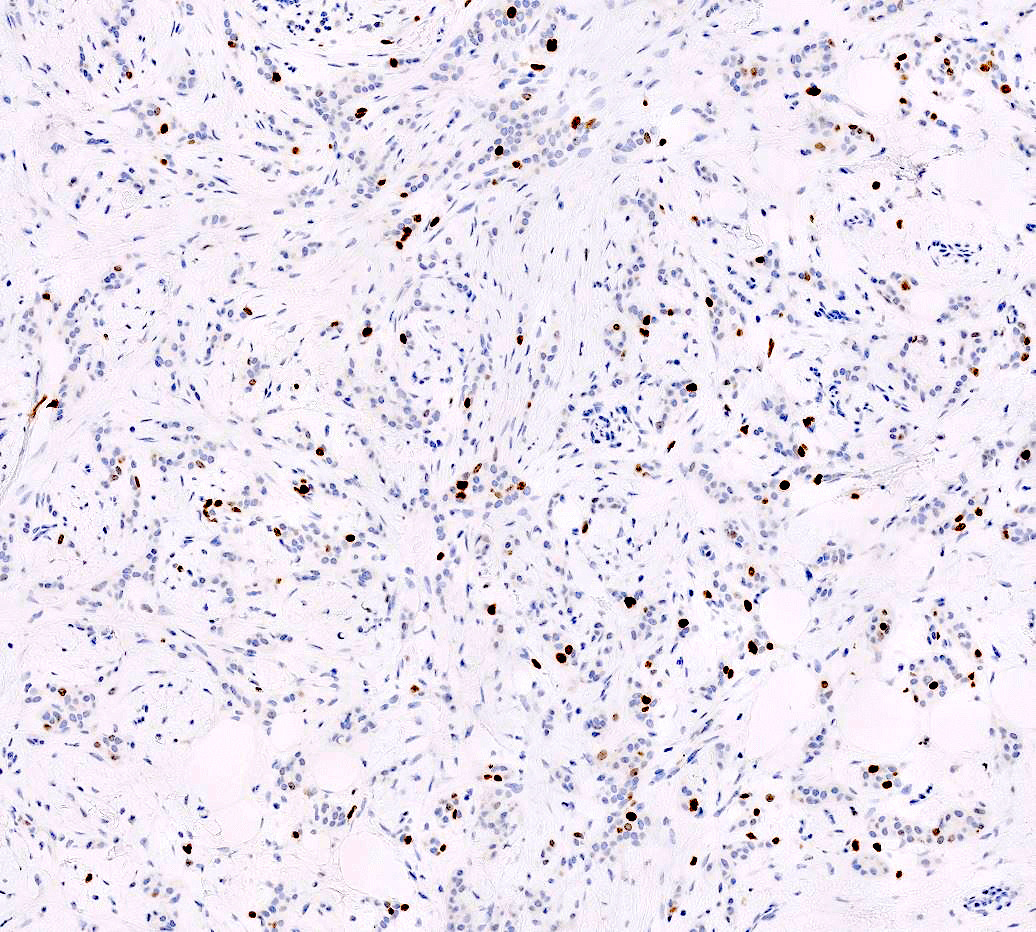
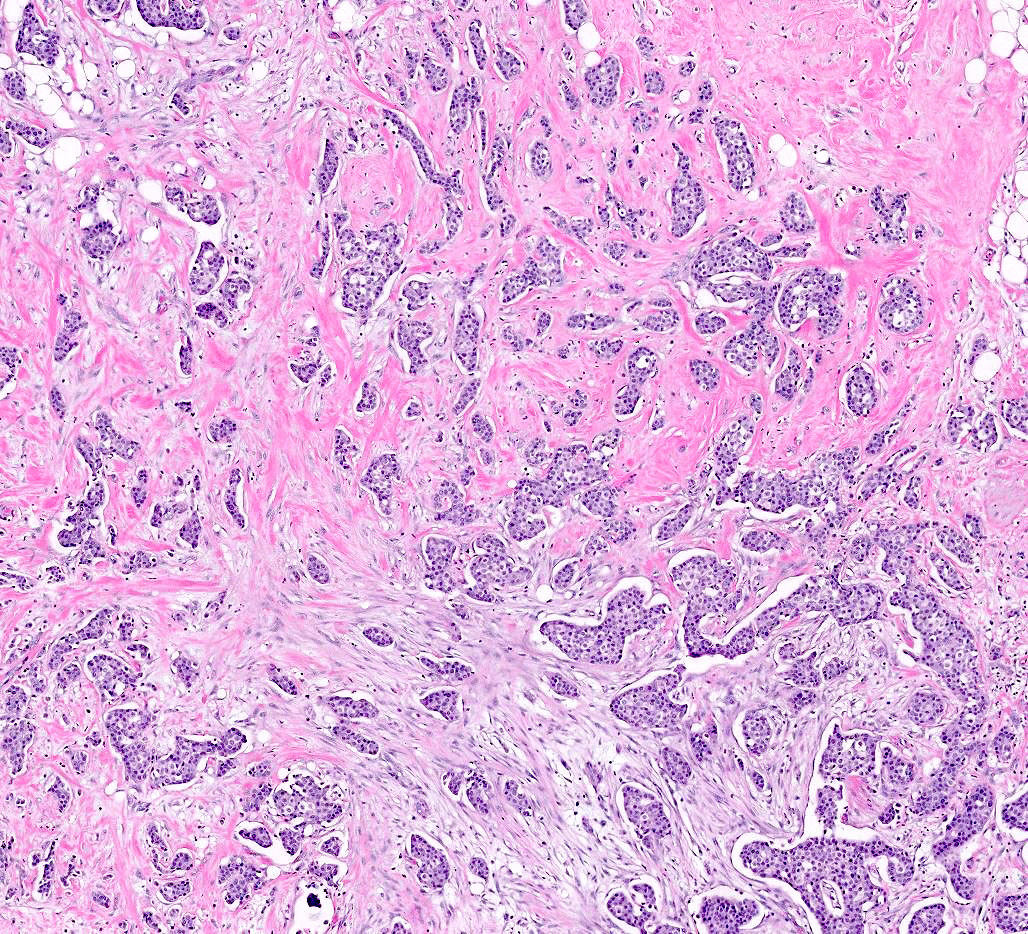
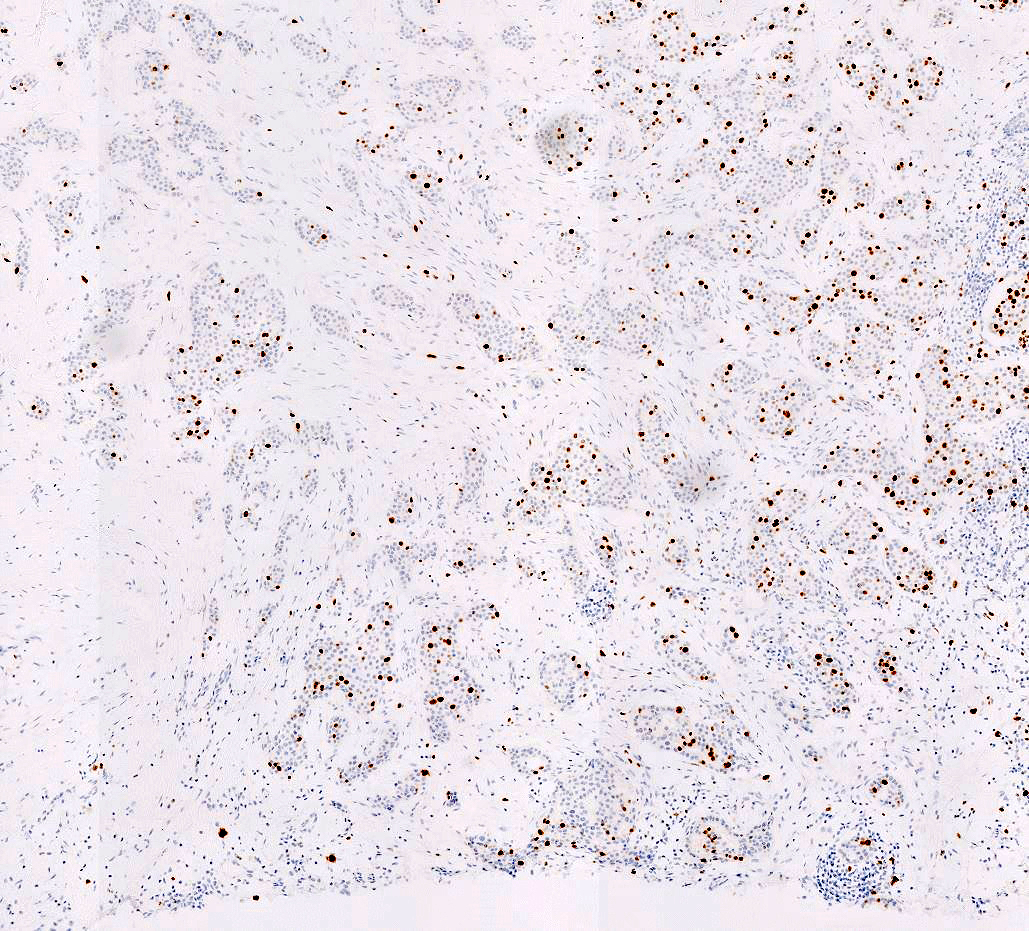
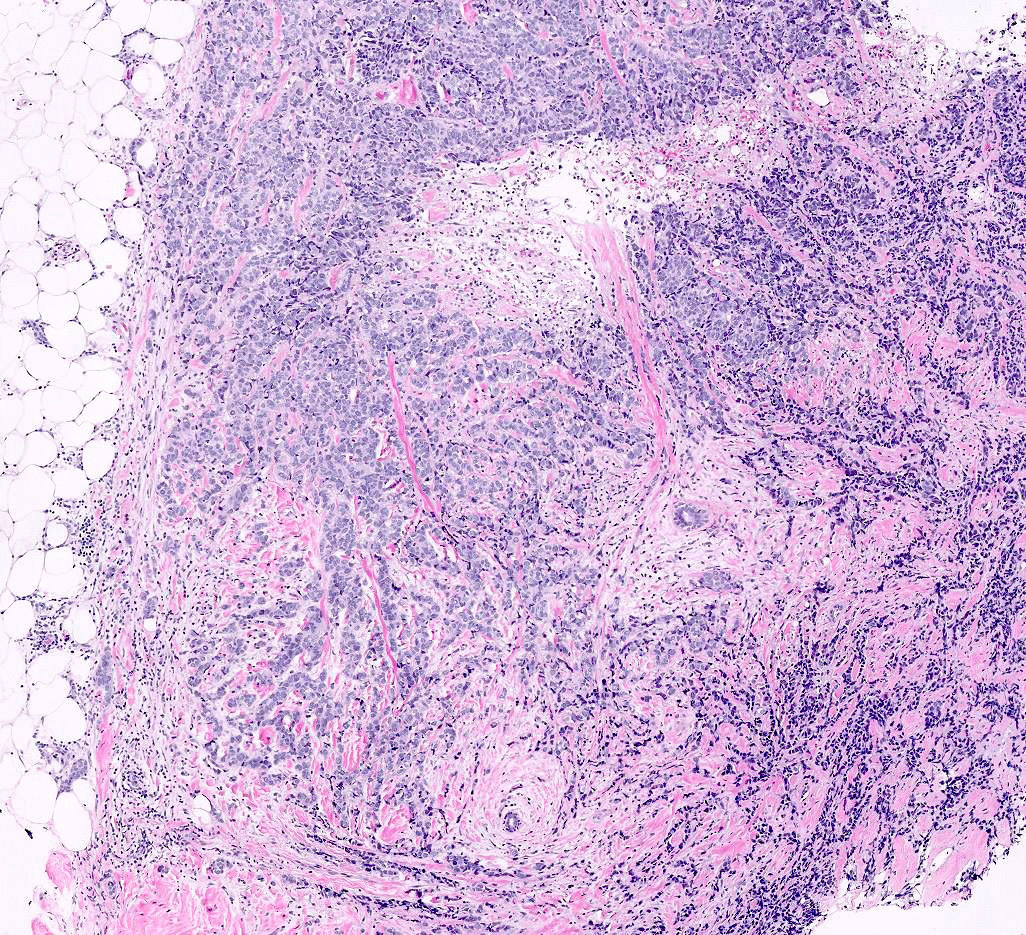
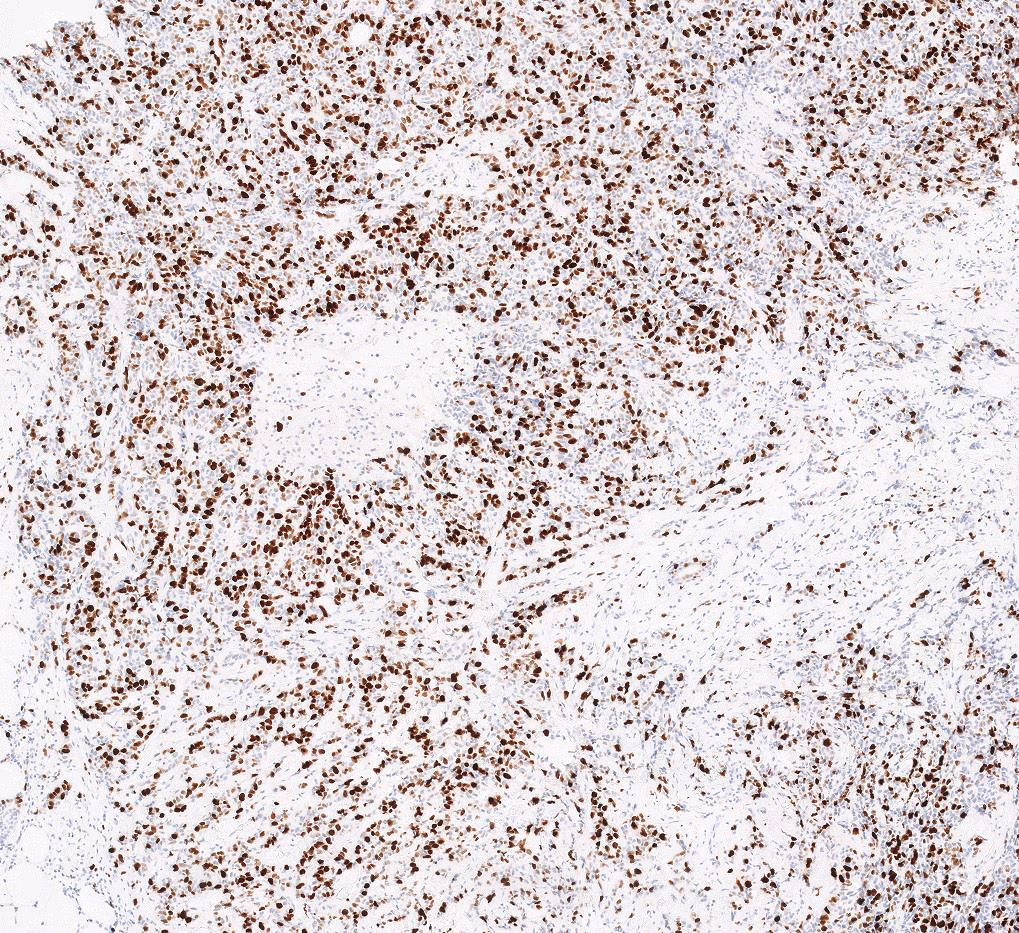
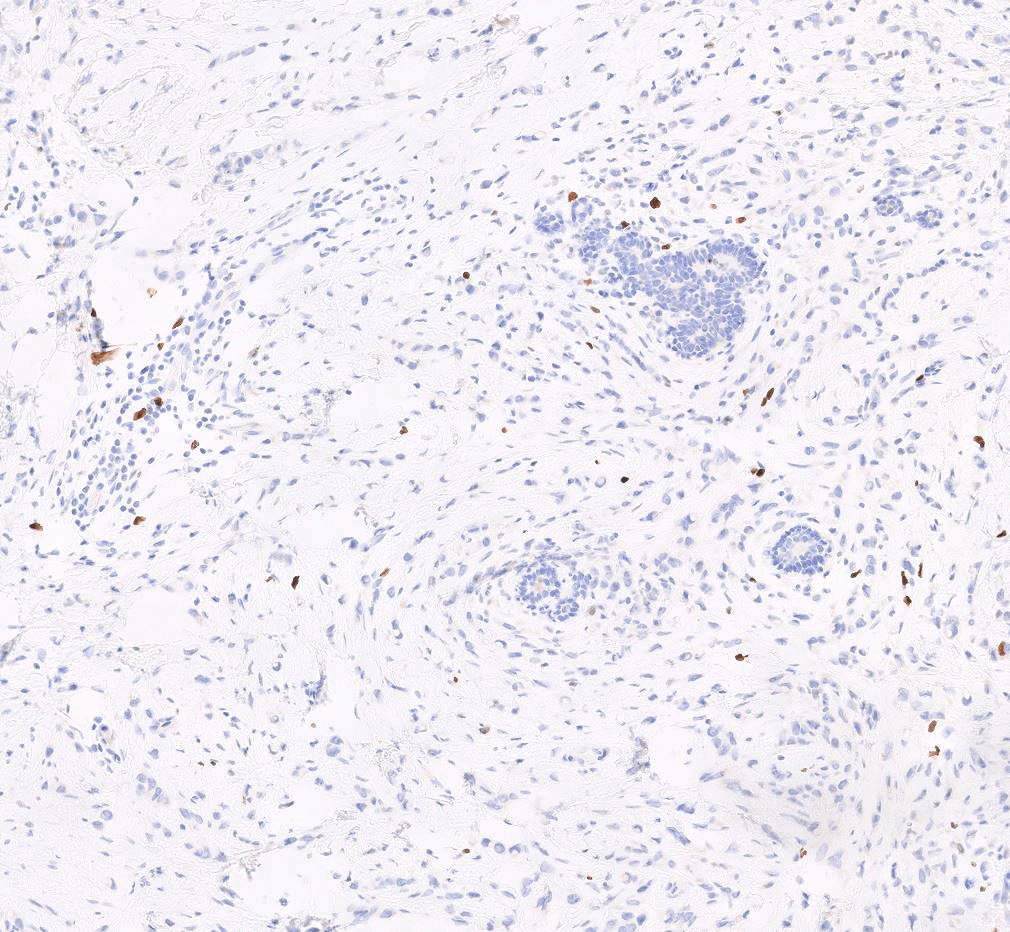
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Anas Mohamed, M.D. and Joseph Geradts, M.D.
Positive staining - normal
- Normal breast tissue demonstrates very low levels of Ki67 index (< 3%) (Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 2021;12:687244)
Positive staining - disease
- Low Ki67 index is observed in benign breast tumors, luminal A carcinomas, low grade ductal carcinomas, lobular carcinomas and tubular carcinomas
- High Ki67 index is observed in triple negative breast carcinomas, including metaplastic and medullary carcinomas, HER2 positive carcinomas, luminal B carcinomas, high grade carcinomas and pleomorphic lobular carcinomas (BMC Res Notes 2019;12:605)
Sample pathology report
- Right breast, core needle biopsy:
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, grade 2
- Ki67 index: 5% (low)
- Left breast, total mastectomy:
- Invasive mammary carcinoma with medullary pattern
- Ki67 index: 40% (high)
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following breast neoplasms is most likely to be associated with an elevated Ki67 labeling index?
- Invasive ductal carcinoma, grade 1
- Invasive lobular carcinoma, classic type
- Metaplastic carcinoma
- Tubular carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
C. Metaplastic carcinoma. High Ki67 index is observed in triple negative breast carcinomas, including metaplastic and medullary carcinomas, as well as HER2 positive carcinomas, luminal B carcinomas, high grade carcinomas and pleomorphic lobular carcinomas (BMC Res Notes 2019;12:605).
Comment Here
Reference: Ki67 breast
Comment Here
Reference: Ki67 breast
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
A. Invasive cribriform carcinoma. Low Ki67 index is observed in benign breast tumors, luminal A carcinomas, low grade ductal carcinomas, lobular carcinomas and tubular carcinomas and lower grade breast cancer subtypes, such as invasive cribriform carcinoma (BMC Res Notes 2019;12:605).
Comment Here
Reference: Ki67 breast
Comment Here
Reference: Ki67 breast