Table of Contents
Definition / general | Development | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Additional referencesCite this page: Luca DC. Basophils. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bonemarrowbasophils.html. Accessed March 31st, 2025.
Definition / general
- 0.5% of all white blood cells (least numerous granulated cells in peripheral blood)
- Named because it stains with basic dyes
Development
- Similar to mast cells but apparently generated by different CD34+ precursor cells in bone marrow (basophils mature in marrow, mast cells in connective tissue)
- Progresses from the multipotent myeloid stem cell via a committed progenitor (basophil colony forming unit, CFU-Baso) to basophilic promyelocyte, to basophilic myelocyte, to basophilic metamyelocyte, to basophil
- Leaves bone marrow as terminally differentiated granulocyte
Pathophysiology
- Basophils and mast cells are effector cells in allergen / IgE mediated immune responses
- They induce type 1 immediate immune response in airways and elsewhere, causing bronchial asthma and other allergic diseases (Allergol Int 2006;55:105)
- Also play a critical role in host defense against helminths (Allergol Int 2006;55:99)
- Factors thought to play key role in basophil production: IL3 (main cytokine), GM-CSF, IL4, IL5 (primary cytokine linked to specific eosinophil and basophil production), stem cell factor (SCF)
- Basophils and their granules contain histamine, sulphated mucopolysaccharides (mostly chondroitin sulfate), peroxidase, low levels of chymase, negligible amount of tryptase, Charcot-Leyden crystal protein, PAF and ECF-A
Clinical features
- Basophil activation test, using CD203c or CD63 as an activation marker, has become a reliable test for in vitro investigation of immediate allergy, complementing other in vitro tests (Clin Mol Allergy 2005;3:9)
- Significant basophilia is more likely to represent neoplasia (chronic myelogenous leukemia, other chronic myeloproliferative disorders, myelodysplastic syndromes, acute leukemias) than reactive processes
- Nonneoplastic basophilia: allergic / hypersensitivity reactions, hypothyroidism, ulcerative colitis, rheumatoid arthritis, renal disease, rare infections (varicella, influenza), irradiation, rare carcinomas and rare drugs (estrogens, antithyroid agents)
- Decreased number of basophils (basophilopenia): certain medications (steroids, epinephrine, thyrotoxicosis therapy), acute stress, acute inflammation
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Basophilic granules are metachromatic (reddish purple) with Toluidine blue and Alcian blue; are also water soluble
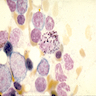
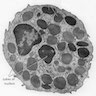
- Basophilic myeloblast: difficult to distinguish from other granulocyte blasts; large round cell with basophilic cytoplasm without granules; N/C ratio is 80%; dispersed chromatin with nucleolus
- Basophilic promyelocyte: intermediate in development between basophilic myeloblast and myelocyte; large round cell with a few undifferentiated cytoplasmic granules; slight chromatin clumping, nucleolus present
- Basophilic myelocyte: round / oval cell; cytoplasm with slight basophilia, moderate cytoplasmic purple black granules of varying size and shape; granules are usually larger than neutrophilic granules; N/C ratio is 50%; chromatin moderately condensed, no distinct nucleolus
- Basophilic metamyelocyte: oval cell with abundant pale cytoplasm, large and fairly uniform specific granules; N/C ratio is 40%; nucleus is small and indented with condensed chromatin, no nucleolus
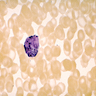
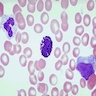
- Basophil: smaller than other white blood cells (10 - 15 microns); cytoplasm is homogenous pale blue but often obscured by purple blue granules (containing heparin and histamine); N/C is 20%; nucleus is often unsegmented or bilobed, chromatin is coarse
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Commonly used: CD9, CD25, CD38
- Also CD11a, CD11b, CD11c, CD13, CD15u, CD17, CD18, CD26, CD31, CD32, CD33, CD35, CD38, CD43, CD44, CD45, CD46, CD47, CD49d, CD50, CD55, CD58, CD59, CD63, CD68, CD71 (dim by flow cytometry), CD85a, CD85h, CD87, CD88, CD99, CD102, CD116, CD121b, CD123, CD125, CD126, CDw128a (CD181), CD203c, HLA-DR (immature basophils, Allergy 2006;61:1063), histidine decarboxylase, 2D7 (J Clin Pathol 2006;59:396) and basogranulin (Am J Clin Pathol 2006;125:273)
- Allergic subjects: CD32, CD122, CD124, CD130 and CD154 (J Allergy Clin Immunol 2000;106:1190)
- Variable: CD14, CD15, myeloperoxidase (usually negative) and a small proportion are chloroacetate esterase - positive
- Cytochemistry: PAS - positive (not the granules), Sudan black - positive and phosphatase (acid and alkaline) - negative
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Granules ~20nm in diameter with a particulate substructure
Additional references