Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Clinical features | Case reports | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Urinary diversion / neobladder. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderurinarydiversion.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Portions of ileum or colon used in adults and children to treat congenital anomalies, dysfunctional bladder or post-cystectomy for malignancy
- Options are to enlarge capacity of bladder (augmentation), channel urine into temporary artificial reservoir while a new bladder is being created or create a neobladder (new bladder after cystectomy)
Terminology
-
Patients who must have their bladder removed usually have three options for urine elimination:
1. Ileal Conduit (Urostomy) – Conduit of small intestine or colon carries the urine to an opening on the abdomen
2. Orthotopic neobladder – Neobladder made from loops of intestine to store the urine and individual can void through normal channels
3. Continent urinary diversion – Creation of an internal pouch from loops of intestine which is connected to an opening on the abdomen through a “one way” passage
Clinical features
- Ileal neobladder produces good functional results (J Urol 1999;161:422)
Complications:
- Intestinal adenocarcinoma in colonic conduits, reflux but only rare renal failure in ileal conduits, highest risk of adenocarcinoma is in augmentation cystoplasty (J Urol 1997;157:482)
- Frequent complications but low reoperation rate in conduit urinary diversion (J Urol 2011;185:562)
- Monitor for carcinoma with cytology (direct smears after centrifugation)
- Note: must also monitor nonfunctionalized bladder, if present (J Urol 2006;176:620)
Case reports
- 39 year old male with tubular adenoma in ileal segment 34 years after augmentation ileocystoplasty (Diagn Pathol 2007 Aug 13;2:29)
- 67 year old man with adenocarcinoma 20 years after ileal neobladder (Urology 2006;68:1343)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Inflamed, atrophic and partially denuded epithelium
- Candida in ileal conduits
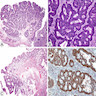
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Normal intestinal cells: aggregates are normally present in urinary diversion specimens, may resemble malignancy
Additional references