Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Beeter MC, Yeh YA. Polypoid / papillary cystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderpolypoidcystitis.html. Accessed December 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Exophytic polypoid to papillary structures characterized histologically by normal or mildly hyperplastic urothelium overlying a congested, chronically inflamed and edematous stroma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:721)
Essential features
- Exophytic bullous, polypoid or papillary structures covered by benign urothelium and composed of stromal cores with varying degree of edema, vascular ectasia, congestion, inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:542)
- Dense fibrosis with chronic inflammation in older polypoid cystitis (Surg Pathol Clin 2008;1:129)
Terminology
- Polypoid cystitis: polypoid (broad based) structure
- Papillary cystitis: papillary (slender, finger-like) papillae
- Bullous cystitis: bullous contour with width greater than height (Amin: Diagnostic Pathology - Genitourinary, Second Edition, 2016)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- No association with age, gender or geographic condition
- Age:
- 20 months to 93 years (J Urol 2013;189:1091, Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:542)
- Mean: 63 years in a review of 41 cases (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:758)
- M:F = 3:1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:758)
- Frequency increased with prolong use of catheter treatment, peaked by 3 months, constant after 3 months (Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 1979;87A:179)
Sites
- Mostly seen in the dome and posterior wall of the bladder, which corresponds to the localization of the tip of the catheter (Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 1979;87A:179)
Pathophysiology
- Injury and inflammatory irritation to the urothelium leading to chronic inflammation and reactive changes
- Edema of the lamina propria
- Inflammation and fibrosis of the lesion in chronic phase (papillary cystitis) (Surg Pathol Clin 2008;1:129)
Etiology
- Catheterization: occurs in more than 80% of patients with indwelling catheters (Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand A 1979;87A:179)
- Vesical fistulae: fistulae between the urinary bladder and the gastrointestinal tract
- Radiation therapy for bladder, prostate or gynecologic cancer
- Stones
Clinical features
- Urinary frequency, urgency, dysuria, hematuria, bladder obstruction
- Pneumaturia and fecaluria in patients with vesico-intestinal fistula (Br J Surg 1964;51:644)
- Associated with vesical fistulae resulting from Crohn's disease, colonic diverticulitis, colon cancer or appendicitis (Urology 1979;13:115)
Diagnosis
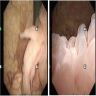
- Polypoid mass or cobblestone appearance on cystoscopy (Surg Pathol Clin 2008;1:129)
- Histopathologic examinations of the polypoid lesions (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;38:11)
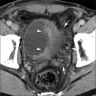
Radiology description
- CT scan reveals irregular thickening of the bladder wall (Urol Ann 2014;6:72)
- Ultrasound shows a vascularized pseudopolypoid mass (Urology 2015;86:1004)
Prognostic factors
- Catheter associated lesions regress within 6 months of removal of the indwelling catheter (J Urol 1983;130:456)
- In non-catheter associated lesions, no recurrence in 6 months to 2 years after initial diagnosis (Int Urol Nephrol 2002;34:293)
- No increased risk for progressing to carcinoma
Case reports
- 21 year old man with Down syndrome presented with hematuria and right flank pain (Urol Case Rep 2015;3:181)
- 38 year old man with paraplegia presented with hematuria (Cases J 2009;2:7333)
- 45 year old man presented with lower urinary tract symptoms (J Endourol Case Rep 2019;5:34)
- 69 year old man presented with dysuria and hematuria (Urol Ann 2014;6:72)
Treatment
- Removal of the indwelling catheter for catheter associated polypoid cystitis (J Urol 1983;130:456)
- Removal of the irritating agent
Gross description
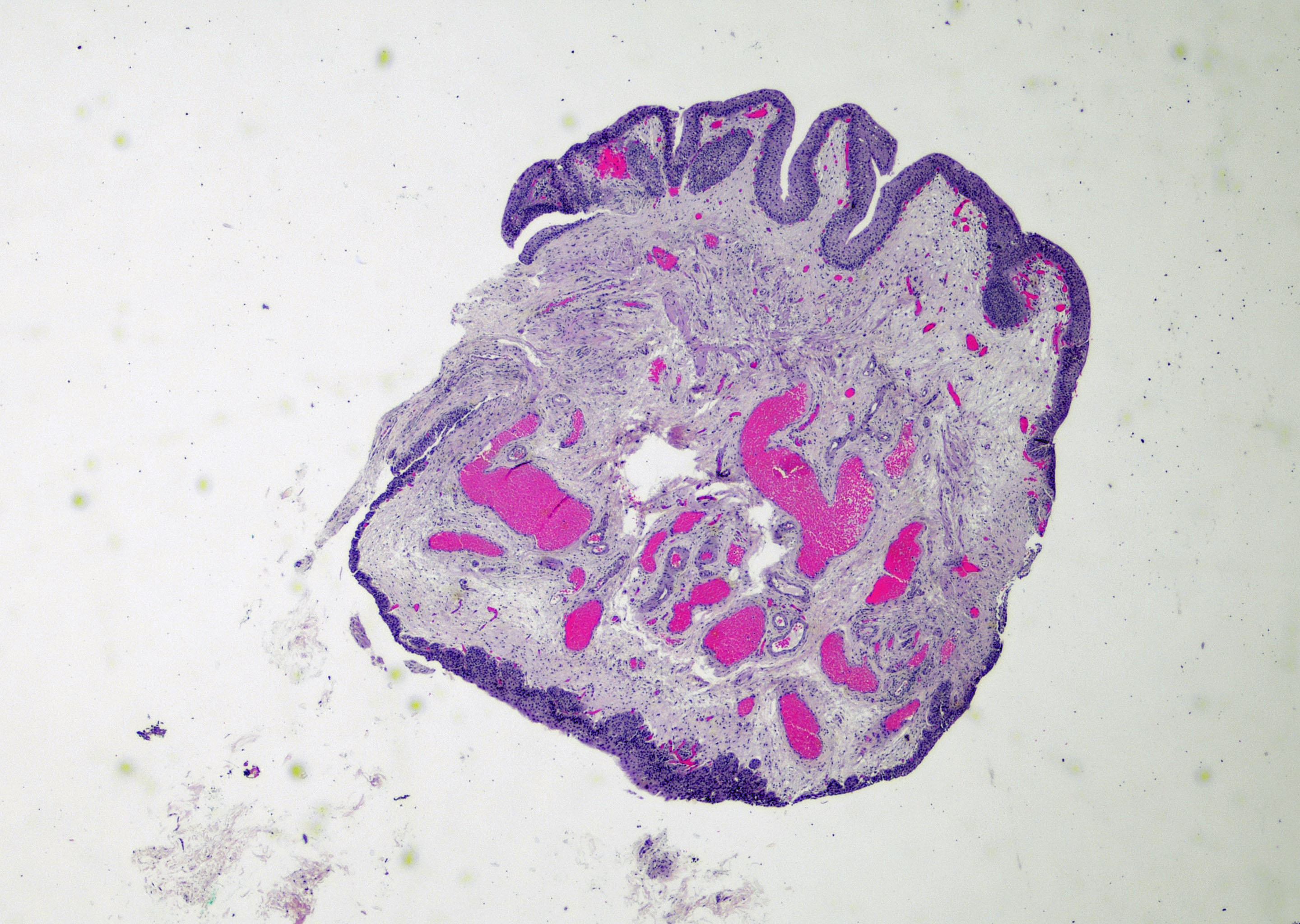
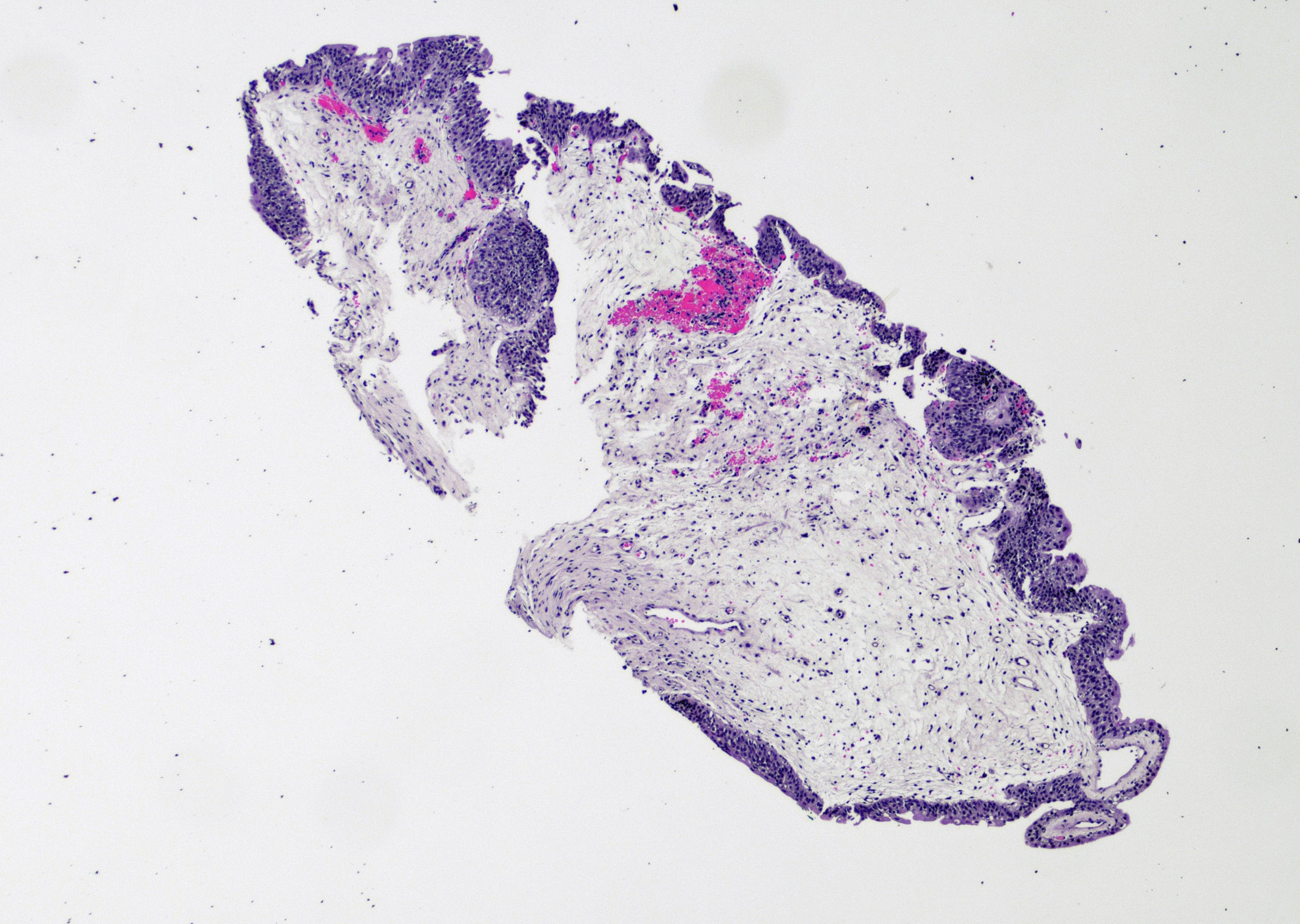
- Broad based, edematous polyp or papillary lesion (cobblestone), usually less than 5 mm (Surg Pathol Clin 2008;1:129)
- Single or multiple lesions, most frequently along the posterior bladder wall (Surg Pathol Clin 2015;8:755)
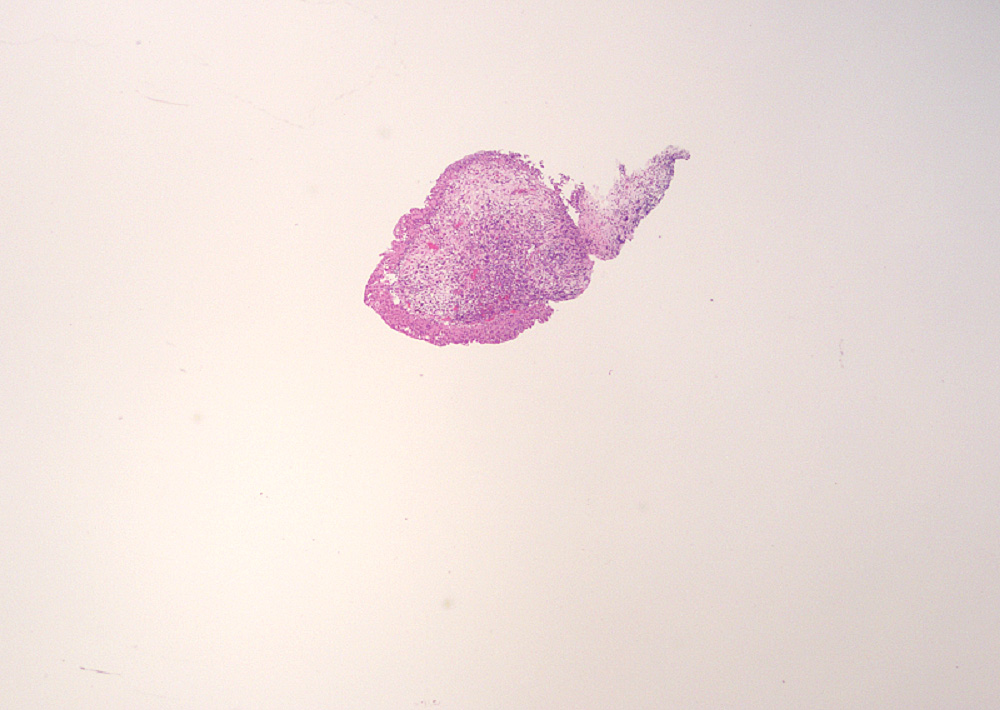
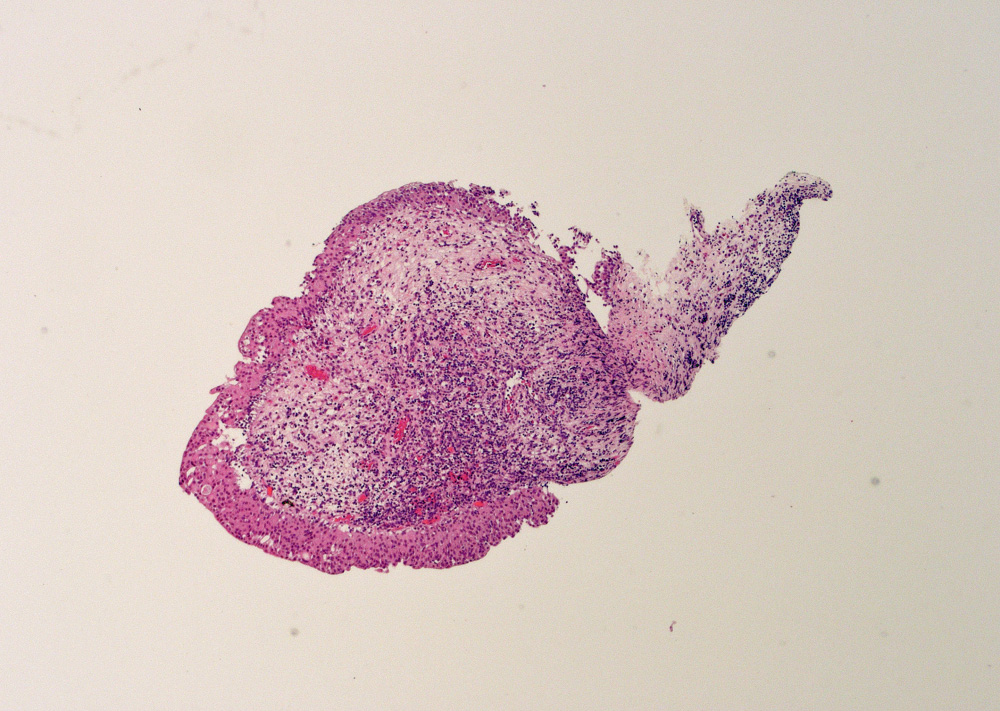
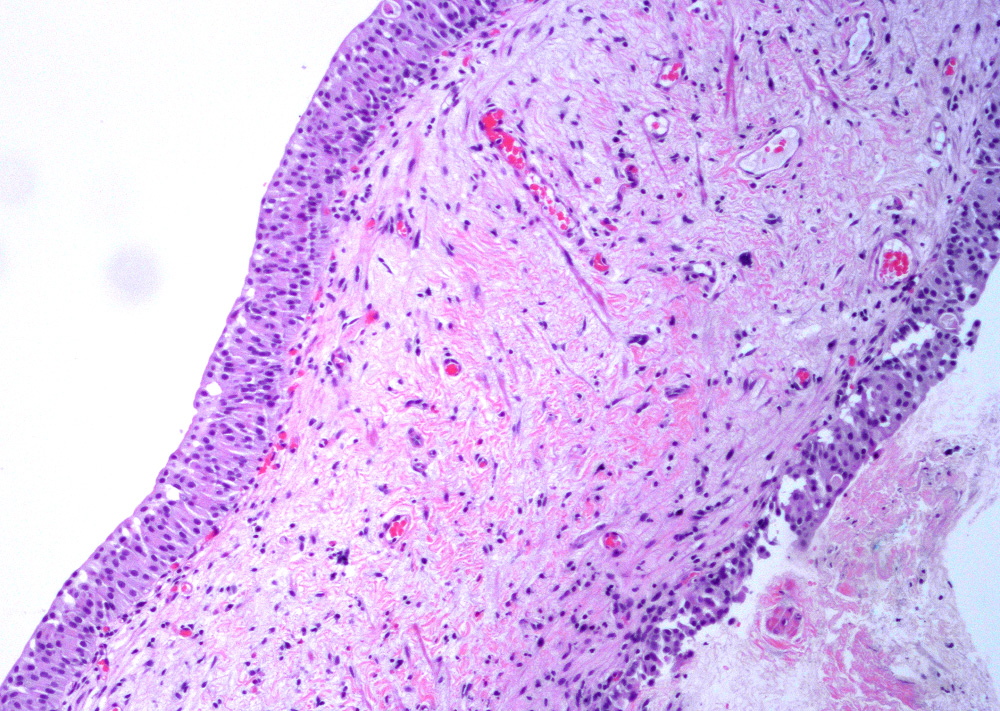
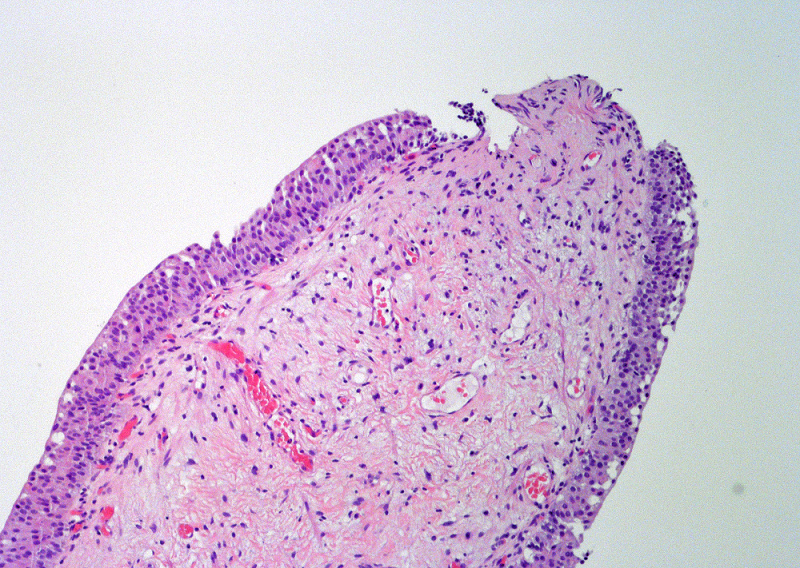
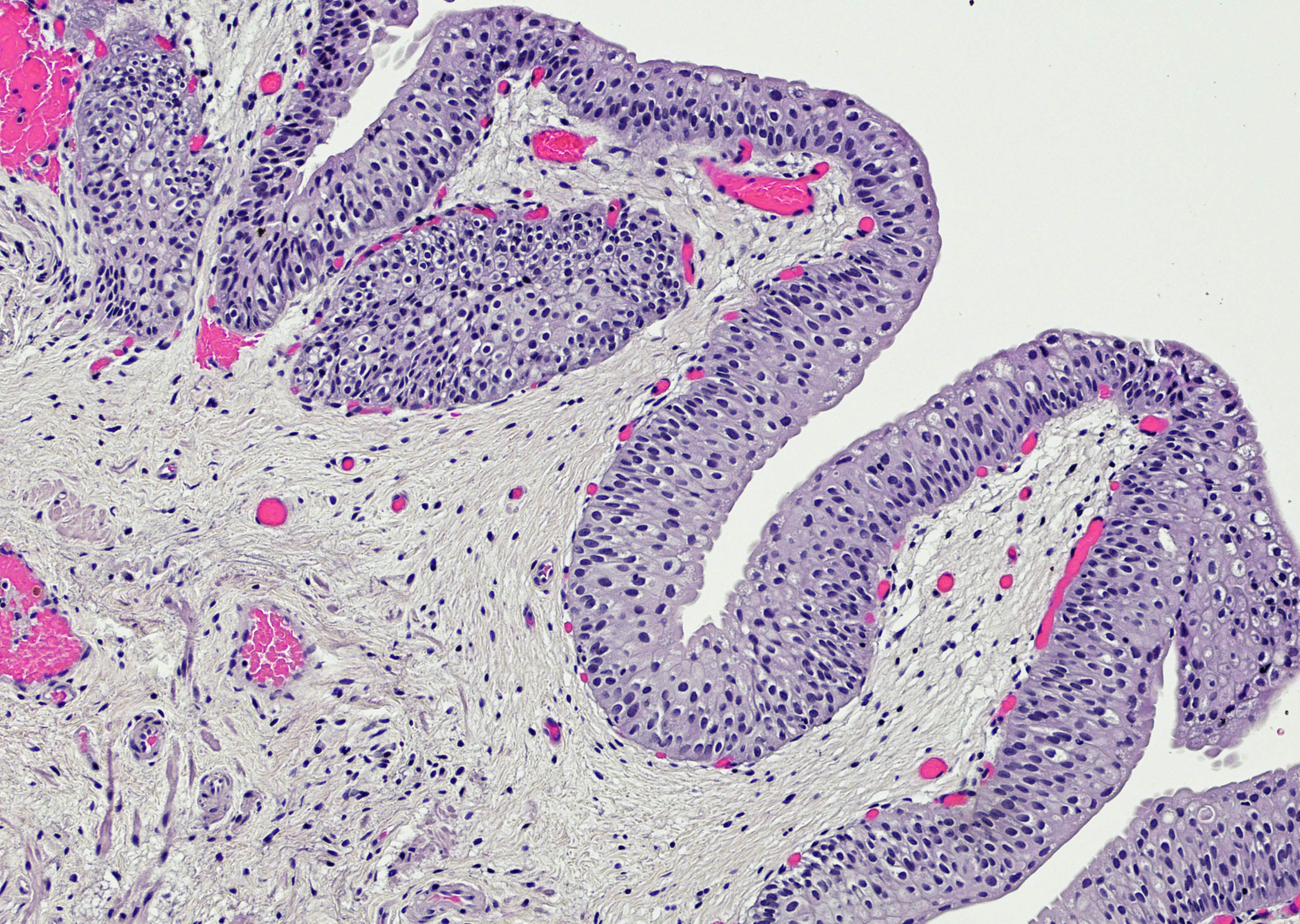
Microscopic (histologic) description
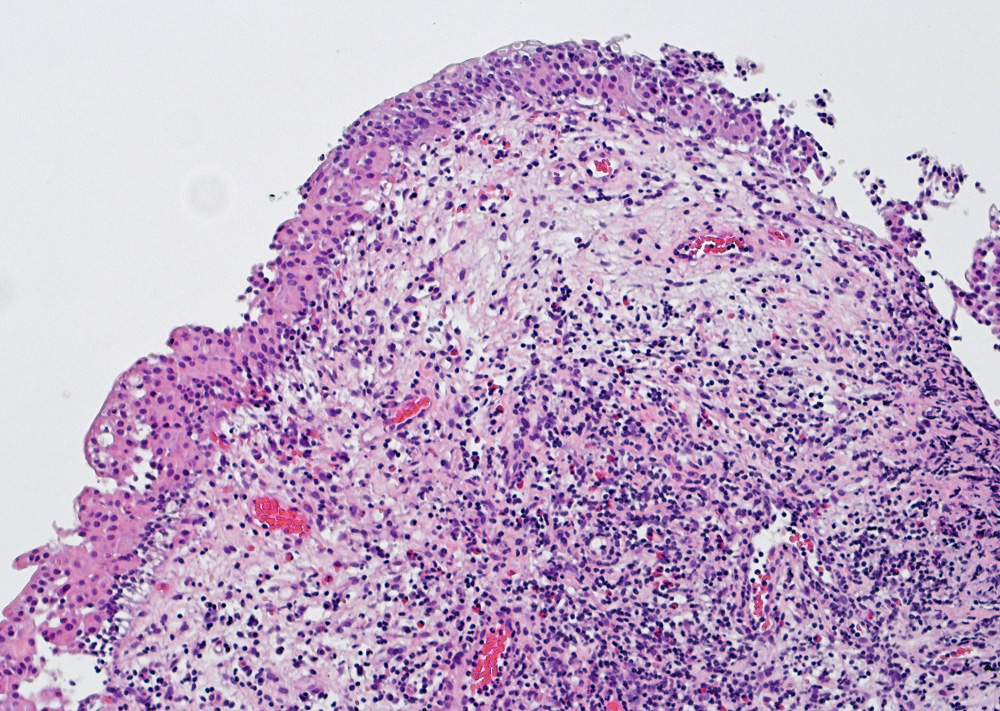
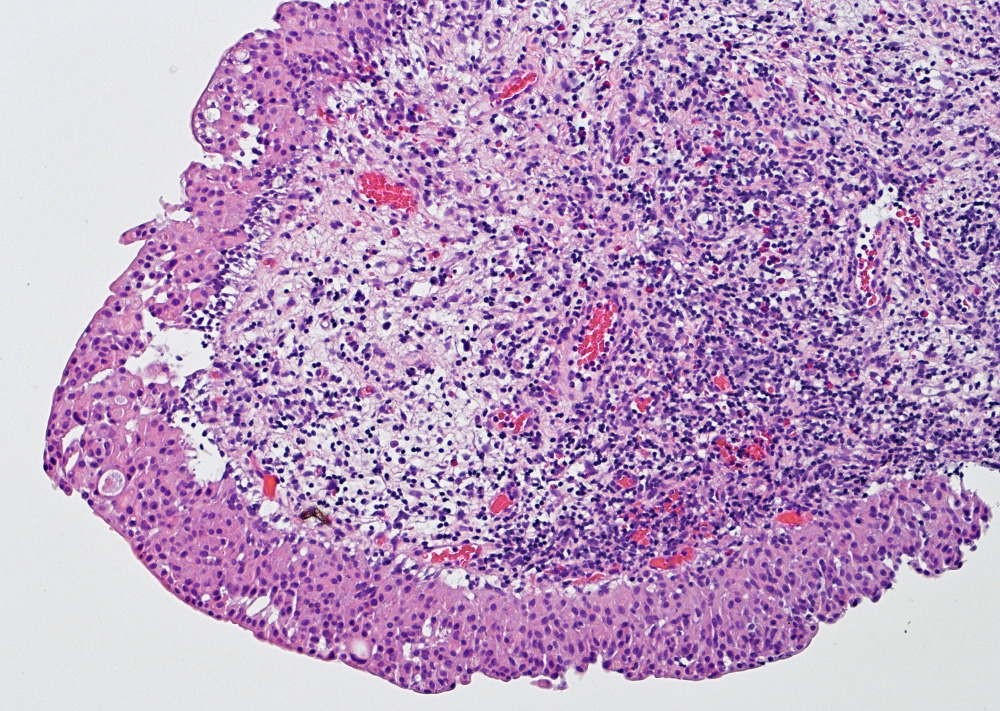
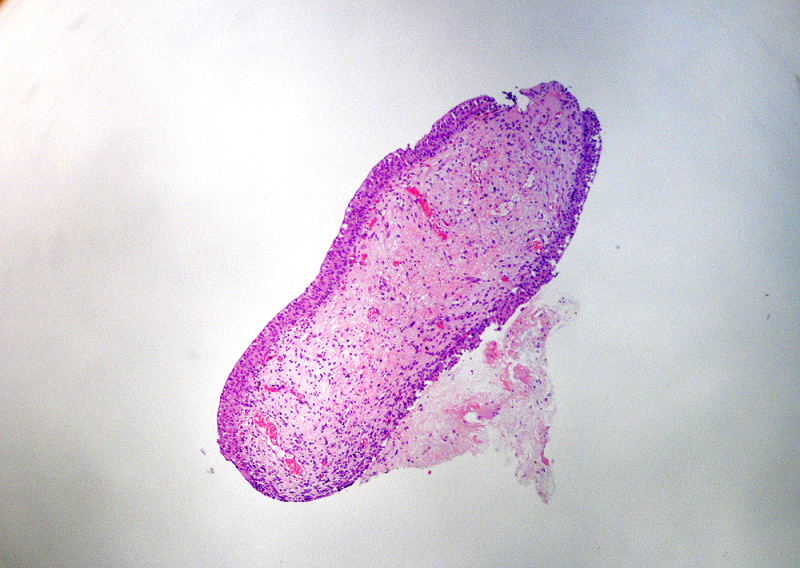
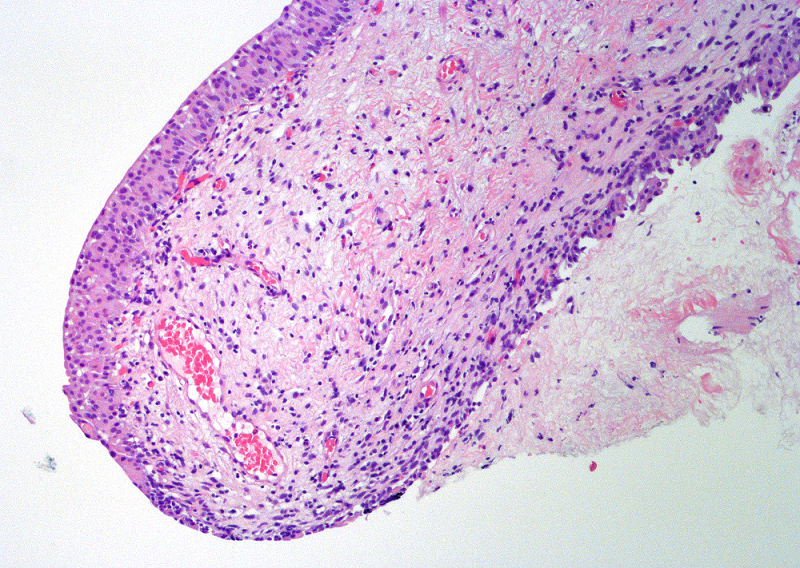
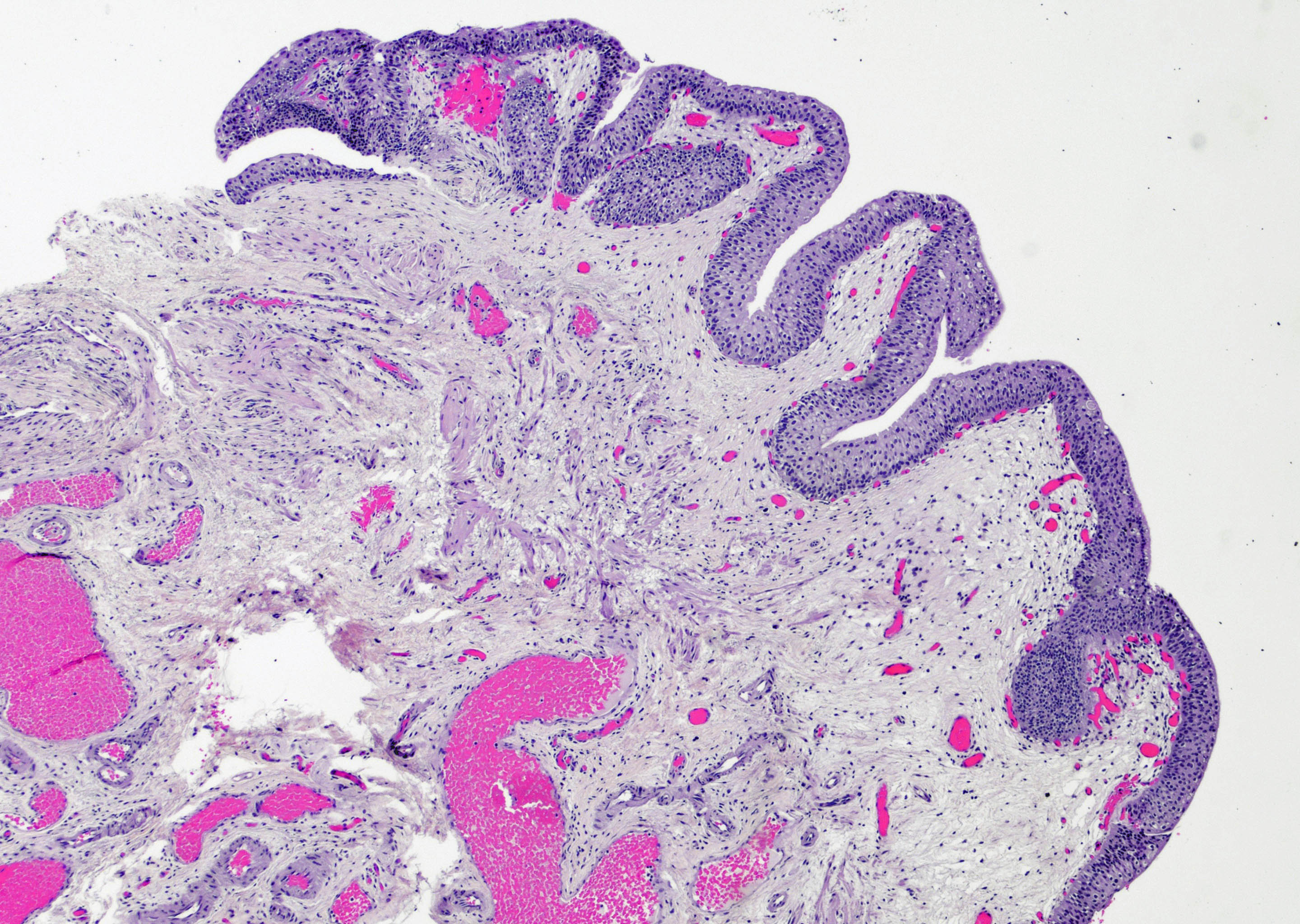
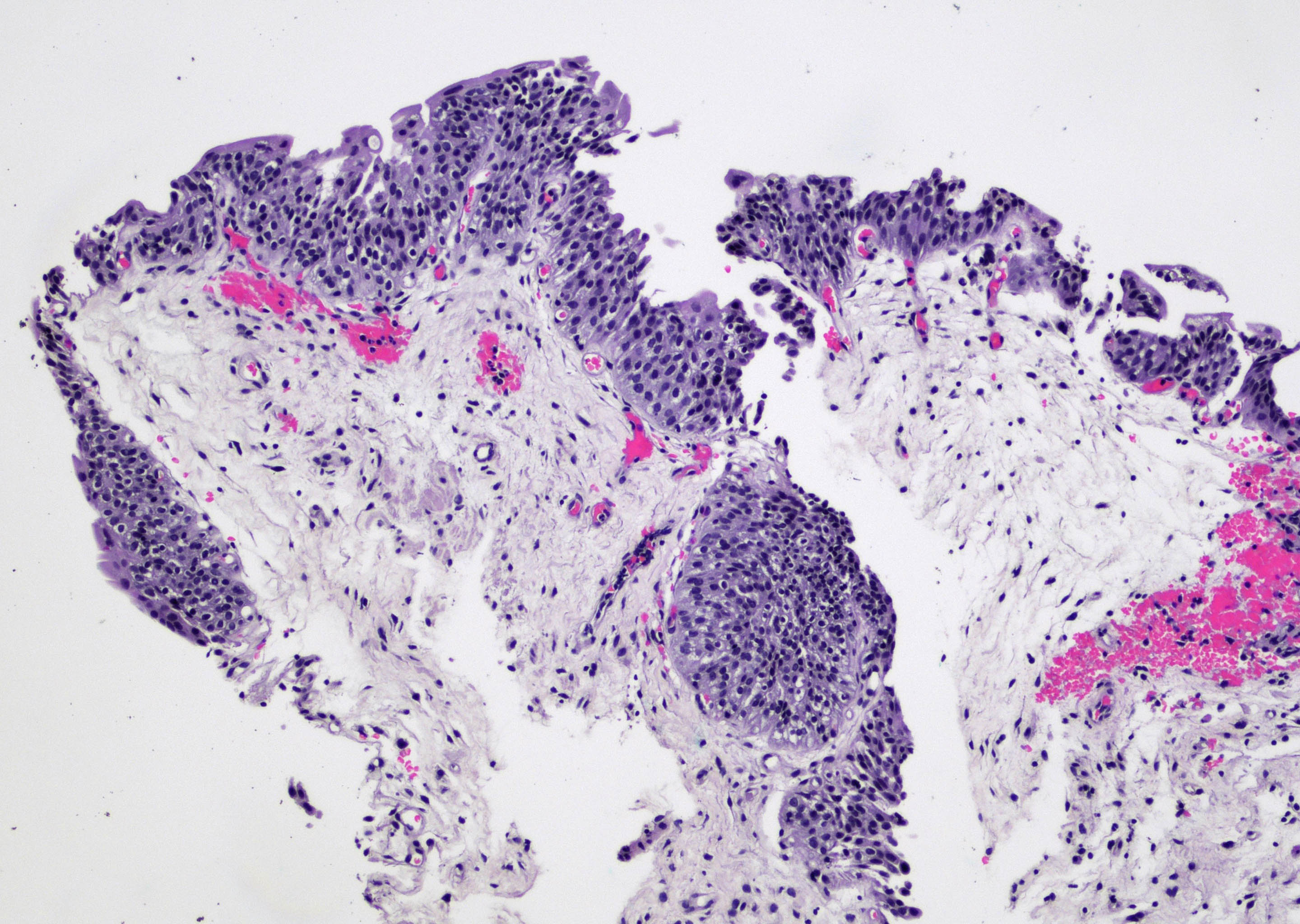
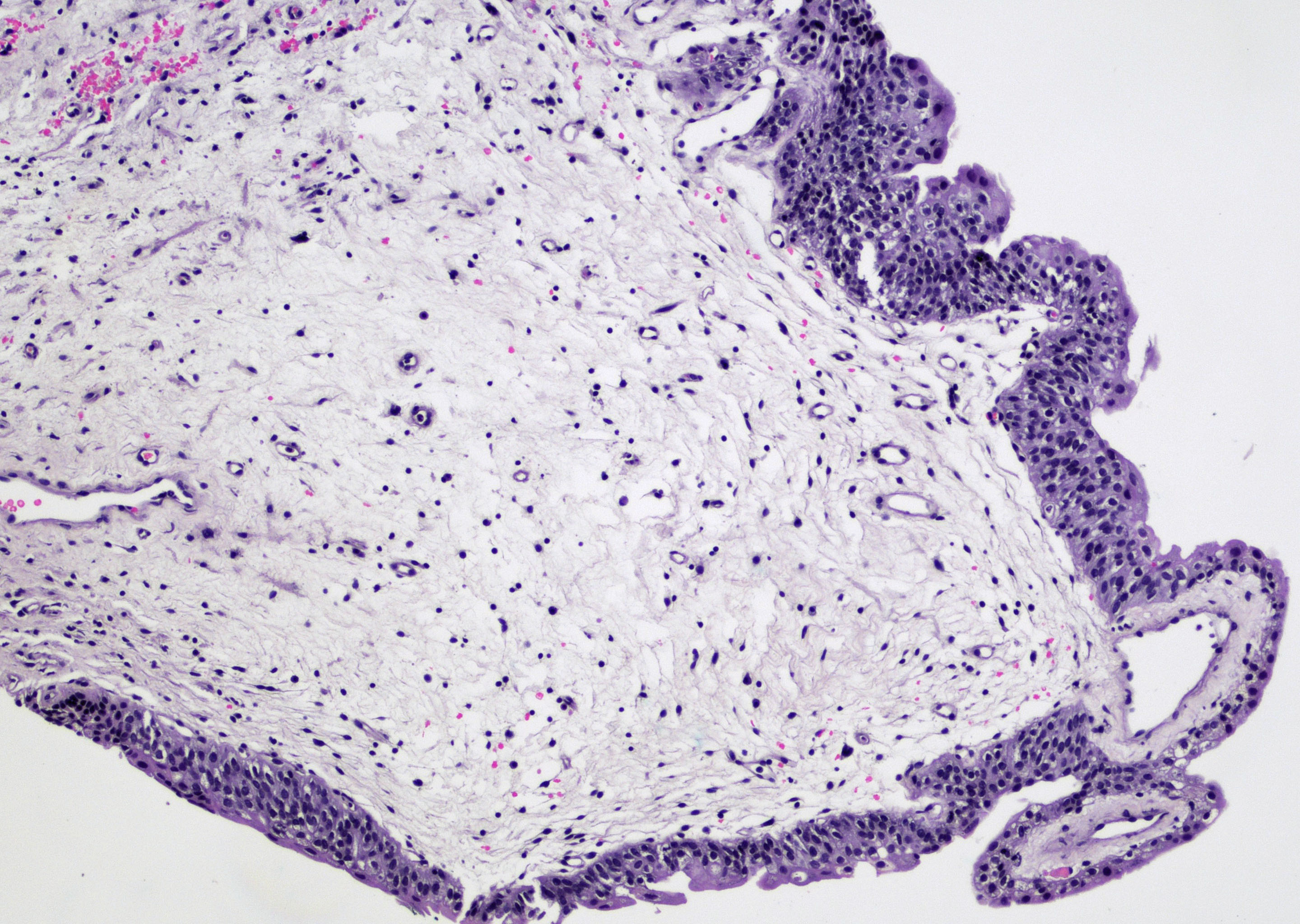
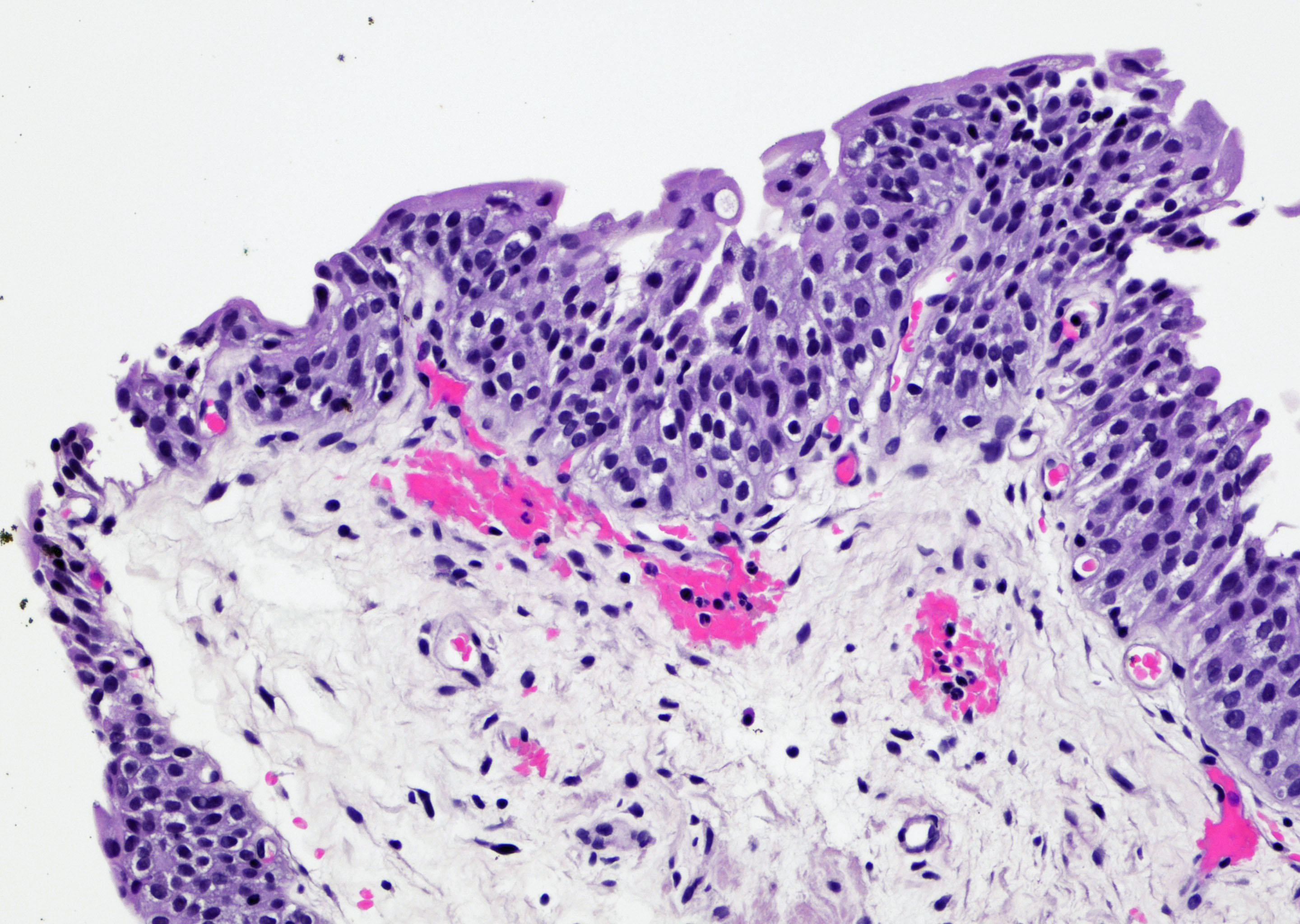
- Variable exophytic lesions: bullous (width > height), polypoid (broad based, width < height) or papillary (narrow based, width < height)
- No simple or complex branching of papillae
- Stromal cores with varying degree of edema, vascular ectasia with congestion, acute and chronic inflammatory infiltrate and fibrosis
- Overlying urothelium may be normal, metaplastic (squamous or mucinous) or hyperplastic (Am J Surg Pathol 1988;12:542)
- Reactive urothelial atypia may be present
- Dense fibrosis with chronic inflammation in older lesions (Surg Pathol Clin 2008;1:129)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Maria Carolina Beeter, M.D. and Y. Albert Yeh, M.D., Ph.D.
Electron microscopy description
- Pleomorphic microvilli present on surface epithelial cells in patients with catheter associated polypoid cystitis (J Urol 1984;131:242)
Sample pathology report
- Urinary bladder, posterior wall, biopsy:
- Polypoid / papillary cystitis (see comment)
- Comment: The bladder lesion biopsy shows a polypoid lesion with focal finger-like papillae lined by benign urothelium. There is marked edema of the lamina propria. Dilated capillaries and rare lymphocytes are noted. Muscularis propria is not identified. These changes are consistent with polypoid / papillary cystitis.
Differential diagnosis
- Papillary urothelial hyperplasia (Pathology 2021;53:44):
- No true branching fronds
- Undulating urothelium or papillary fronds thicker than normal urothelium
- No urothelial atypia, stromal edema or inflammation
- Urothelial papilloma (Pathology 2021;53:44):
- Slender true fibrovascular stalks
- Normal appearing urothelium
- Prominent umbrella cells with cytoplasmic vacuolization
- No urothelial atypia
- Papillary urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential (Zhou: Uropathology, 1st Edition, 2012):
- True fibrovascular cores with simple or minimal branching
- Papillae with thickened urothelium
- Monotonous urothelial cells arranged in a parallel pattern (no loss of polarity)
- May have rare mitoses in the basal layer
- Absence or minimal cytologic atypia
- Noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma, low grade (Adv Anat Pathol 2021;28:179):
- True fibrovascular cores with complex branching and confluence between papillae
- Hyperplastic urothelial cells with loss of polarity
Additional references
Board review style question #1
- A 65 year old man presents with intermittent hematuria. He has a history of indwelling catheter use. His cystoscopy shows a small exophytic lesion, which is biopsied. The histologic image is shown above. What is the diagnosis?
- Noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma, low grade
- Polypoid cystitis
- Urothelial carcinoma in situ
- Urothelial papilloma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
- A 64 year old man presented with dysuria and hematuria. Cystoscopic examination showed a 5 mm mass arising in the posterior bladder wall. Transurethral bladder tumor resection was performed. A histopathological image is shown above. What is the diagnosis of this lesion?
- Noninvasive papillary urothelial carcinoma, low grade
- Polypoid / papillary cystitis
- Urothelial neoplasm of low malignant potential
- Urothelial papilloma
Board review style answer #2