Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Brown ML, Tretiakova M. Nested. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladdernested.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Morphologic variant of urothelial carcinoma characterized by unusually bland, nested pattern of invasion but with clinical outcomes similar to conventional invasive high grade urothelial carcinoma (Virchows Arch 2014;465:199)
Essential features
- Cytologically bland nested pattern that could be difficult to distinguish from florid von Brunn nests; particularly challenging in superficial biopsies
- Often deeply invasive with increasing irregularity in the deeper portion
- Clinical outcomes are similar to invasive high grade urothelial carcinoma of matched clinical stage
Terminology
- Nested urothelial carcinoma has been expanded to include: large nested carcinoma (Histopathology 2019;74:77)
ICD coding
- Location based ICD-10 coding:
- Renal pelvis, including pelviureteric junction and renal calyces
- Ureter, including ureteric orifice of bladder
- Bladder
- C67.0 - malignant neoplasm of trigone of bladder
- C67.1 - malignant neoplasm of dome of bladder
- C67.2 - malignant neoplasm of lateral wall of bladder
- C67.3 - malignant neoplasm of anterior wall of bladder
- C67.4 - malignant neoplasm of posterior wall of bladder
- C67.5 - malignant neoplasm of bladder neck
- C67.6 - malignant neoplasm of ureteric orifice
- C67.7 - malignant neoplasm of urachus
- C67.8 - malignant neoplasm of overlapping sites of bladder
- C67.9 - malignant neoplasm of bladder, unspecified
Epidemiology
- Very rare in renal pelvis and overall rare in genitourinary tract; only a few hundred cases reported (Adv Urol 2014;2014:192720)
- In bladder, mean age is 68 years with a male predominance; however, 3 of 4 cases reported in renal pelvis are in women ages 49 - 80 (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1725, Pathol Res Pract 2009;205:508, Anal Quant Cytol Histol 2011;33:340, Pol J Pathol 2014;65:74, Urology 2007;69:778.e15)
- Less than 1% of reported urothelial carcinomas (Eur Urol Focus 2020;6:653)
Sites
- Renal pelvis, ureter, bladder
Pathophysiology
- TERT promotor mutations (Histopathology 2019;74:77)
Etiology
- No specific risk factors to development of nested variant reported
- General risks factors for urothelial carcinoma: smoking, aromatic amine exposure, arsenic exposure
Clinical features
- Hematuria, dysuria, flank pain (Urology 2020;144:9)
Diagnosis
- Cystoscopy
- CT scan
- MRI
Laboratory
- Hematuria
Radiology description
- Bladder with irregular wall thickening and little protrusion into the bladder lumen with gradual contrast enhancement on dynamic contrast enhanced MRI (Abdom Radiol (NY) 2020;45:2279)
Prognostic factors
- In bladder, data demonstrates outcomes similar to conventional invasive high grade urothelial carcinoma (Mod Pathol 2003;16:1289)
- Often diagnosed at advanced stage and with nodal invasion (Histopathology 2019;74:77)
Case reports
- 26 year old man with nested variant of urothelial carcinoma (Hinyokika Kiyo 2020;66:347)
- 49 year old woman with pelvic urothelial carcinoma with nested pattern of growth (Anal Quant Cytol Histol 2011;33:340)
- 54 year old woman with unusual nested carcinoma (Urol Ann 2013;5:287)
- 73 year old woman with nested variant of urothelial carcinoma (Urology 2020;144:9)
- Urothelial carcinoma nested variant of renal pelvis and ureter (Urology 2007;69:778.e15)
Gross description
- Thickened, irregular renal pelvis with or without associated papillary component
Frozen section description
- Not typically diagnosed on frozen section
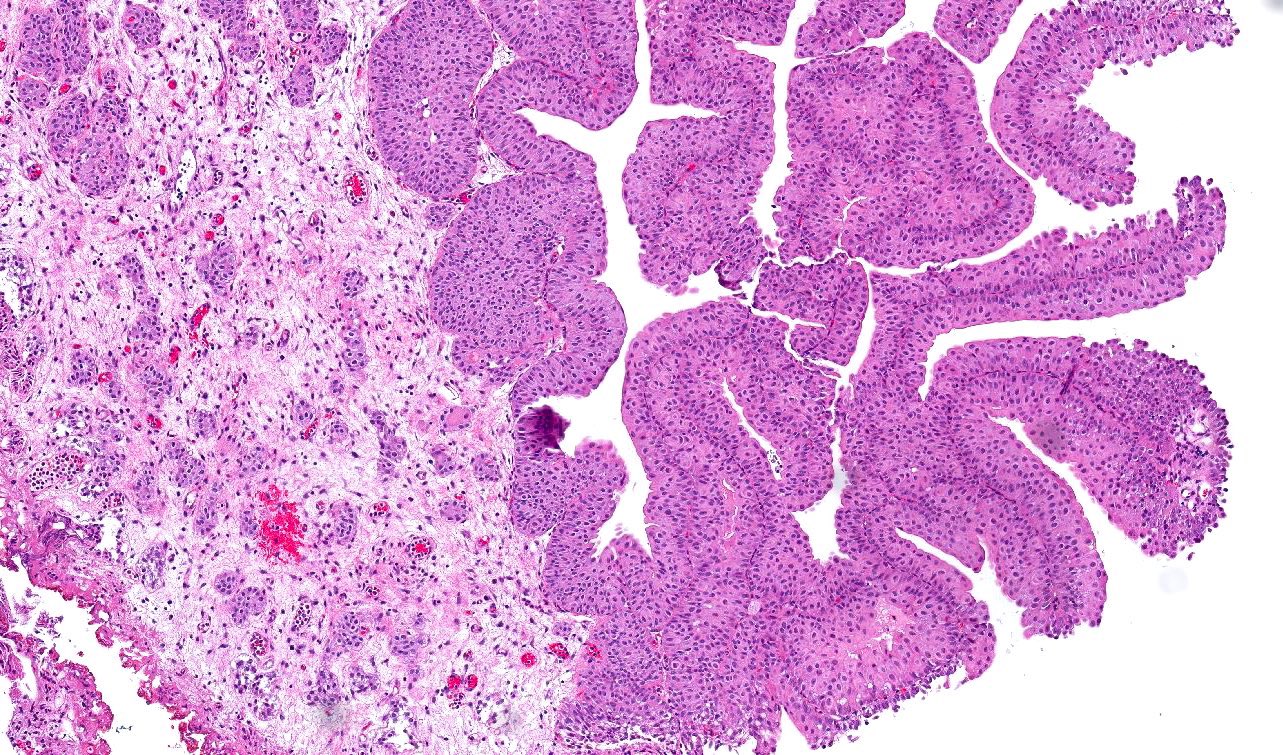
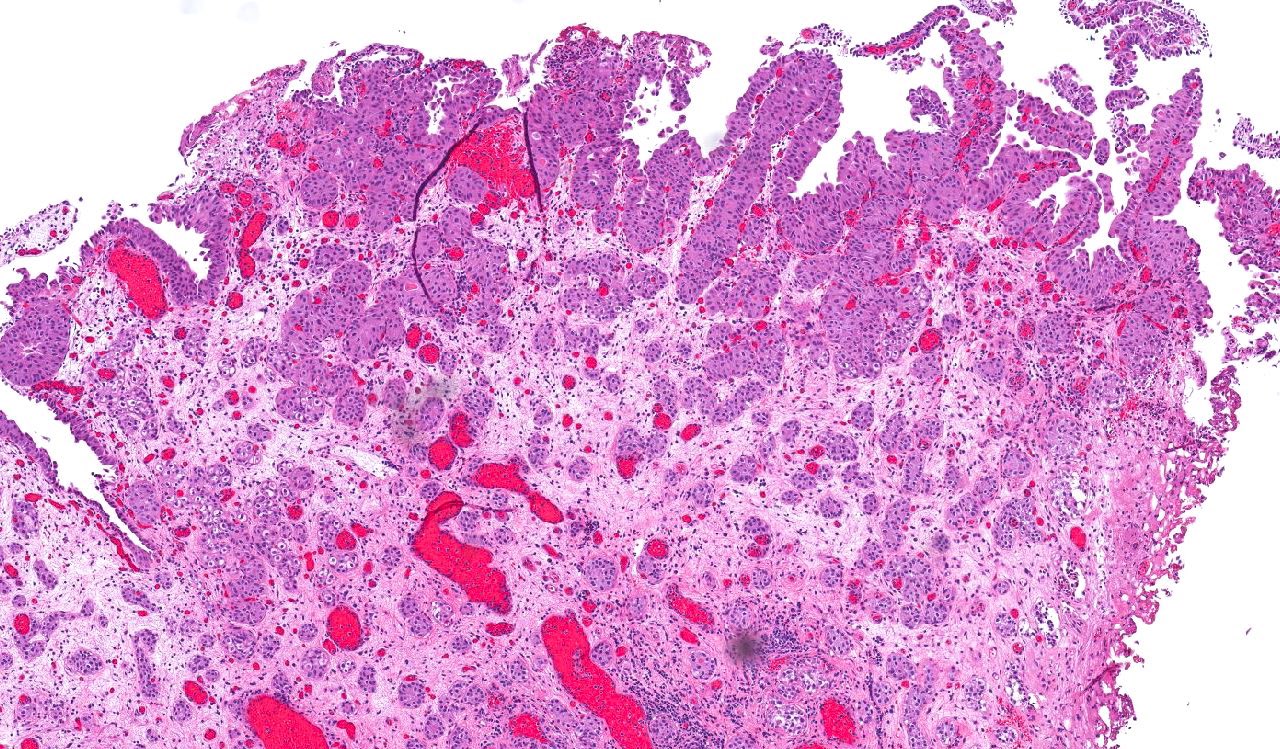
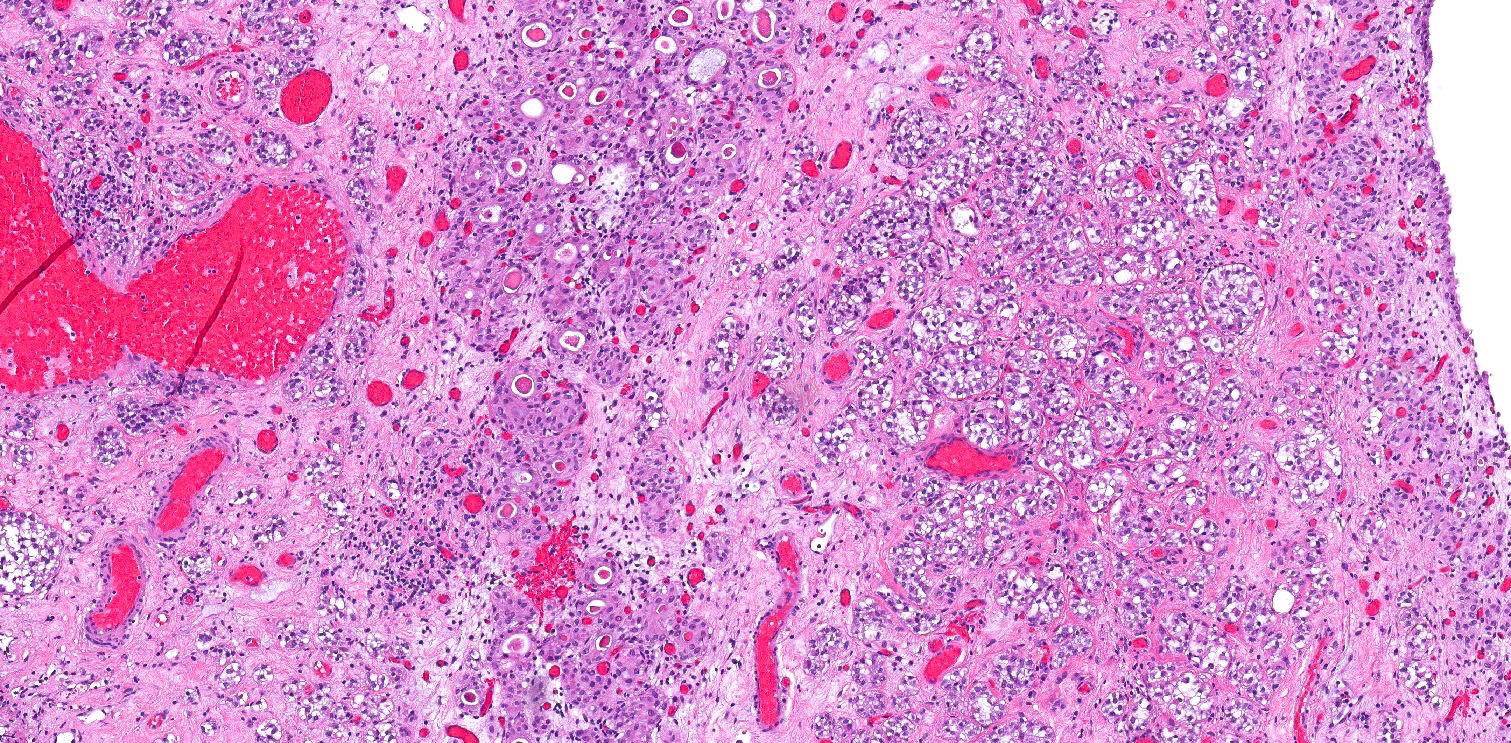
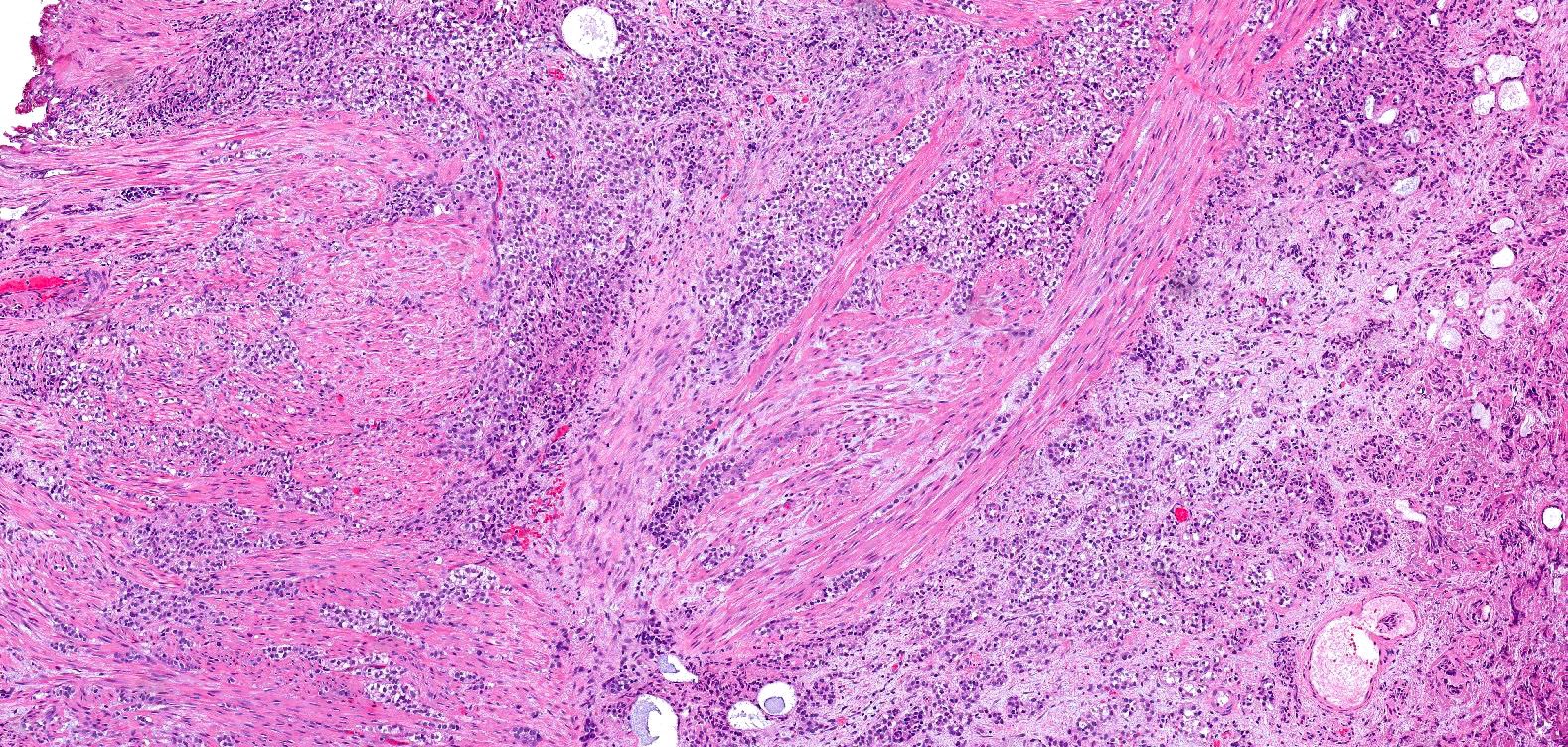
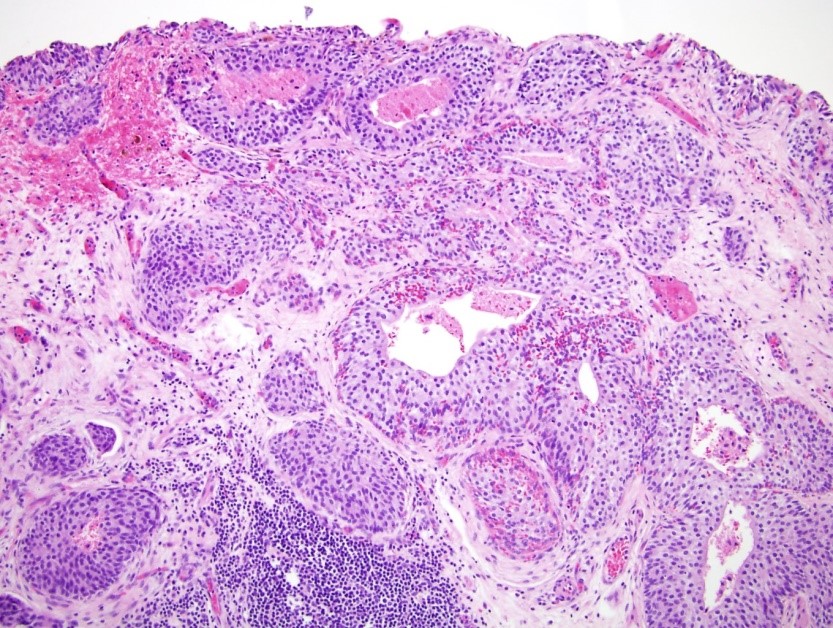
Microscopic (histologic) description
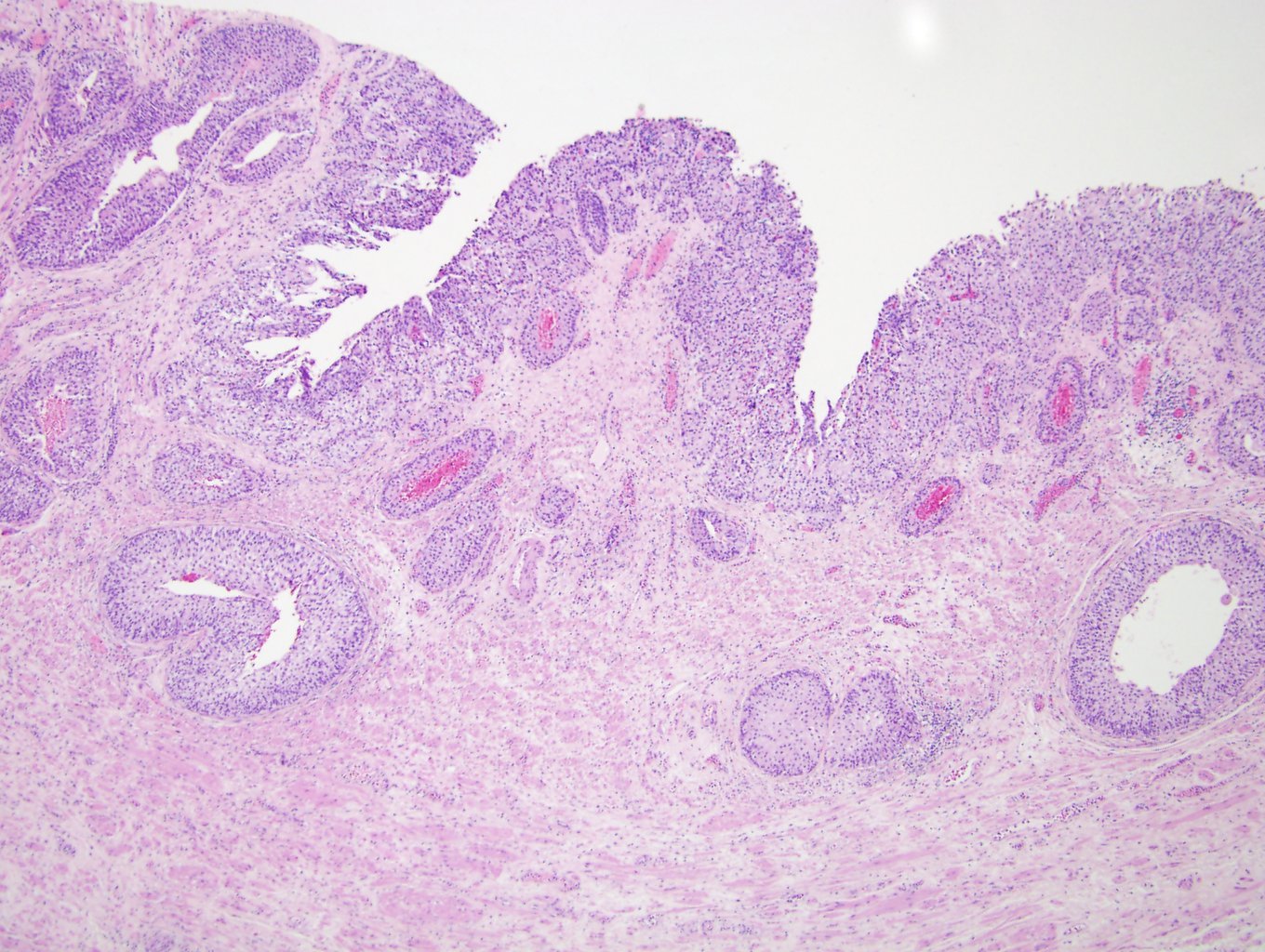
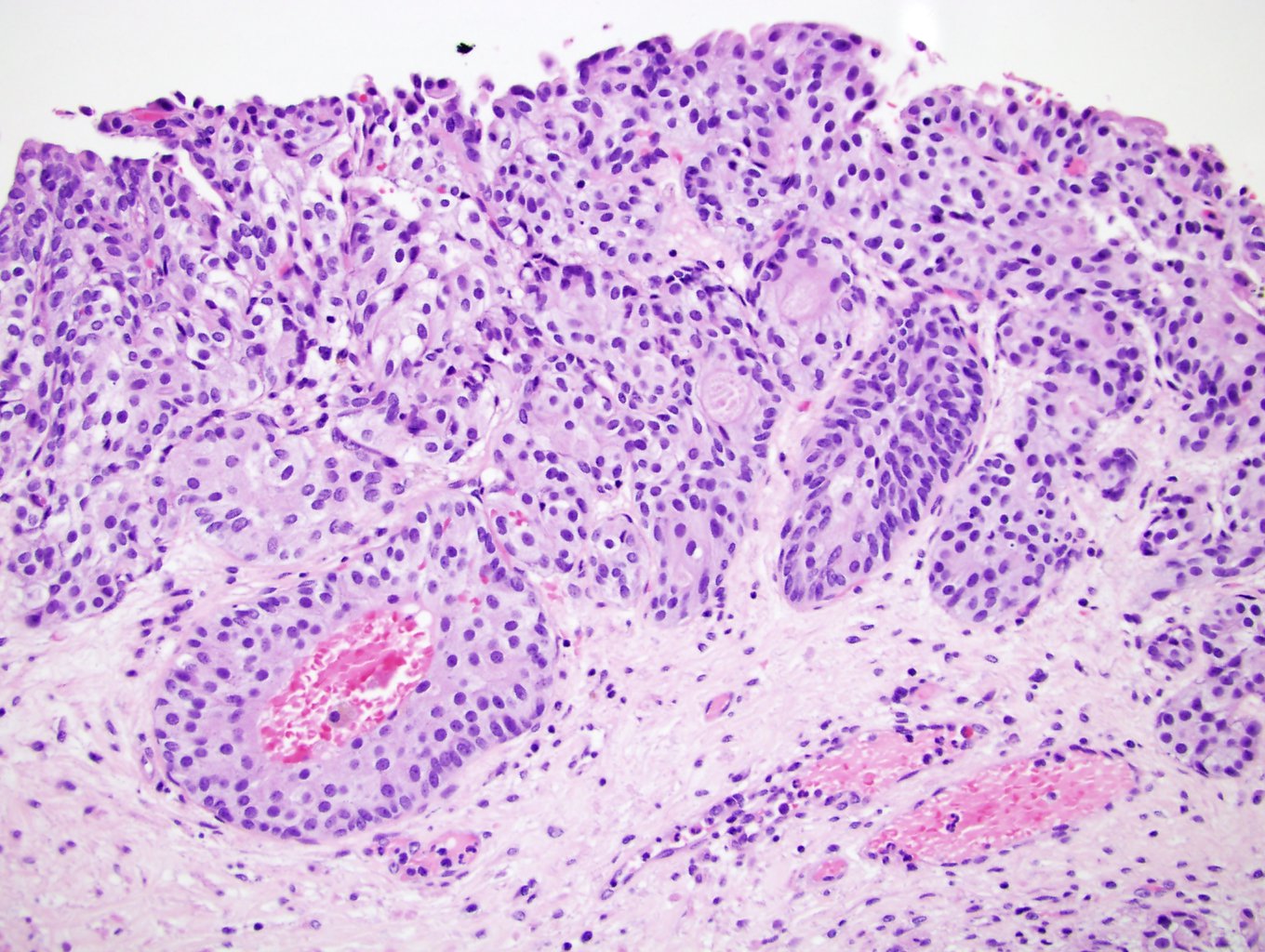
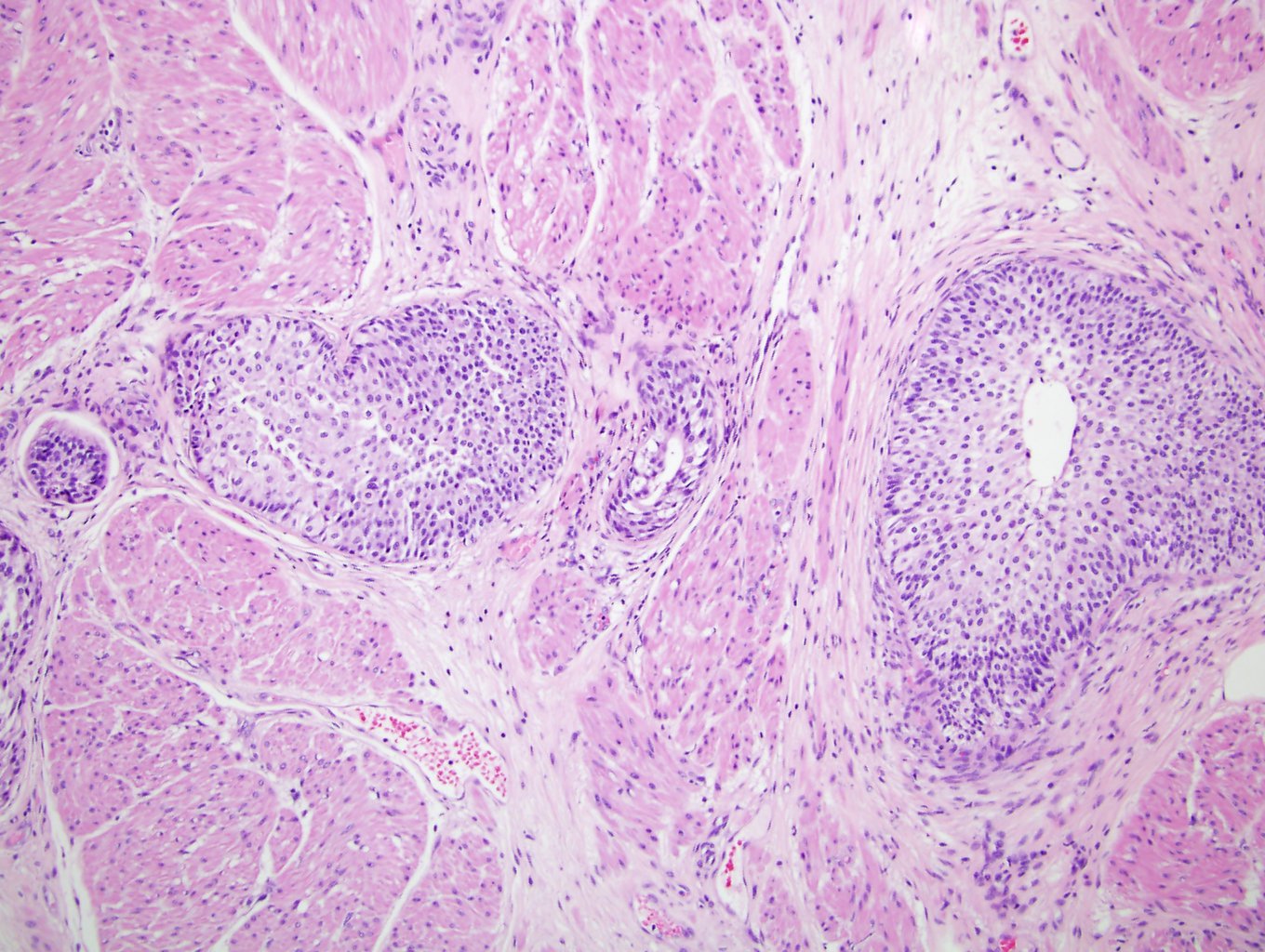
- Anastomosing, irregularly sized nests lacking cytoarchitectural orientation to overlying urothelium and with more irregular projections into stroma, particularly at deep aspect (Mod Pathol 2009;22:S96)
- Overlying urothelium is usually unremarkable
- Cytologically bland, usually with focal atypia
- Low to intermediate nuclear grade and occasional nuclear enlargement and greater cytologic atypia in deep aspects of tumor (Histopathology 2019;74:77, Mod Pathol 2009;22:S96)
- May exhibit small tubular lumens which may contain necrotic cellular debris (Histopathology 2019;74:77, Stanford Medicine: Nested Variant Urothelial (Transitional Cell) Carcinoma [Accessed 19 April 2021])
- Stroma may be normal or desmoplastic
- A component of conventional urothelial carcinoma is present in 64% of cases (Hum Pathol 2010;41:163)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Similar to conventional urothelial carcinomas with CK7 (93% of cases), CK20 (68%), p63 (92%) and CK903 (92%) expression (Hum Pathol 2010;41:163)
- Ki67 variable (2 - 35%) (Mod Pathol 2003;16:1289)
Negative stains
- p53, BCL2 usually negative
- Loss of p27 expression in deeper component of tumor (Mod Pathol 2003;16:1289)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Loss of p27, a cyclin dependent kinase inhibitor (p53 independent), may dictate the behavior; loss of p27 has been associated with increased proliferation and progression of disease (Mod Pathol 2003;16:1289)
- Luminal molecular phenotype (FOXA1+ / CK5/6-) (Am J Clin Pathol 2021;155:588)
- TERT promotor mutations (Histopathology 2019;74:77)
Sample pathology report
- Bladder, transurethral resection:
- High grade urothelial carcinoma with nested growth (60%) (see comment)
- Comment: Invasive of lamina propria (pT1)
- Angiolymphatic invasion absent
- Muscularis propria present, no tumor
Differential diagnosis
- Florid von Brunn nests:
- Relatively round and evenly spaced with uniform linear border at base versus nested carcinoma, which has anastomosing, smaller, irregularly sized nests lacking orientation to overlying urothelium and more irregular projections into stroma and muscle invasion (Mod Pathol 2009;22:S96)
- Wide variability in staining for Ki67, p53, p27 and CK20 seen in both florid von Brunn nests and nested variant of urothelial carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:1243)
- Inverted papilloma:
- Has more cytoarchitectural organization within nests
- Cells maintain peripheral palisading
- Nephrogenic adenoma:
- May be nested, tubular and have irregular stromal interface but nests are composed of only a single layer of cuboidal or flattened cells and is more likely to contain other architectural patterns (cystic, papillary) and have surrounding stromal edema and inflammatory infiltrate (Mod Pathol 2009;22:S96)
- Paraganglioma and carcinoid:
- Characteristic vascular pattern and chromatin features
- Positive for neuroendocrine markers
Board review style question #1
Nested variant of urothelial carcinoma is most commonly identified in which patients?
- Women aged 30 - 50
- Women older than 80
- Men older than 60
- Men younger than 50
- Pediatric populations (< 18)
Board review style answer #1
C. Men older than 60. The nested variant of urothelial carcinoma is most commonly identified in men older than 60 with a similar occurrence to that of classic urothelial carcinoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Nested urothelial carcinoma
Comment Here
Reference: Nested urothelial carcinoma
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2