Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Sites | Etiology | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Roychowdhury M. Follicular cystitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderfollicular.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
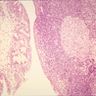
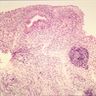
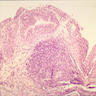
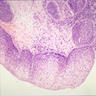
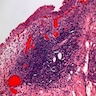
- Nonspecific inflammatory disease of the bladder, with lymphoid follicles in lamina propria, often with chronic cystitis
Terminology
- Also called cystitis follicularis
Sites
- Trigone is the most common site (Paraplegia 1995;33:565)
Etiology
- Associated with prolonged urinary tract infection secondary to bladder outlet obstruction, neurogenic or muscular dysfunction of the bladder (commonly Salmonella or other gram- infection), intravesical chemotherapy or bcg (Clin Cancer Res 2003;9:5550)
Case reports
- 70 year old woman with follicular cystitis (Arch Esp Urol 2007;60:77)
Gross description
- Mucosal nodularity or granularity
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Large number of plasmacytic cells and lymphocytes with lymphoid follicles scattered within the bladder mucosa and submucosa
- Overlying urothelium may have mild atypia
Cytology description
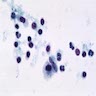
- Reactive epithelial cells (suggested by nuclear pleomorphism without alteration of nuclear/cytoplasmic ratio and glandular metaplasia including cystitis cystica and glandularis) mixed with tissue fragments and cellular aggregates reflecting the structure of lymphoid follicles with a pleomorphic lymphoid population, intermixed histiocytes and scattered tingible body macrophages (Diagn Cytopathol 2002;27:205)
Differential diagnosis
- Follicular lymphoma: very rare in bladder; closely packed follicles containing small cleaved cells without nucleoli (centrocytes) and larger noncleaved cells with moderate cytoplasm, open chromatin and multiple nucleoli (centroblasts); minimal or no apoptotic cells or tingible body macrophages; BCL2+ within follicles, usually t(14;18)(q32;q21)
- Other non-Hodgkin lymphoma: monomorphic atypical lymphoid population
- Granulomatous process in cases with histiocyte predominance (low number of lymphocytes)
- Cystitis with sporadic lymphocytes: no germinal centers, usually no overlying epithelial atypia
- Tuberculosis: may resemble follicular cystitis at cystoscopy; histologically has granulomas, with or without central caseation