Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Chaux A. Arteriovenous malformation. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/bladderAVM.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- By definition, direct communication is present between arterioles and venules
Sites
- More common in CNS, intestine, lung, extremities
- Very rare in urinary bladder
Etiology
- Can be congenital or acquired (post-traumatic)
Clinical features
- The most common symptom is hematuria (gross or micro, persistent or intermittent, may be massive)
- Other symptoms include dysuria, difficulty in voiding and urinary retention
- Some cases are asymptomatic
Case reports
- Treated with transurethral resection (Int J Urol 2005;12:409)
Treatment
- Excision is adequate therapy
Gross description
- Large, broad-based, exophytic masses up to 6 cm (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1213)
- Hemorrhagic, sometimes necrotic, surface
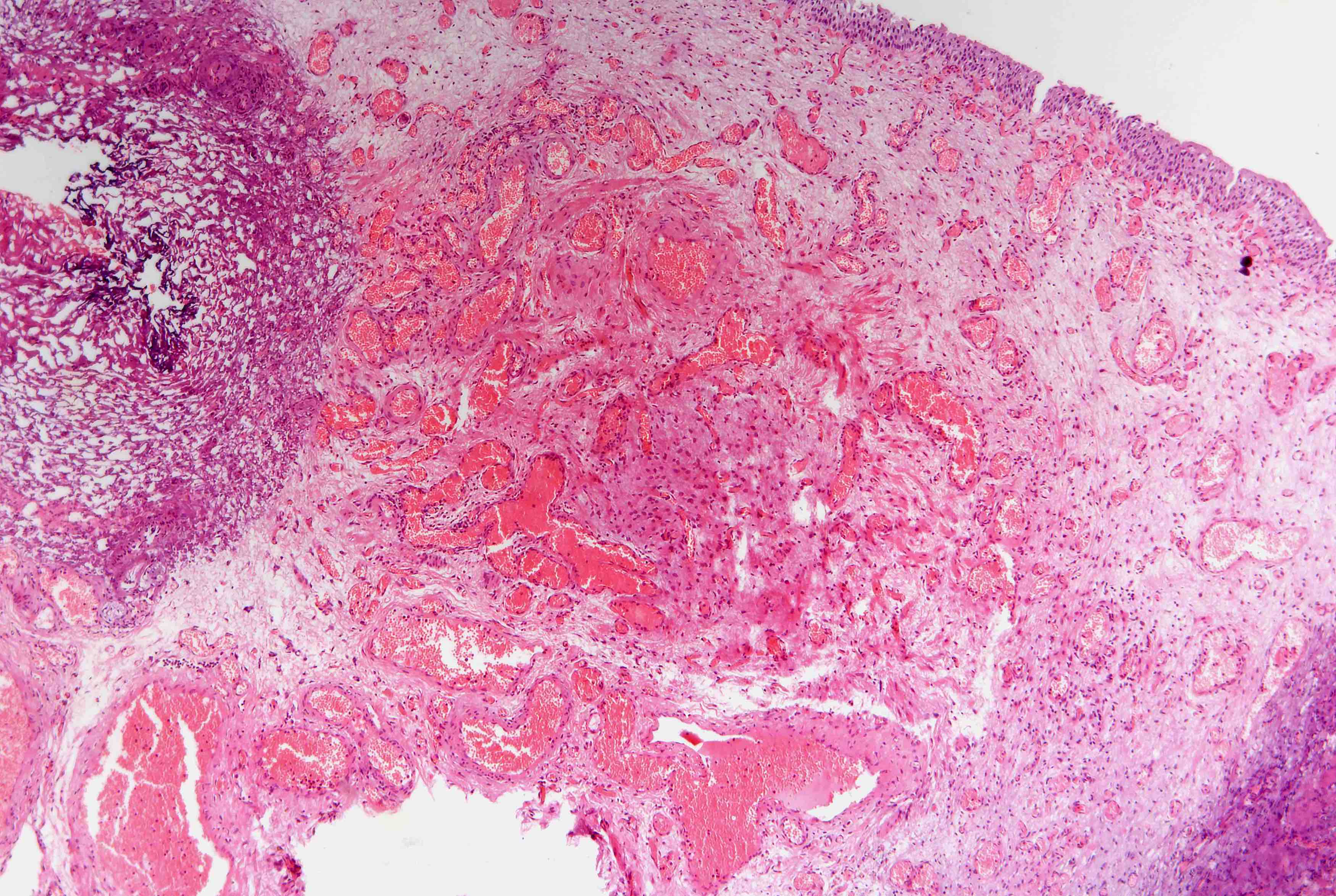
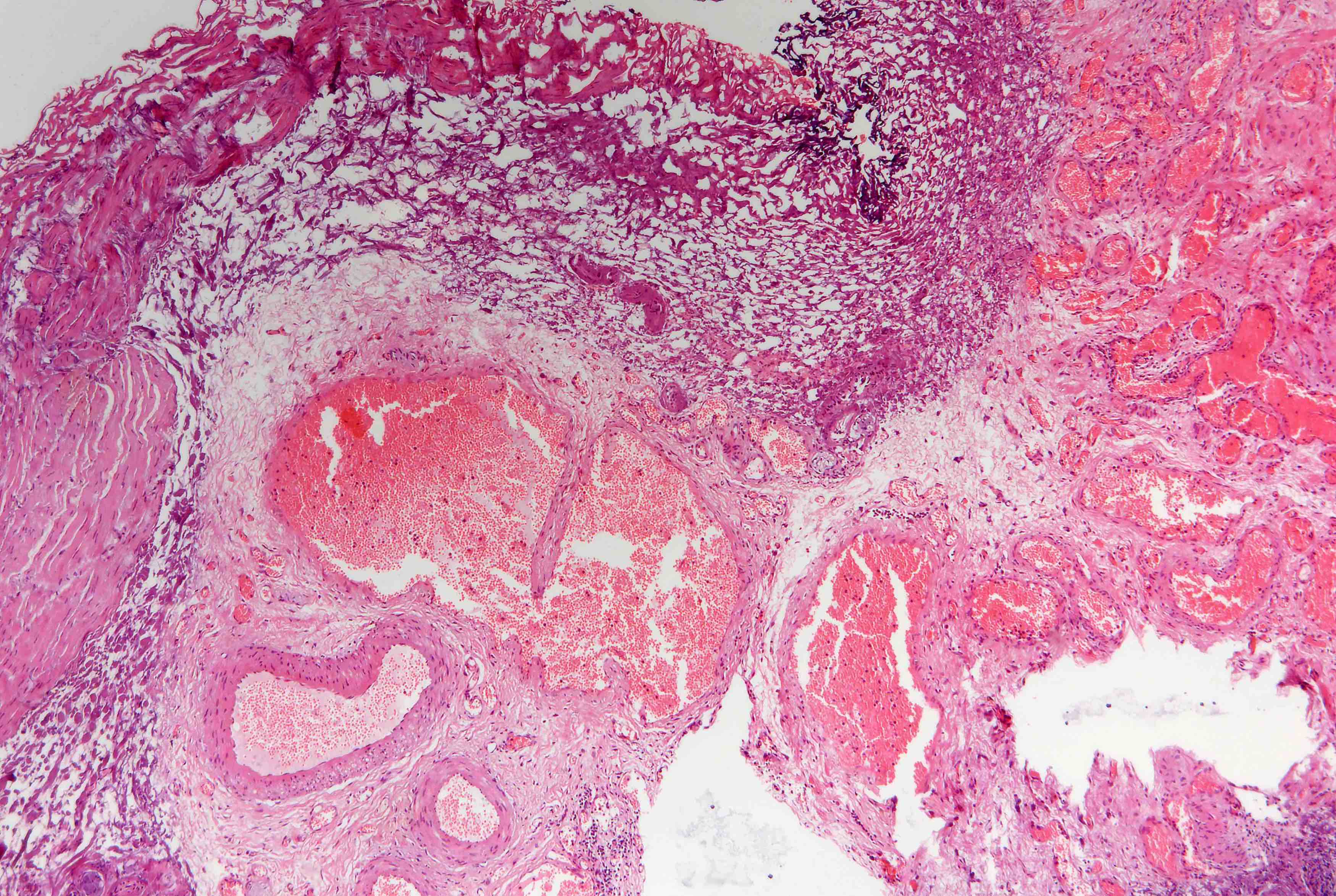
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Admixture of malformed vessels such as capillaries, arteries and venules
- Abrupt changes in thickness of medial and elastic layers of vessels, abnormal vascular dilation
- Often advanced small vessel disease, hemorrhage, ulceration (Hum Pathol 1986;17:94)
- Involves submucosa but not muscularis propria
- May be associated with pseudocarcinomatous epithelial hyperplasia of bladder (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:92)
Microscopic (histologic) images