Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Diagrams / tables | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Pezhouh MK. Anatomy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/appendixnormalanatomy.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Anatomy
- Commonly located in retrocecal or pelvic region
- Arises from posteriomedial cecum, usually lies posterior to cecum or ascending colon, may overlie pelvic brim and impinge on bladder; also other locations
- Locate by following the 3 teniae coli of the large bowel, which all terminate at base of appendix
- Same 4 layers as gut (mucosa, submucosa, muscularis externa / propria, serosa)
- Orifice is ~2.5 cm below ileocecal valve; may be covered by small flap of mucosa
- No known function; may have role in mucosal immunity
- Vasculature / lymphatics / innervation
- Vascular supply from posterior cecal branch of ileocolic artery, a branch of superior mesenteric artery
- Drains into ileocolic vein, then superior mesenteric vein and portal circulation
- Lymphatics drain into ileocolic lymph nodes
- Innervation from vagus nerve and superior mesenteric plexus
- Mesoappendix
- Adipose tissue plus appendiceal vessels and occasionally small lymph nodes
- Anchors appendix
- Abnormal positions of appendix
- Left sided appendix is associated with congenital anomalies including situs inversus and midgut malrotation; appendicitis is in the differential diagnosis of left lower quadrant pain in these patients (World J Gastroenterol 2010;16:5598)
Essential features
- Appendix arises from posteromedial aspect of cecum, is lined by large bowel type epithelium and is variable in length from 2 - 20 cm
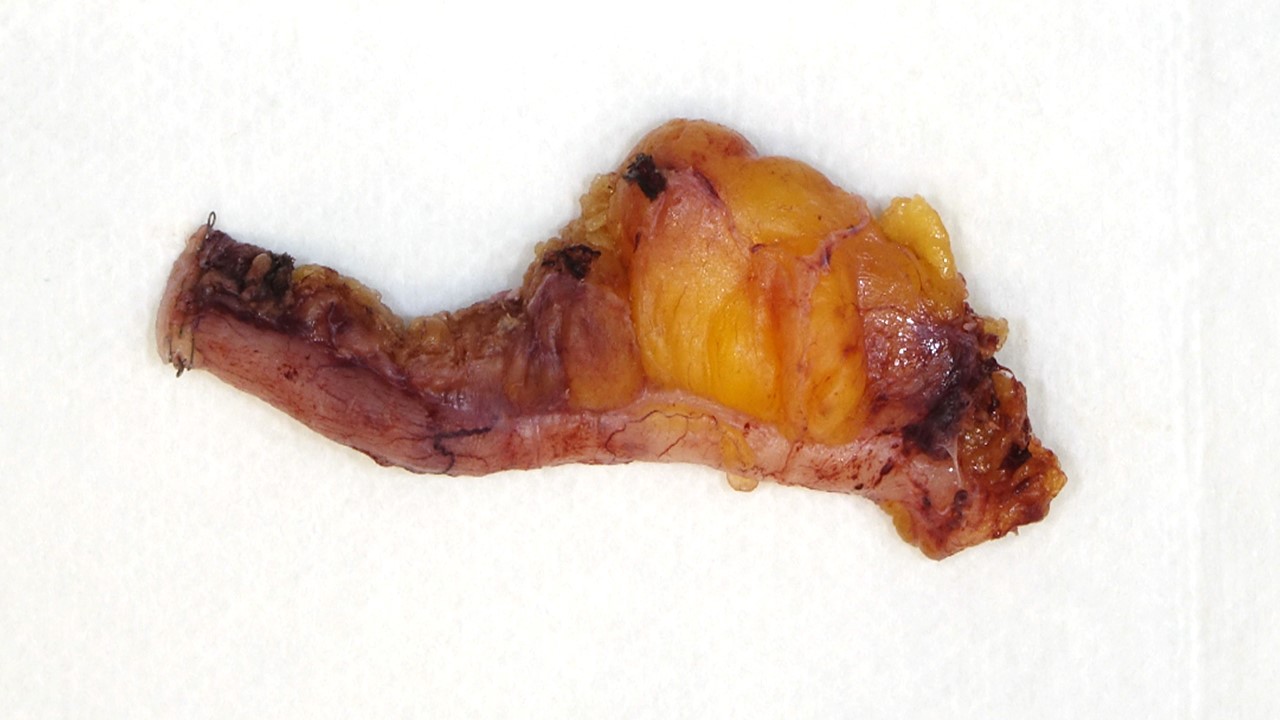
Gross description
- Blind vermiform structure with attached mesoappendix
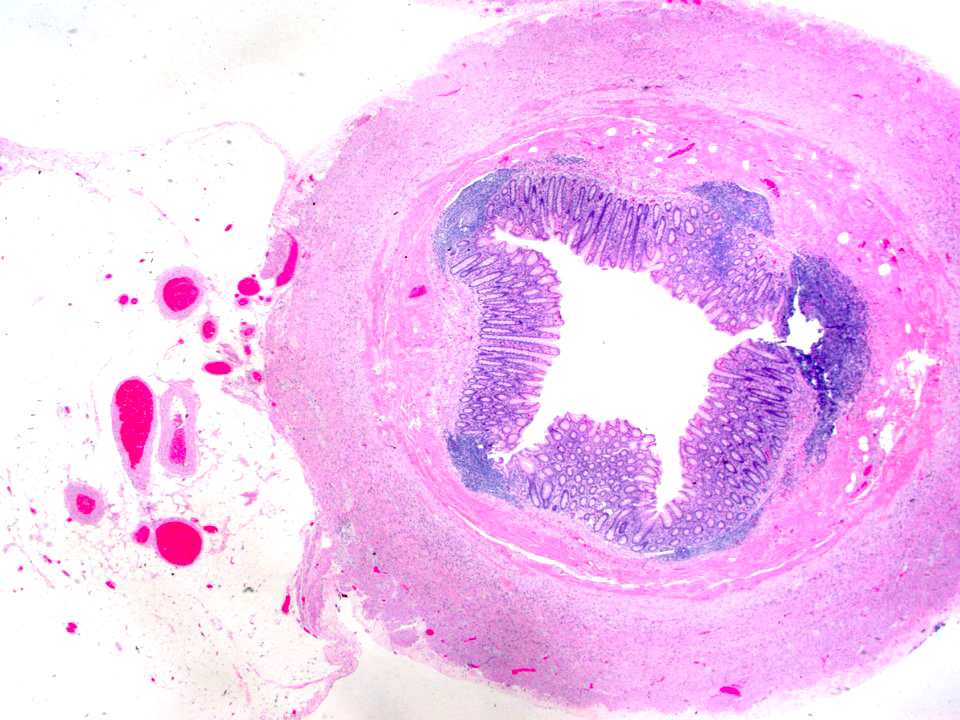
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Large bowel type epithelium
- Rich lymphoid tissue in mucosa and submucosa that may disrupt the muscularis mucosa, obliterate the lumen and distort the crypt architecture (lymphoid tissue atrophies with age)
- Epithelium contains occasional Paneth cells at crypt bases (basal nucleus, conspicuous nucleoli, abundant eosinophilic supranuclear granules)
- Lamina propria also contains plasma cells, occasional eosinophils
- Muscularis propria contains complete longitudinal and circular layers and prominent ganglion cells
- Presence of neutrophils is not typical and suggests acute appendicitis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
A. Focal lymphoid follicle. Focal small lymphoid follicles can normally be seen in a normal appendix. Answers B and D are incorrect because they are features of acute appendicitis. Answer C is incorrect as tubular adenoma is not a normal finding anywhere in the GI tract.
Comment Here
Reference: Appendix - Anatomy
Comment Here
Reference: Appendix - Anatomy