Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Forgó E, Longacre TA. Condyloma acuminatum. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/anuscondyloma.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Benign papillomatous squamous proliferation with a fibrovascular core, caused by human papillomavirus (HPV) infection
- Giant condyloma acuminatum with features of deep growth and local destruction, also known as Buschke-Löwenstein tumor
Essential features
- Benign papillomatous squamous proliferation with a fibrovascular core
- Koilocytic change in upper 33% of squamous epithelium
- Caused by HPV serotypes 6 and 11
- High grade dysplasia and carcinoma prevalence higher in HIV positive patients
Terminology
- Anal wart
- Anogenital wart
- Anal condyloma
ICD coding
- ICD-11: 1A95.0 - anal warts
Epidemiology
- M = F; third decade of life
- More common in young men who have sex with men, HIV positive
- Risk factors: immunodeficient state, increased contacts (J Med Case Rep 2015;9:9, Acta Gastroenterol Belg 2021;84:343)
- Giant condyloma acuminatum: M > F
Sites
- Most common: upper anal canal and anal transition zone
- Less common: lower anal canal and perianal skin
- May be associated with coinfection in other genital sites (i.e., cervix, vulva, penis)
Pathophysiology
- HPV transient productive infection of basal layer of squamous epithelium
- Low oncogenic risk subtypes: HPV serotypes 6, 11
Clinical features
- Most common: asymptomatic
- Discomfort, pruritis, bleeding, eczematous rash
- Painless mass
Diagnosis
- Anoscopy with biopsy
Radiology description
- CT / MRI used to exclude malignant transformation (Gastrointest Radiol 1991;16:267, Radiology 1984;150:651)
Prognostic factors
- Recurrence ranges from 5% to 70% depending on treatment
- High grade dysplasia and carcinoma prevalence is higher in HIV positive patients (Dis Colon Rectum 2017;60:1078)
- Giant condyloma acuminatum (Buschke-Löwenstein tumor) has aggressive destructive local behavior with propensity for infections and fistulations (Ann Ital Chir 2018;89:291)
Case reports
- 50 year old man with giant condyloma acuminatum with deep infiltration (Dermatology 2009;218:56)
- 53 year old man with perianal giant condyloma acuminatum (Buschke-Löwenstein tumor) (Case Rep Surg 2012;2012:507374)
- 57 year old man with malignant transformation of giant condyloma acuminatum (Dis Colon Rectum 1981;24:462)
- 58 year old woman with coexistence of condylomata acuminata with warty squamous cell carcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma (Med Arch 2017;71:72)
Treatment
- Small condyloma can regress and be treated conservatively with patient applied therapies: imiquimod, podophyllotoxin, sinecatechins
- First line clinician administered therapies: cryotherapy, trichloroacetic acid
- Large condyloma and those in anal canal require wide surgical removal: excision, laser, electrosurgery
- References: UpToDate: Condyloma Acuminata [Accessed 4 March 2022], Dermatol Ther 2020;33:e13193, Clin J Gastroenterol 2021;14:439, Int J STD AIDS 2012;23:362, Am J Obstet Gynecol 1985;153:545
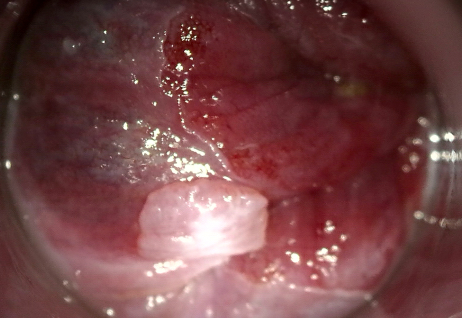
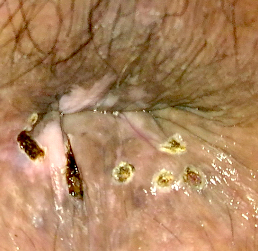
Clinical images
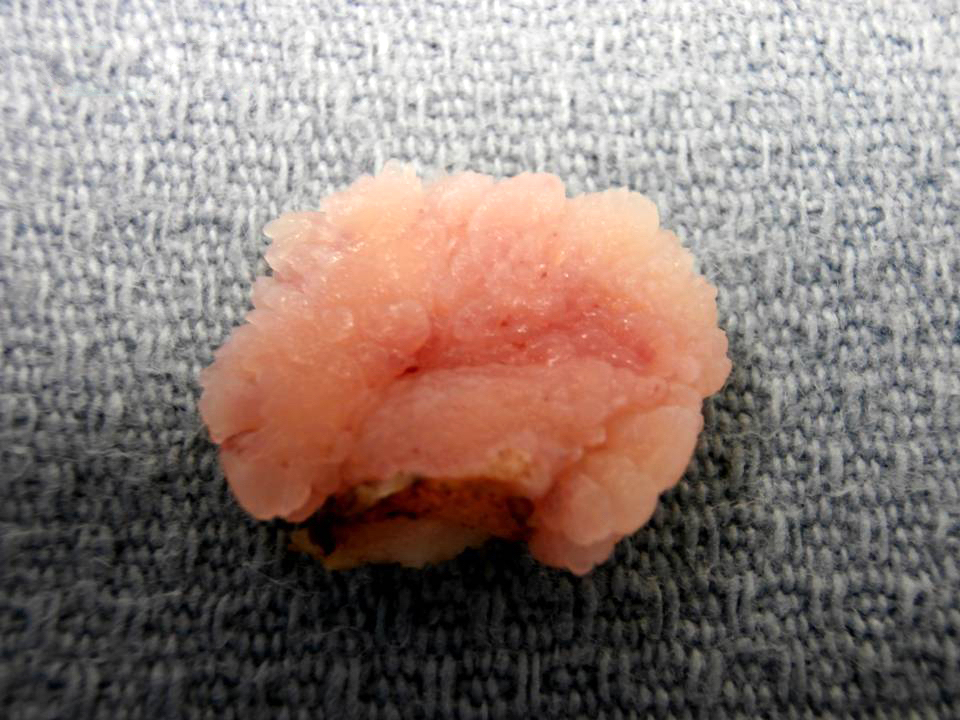
Gross description
- Fleshy, warty, cauliflower-like lesion
- May be flat lesion in anal canal
- Single or multiple (more common)
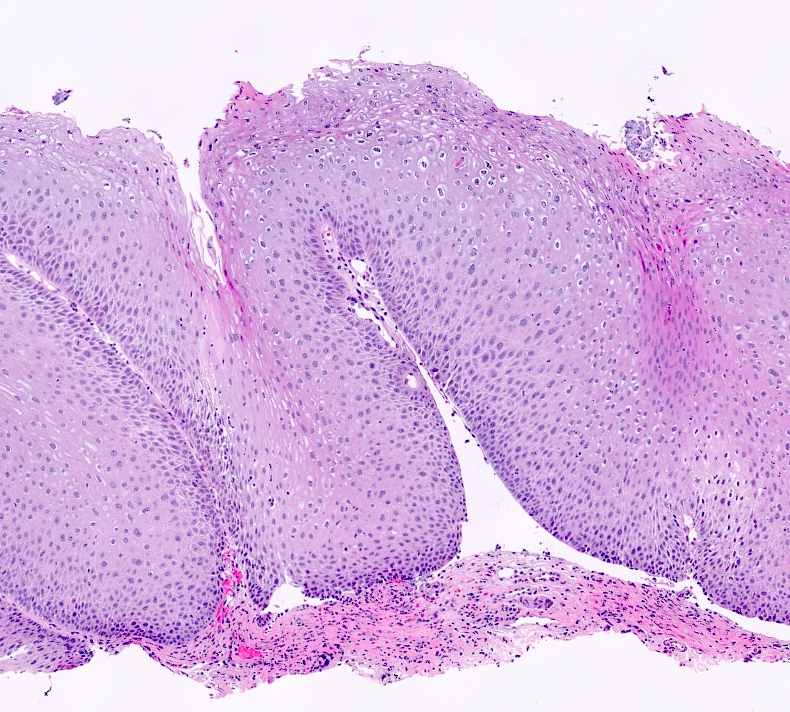
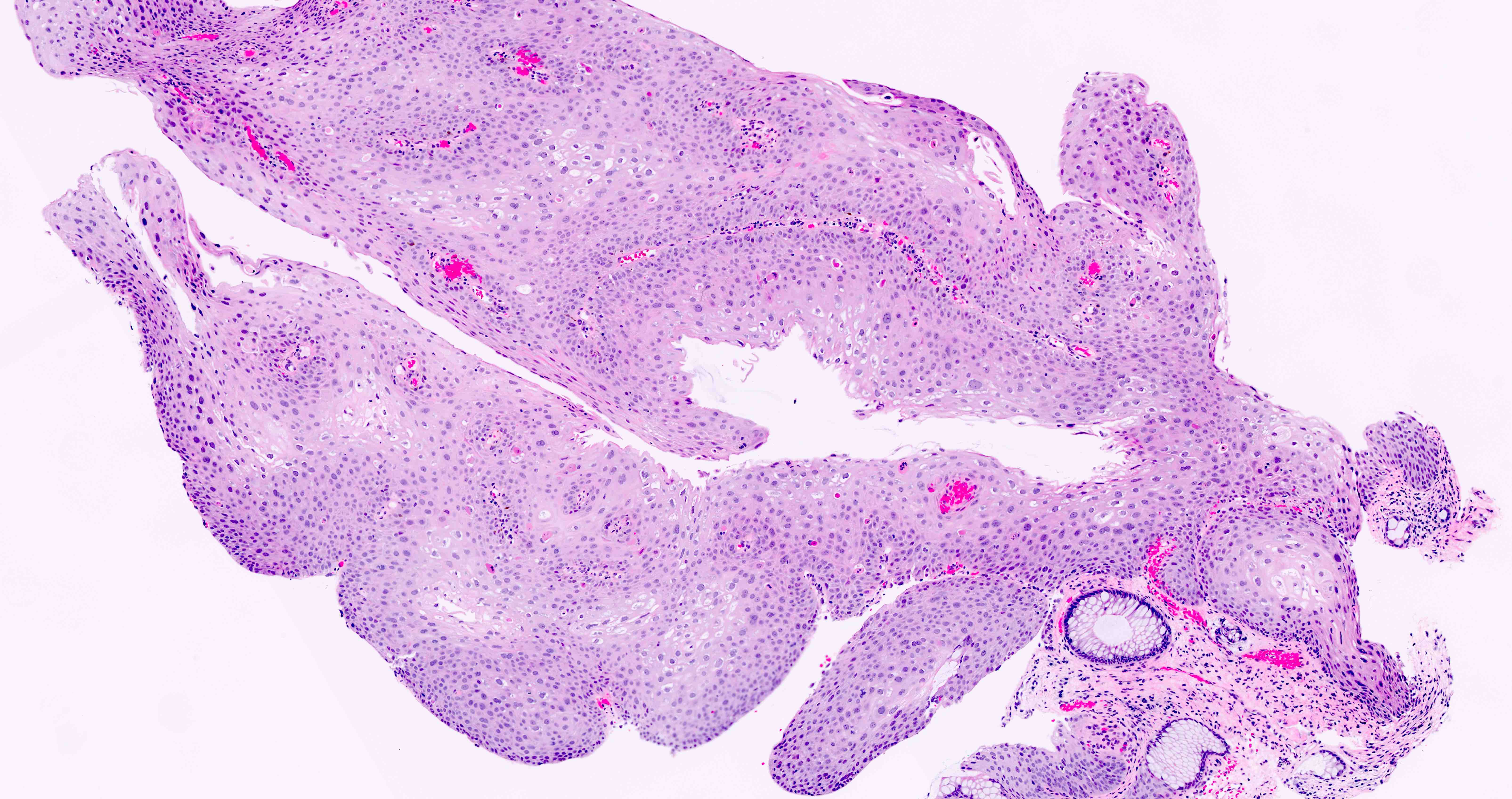
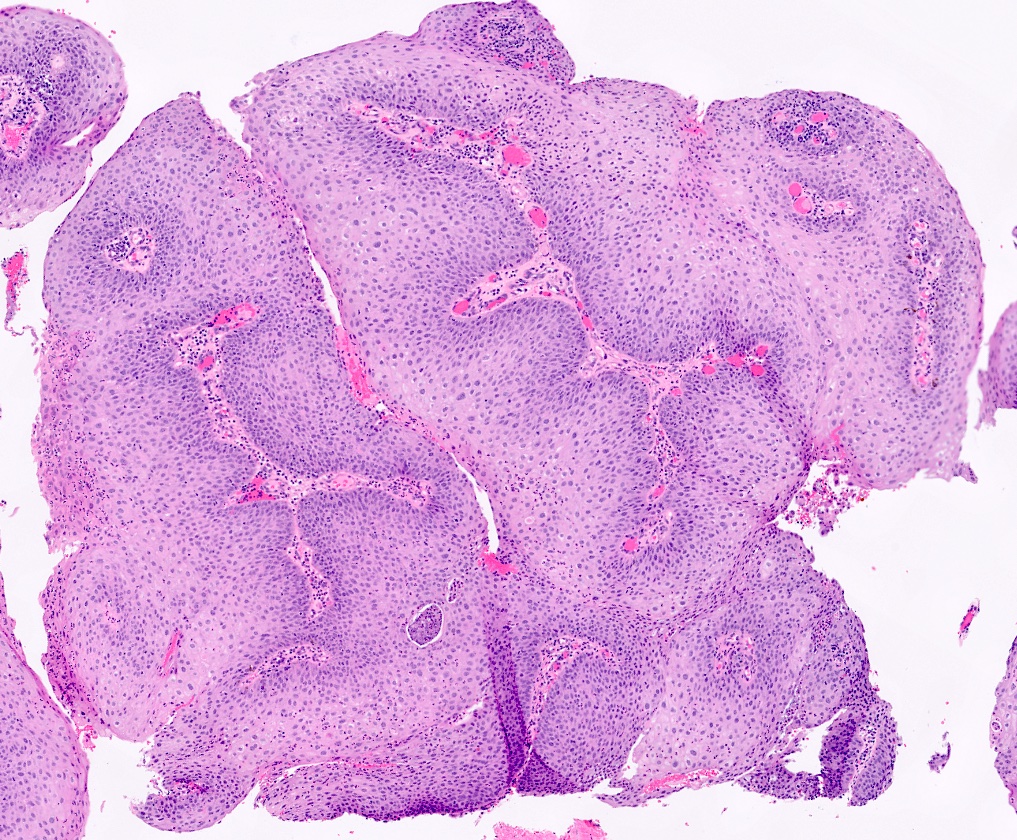
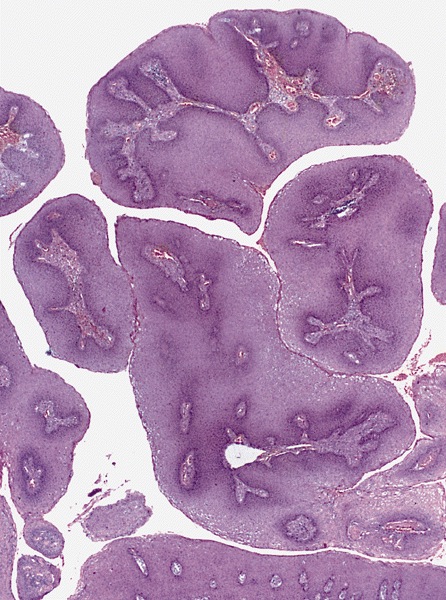
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Hyperplastic papillary exophytic squamous epithelium
- Marked acanthosis
- Parakeratosis
- Fibrovascular core
- Koilocytosis (irregular nuclei, bi and multinucleation, perinuclear vacuolization) confined to upper third of squamous epithelium
- No dysplasia or invasive squamous cell carcinoma
- Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL [condyloma acuminatum]) terminology applied according to the Lower Anogenital Squamous Terminology (LAST) project (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2012;136:1266)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
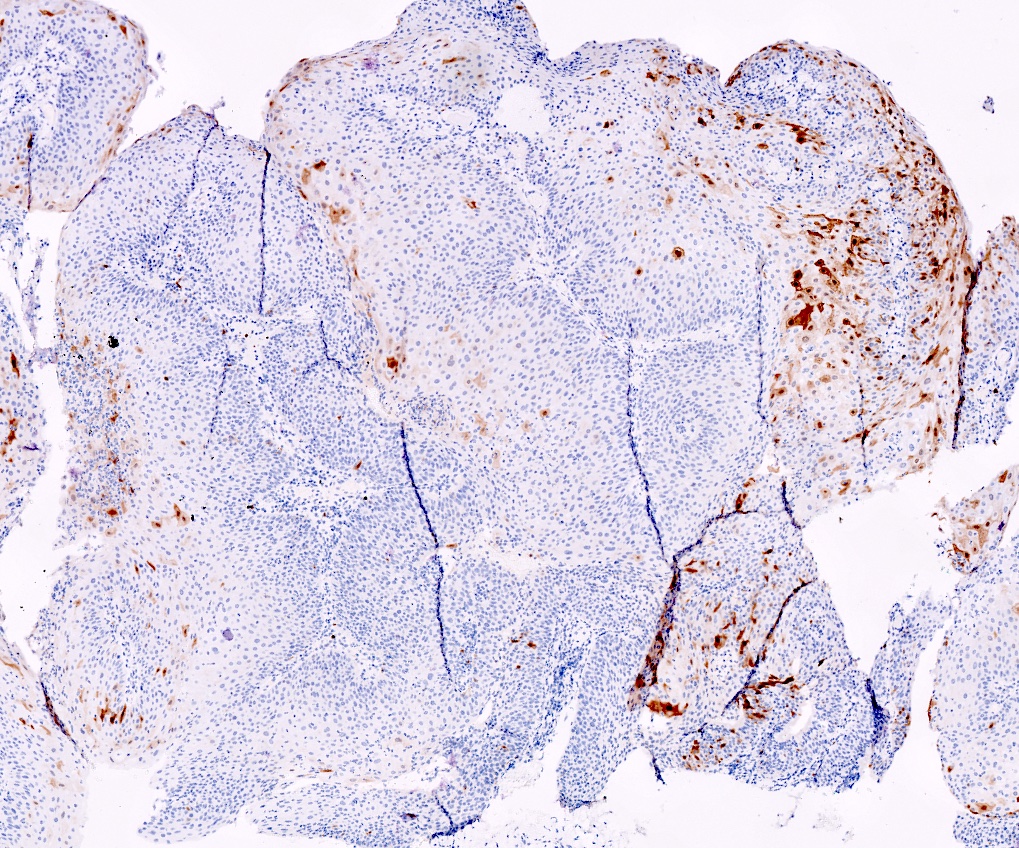
- Negative p16 if without dysplasia (no overexpression / nonblock positivity)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- In situ hybridization (ISH) and PCR positive for low risk HPV 6 and 11 serotypes
Sample pathology report
- Anus, perianal lesion, biopsy:
- Low grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (AIN 1 / condyloma acuminatum)
Differential diagnosis
- Verrucous carcinoma:
- Pushing invasion of underlying stroma
- Fibroepithelial polyp:
- Lacks papillary proliferation of squamous epithelium, no koilocytes
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 50 year old HIV positive man is found to have a papillary perianal growth. The H&E section above demonstrates papillary squamous epithelium with koilocytic change in the upper third of the squamous epithelium, without cytologic atypia. p16 immunohistochemical stain is also shown. Which of the following HPV serotypes are associated with this lesion?
- HPV 6 and 11
- HPV 16 and 18
- HPV 31, 33 and 35
- HPV 45
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
According to the Lower Anogenital Squamous Terminology (LAST) project, what is the appropriate terminology for anal condyloma acuminatum?
- AIN 1
- ASIN-L
- Condyloma acuminatum
- LSIL
- LSIL (condyloma acuminatum)
Board review style answer #2