Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Tretiakova M. Oncocytic. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/adrenocorticalcarcinomaoncocytic.html. Accessed January 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Malignant epithelial tumor of adrenal cortical cells with predominantly oncocytic morphology
Essential features
- Rare variant of adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC); less than 70 cases reported
- Composed entirely or predominantly (> 90%) of oncocytic cells with abundant cytoplasmic mitochondria (WHO 2022) (Int J Surg Pathol 2004;12:231, Hum Pathol 2021;110:50)
- Tend to be lower stage, rarely invade adjacent organs and seem to represent more indolent variant of ACC with delayed recurrence and improved survival, despite a larger average size and aggressive morphologic appearance (Surgery 2019;166:524, Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Positive for inhibin, calretinin, MelanA, synaptophysin and mitochondrial antigen
Terminology
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC), oncocytic variant
- Adrenocortical carcinoma, oncocytic type
- Oncocytic adrenocortical carcinoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Oncocytic ACC is the most common ACC histologic variant (Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98)
- Accounts for 11 - 22% of ACC cases (Adv Anat Pathol 2014;21:151, Surgery 2019;166:524, Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98)
- Median age: 48, range: 1 - 83 (Biomedicines 2021;9:175, Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2021;12:20406223211033103)
- No gender predilection: M:F = 1:1.1 (Biomedicines 2021;9:175, Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2021;12:20406223211033103)
- 24% of all adrenocortical oncocytic tumors are malignant ACC (Surgery 2018;164:1351)
Sites
- Left adrenal more commonly affected: left to right ratio = 1.6:1 (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Rare cases of ACC in ectopic adrenal rests (Ecancermedicalscience 2020;14:1135)
Pathophysiology
- Molecular evidence for an adenoma to carcinoma progression (Virchows Arch 2012;460:9, PLoS One 2013;8:e73959)
- Common deletion in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA 4977 bp) in benign, borderline and malignant oncocytic adrenocortical tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1882)
- Insulin-like growth factor 2 (IGF2) proposed as the main oncogene in ACC tumorigenesis with 10 - 80 fold higher mRNA and protein expression compared to normal adrenal cortex or adenoma (Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2015;44:399, Ther Adv Chronic Dis 2021;12:20406223211033103)
Etiology
- Sporadic with no established risk factors
- Acquired genetic mutations of several driver genes (i.e. IGF2, CDKN2A, TERT, RB, ZNRF3, CDK4), although significantly less common than in conventional ACC (Cancer Cell 2016;29:723, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2015;44:399, Biomedicines 2021;9:174, Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98)
- 8% of oncocytic ACC had no detectable molecular alterations (Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98)
- Case report of oncocytic ACC in patient with Lynch syndrome (J Endocr Soc 2019;3:784)
Clinical features
- Hormone production in 30 - 44% tumors (Hum Pathol 2011;42:489, Surgery 2019;166:524, Urol Int 2013;91:125, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Cortisol with Cushing syndrome in majority of functional tumors
- Sex hormone or multiple hormones common
- Aldosterone production extremely rare
- Oncocytic ACC compared to conventional is typically larger at presentation but more often stage I or II (Surgery 2019;166:524)
- Majority of symptoms related to large tumor size and abdominal mass:
- Pain, discomfort, vomiting
- Weight loss, weakness
- Incidental finding in 11% of cases (Surgery 2019;166:524)
- Metastases documented in 13 - 21% of cases, recurrence in 14% of cases (Biomedicines 2021;9:175, Surgery 2018;164:1351)
Diagnosis
- Only definitive criteria for malignancy are distant metastasis or local angioinvasion
- Oncocytic ACC commonly characterized by large size and signal heterogeneity on CT and MRI, although distinguishing from benign tumors could be challenging due to low lipid content in both (Radiographics 2009;29:1319, Radiographics 2009;29:1333, Hum Pathol 2016;53:63, Hell J Nucl Med 2015;18:97, Surgery 2019;166:524, Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 2018;6:179)
- Loss / disruption of reticulin framework is distinctive between oncocytic ACC and oncocytoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1882)
- Weiss system for malignancy not applicable since at least 3 parameters (eosinophilic cytoplasm, high nuclear grade and diffuse architecture) are intrinsically present in this tumor type, irrespective of the biological and clinical behavior (Int J Surg Pathol 2004;12:231)
- Modified scoring Lin-Weiss-Bisceglia (LWB) system was proposed specifically for oncocytic ACC (Hum Pathol 2011;42:489, Adv Anat Pathol 2014;21:151):
| LWB diagnostic algorithm for oncocytic ACC | |
| 1 | Major criteria: |
| High mitotic rate (> 5 mitoses/50 HPF) | |
| Atypical mitotic figures | |
| Venous invasion | |
| 2 | Minor criteria: |
| Large size (> 10 cm) or weight (> 200 g) | |
| Necrosis | |
| Sinusoidal invasion | |
| Capsular invasion |
- One major criterion indicates malignancy, minor criteria indicates uncertain malignant potential (borderline) and the absence of all major and minor criteria indicates benign
Laboratory
- Same as conventional ACC
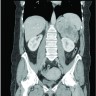
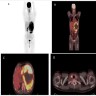
Radiology description
- Abdominal computed tomography (CT):
- Large adrenal mass with heterogeneous enhancement, central necrosis and areas of calcification (Can Urol Assoc J 2020;14:E45, Surgery 2019;166:524)
- On magnetic resonance imaging (MRI):
- Isointense to hypointense signal on T1 imaging, a hyperintense signal on T2 images and a heterogeneous signal drop on chemical shift (Surgery 2019;166:524)
- Because oncocytic tumors are lipid poor, CT, MRI or PET imaging are unable to distinguish benign from malignant lesions regardless of size, attenuation or handling of the contrast agent (Surgery 2019;166:524, Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 2018;6:179)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Pure oncocytic ACC has a better prognosis than conventional ACC (Horm Cancer 2011;2:333)
- Overall median survival for oncocytic ACC is 58 - 60 months, 2 fold longer than for conventional ACC (Hum Pathol 2011;42:489, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Overall 5 year survival rate after surgery is 47 - 60% (Urol Int 2013;91:125, Surgery 2018;164:1351)
- 5 year overall survival is stage dependent: 100% for stage I, 88% for stage II and 43.3% of stage III & IV (Surgery 2018;164:1351)
- Helsinki score, which incorporates the Ki67 proliferation index, appears to be the most specific and sensitive prognostic score for oncocytic ACC (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1708)
Case reports
- 18 month old boy with oncocytic ACC and rhabdomyosarcoma (J Clin Res Pediatr Endocrinol 2021;13:225)
- 26 year old woman with adrenocortical oncocytic carcinoma arising in ectopic adrenal tissue (Ecancermedicalscience 2020;14:1135)
- 37 year old man, asymptomatic with oncocytic ACC and papillary thyroid carcinoma incidentally detected by F18 FDG PET / CT (Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 2018;6:179)
- 45 year old man with nodal and pulmonary metastases of pleomorphic sarcoma arising in oncocytic adrenal cortical carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:470)
- 54 year old man with recurrent oncocytic adrenocortical carcinoma (Ann Ital Chir 2021;92:293)
- 70 year old man with oncocytic ACC incidentally discovered as retroperitoneal mass (Endocr J 2020;67:883)
Treatment
- Surgical (Surgery 2019;166:524):
- Radical resection - treatment mainstay
- Lymphadenectomy in 75% of cases
- Guidelines for adjuvant treatment with mitotane, cytotoxic chemotherapy and radiation therapy are similar to conventional ACC but data is limited
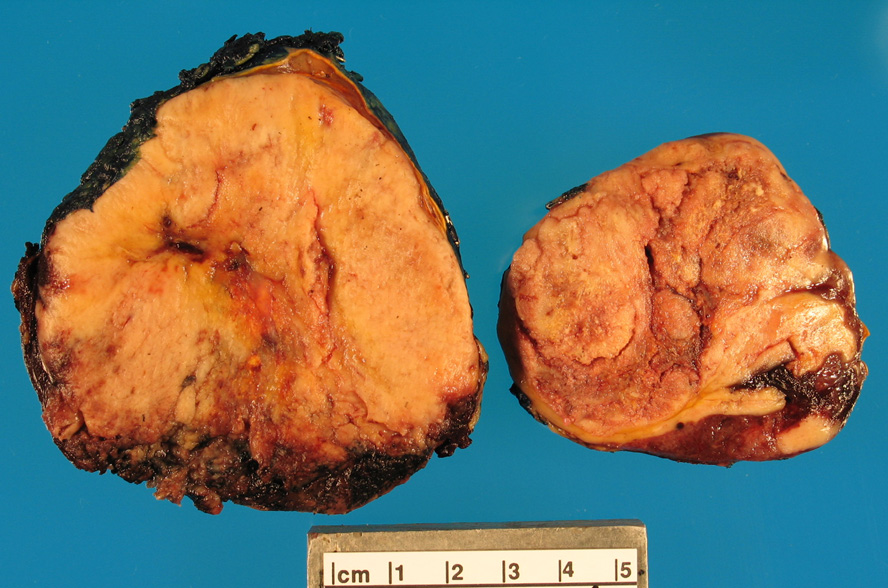
Gross description
- Median tumor size: 19.8 cm (range: 4.2 - 28.5 cm) (Surgery 2019;166:524)
- Median weight: 552 g (range: 50 - 5720 g) (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Yellow to brown lobular tumor rimmed by adjacent normal adrenal gland (Adv Anat Pathol 2014;21:151)
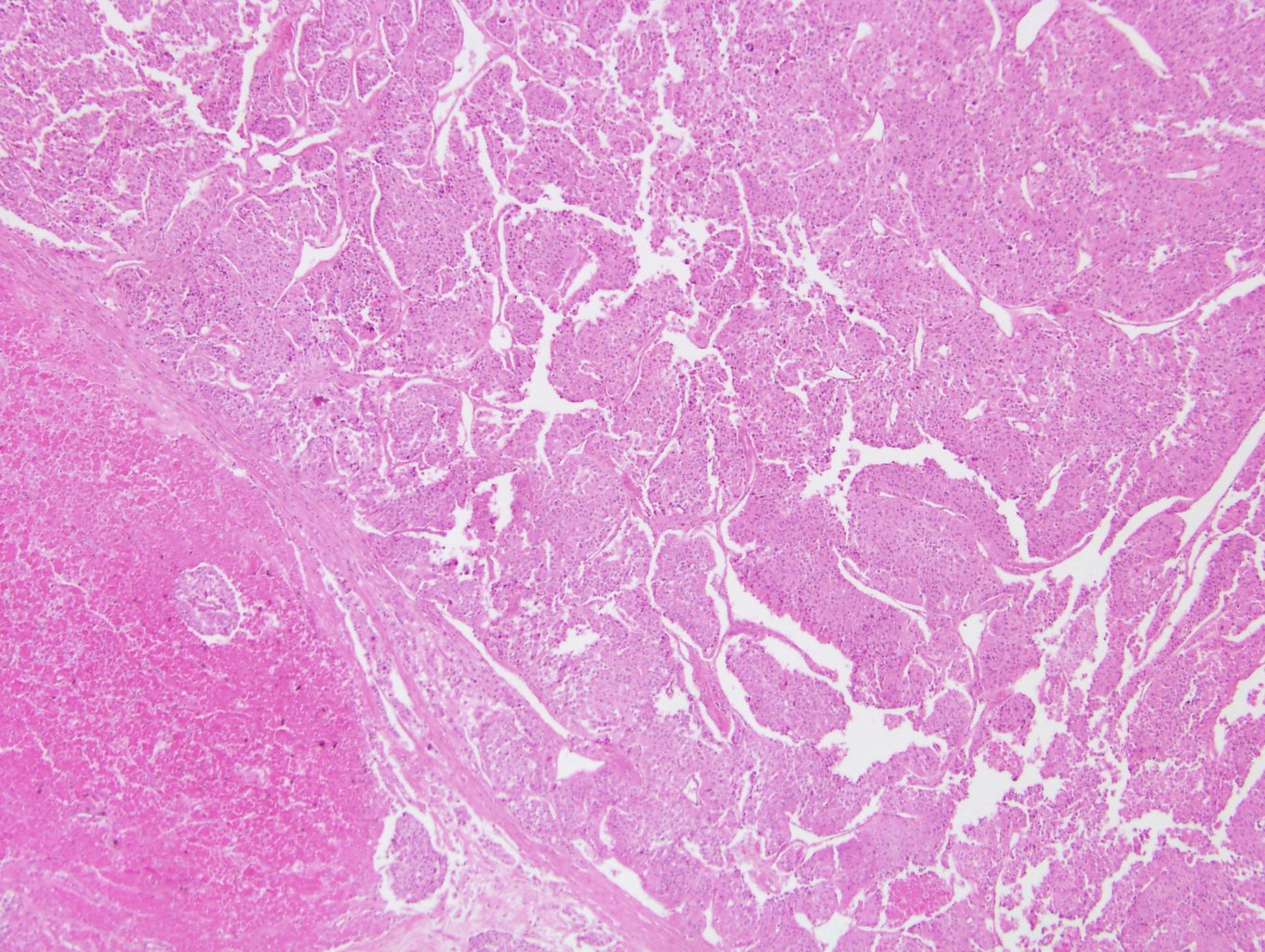
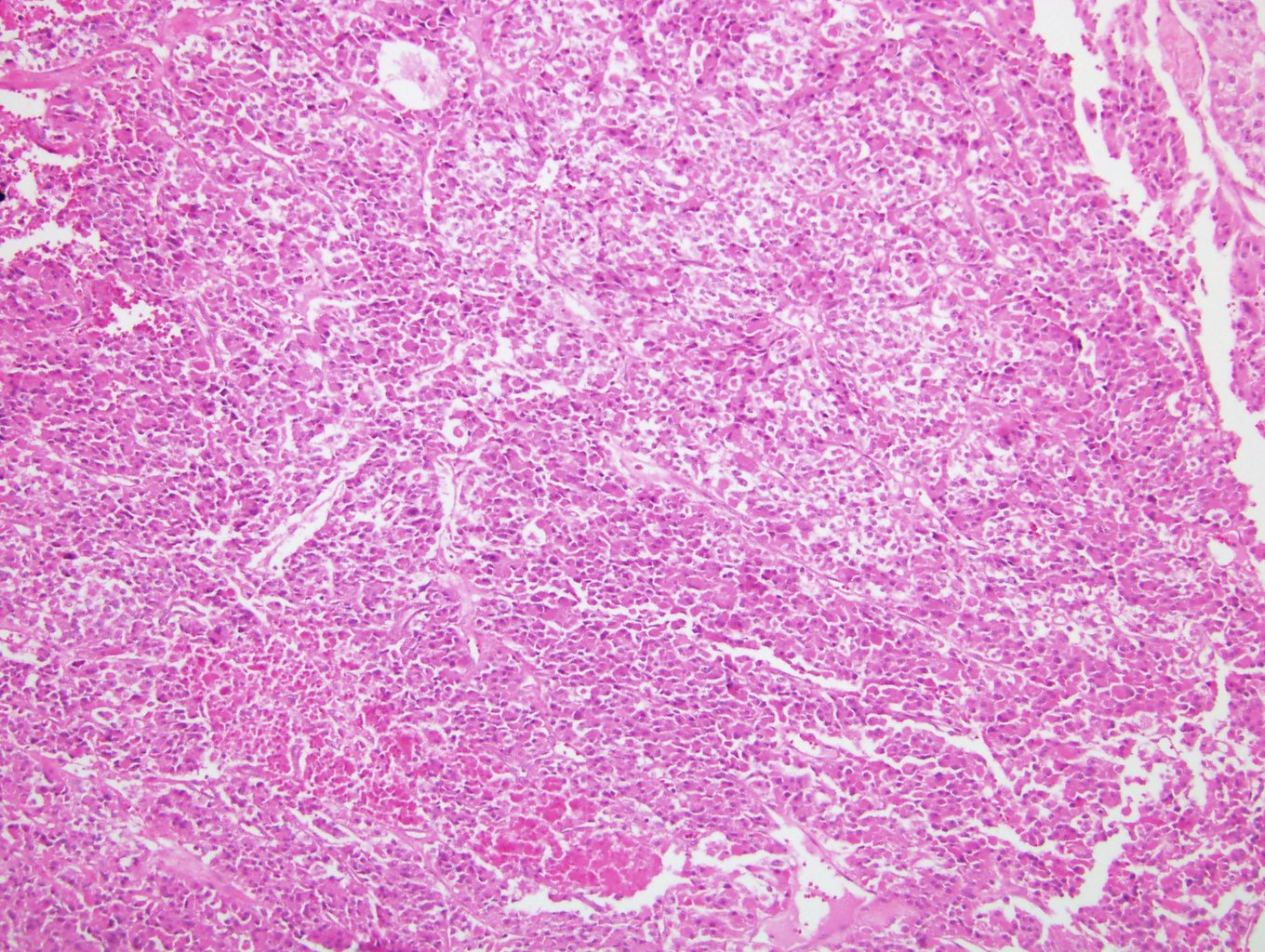
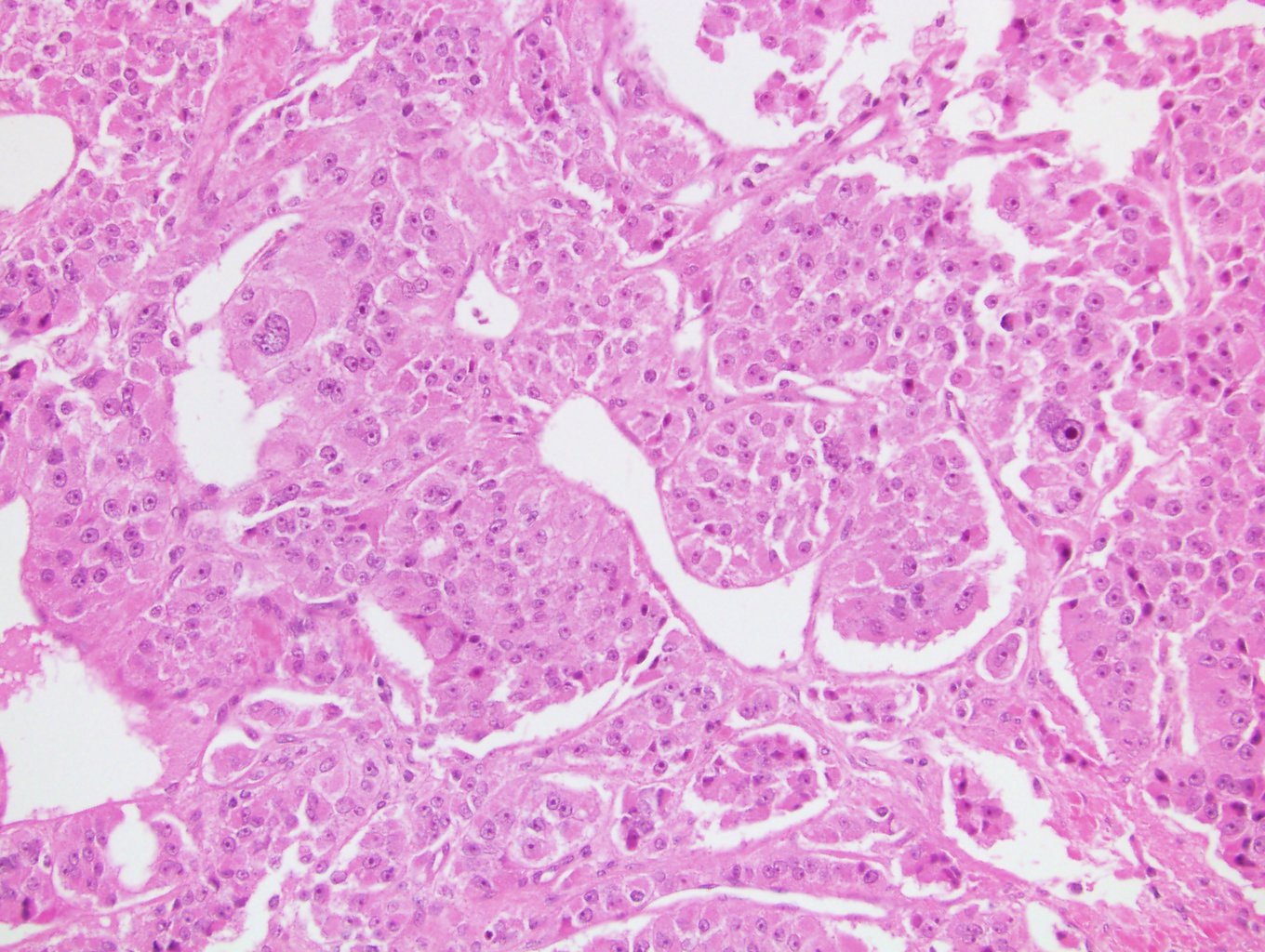
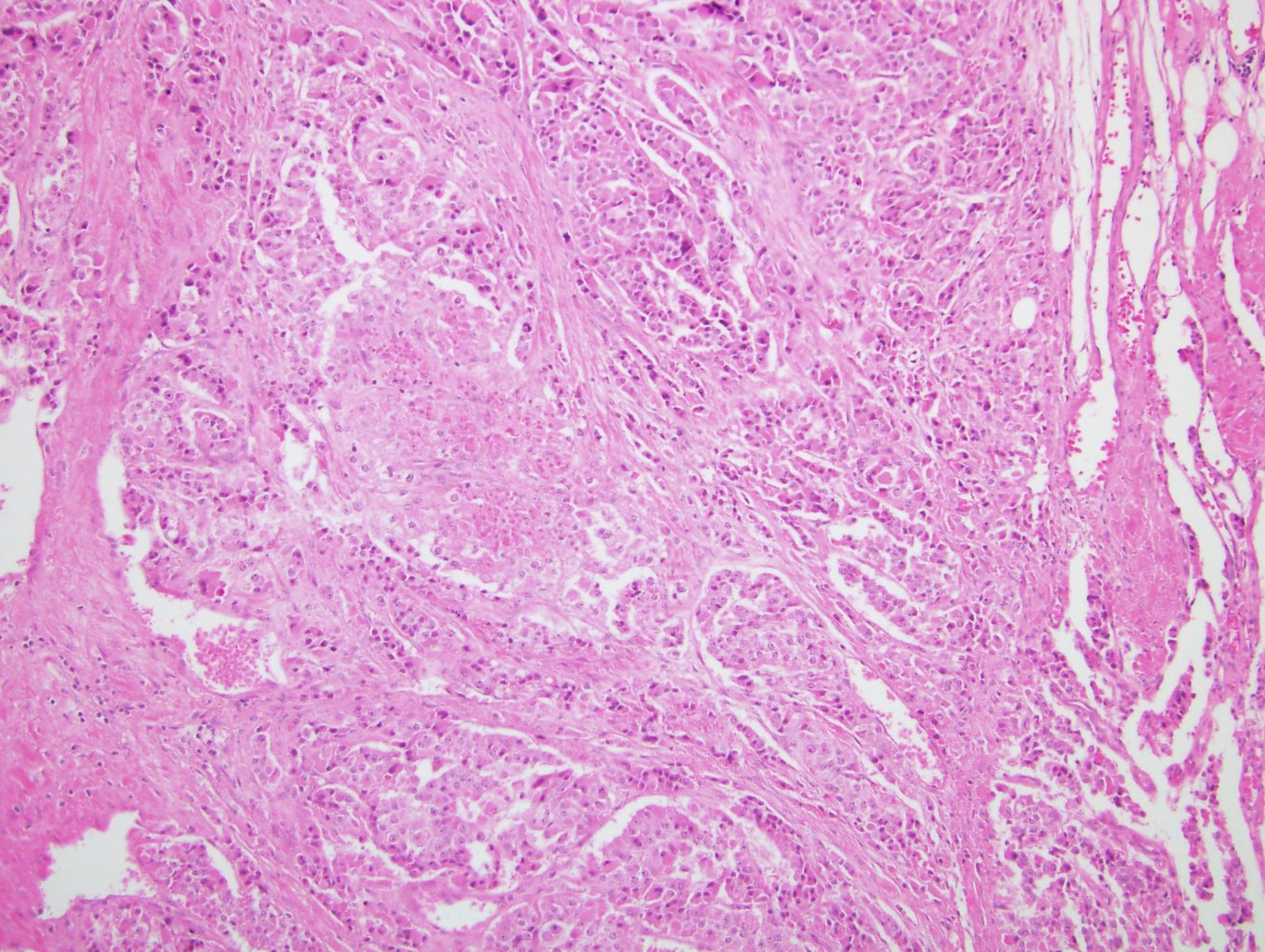
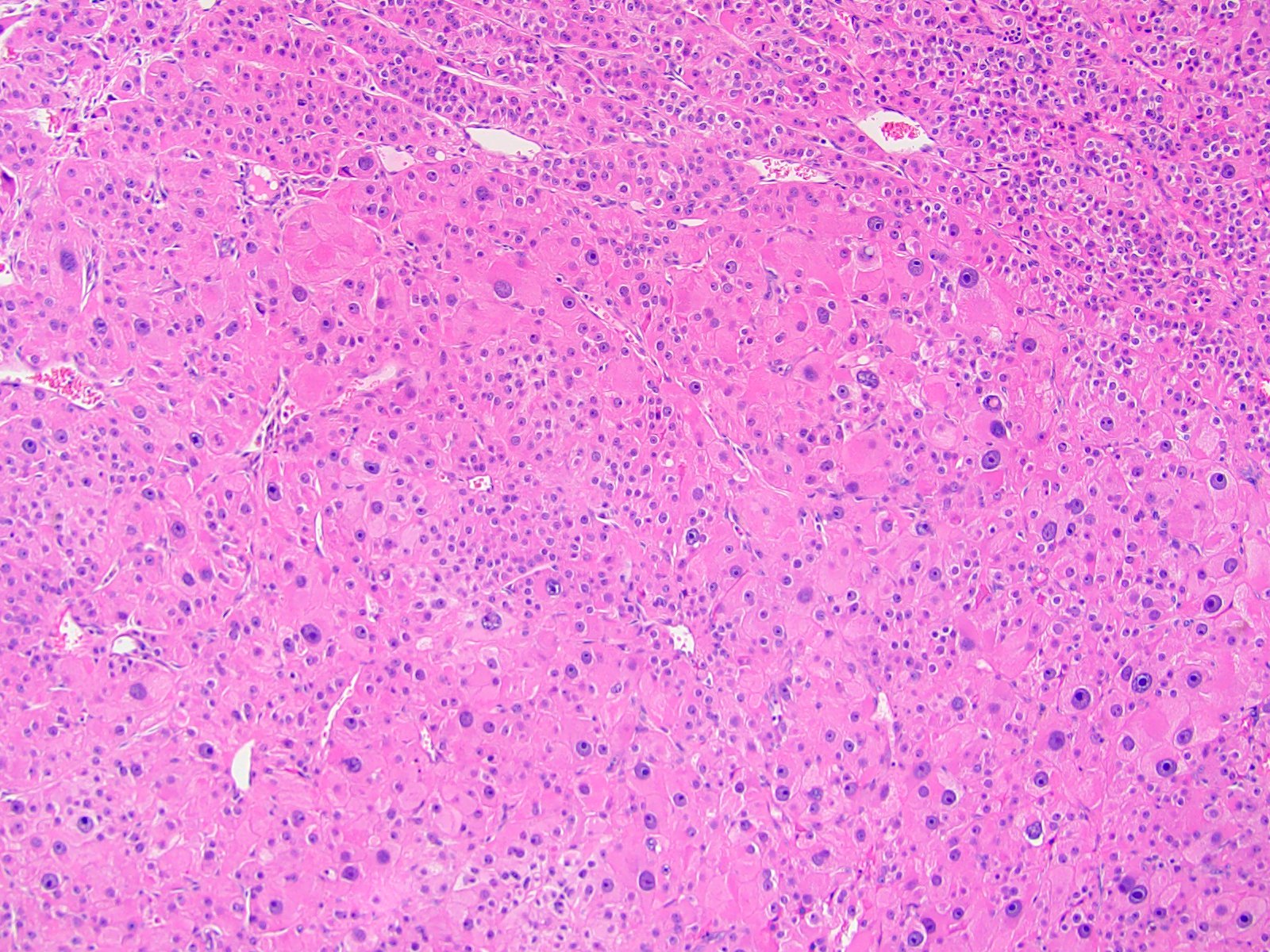
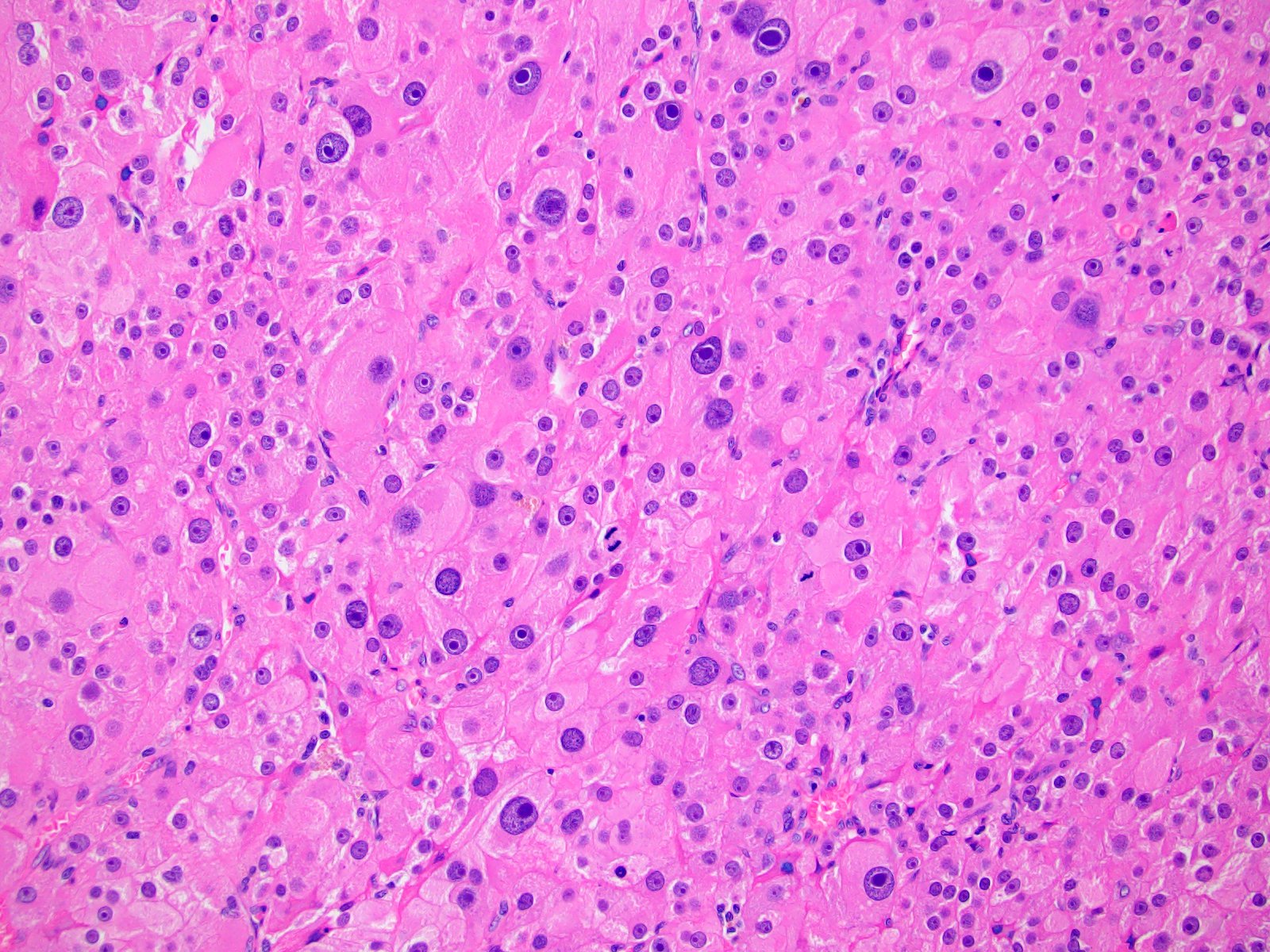
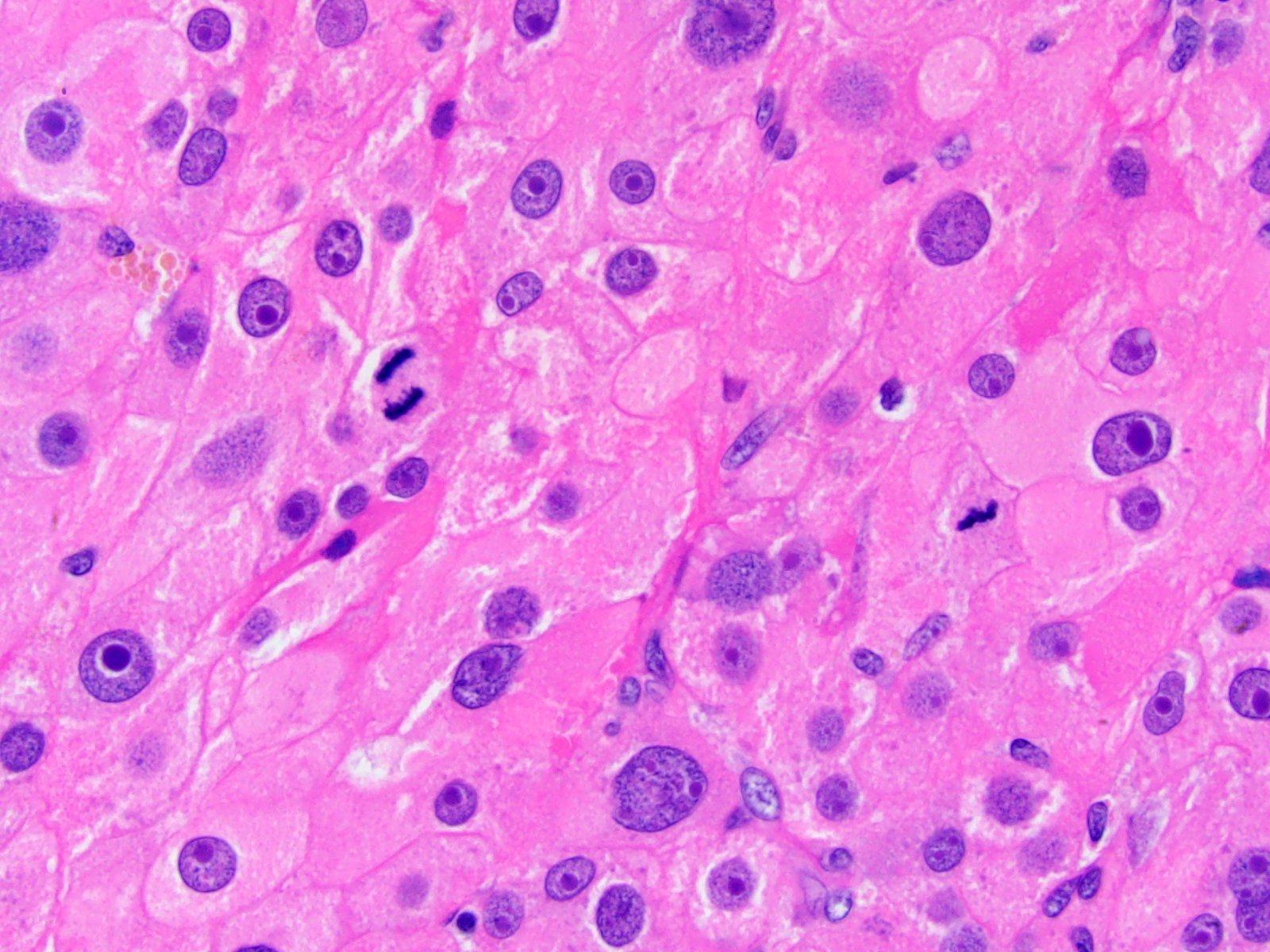
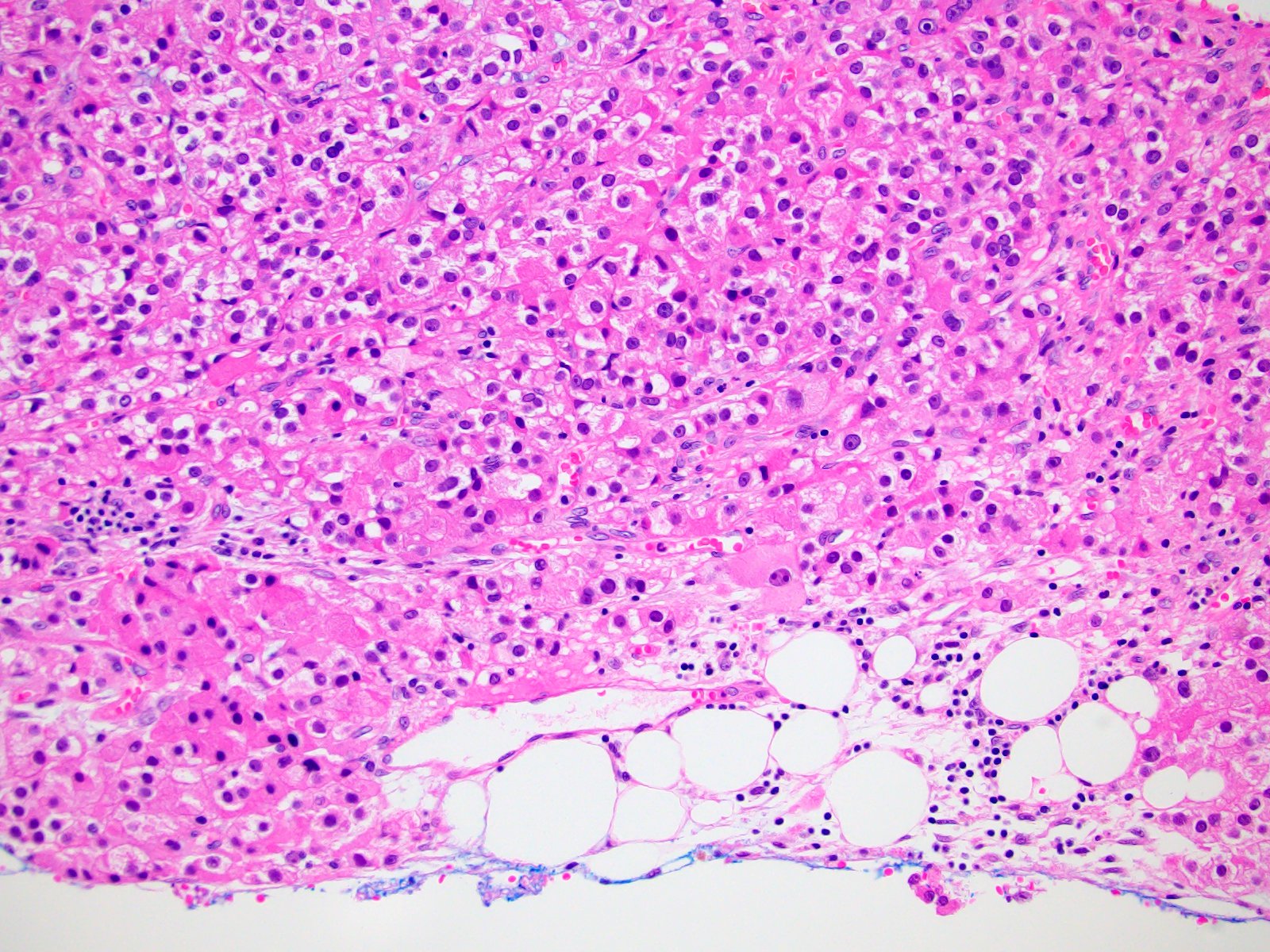
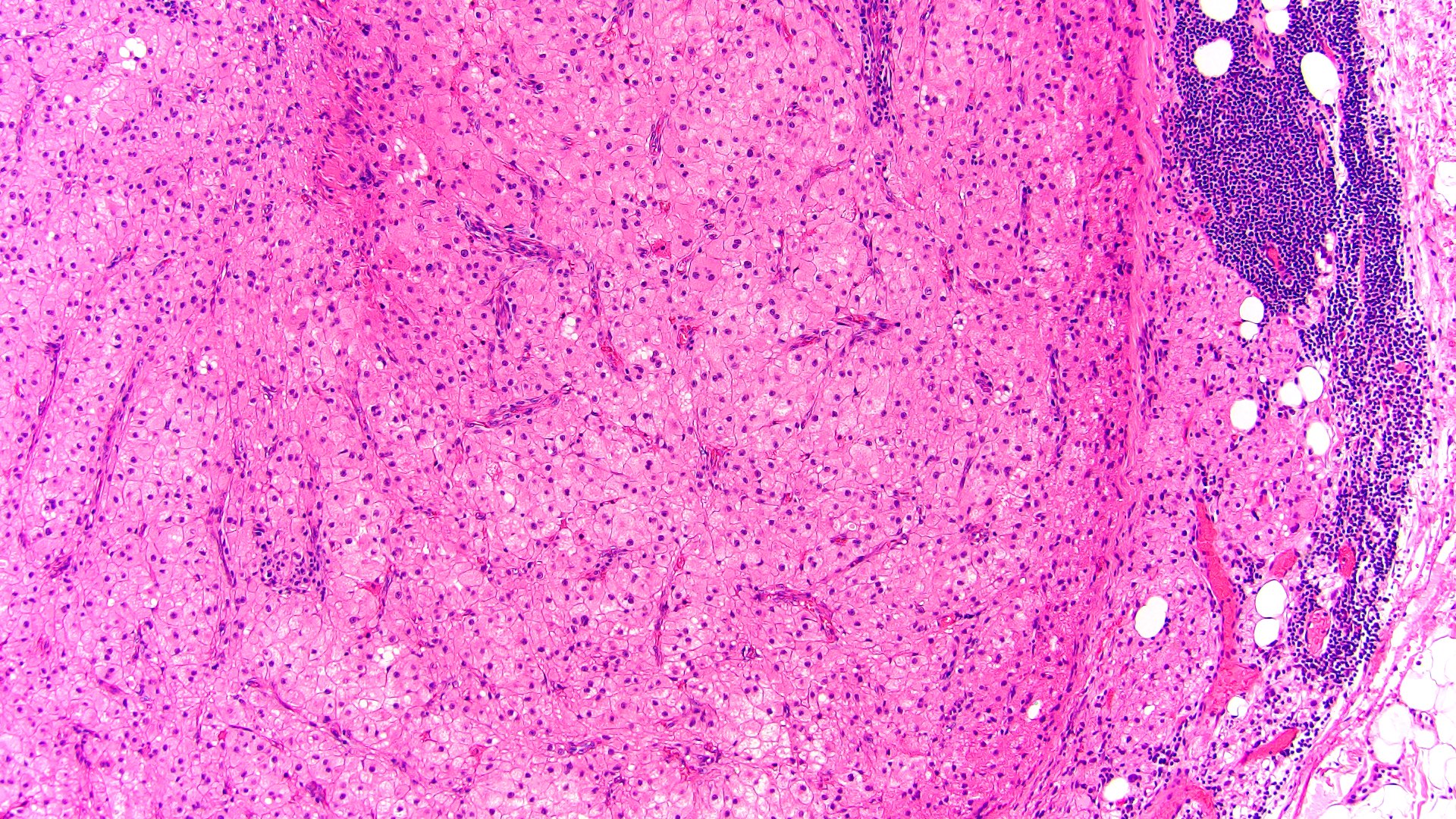
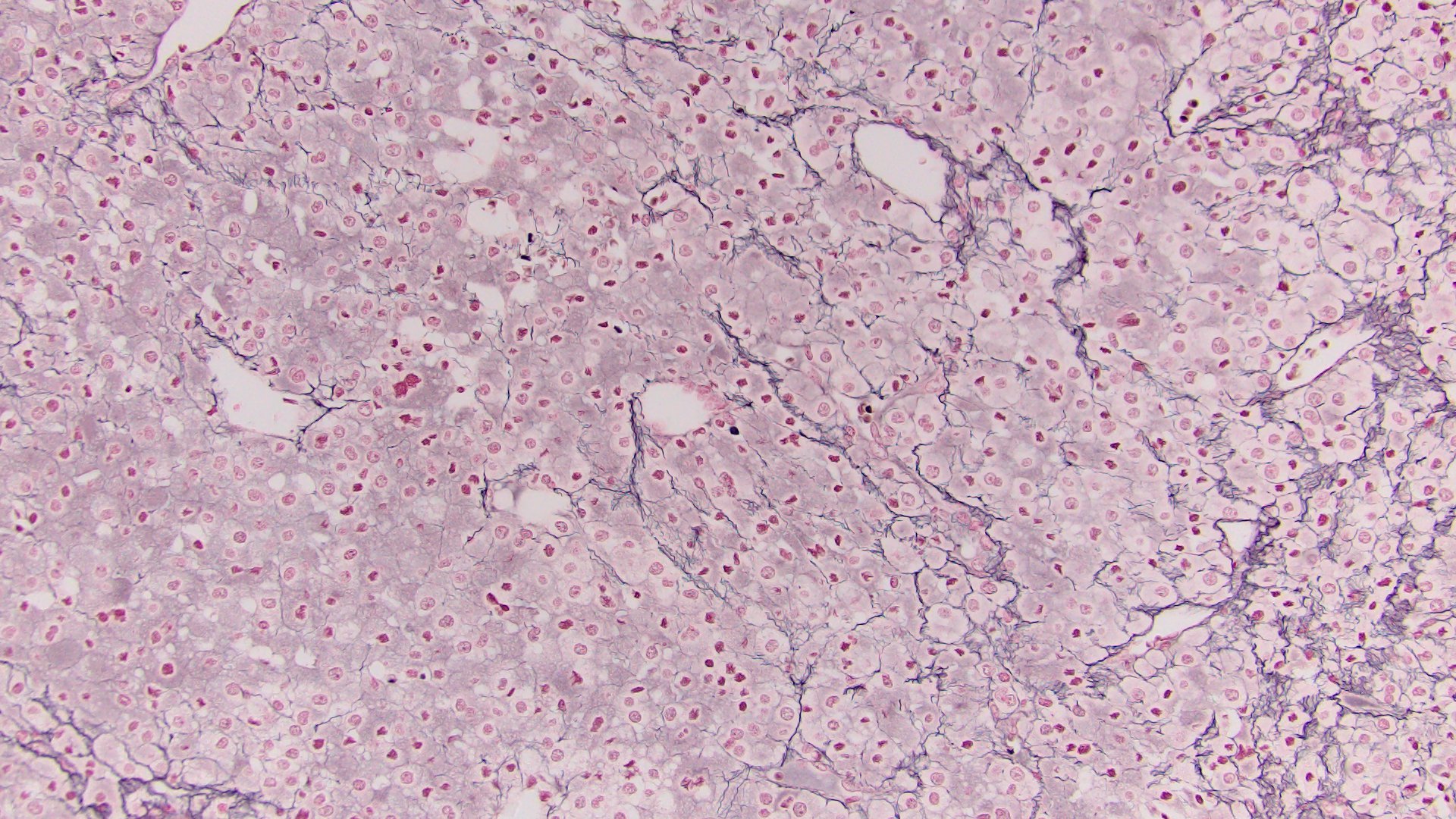
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Solid, diffuse, trabecular or glandular growth patterns
- Pleomorphic polygonal cells with abundant granular and deeply eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Large nuclei and prominent nucleoli, occasional binucleated giant cells
- Extracapsular extension, blood vessel invasion, necrosis and mitotic figures (Int J Surg Pathol 2004;12:231, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1882, Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:603, Hum Pathol 2011;42:489)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Inhibin, MelanA, calretinin, vimentin, synaptophysin, antimitochondrial antibody
- Variable SF1, AE1 / AE3, CK18, CAM 5.2, p53, NSE (Hum Pathol 2011;42:489, Surgery 2018;164:1351, Hum Pathol 2013;44:822)
- Disrupted reticulin network (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1433)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Abundant mitochondria
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Compared to conventional ACC oncocytic variant characterized by:
- Similar but less common somatic mutations of ACC driver genes
- Lower mutation burden of β catenin and p53 / Rb pathways (Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98)
- Reduced expression of miR-483-3p, miR-483-5p and miR-210 compared to other ACC variants (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1555)
- Common deletion in mitochondrial DNA (mtDNA 4977 bp) (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1882)
Sample pathology report
- Adrenal gland, left, adrenalectomy:
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma with the following features:
- Tumor size: 15 cm x 11 cm x 10 cm
- Tumor (gland) weight: 450 g
- Tumor extent: organ confined
- Histologic type: pure oncocytic variant
- Histologic grade: low grade
- Necrosis: present
- Lymphovascular invasion: absent
- Margins: free of tumor
- pTNM, AJCC 8th edition: pT2 NX MX
- Ancillary studies: Ki67 mitotic rate 7%
- Reticulin stain: disruption of reticulin framework
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma with the following features:
Differential diagnosis
- Adrenal cortical oncocytoma:
- Smaller, no necrosis, mitoses or angioinvasion
- Diagnostic algorithm (Lin-Weiss-Bisceglia) and retained reticulin stain
- Ki67 proliferation index with cut off < 5% for adenomas
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma, conventional:
- Clear or vacuolated cells > 25% tumor
- Pheochromocytoma:
- Zellballen or nested pattern
- Basophilic or amphophilic cytoplasm, bizarre smudged nuclei
- Positive for chromogranin, CD56, GATA3; S100+ sustentacular cells
- Renal cell carcinoma with eosinophilic features:
- Hepatocellular carcinoma:
- Trabecular pattern, bile pigment, glandular architecture
- Also shows loss of reticulin framework
- Positive for HepPar1, arginase1, glypican 3, keratins, CEA
- Metastatic tumors:
- More likely to be bilateral; check clinical history
- Often glandular, squamous or small cell morphology
- Most commonly of lung origin
- Also melanoma and carcinomas from breast, colorectal and bladder
- References: Endocr Res 2000;26:861, Endocr Relat Cancer 2009;16:573, Histopathology 2014;64:567, Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:201, J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2015;100:841, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1433, Endocr Pathol 2006;17:345, J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2010;95:E161, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2010;18:414, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:423, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:678, Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2014;22:24, Surgery 2018;164:1351
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 47 year old woman presents to a clinic complaining of abdominal distention and constipation. Imaging studies reveal a low fat heterogeneous enhancing 14 cm mass in the left adrenal gland with central necrosis. An adrenalectomy was done and representative morphologic picture of pure oncocytic neoplasm is shown in the photo. Which one of the listed criteria will be sufficient for the diagnosis of adrenal cortical carcinoma?
- Capsular invasion
- Presence of necrosis
- Sinusoidal invasion
- Tumor weight 350 g
- Venous invasion
Board review style answer #1
E. Venous invasion. Oncocytic adrenocortical tumors should be diagnosed using modified scoring Lin-Weiss-Bisceglia (LWB) system. Presence of 1 major criteria indicates malignancy, minor criteria indicates uncertain malignant potential (borderline) and the absence of all major and minor criteria indicates benign. From all listed answers, only venous invasion belongs to major criteria and would quality this tumor as adrenocortical carcinoma. (Hum Pathol 2011;42:489, Adv Anat Pathol 2014;21:151)
Comment Here
Reference: Oncocytic variant
Comment Here
Reference: Oncocytic variant
Board review style question #2
When comparing to conventional adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC), which statement is accurate in characterizing oncocytic ACC variant?
- Typically smaller at presentation
- Affects male patients more often
- More aggressive with higher metastatic rate and shorter survival
- Difficult to distinguish from benign oncocytic tumors on imaging
- Requires different therapy approach
Board review style answer #2
D. Difficult to distinguish from benign oncocytic tumors on imaging. Because all oncocytic tumors are lipid poor, CT, MRI or PET imaging are unable to distinguish benign from malignant lesions regardless of size, attenuation or handling of the contrast agent. Answers A and C are incorrect, because oncocytic ACC, despite larger size at presentation and aggressive morphologic appearance, tends to be lower stage, less frequently metastasizes and seems to represent more indolent variant of ACC with delayed recurrence and improved survival. Answers B and E are false since patient population and therapy approaches are similar for both conventional and oncocytic ACC. (Surgery 2019;166:524, Asia Ocean J Nucl Med Biol 2018;6:179, Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
Comment Here
Reference: Oncocytic variant
Comment Here
Reference: Oncocytic variant