Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Tretiakova M. Myxoid . PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/adrenocorticalcarcinomamyxoid.html. Accessed December 3rd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare variant of malignant epithelial tumor of adrenal cortical cells with extracellular myxoid component
Essential features
- Uncommon variant of adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC), ~50 cases reported
- Characterized by the presence of variably abundant extracellular myxoid component (5 - 90%) resembling carcinomas with extracellular mucin secretions or myxoid tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, Histopathology 2018;72:82)
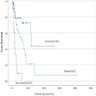
- Compared with conventional ACC, myxoid variant has slightly more aggressive clinical behavior and shorter overall survival on univariate and multivariate analyses (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1555, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764)
- Positive for Alcian blue, inhibin, calretinin, MelanA, synaptophysin; negative for keratins and other epithelial markers
Terminology
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma (ACC), myxoid variant
- Adrenocortical carcinoma, myxoid type
- Myxoid adrenocortical carcinoma
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8370/3 - adrenal cortical carcinoma
Epidemiology
- Accounts for 10 - 12% of ACC cases in 2 large studies (Arkh Patol 2021;83:10, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973)
- Mean age: 48; age range: 16 - 82 (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764, Virchows Arch 2012;460:9)
- Unlike conventional ACC, no gender predilection (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
Sites
- Left adrenal more commonly affected: left to right ratio = 1.5:1 (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
Pathophysiology
- Molecular evidence for an adenoma to carcinoma progression (Virchows Arch 2012;460:9, PLoS One 2013;8:e73959)
Etiology
- Sporadic with no established risk factors
- Acquired genetic mutations of several driver genes (i.e. IGF2, CDKN2A, TERT, RB, ZNRF3, CDK4), similar to conventional ACC (Cancer Cell 2016;29:723, Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am 2015;44:399, Biomedicines 2021;9:174, Turk Patoloji Derg 2015;31:98, Mod Pathol 2018;31:1257)
- 2 case reports of myxoid ACC in patients with MEN1 syndrome (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Hormone production in 57 - 70% of tumors (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973, Virchows Arch 2012;460:9, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Cortisol with Cushing syndrome in ~70% of functional tumors
- Hyperaldosteronism (~10%)
- Sex hormone or multiple hormones (~20%)
- In nonfunctional tumors, symptoms related to large size of abdominal mass include
- Pain, discomfort, vomiting
- Loss of weight, weakness
- Majority of myxoid ACC present with advanced tumor stage III / IV (J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764)
- Metastases eventually developed in 68 - 88% of patients, most commonly to liver and lungs / pleura (J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Tumor recurrence was documented in 43% of cases with median time of recurrence after surgery being 4.8 months (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- High incidence of postoperative recurrence, even in nonmetastatic disease, was postulated to be caused by micrometastases at the time of surgery (World J Surg 2010;34:1380)
Diagnosis
- Only definitive criteria for malignancy are distant metastasis or local invasion
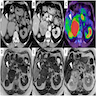
- Myxoid ACC on imaging characterized by large size, irregular contours and significant signal heterogeneity (Endocr J 2019;66:739)
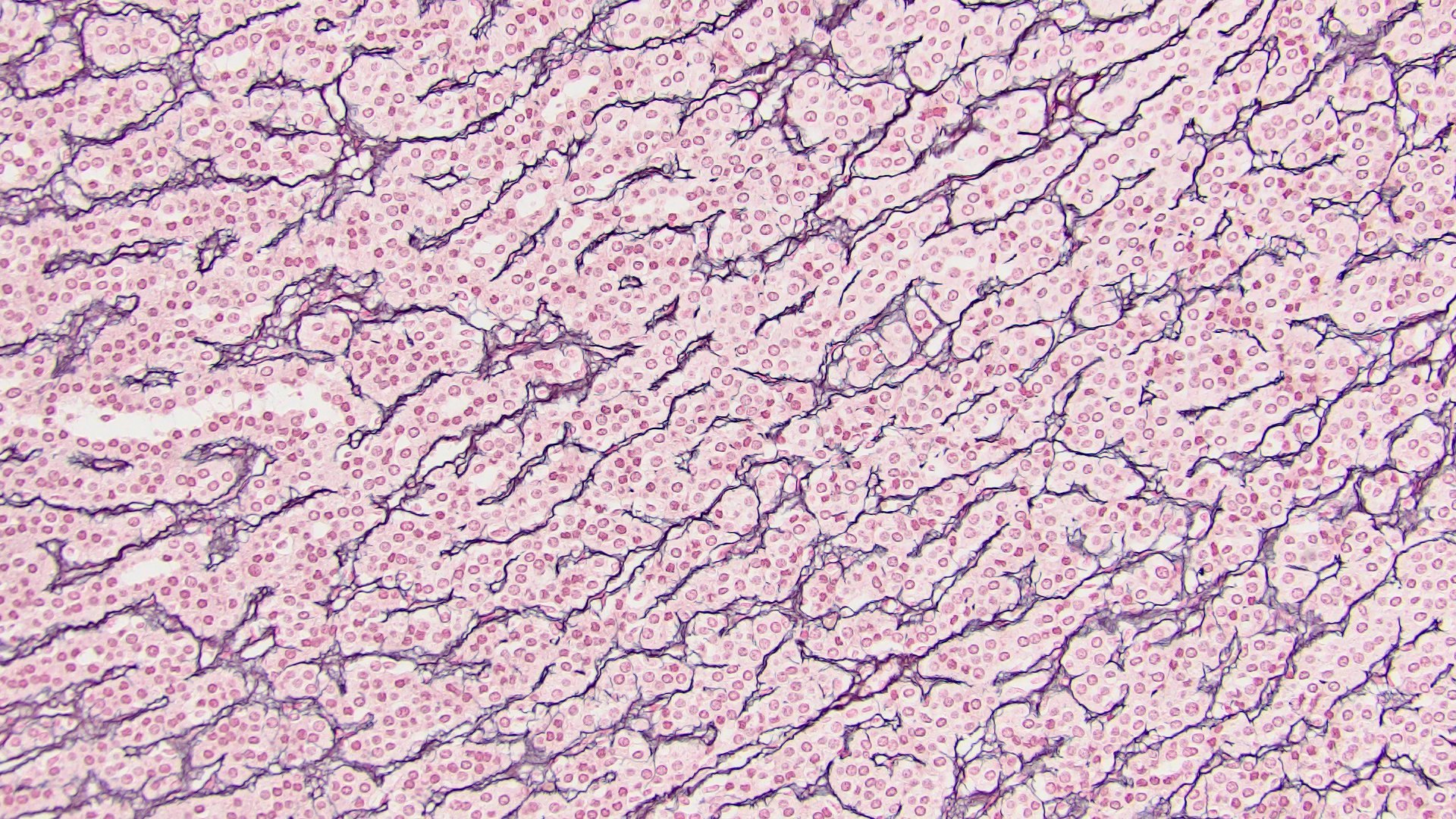
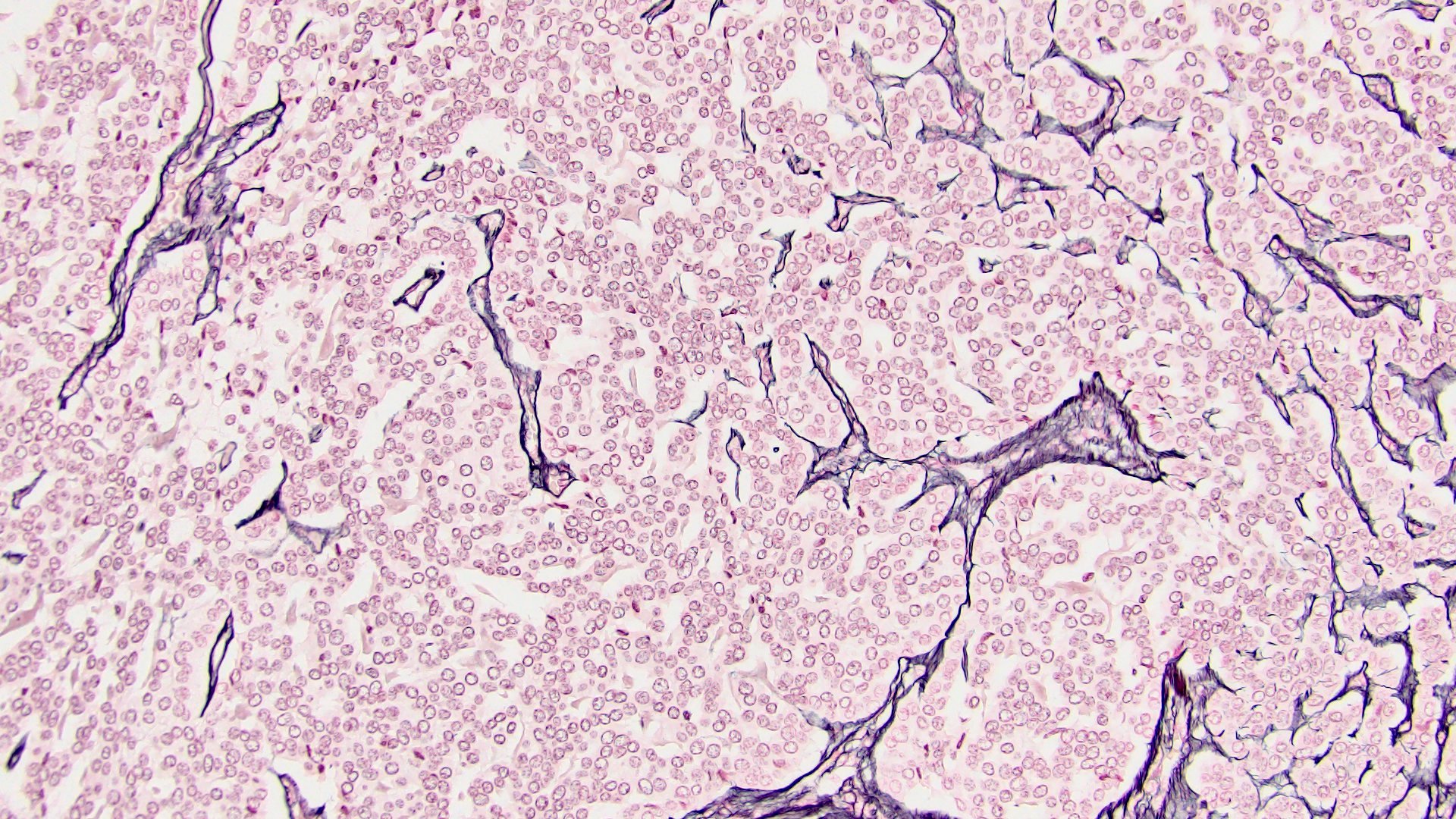
- Loss / disruption of reticulin framework (J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764)
- Mean Weiss score in myxoid ACC is 5 - 7 (J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973)
Laboratory
Radiology description
Prognostic factors
- Myxoid ACC has slightly worse prognosis than conventional ACC (Horm Cancer 2011;2:333)
- Overall median survival for myxoid ACC is 29 months (Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Behavior of myxoid ACC is difficult to predict: even tumors with low Weiss score could have fatal outcome (Histopathology 2018;72:82)
- p53 / Rb1 pathway activation was associated with high tumor stage, high Ki67 index, aggressive disease status and shorter disease free survival
- Overexpression of miR-483-3p, miR483-5p and miR-210 indicate poor prognosis (similar to conventional ACC) and are associated with male sex, presence of necrosis, high Ki67 proliferation index, mitotic count and increased SF1 expression on IHC (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1555)
Case reports
- 38 year old man with myxoid ACC and extensive lipomatous metaplasia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:227)
- 38 year old woman who underwent robot assisted laparoscopic adrenalectomy for myxoid ACC (Case Rep Urol 2019;2019:9794345)
- 68 year old woman with myxoid ACC and MEN1 syndrome (Endocr J 2019;66:739)
- 82 year old woman with myxoid ACC presenting as primary hyperaldosteronism (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:803)
Treatment
- Surgical: radical resection, treatment mainstay (Surgery 2019;166:524)
- Guidelines for adjuvant treatment with mitotane, cytotoxic chemotherapy and radiation therapy are similar to conventional ACC
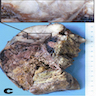
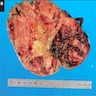
Gross description
- Median tumor size is 12 - 19.8 cm (range: 7 - 24 cm) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Median weight is 552 - 707 g (range: 38 - 3200 g) (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
- Partially encapsulated yellow-brown with gelatinous myxoid areas, hemorrhage and necrosis (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, Biomedicines 2021;9:175)
Gross images
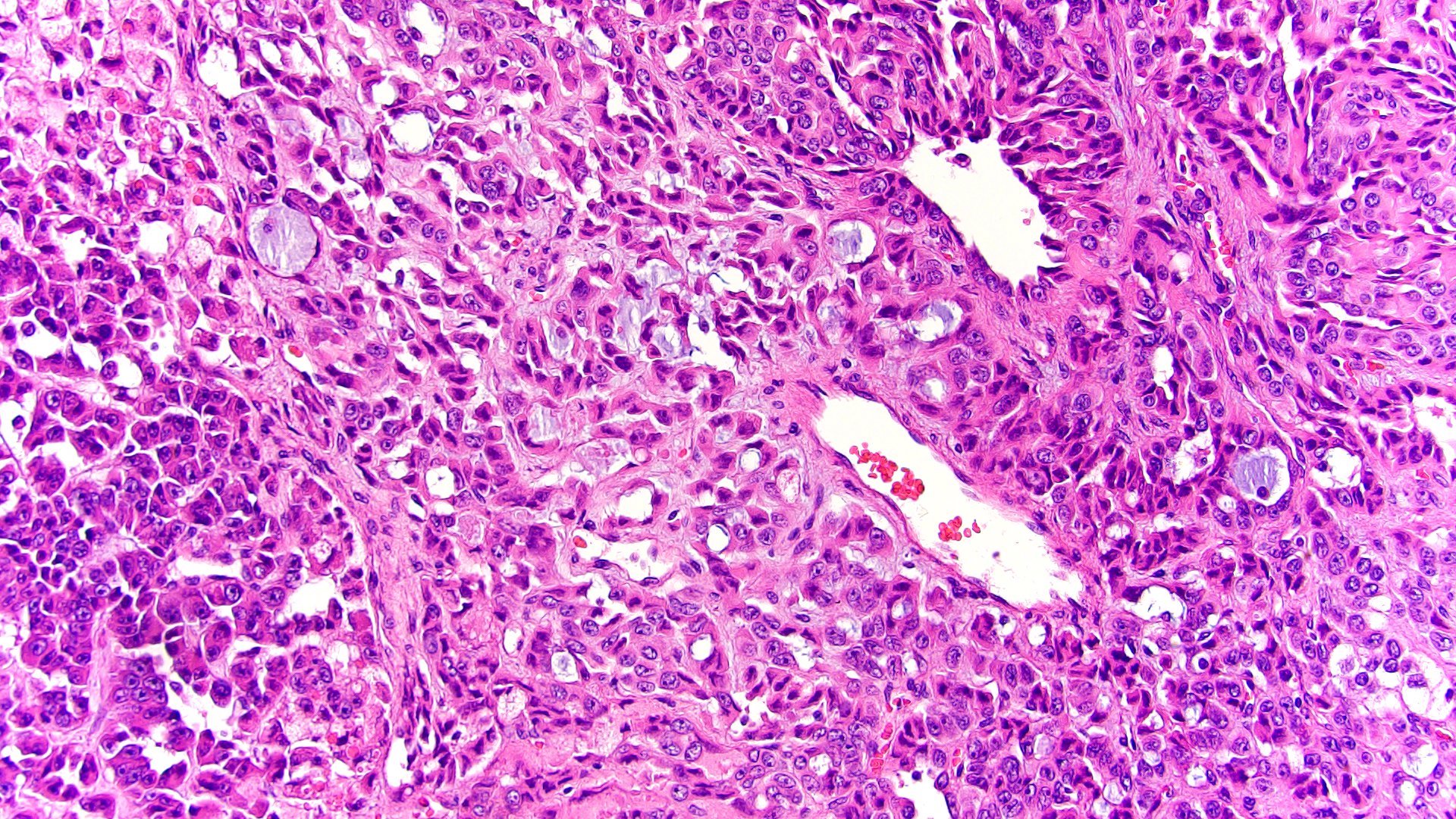
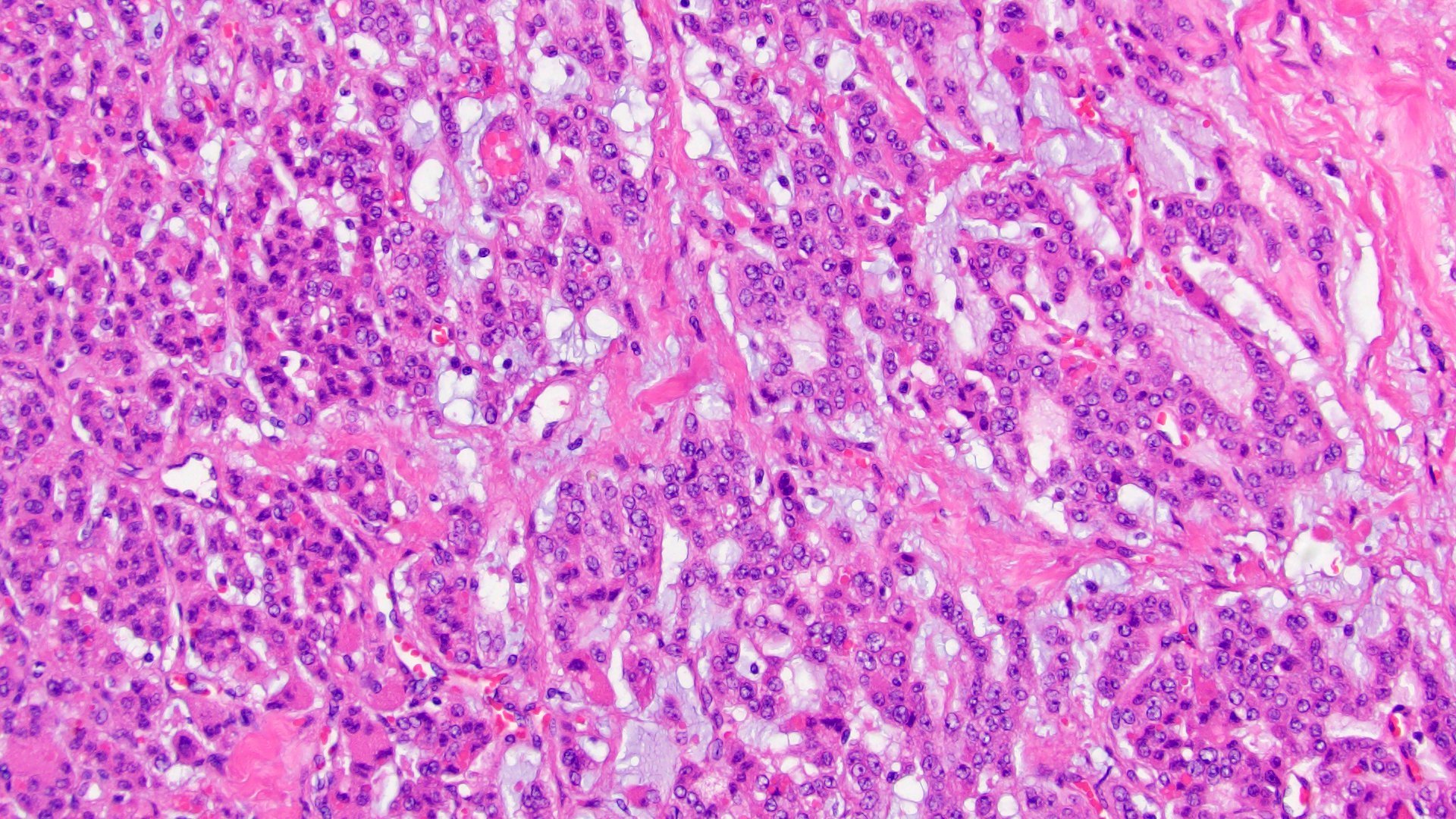
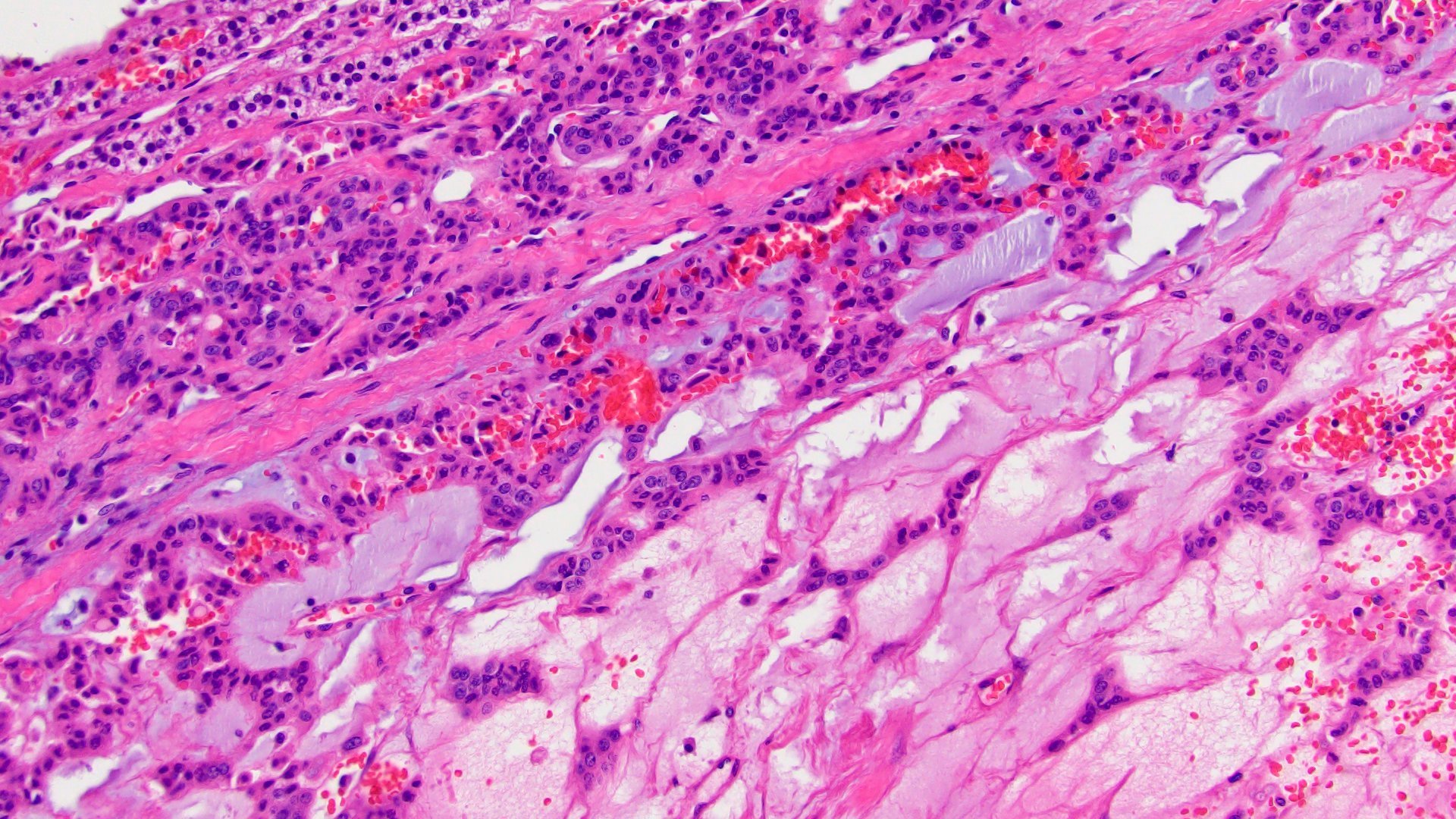
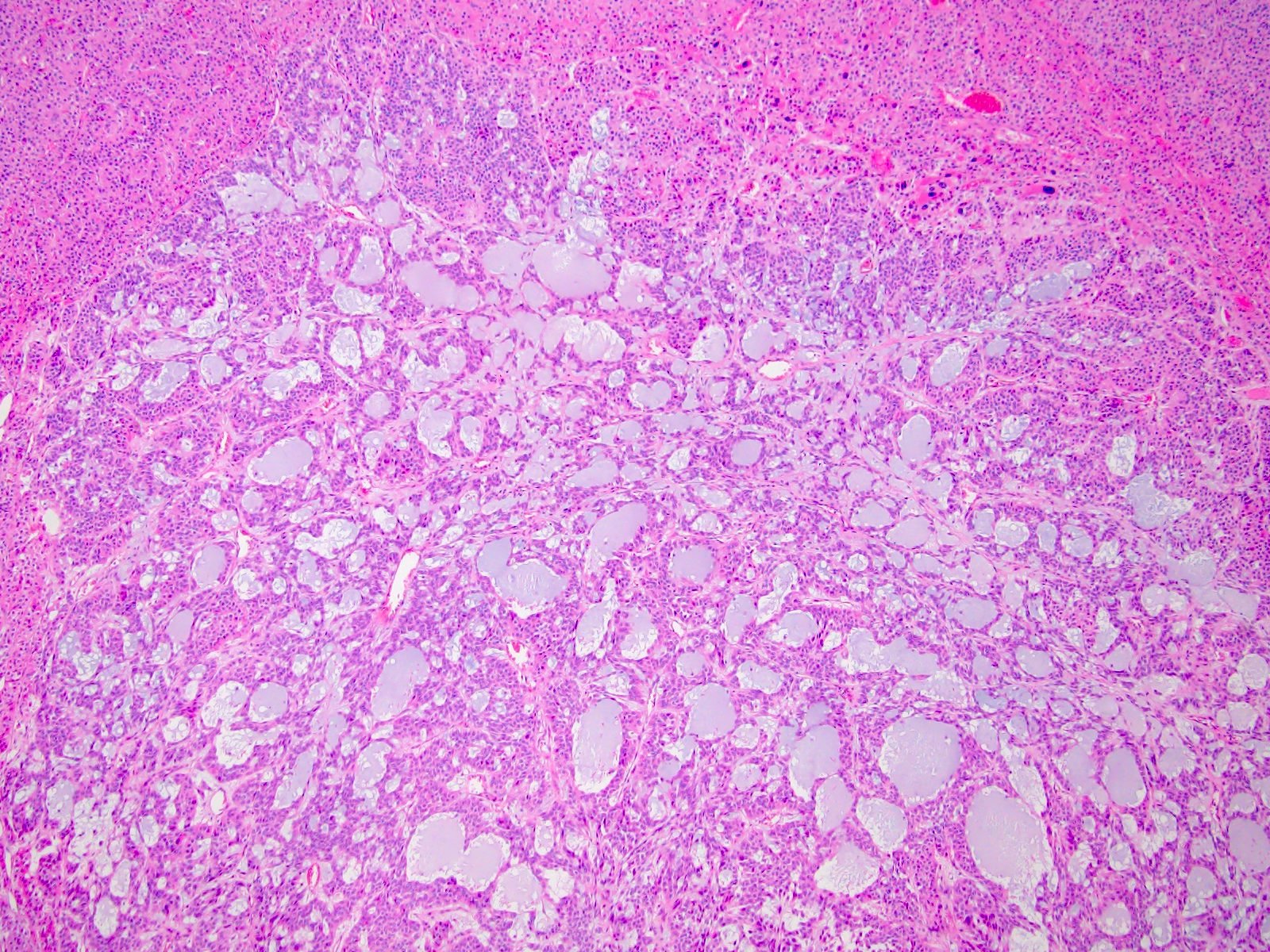
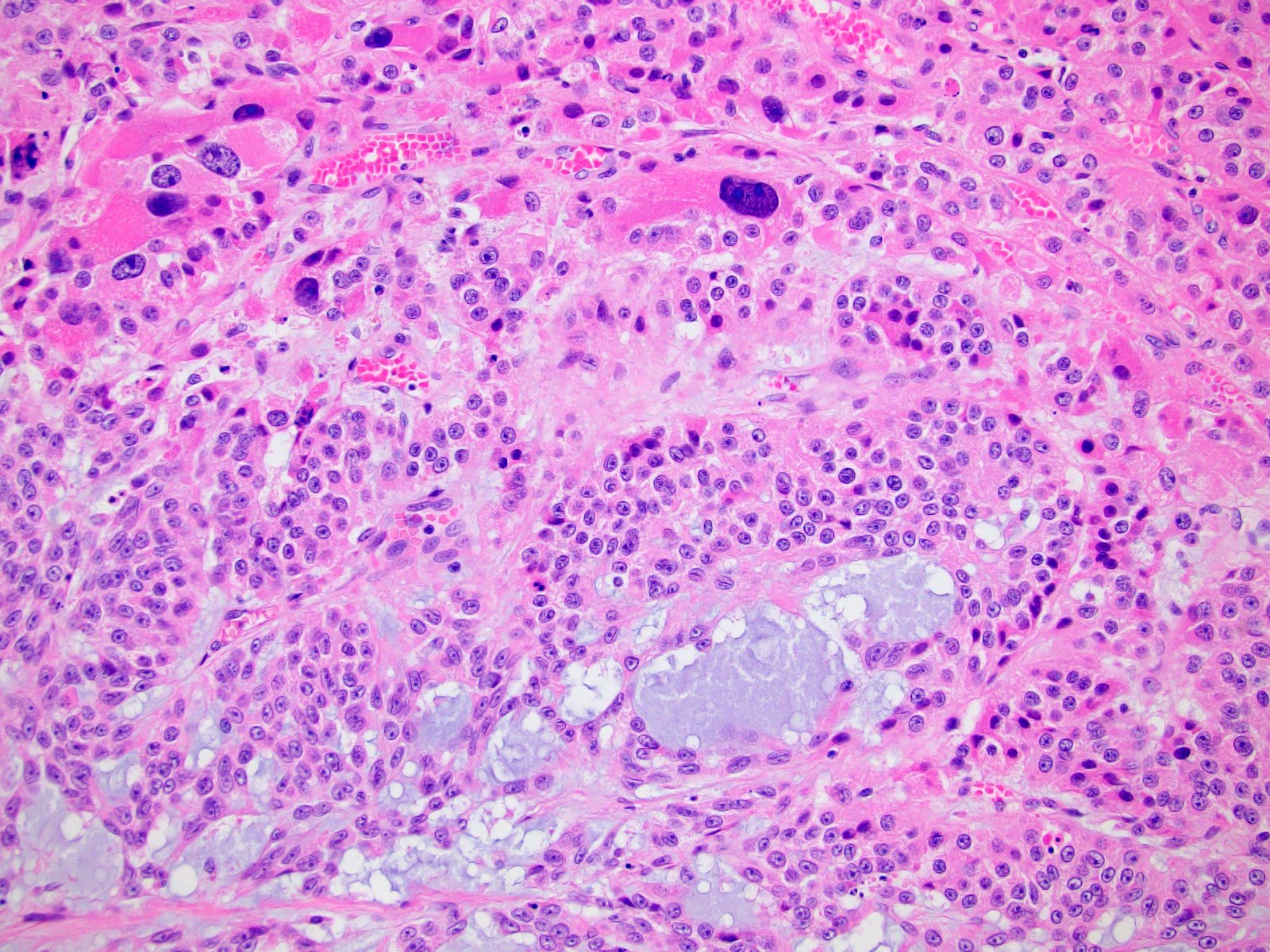
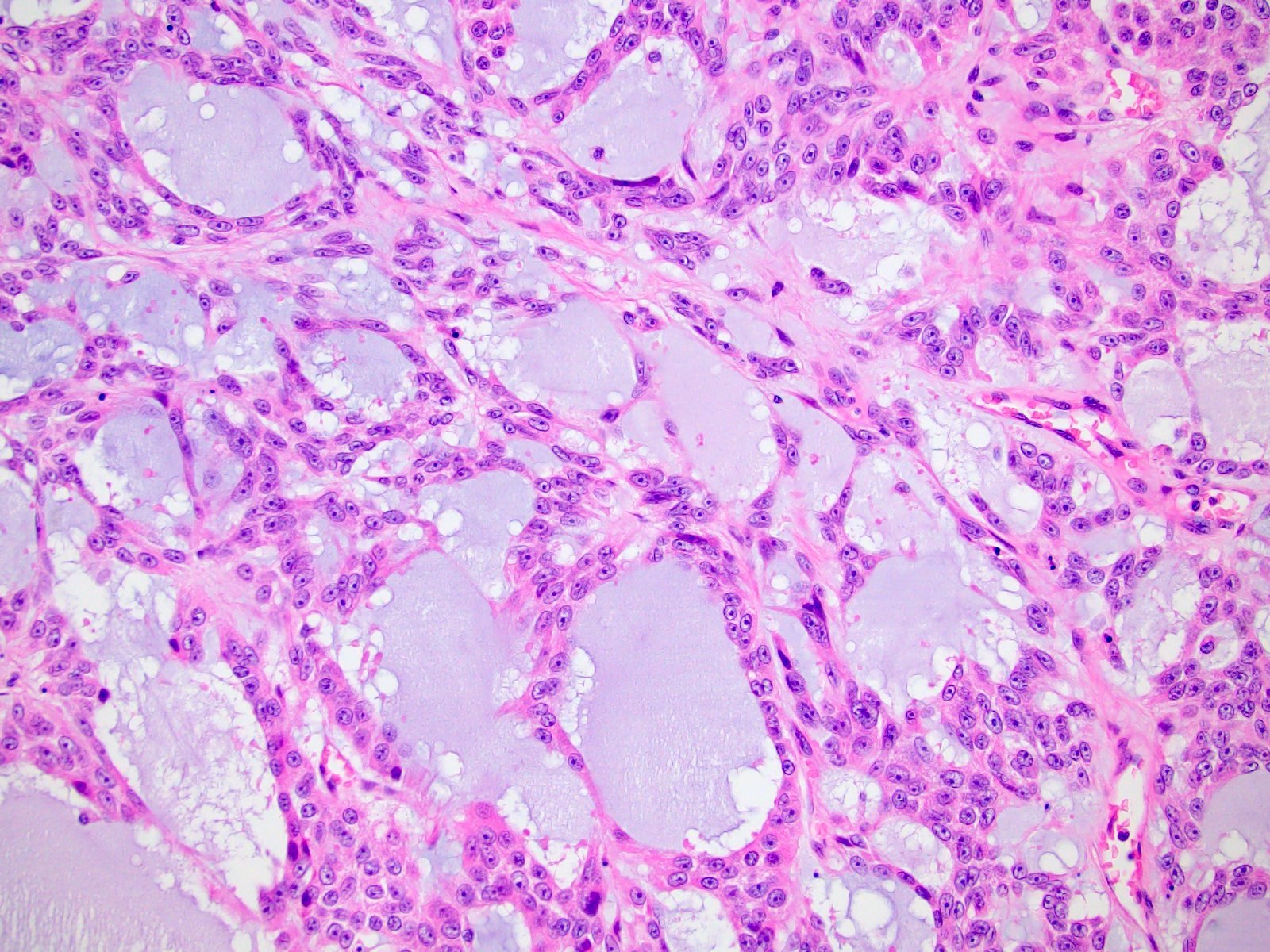
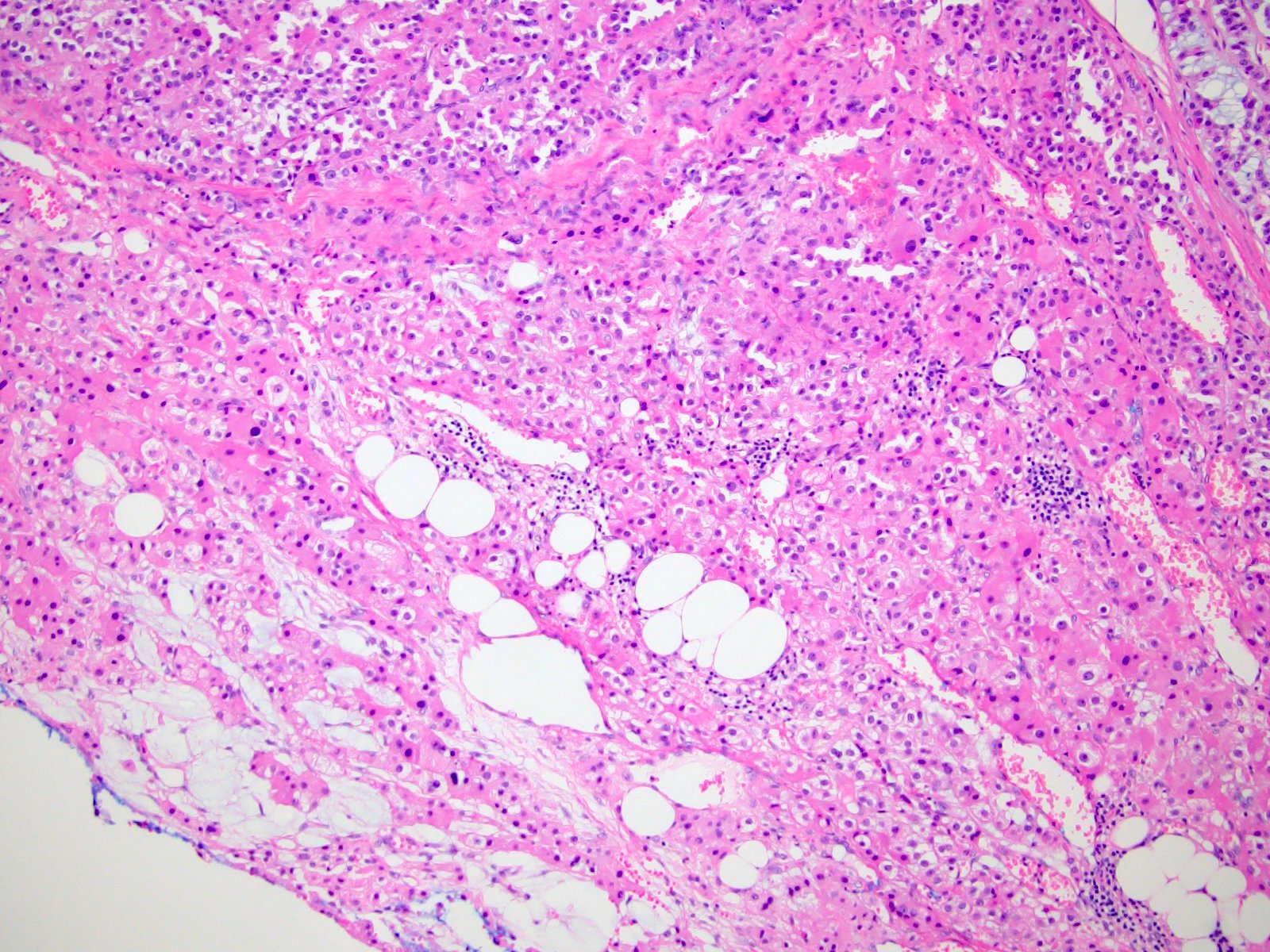
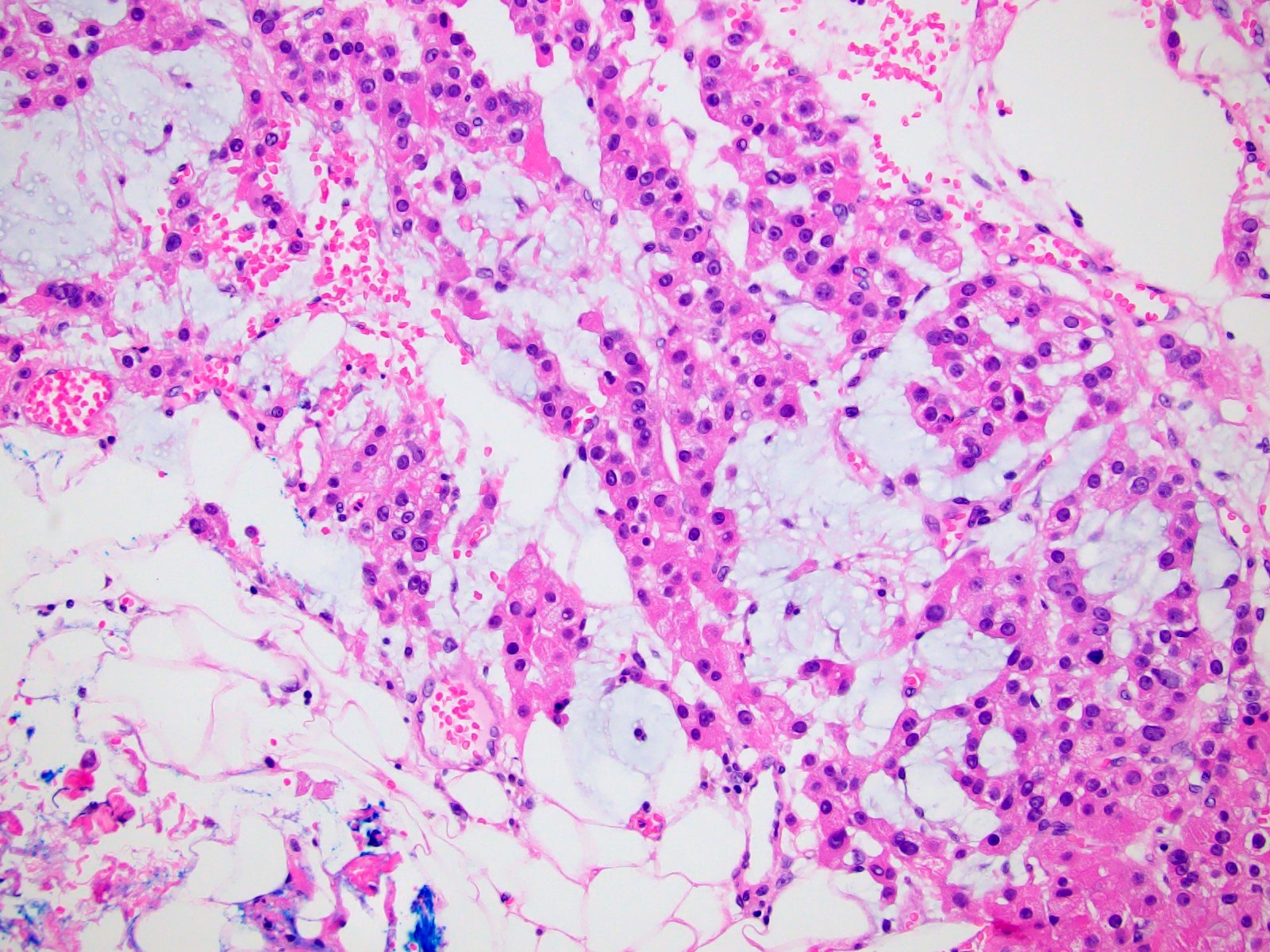
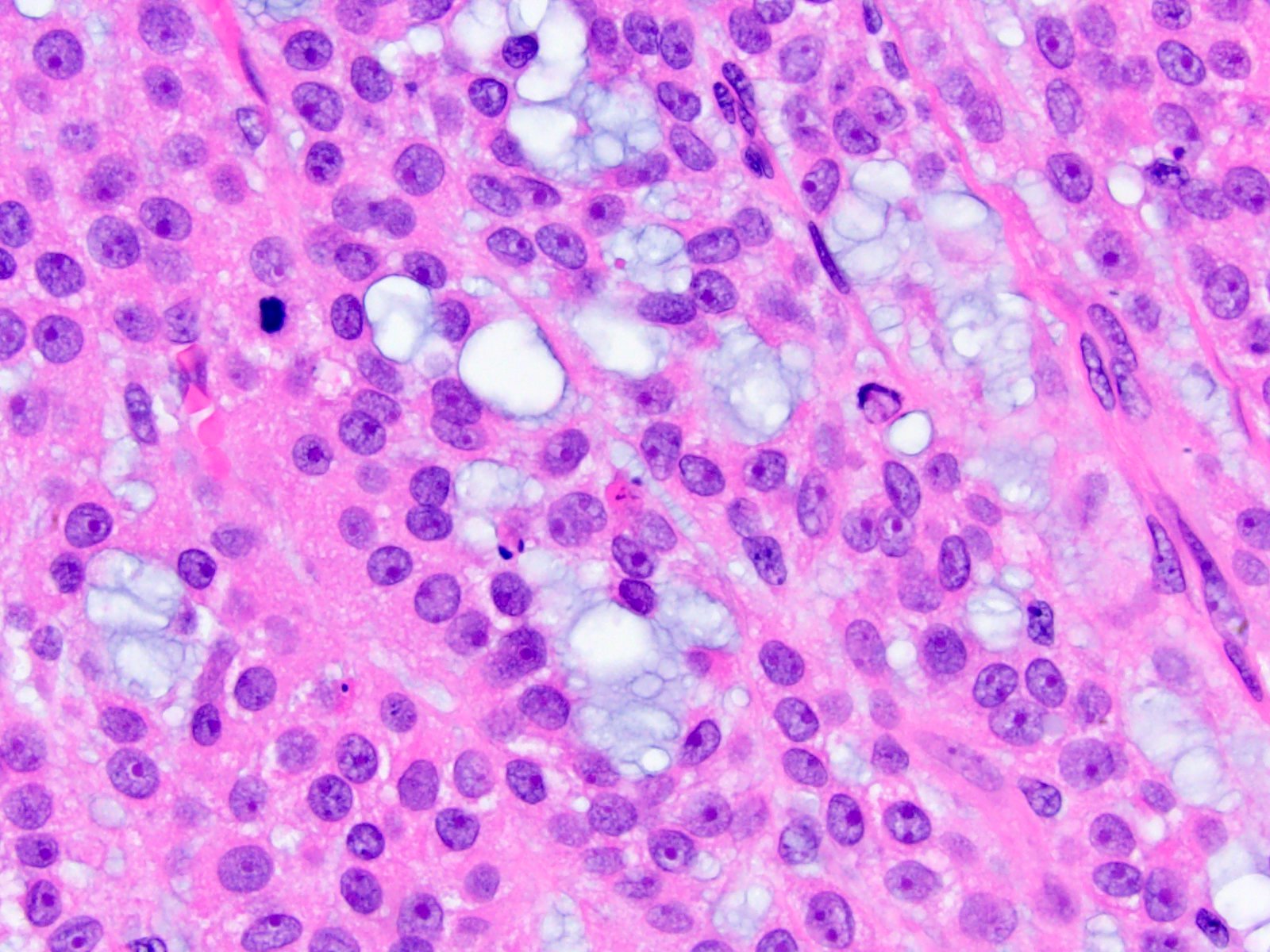
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Variable amounts (5 - 90%) of light basophilic, amorphous, mucinous material (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973)
- 2 distinct morphologic groups (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973, Ann Diagn Pathol 2008;12:344, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783):
- Group 1: predominant myxoid stromal component with pools of copious mucin; tumor cells are small, uniform, mildly atypical and arranged in delicate arborizing cords, pseudoglands or microcysts (may resemble adenoid cystic carcinoma)
- Group 2: focal myxoid changes (< 20%) in tumors otherwise similar to conventional ACC with large atypical eosinophilic cells with diffuse, trabecular or alveolar architecture
- Group 1 may represent true myxoid ACC as a distinctive variant, whereas group 2 may be result of myxoid degenerative changes of conventional ACC (Virchows Arch 2012;460:9, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973)
- Histochemical mucin staining pattern favors acid mucopolysaccharides of connective tissue type, not intracellular (Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:803)
- Capsular invasion, sinusoidal invasion and necrosis are present in 80 - 90% of cases (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, J Korean Med Sci 2017;32:764)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Maria Tretiakova, M.D., Ph.D.
Positive stains
- Alcian blue uniformly positive highlighting extracellular acidic mucosubstance
- Inhibin, MelanA, calretinin, vimentin, synaptophysin, CD56: uniform expression
- EGFR (membranous), SF1, neurofilament: variable expression
- Disrupted reticulin network
- Ki67 proliferation rates are very high (18 - 32%) (Ann Diagn Pathol 2008;12:344, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783)
Negative stains
- Negative or focal weak staining with PAS and mucicarmine
- Cytokeratins and EMA typically negative
- HMB45, S100, SMA, chromogranin
- References: Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:1433, Ann Diagn Pathol 2008;12:344, Int J Surg Pathol 2011;19:803, Hum Pathol 2014;45:1555, Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:973, Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783, Virchows Arch 2012;460:9
Electron microscopy description
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Molecular alterations are similar to conventional ACC, including high mutation burden and massive DNA loss followed by whole genome doubling (Histopathology 2018;72:82)
- Most frequently affected by somatic mutations, copy number alterations and epigenetic silencing were p53 (21%), ZNRF3 (19%), CDKN2A (15%), CTNNB1 (16%), TERT (14%) and PRKAR1A (11%) (Cancer Cell 2016;30:363)
- Another study of 7 myxoid ACC showed very frequent gain of TERT (43%) and CDK4 (86%) and loss of RB1 (28%), CDKN2A (28%), ZNRF3 (14%) (Mod Pathol 2018;31:1257)
- High expression of miR-483-3p, miR483-5p and miR-210 was similar to conventional ACC (Hum Pathol 2014;45:1555)
- EGFR protein overexpression without mutations or amplification; increased EGFR copy number in one case (Am J Clin Pathol 2011;136:783)
Sample pathology report
- Adrenal gland, left, adrenalectomy:
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma with the following features:
- Tumor size: 12 cm x 10 cm x 9 cm
- Tumor (gland) weight: 300 g
- Tumor extent: capsular invasion
- Histologic type: myxoid variant (30% tumor)
- Histologic grade: high grade
- Necrosis: present
- Lymphovascular invasion: present
- Margins: positive
- pTNM, AJCC 8th Edition: pT3 NX MX
- Ancillary studies: Ki67 mitotic rate 25%
- Reticulin stain: disruption of reticulin framework
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma with the following features:
Differential diagnosis
- Adrenal cortical carcinoma, conventional:
- No myxoid component
- Metastatic mucin producing carcinomas:
- More likely to be bilateral; check clinical history
- Carcinoma with myxoid areas, especially adenoid cystic (cytokeratin+, p63+)
- Other myxoid neoplasms in retroperitoneum:
- Chordoma:
- S100+
- ACC markers-
- Benign or malignant nerve sheath tumor:
- S100+
- Myxoid leiomyoma and leiomyosarcoma
- SMA+
- Myxoid malignant fibrous histiocytoma
- Extraskeletal myxoid chondrosarcoma
- Chordoma:
Board review style question #1
Which of the following features is characteristic for myxoid variant of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC), shown in the picture?
- Has unique immunohistochemical, molecular and genomic profiles
- More common than other variants of ACC
- More indolent than conventional ACC
- Must have ≥ 50% extracellular mucinous component
- Should be distinguished from metastatic mucin producing carcinoma
Board review style answer #1
E. Should be distinguished from metastatic mucin producing carcinoma. Myxoid variant of adrenocortical carcinoma (ACC) is characterized by the presence of extracellular myxoid component. In some cases, tumors exhibit striking resemblance with myxoid tumors, adenoid cystic and other mucin producing carcinomas, which have to be ruled out in the right clinical context. Answer A is incorrect because there is a substantial overlap in immunohistochemical, molecular and genomic profiles of myxoid and conventional ACC variants. Answer B is incorrect because myxoid ACC is less common than conventional or oncocytic variants of ACC with only ~50 cases reported to date. Answer C is incorrect because compared with conventional ACC, myxoid variant has more aggressive clinical behavior with higher rate of tumor recurrence, metastases and shorter overall survival. Answer D is incorrect because myxoid extracellular matrix is variably abundant from 5 - 90% of tumor volume.
Comment Here
Reference: Adrenal cortical carcinoma - Myxoid variant
Comment Here
Reference: Adrenal cortical carcinoma - Myxoid variant