Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Anthuvan J, Zynger DL. Cysts. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/adrenalcysts.html. Accessed April 3rd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Nonneoplastic and nonfunctional fluid filled lesions in the adrenal gland (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398)
Essential features
- Nonneoplastic cystic lesion of the adrenal gland that usually has an endothelial lining or no visible lining
- Represent 1 - 3% of adrenal masses (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Cureus 2022;14:e32564)
- Vast majority are endothelial cysts and pseudocysts; epithelial and parasitic cysts are rare (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274)
- Cystic neoplasms are not described below; refer to the respective neoplastic topic for cystic change in neoplastic lesions
Epidemiology
- Age
- Endothelial cyst: mean of 48 - 50 years (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Pseudocyst: mean of 42 - 51 years (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Gender
- Endothelial cyst: 80 - 88% female (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Pseudocyst: 33 - 67% female (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
Sites
- Adrenal cortex or medulla
- No predilection for laterality (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Unlikely to be bilateral (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
Pathophysiology
- Nonneoplastic adrenal cysts are classified in 4 categories (frequencies are from 3 surgical resection cohorts, n = 14 - 42)
- Endothelial (36%, 44%, 52%) (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Pseudocysts (43%, 50%, 50%) (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Epithelial (including mesothelial) (5%, 6%, 14%) (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Parasitic (0%) (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Endothelial cysts
- Theorized to be lymphangiomatous or hemangiomatous in origin
- Some authors have used immunostains to characterize the lining although this may not be indicative of origin; often has a hybrid expression profile and has no clinical utility (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, BMJ Case Rep 2023;16:e254535, Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Ann Diagn Pathol 2022;57:151888, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Pathogenesis is thought to be related to postobstructive lymphatic channel or blood vessel ectasia or vascular malformation (Clin Radiol 2022;77:479, Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44, J Urol 1959;81:711)
- Pseudocysts
- A vascular origin has been suggested by many authors with the theory that over time the vascular lining has degenerated (perhaps due to repeated bleeding) and is no longer present (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Hum Pathol 1989;20:660, Ann Surg 1952;136:217, Am J Pathol 1979;95:423)
- Sometimes pseudocysts are reclassified as endothelial cysts upon retrospective review, which identifies an endothelial lining that was initially missed (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274)
- Several immunohistochemical studies reveal expression of endothelial markers in vascular channels and at the edge of pseudocysts (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Mod Pathol 1997;10:530, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:121, Am J Surg Pathol 1989;13:740)
- Other possible etiologies are adrenal hemorrhage secondary to numerous causes including trauma, coagulopathy or pregnancy and others (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Hum Pathol 1989;20:660)
- Epithelial cysts
- Mesothelial lining identified in most cases, possibly related to the presence of mesothelium during embryogenesis (Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Parasitic cysts
- Usually a manifestation of a disseminated hydatid infection (World J Surg 2004;28:97)
- Typically result from Echinococcus granulosus
- Rarely, can be associated with leishmaniasis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:1553, Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 2002;21:682)
Clinical features
- Often incidental finding on imaging for other indications (Hum Pathol 1989;20:660, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- Larger cysts are more likely to present with symptoms of mass effect, with flank / abdominal pain, palpable abdominal mass and gastrointestinal distress being the most common symptoms (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274)
Diagnosis
- Typically incidental finding on radiology imaging, which is then further evaluated via hormonal analysis (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- Fine needle aspiration (FNA) may be utilized to characterize the lesion
- Approximately half undergo surgical resection with histopathologic microscopic examination (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- Definitive diagnosis and cyst subtyping is made by microscopic examination of tissue
Laboratory
- Most adrenal cysts are hormonally nonfunctional
- It is important to rule out a functional cystic tumor through adrenal hormone testing
- Proposed testing regimen involves evaluation of serum potassium and aldosterone, dexamethasone suppression test, dehydroepiandrosterone sulfate (DHEA-S) and 24 hour urine metanephrines (Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44)
- Some cases of adrenal cysts with adrenal hormone excess have been described in the literature but may be secondary to hemorrhage into adrenal adenoma and their true prevalence is debatable (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398)
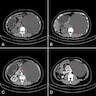
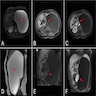
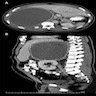
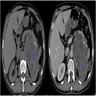
Radiology description
- Generally adrenal cysts are rounded, well demarcated hypoechoic or anechoic lesions that rarely display contrast enhancement (with the exception of rim enhancement due to enhancement of normal surrounding adrenal tissue) (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Urol Int 2008;80:31, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Clin Radiol 2022;77:479)
- Tend to be low attenuating (< 20 Hounsfield units) (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398)
- Occasionally, increased intracystic attenuation can be present, likely due to hemorrhage, debris or calcification (Clin Radiol 2022;77:479, Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44, Eur J Endocrinol 2023;188:407)
- Calcification, when present, is very often in a peripheral pattern, although septate and scattered patterns are possible too (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Urol Int 2008;80:31)
- Differentiating factors on imaging can exist between the 4 subtypes of adrenal cysts (see table)
- Lack of contrast enhancement can be an aid in differentiating adrenal cysts from other adrenal lesions
- Malignancy may be more likely in cases where adrenal cystic lesions have wall thickness > 5 mm and central calcification (Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44, Surg J (N Y) 2022;8:e112)
| Endothelial cysts |
|
| Pseudocysts |
|
| Epithelial cysts |
|
| Parasitic cysts |
|
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Most radiologically diagnosed adrenal cysts are slow growing (if they grow at all) and have favorable prognosis, with low risk of new or recurrent cysts with appropriate medical treatment (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- Complications can include rupture, massive hemorrhage, infection and arterial hypertension from compression and distortion of adjacent renal tissue (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Clin Radiol 2022;77:479, Eur J Radiol 2007;62:359)
- Managing with cystic aspiration shows a relatively high rate of recurrence, whereas those treated with adrenalectomy show almost no cyst recurrence (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, BMJ Case Rep 2023;16:e254535)
Case reports
- 38 year old woman with giant endothelial cyst (Cureus 2023;15:e37086)
- 41 year old woman with pseudocyst (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;72:178)
- 55 year old man with giant pseudocyst (J Pak Med Assoc 2023;73:1317)
- 55 year old man with large hydatid cyst (Int J Surg Case Rep 2020;70:154)
Treatment
- Nonfunctional, asymptomatic cysts may be managed conservatively by follow up imaging to evaluate for growth
- Surgical resection may be indicated if there are indeterminate radiographic findings, risk of malignancy, adrenal hormonal abnormalities, symptoms of mass effect, large cyst size (> 5 cm), parasitic cysts, high cyst growth rate on follow up imaging and other anomalies such as superior vena cava syndrome (SVC syndrome) (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Clin Radiol 2022;77:479, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, Surg J (N Y) 2022;8:e112)
- Percutaneous fine needle aspiration (FNA) can be palliative and diagnostic but has a high rate of fluid reaccumulation (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- 50% of radiologically detected cysts result in surgical resection (Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- Laparoscopic adrenal sparing cystectomy is the procedure of choice but full adrenalectomy is typically the procedure that occurs clinically (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Urol Int 2008;80:31, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429)
- Cyst unroofing, sclerotherapy and marsupialization are other potential therapies (Clin Radiol 2022;77:479, BMJ Case Rep 2023;16:e254535, Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44)
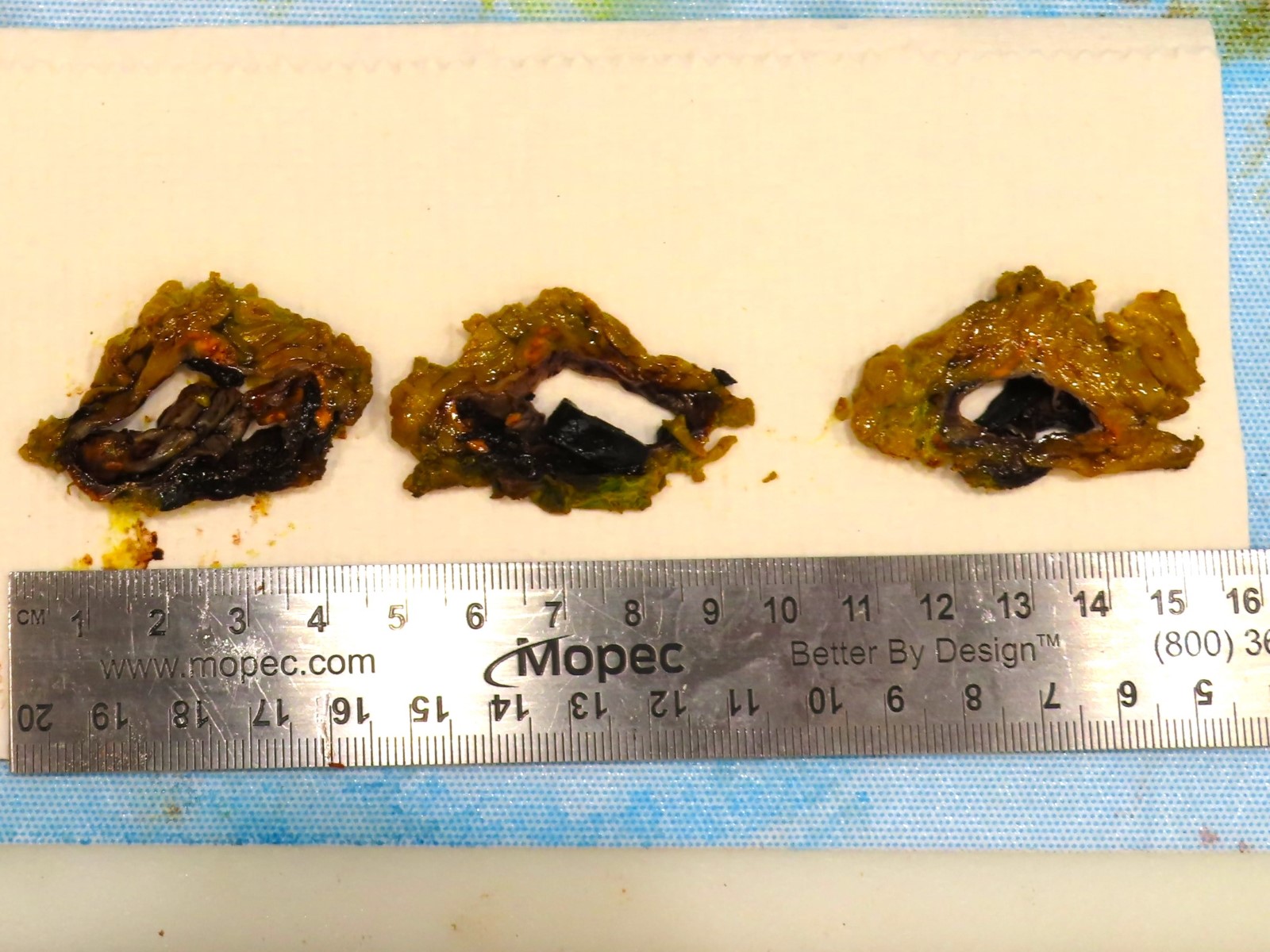
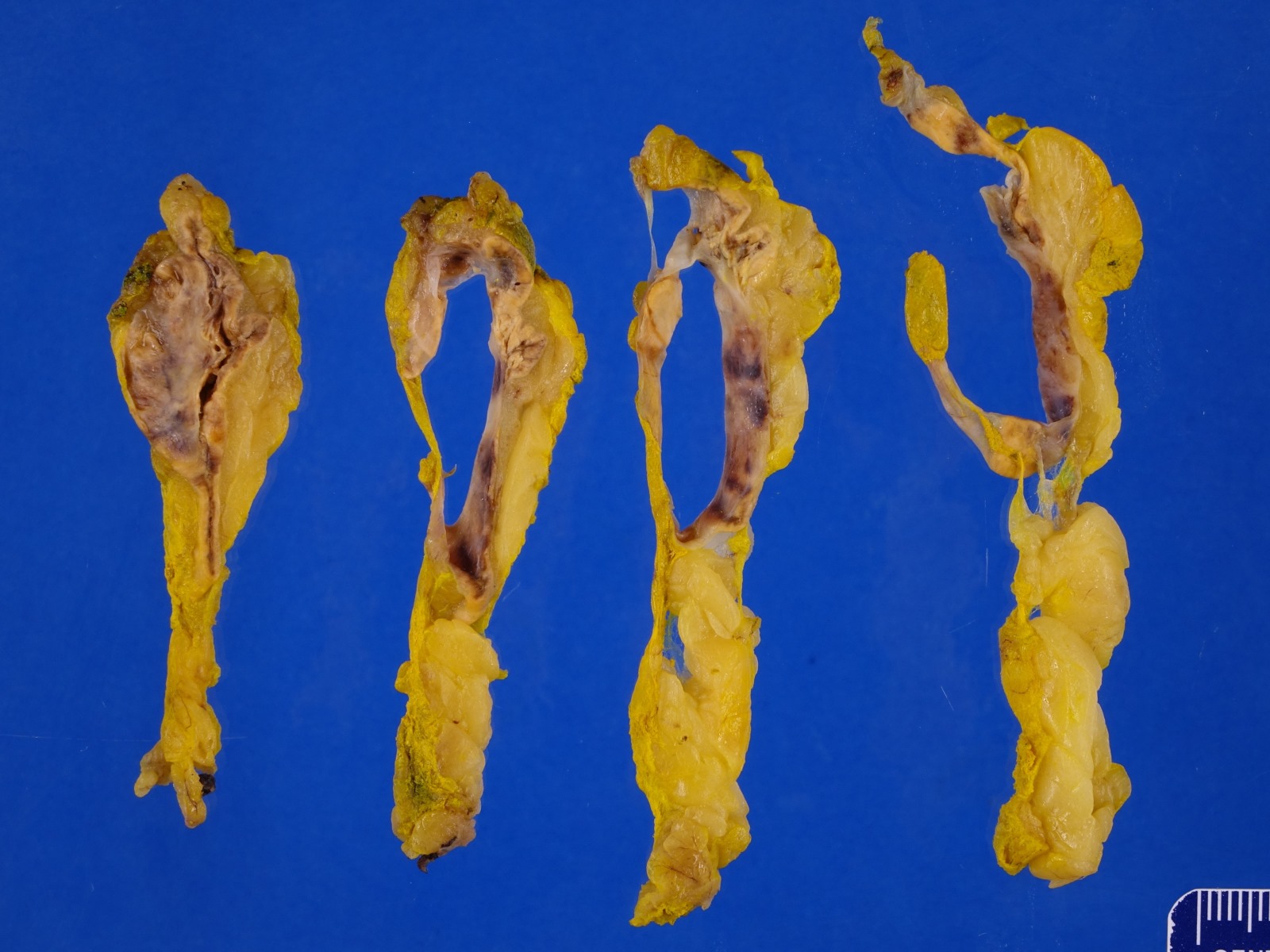
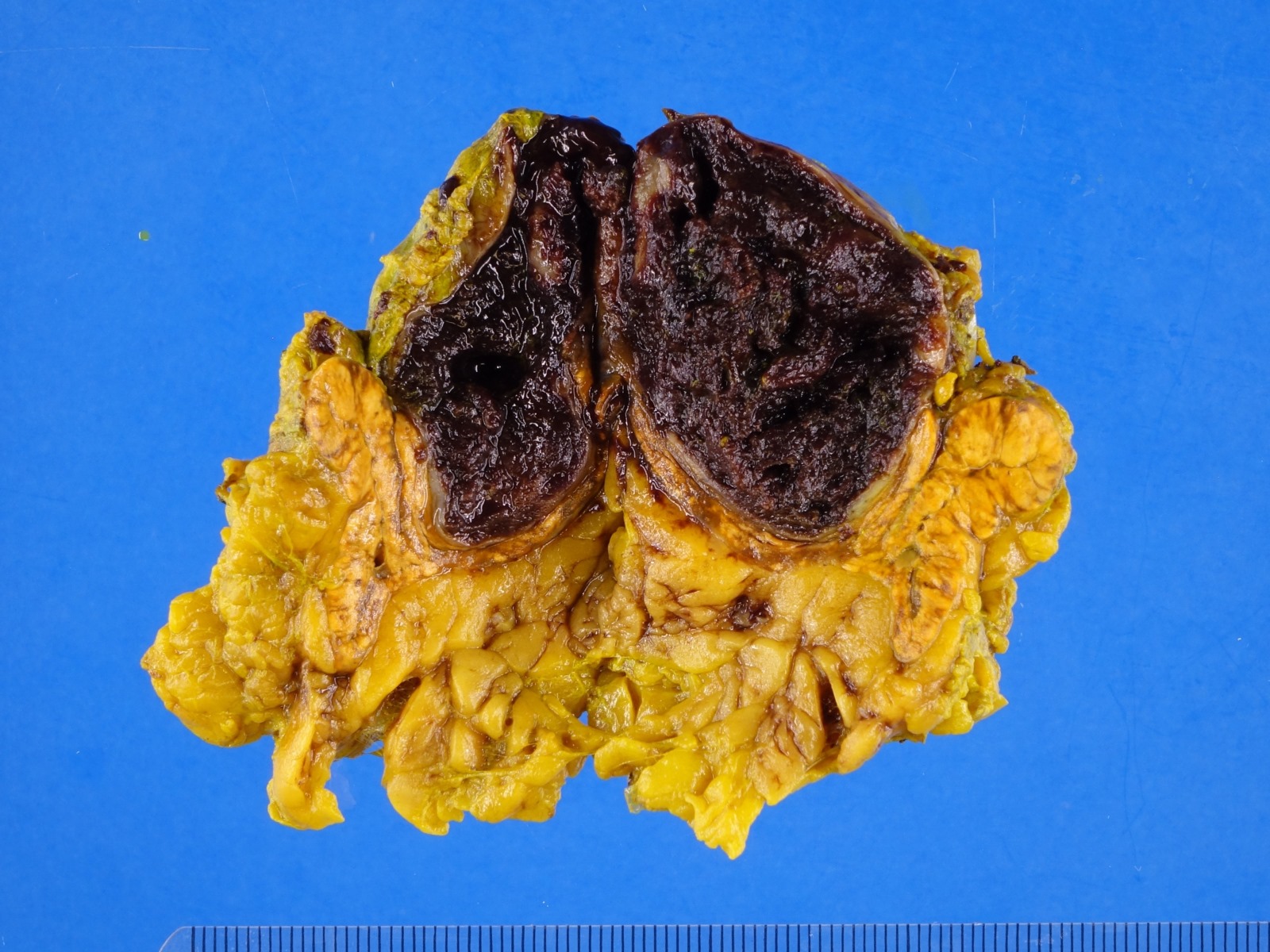
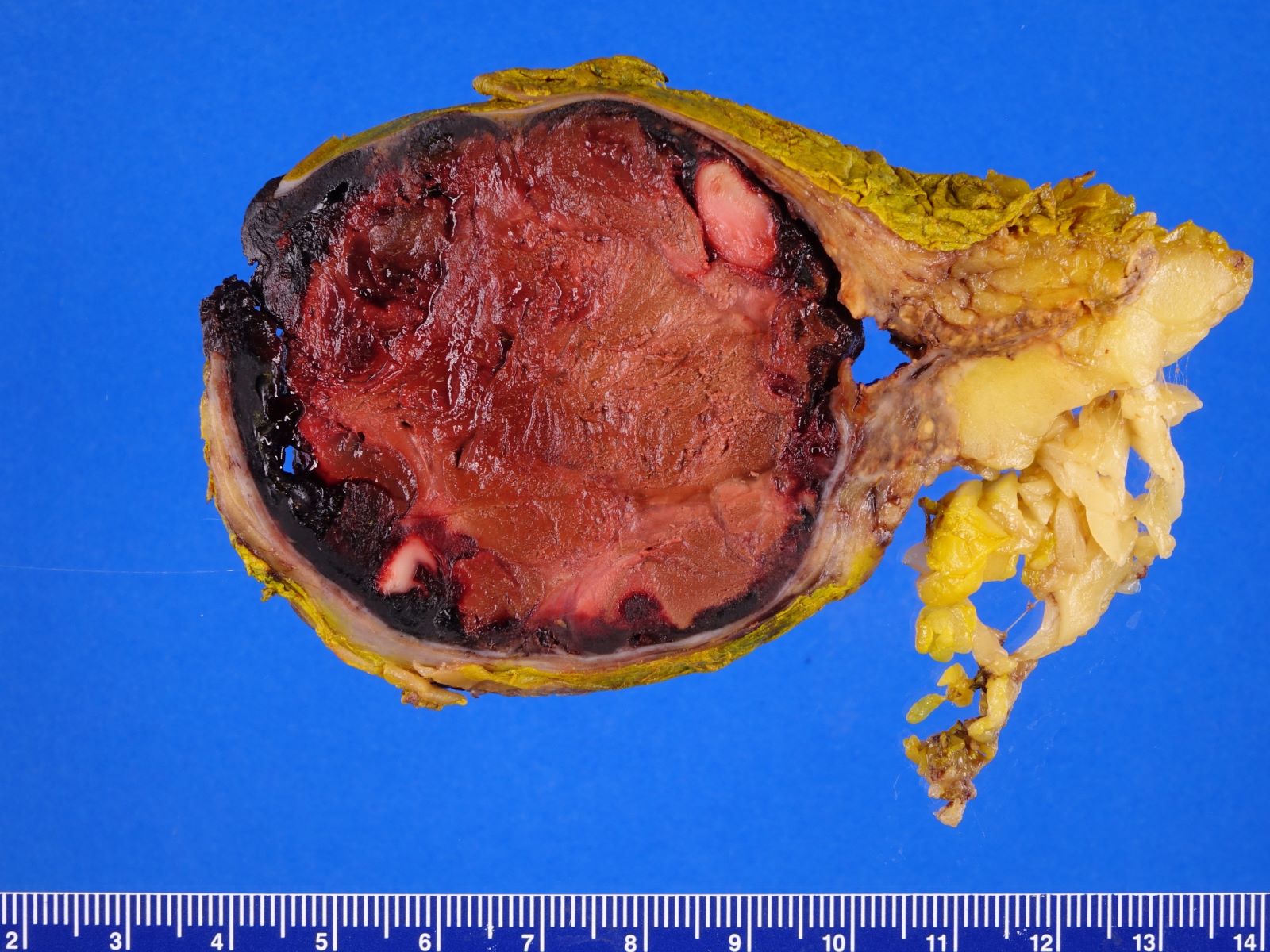
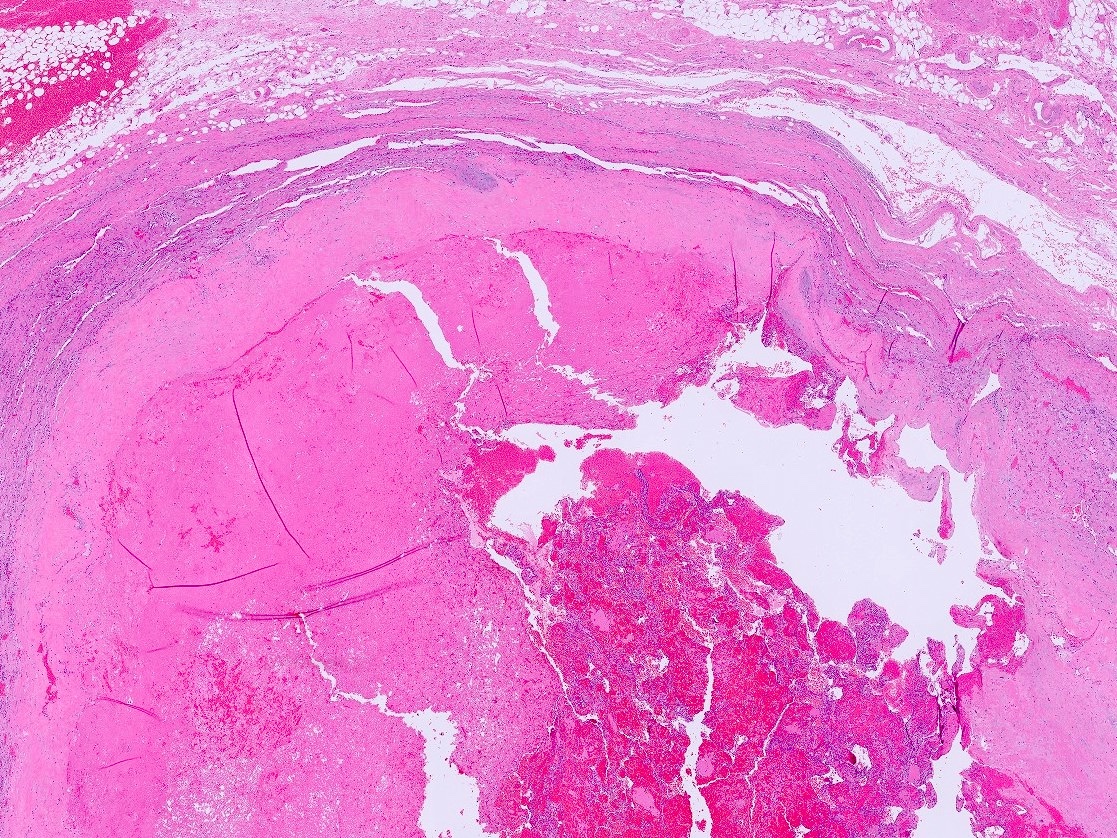
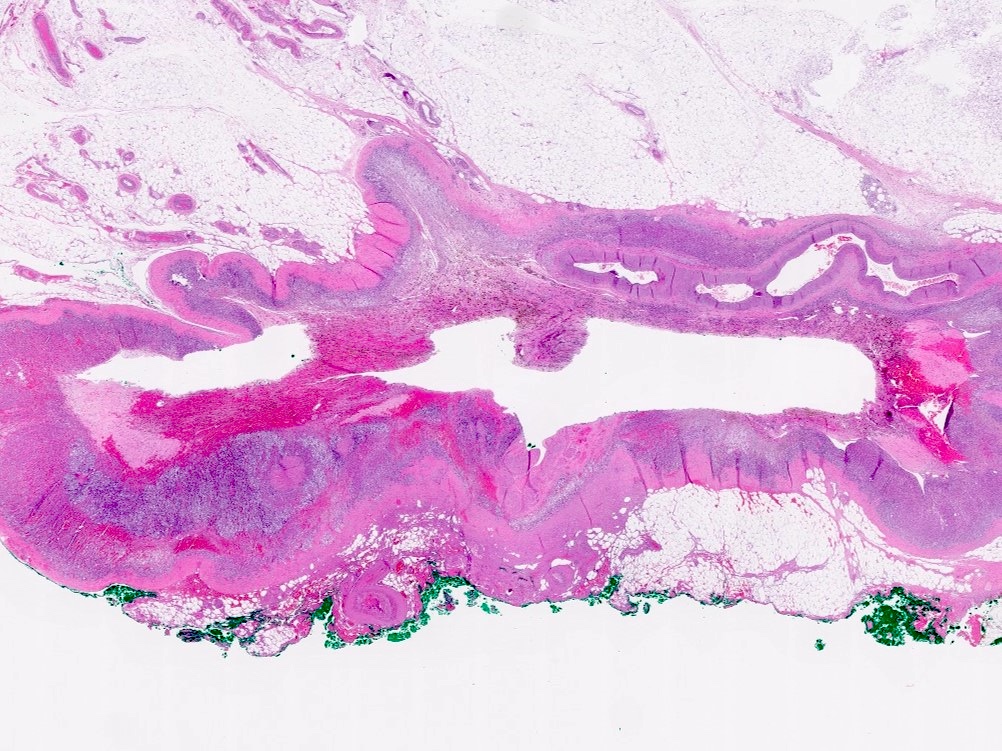
Gross description
- Generally, unilocular or multilocular, well circumscribed and encapsulated lesion containing fluid
- Size
- Endothelial cyst: mean of 6.0 - 9.0 cm (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Pseudocyst: mean of 5.6 - 7.8 cm (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Endothelial cysts tend to be thinner walled, multilocular and contain yellow tinged, clear or milky fluid (Case Rep Endocrinol 2021;2021:6662492, Hum Pathol 2013;44:1797, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:1722, Am J Surg 1977;134:363)
- In comparison to endothelial cysts, pseudocysts are thicker walled, unilocular and contain yellow brown or bloody amorphous material (Clin Radiol 2022;77:479, BMJ Case Rep 2023;16:e254535, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2006;130:1722, Am J Surg 1977;134:363)
Gross images
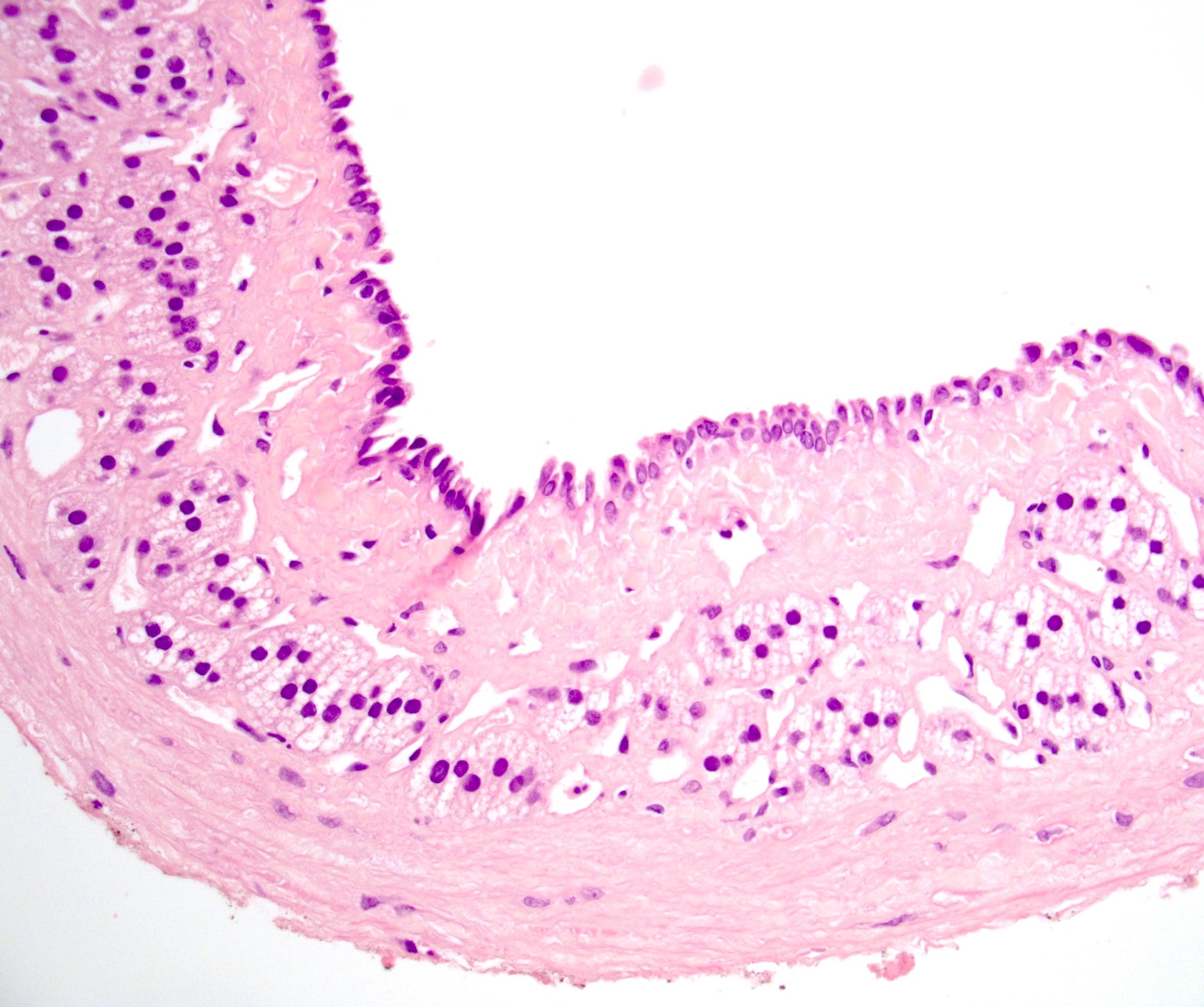
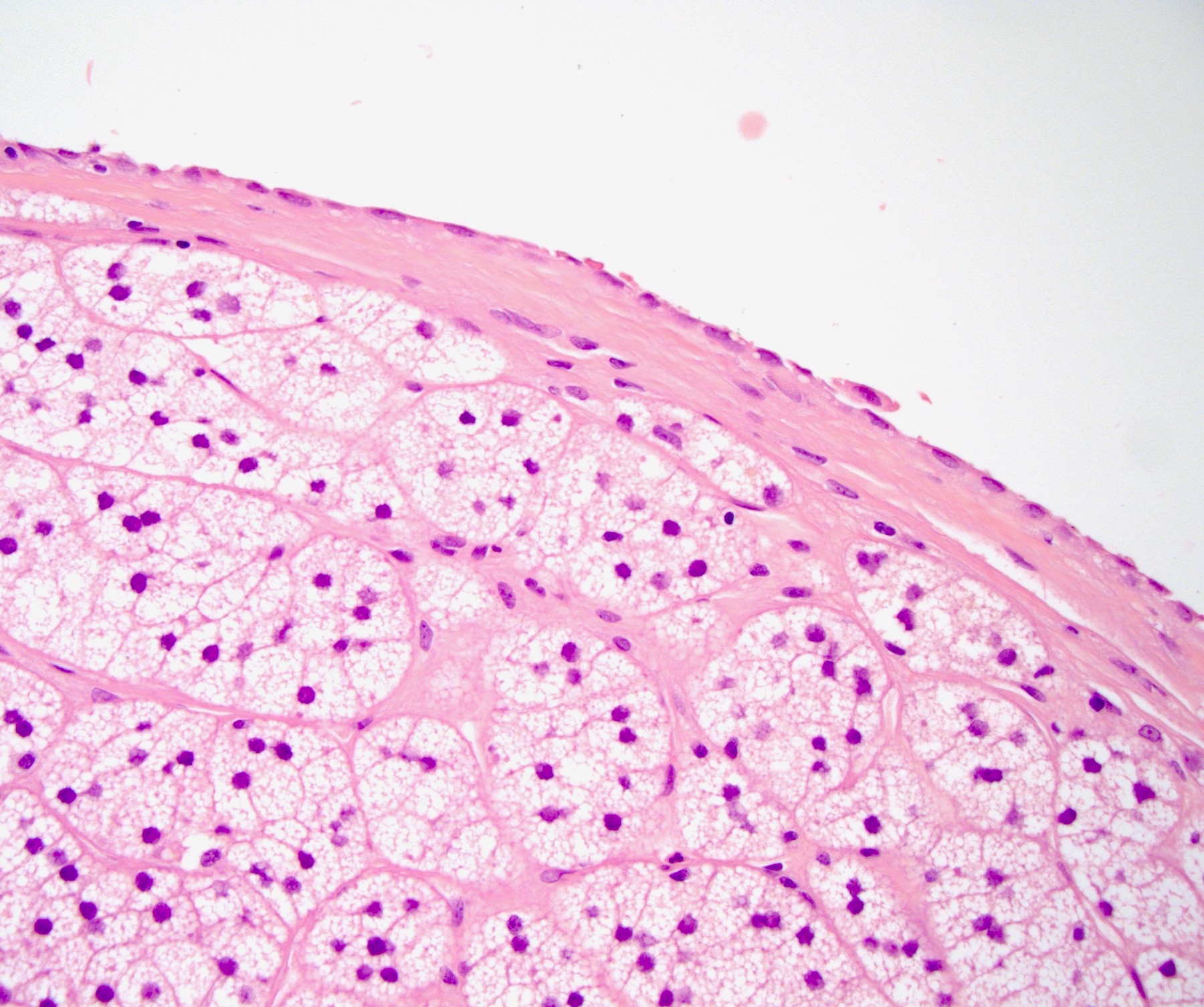
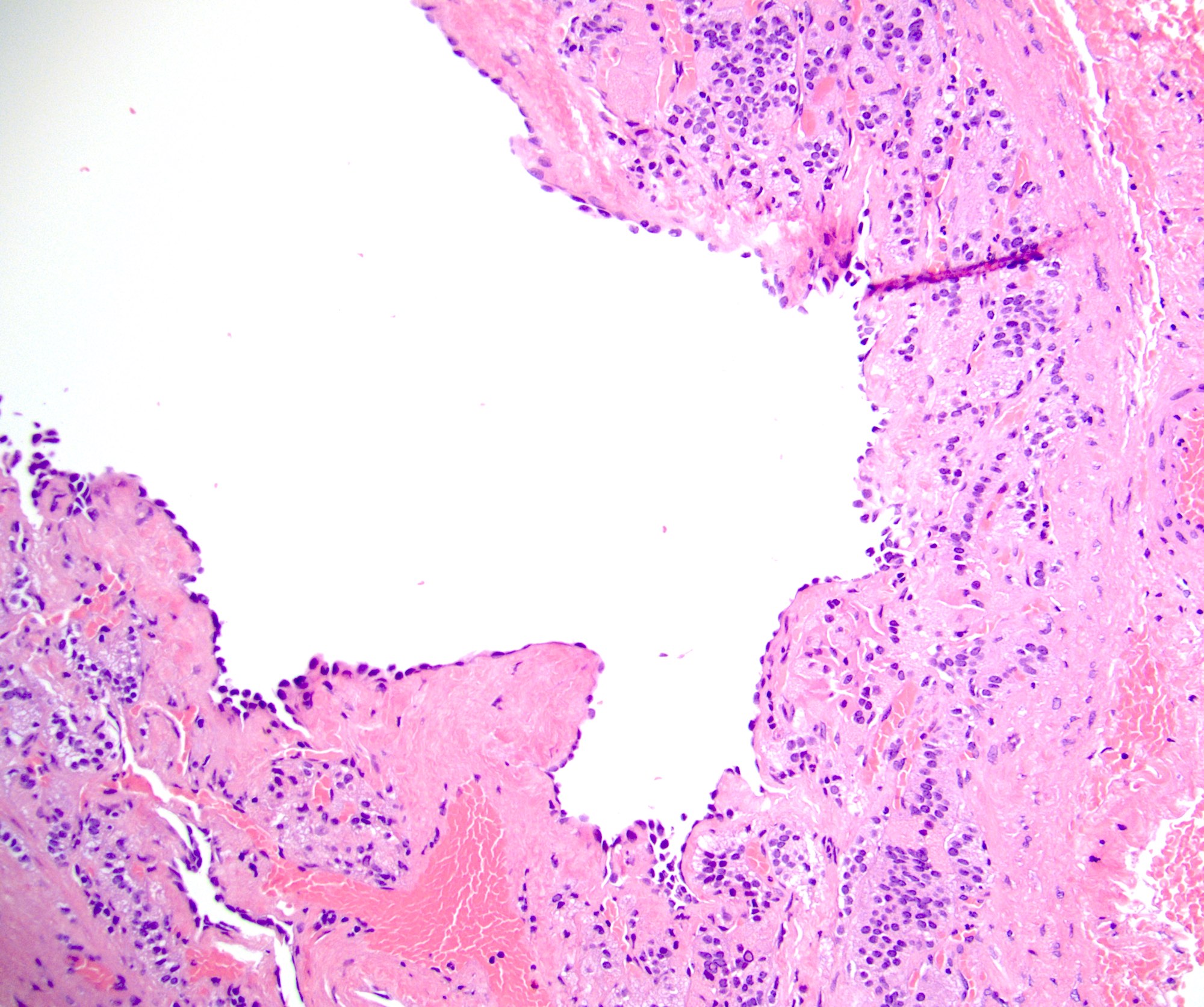
Microscopic (histologic) description
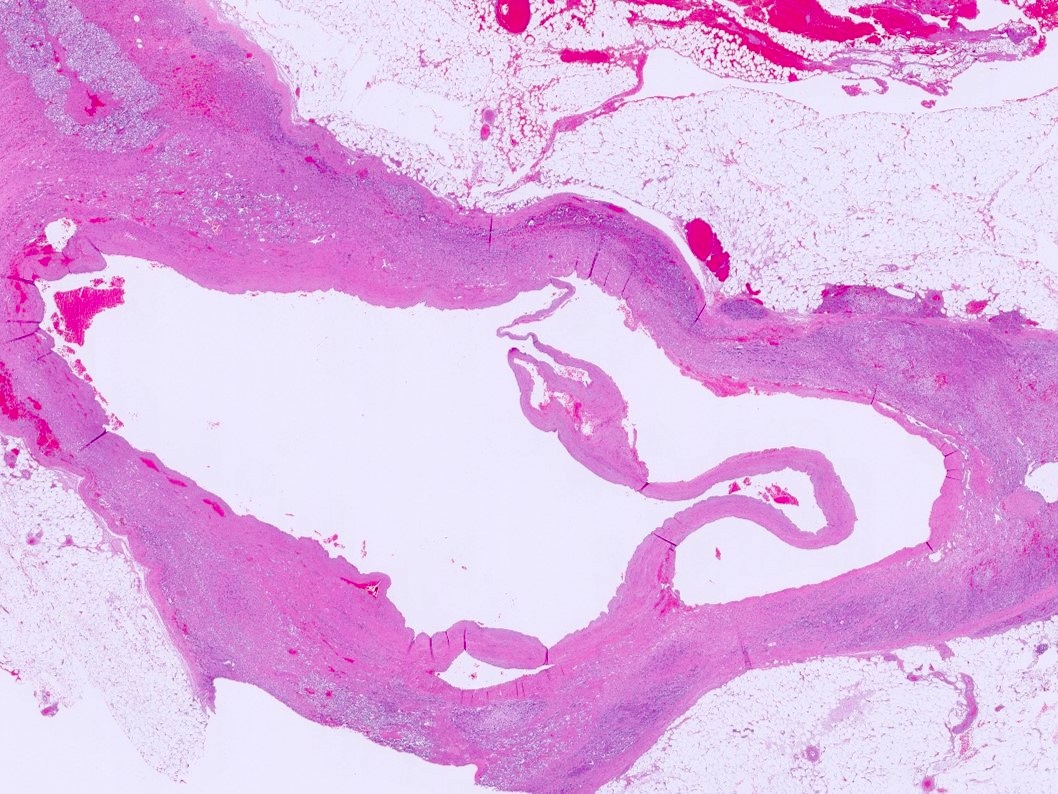
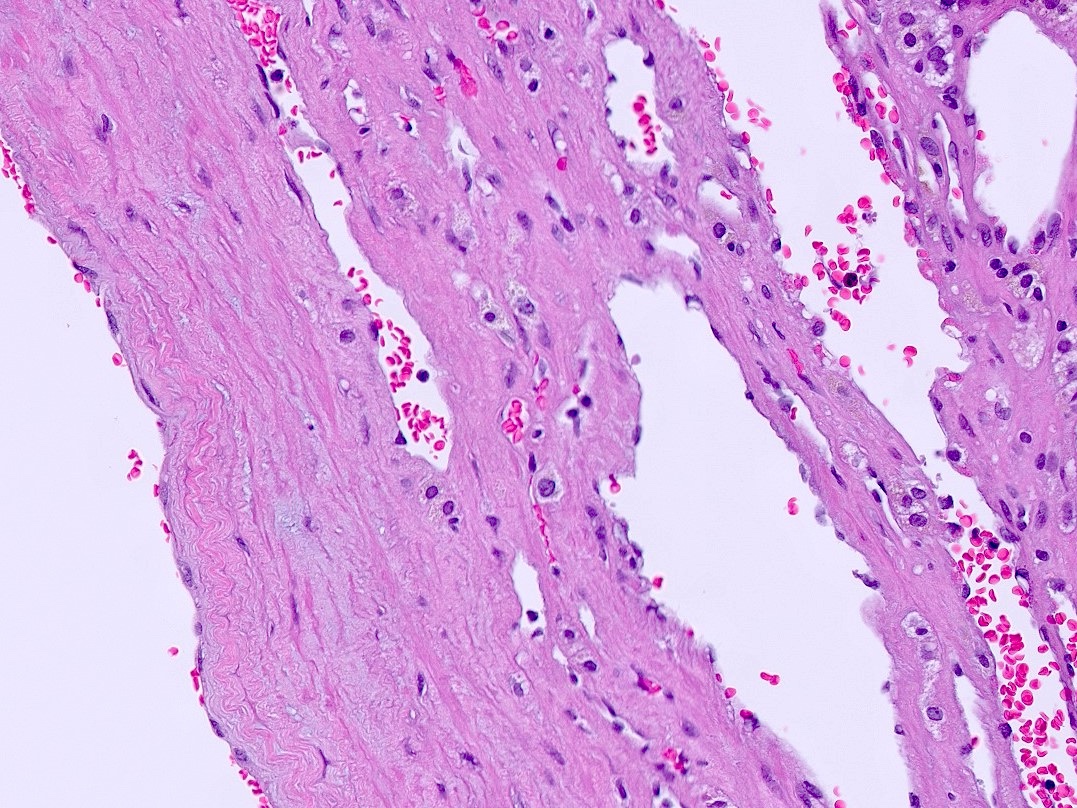
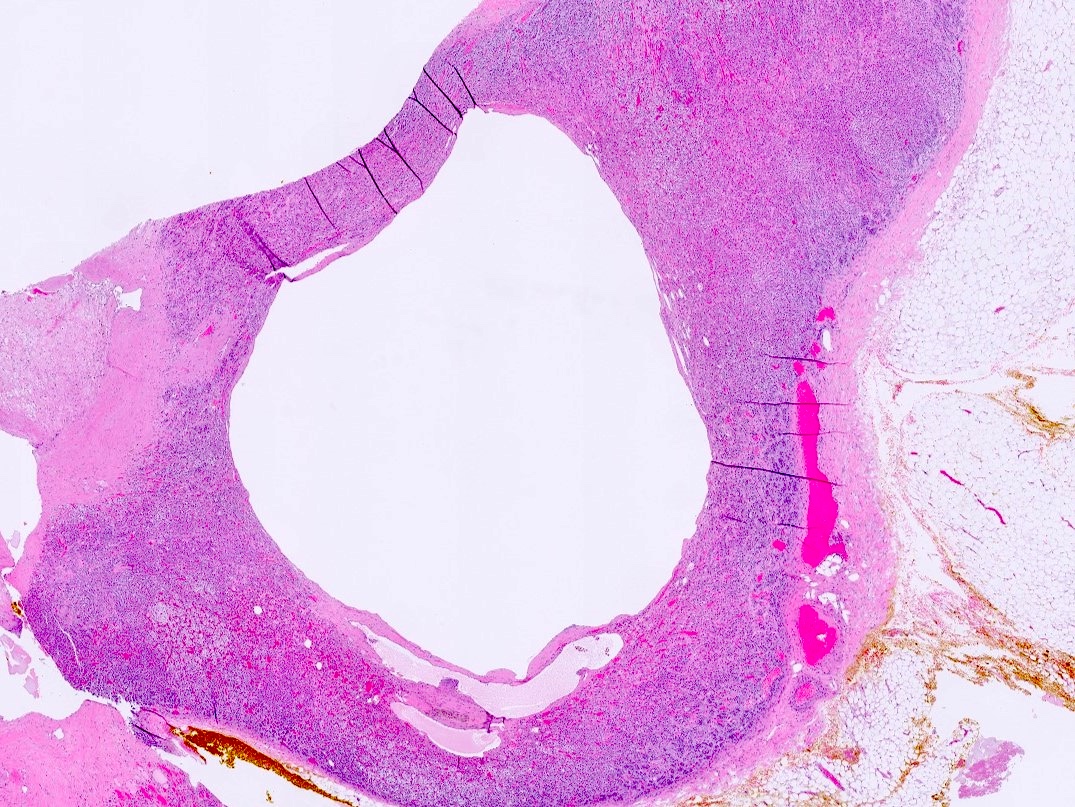
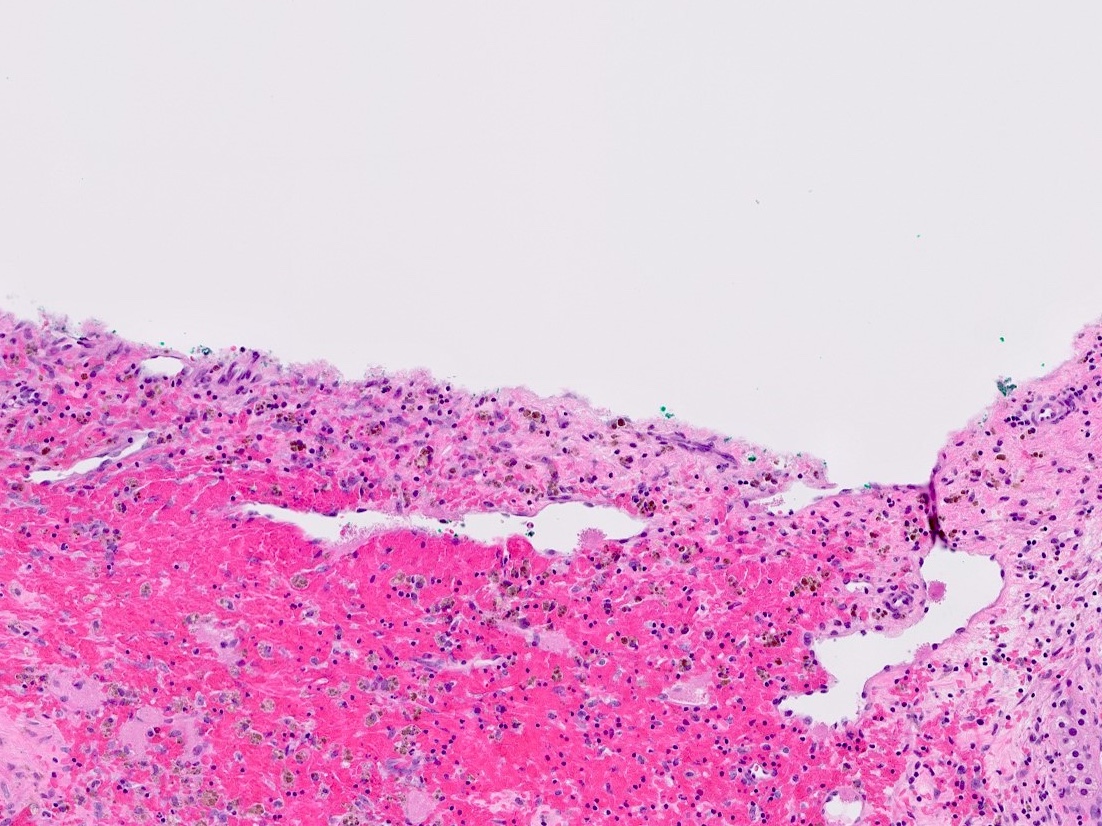
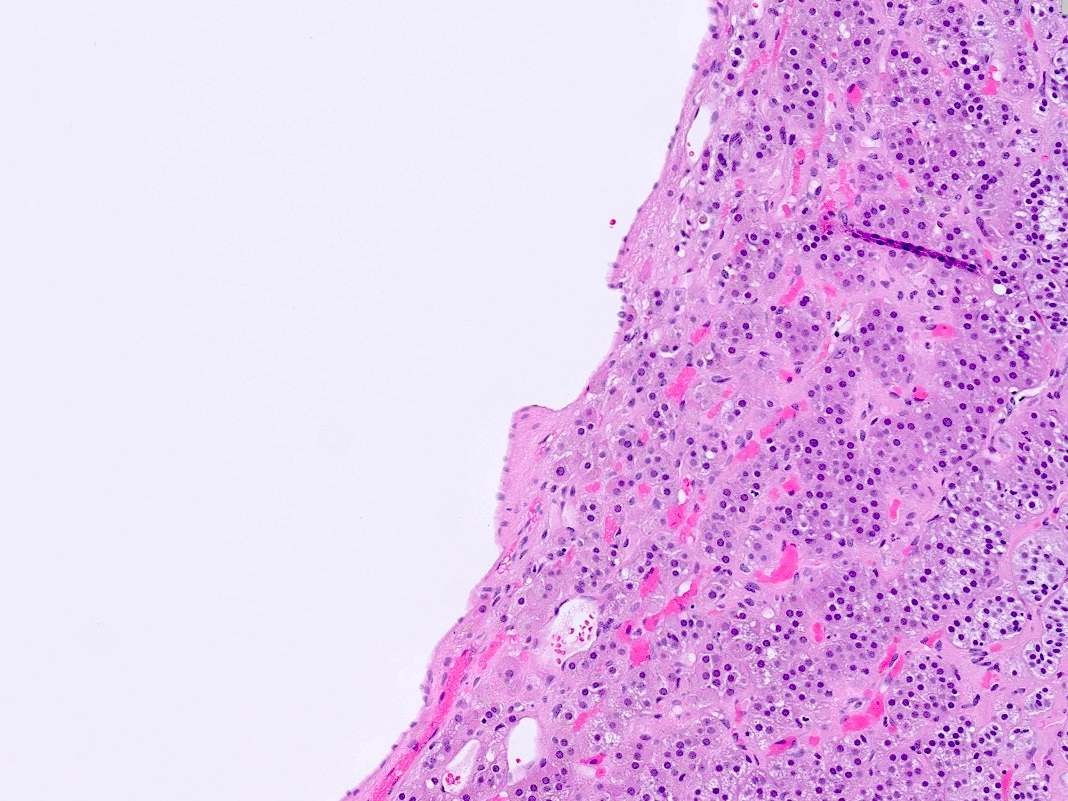
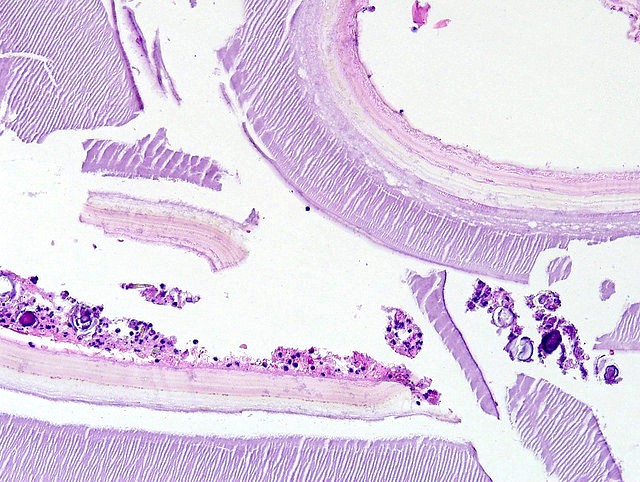
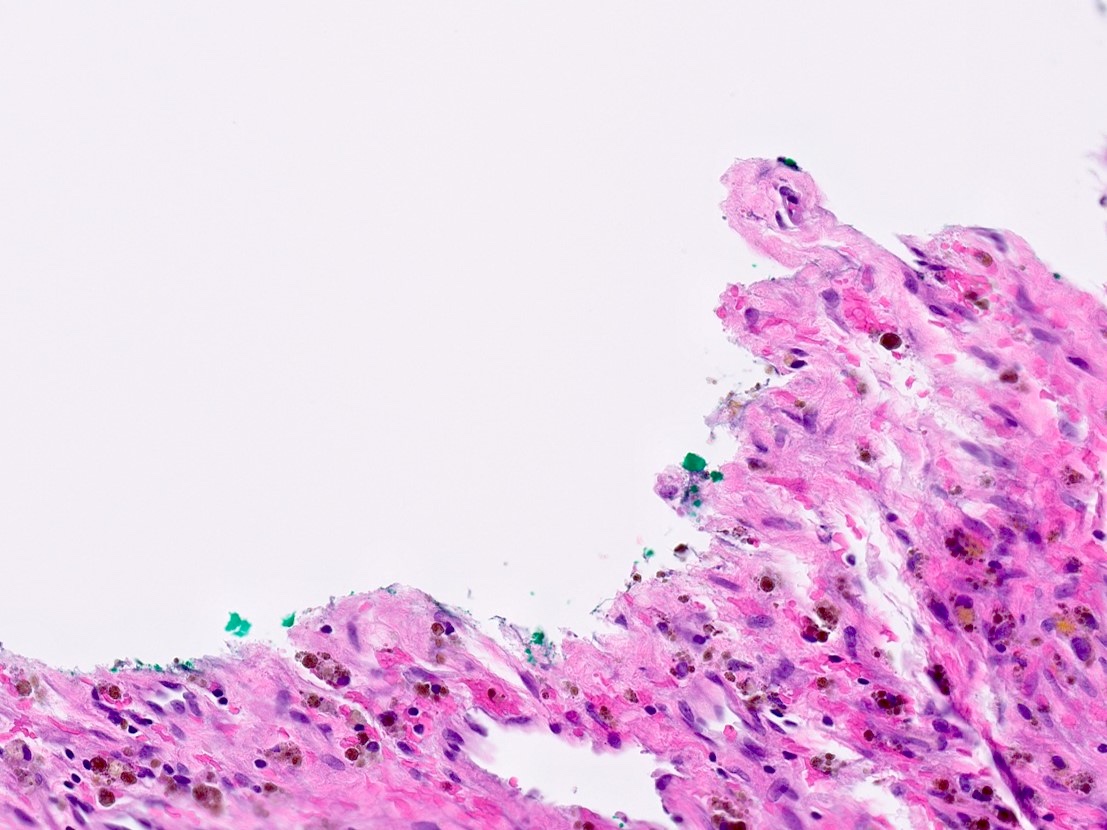
- Endothelial cysts
- Cyst lining of flattened, bland endothelium
- Endothelial lining may be difficult to visualize
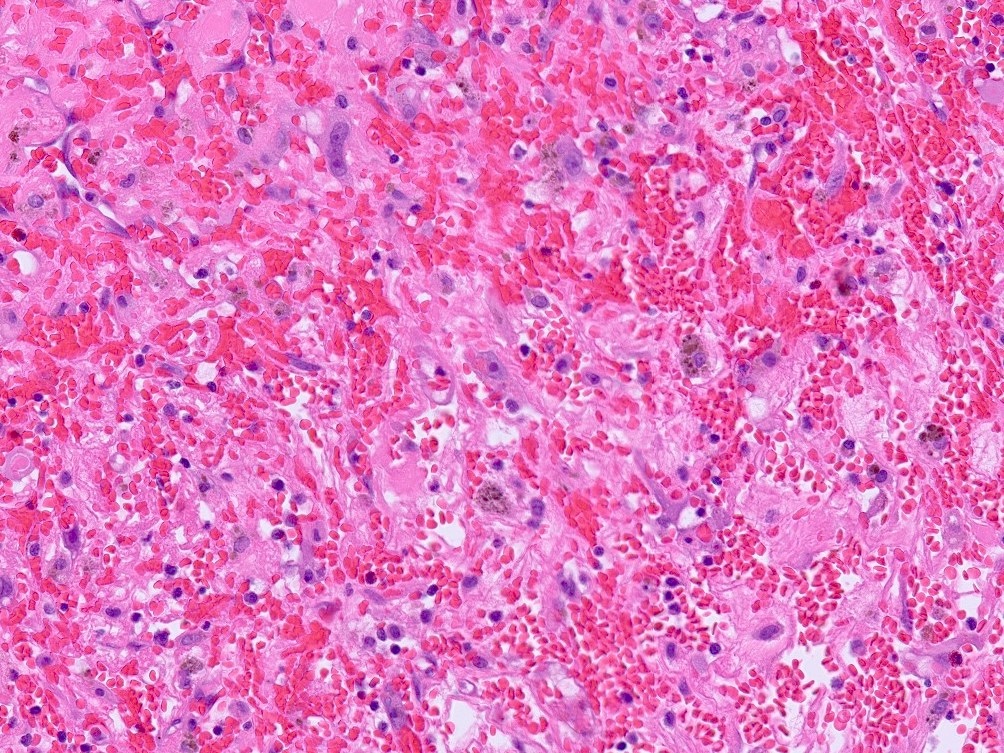
- Cyst wall and contents of hemorrhage, debris and calcification
- Revascularization and papillary endothelial hyperplasia often present
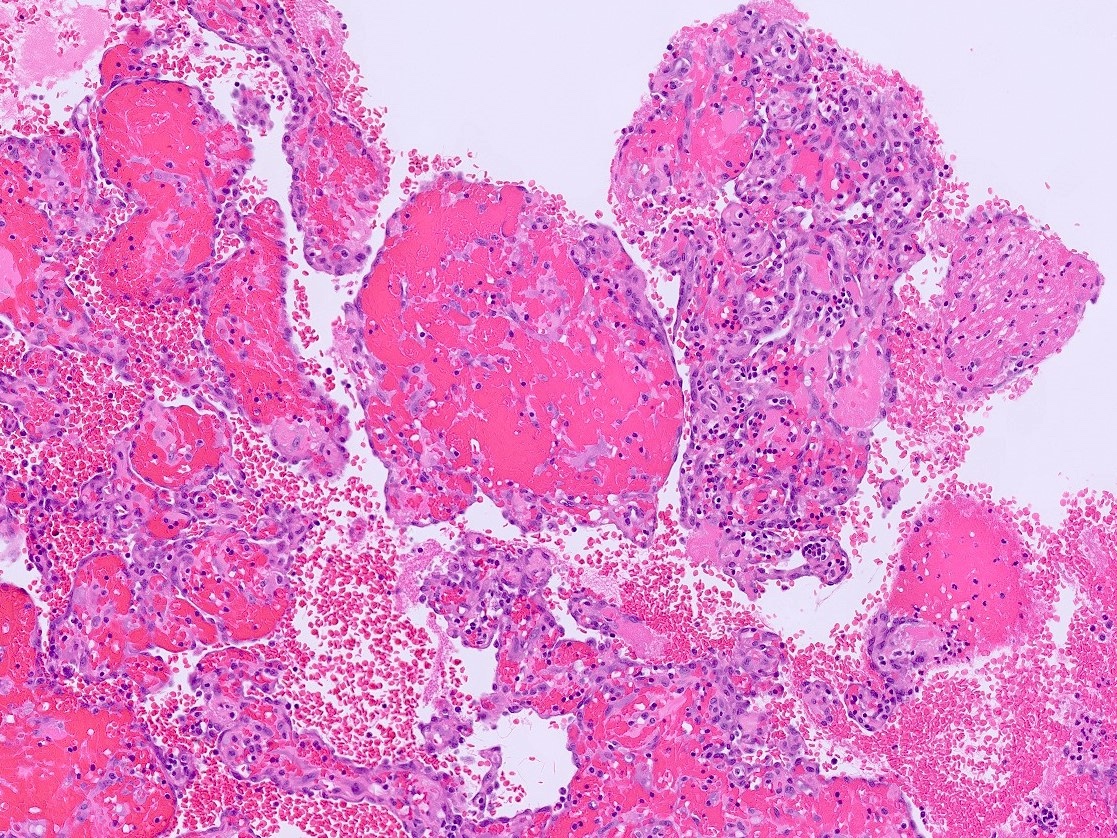
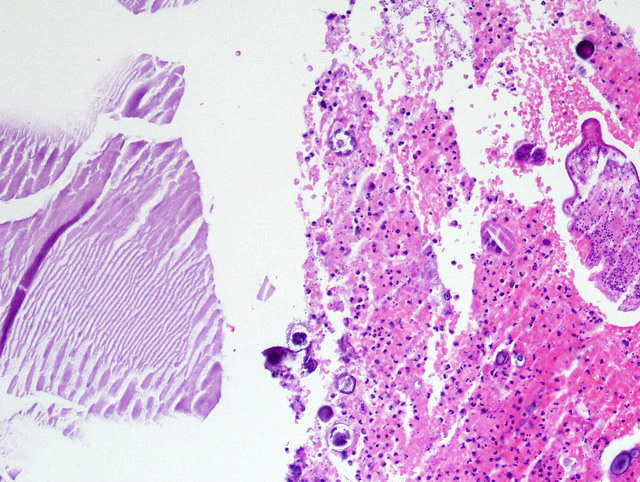
- Pseudocysts
- No cyst lining is present; careful search for intact lining may reveal endothelium, reclassifying a pseudocyst as an endothelial cyst
- Cyst wall and contents of hemorrhage, debris and calcification
- Revascularization and papillary endothelial hyperplasia often present
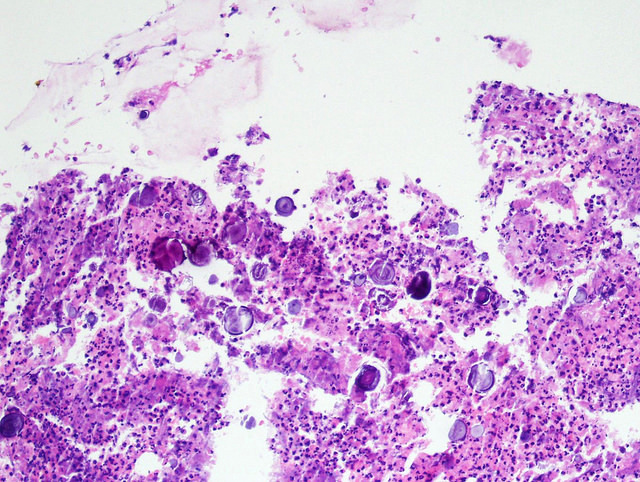
- Epithelial cysts
- Lined by a single layer of bland epithelium
- Epithelium is cuboidal, hobnailed to flattened and can mimic endothelium
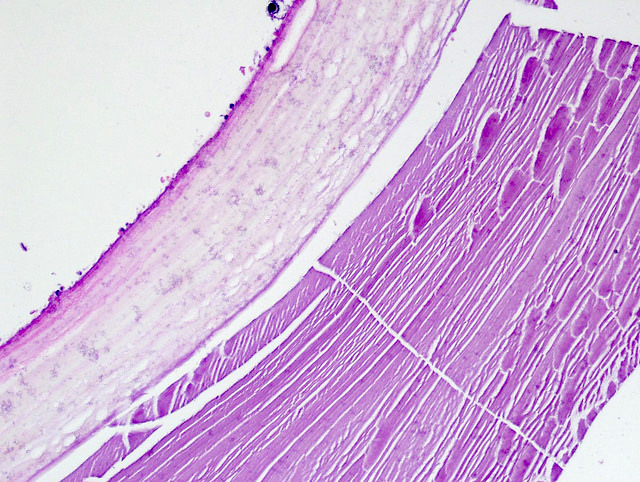
- Hydatid cysts
- Thick laminated / striated, acellular cyst wall
- Cyst wall may be calcified
- Inner germinal epithelial lining
- Within the cyst, brood capsules containing daughter cysts form
- Cyst contains pale eosinophilic proteinaceous material, debris and calcifications; may be able to identify calcified spherical scolices in the cyst contents
- Pale refractile hooklets may be present but are difficult to visualize
Microscopic (histologic) images
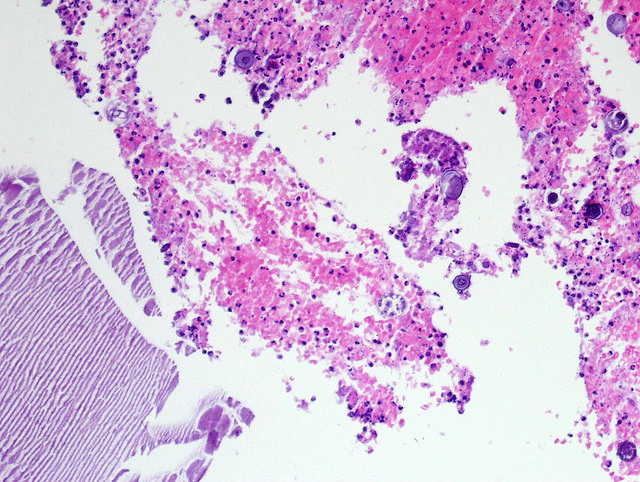
Cytology description
- Percutaneous fine needle aspiration (FNA) has been suggested as a palliative and diagnostic tool in cases where the cyst is nonfunctional and there is low suspicion for malignancy (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Urol Int 2008;80:31, BMJ Case Rep 2023;16:e254535, Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44)
- While FNA appears to be strong diagnostically, its role for treatment is debatable as these cysts have a relatively high rate of fluid reaccumulation (Nat Rev Endocrinol 2023;19:398, Eur J Endocrinol 2022;187:429, BMJ Case Rep 2023;16:e254535, Curr Urol Rep 2010;11:44)
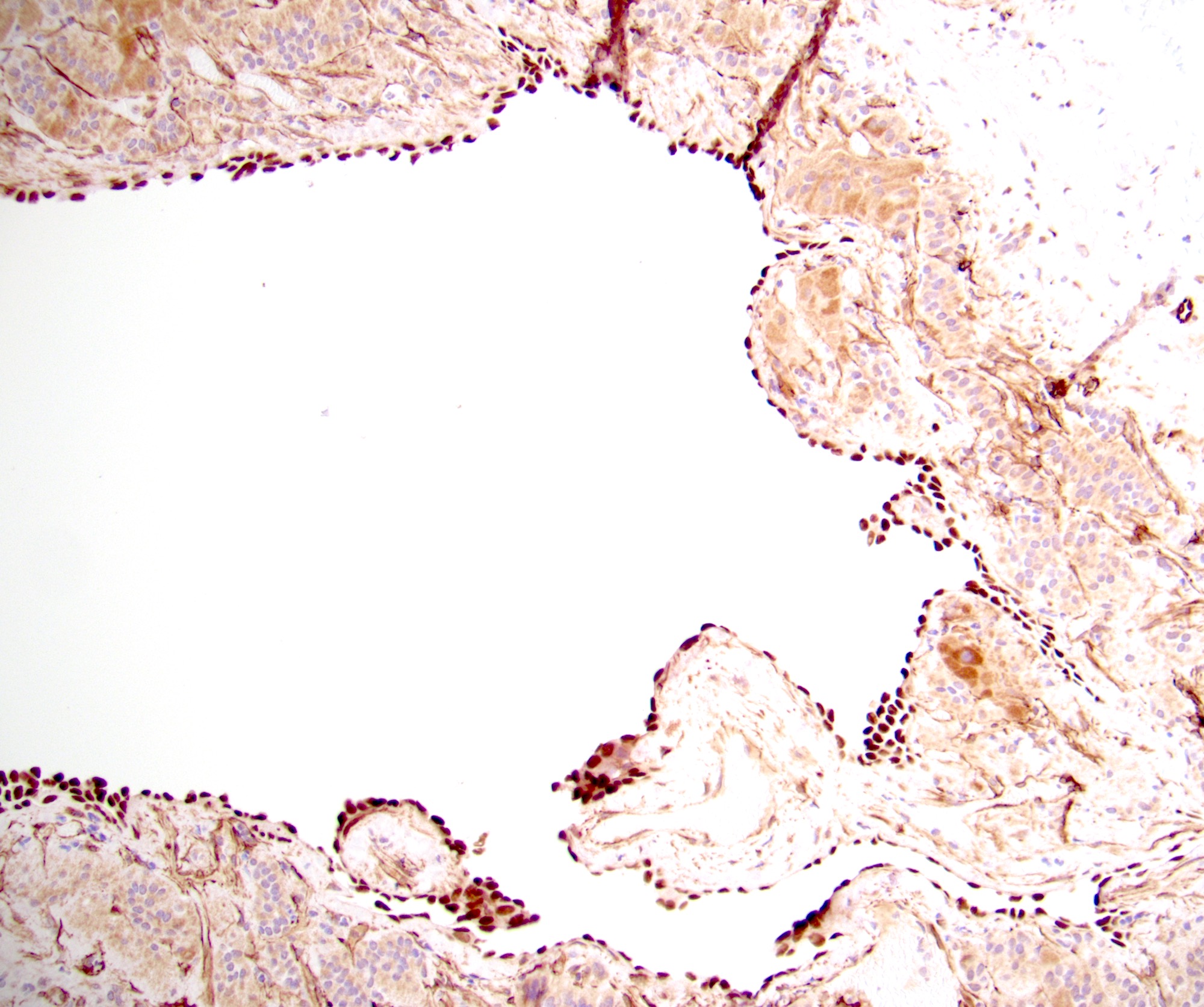
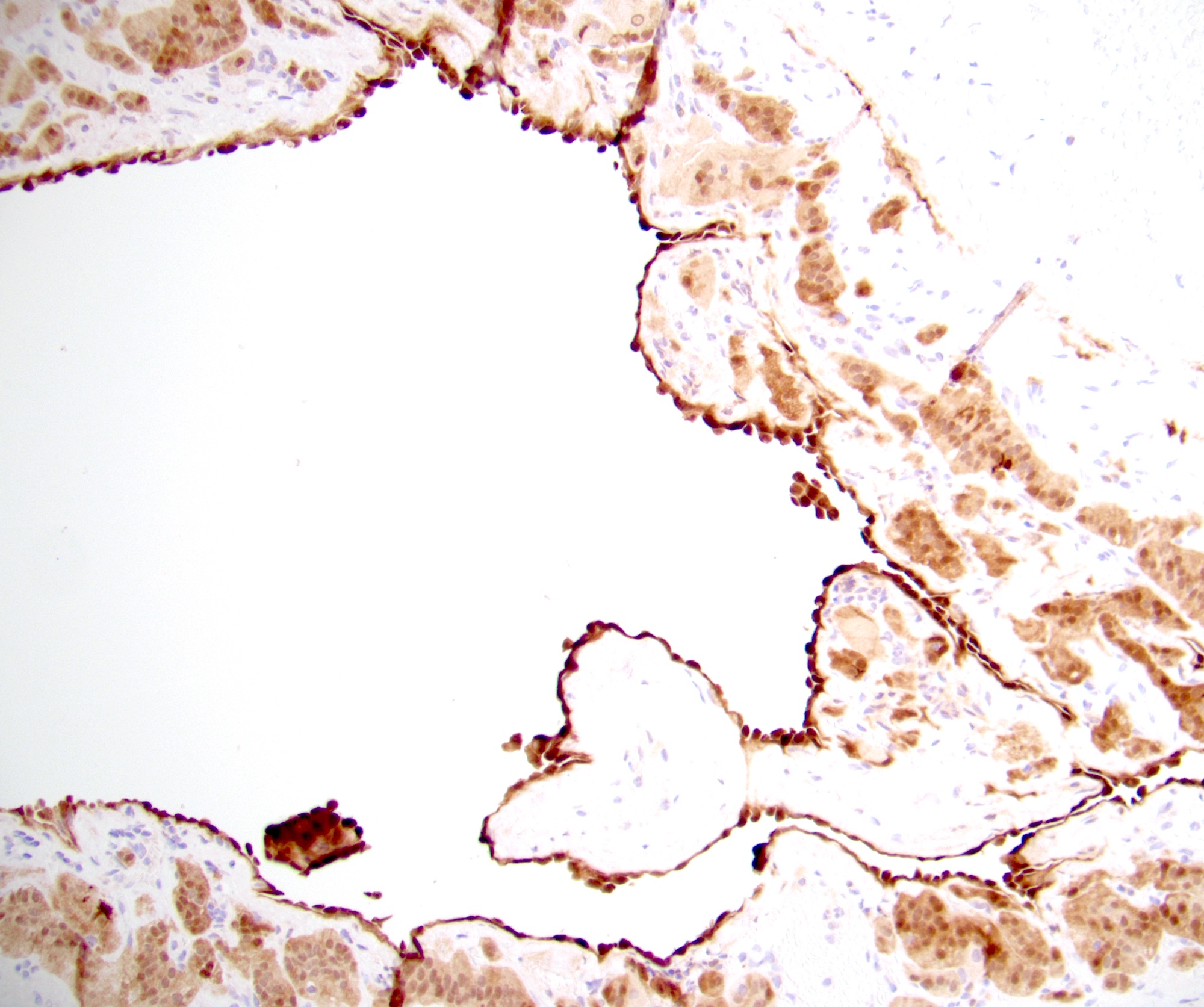
Positive stains
- Endothelial cysts
- D2-40, ERG, CD31 or CD34 (can show a mixture of lymphatic and angiomatous expression) (Endocr Pathol 2008;19:274, Ann Diagn Pathol 2022;57:151888, Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531)
- Epithelial cysts
Negative stains
- Endothelial cysts
- Pseudocysts
- Epithelial cysts
Sample pathology report
- Left adrenal gland, adrenalectomy:
- Endothelial cyst, 3.3 cm (see comment)
- Comment: CD34 and D2-40 are positive. AE1 / AE3 and CK5/6 are negative.
Differential diagnosis
- Pheochromocytoma with hemorrhage and cystic change:
- Usually has symptoms of catecholamine excess
- Solid areas should be present
- Positive: synaptophysin, chromogranin
- Adenomatoid tumor with cystic change:
- Myelolipoma with hemorrhage and cystic change:
- Adipose and myeloid elements are part of the lesion
- Lacks epithelial lined microcysts and tubules
- Negative: AE1 / AE3, CK7, CK5/6, calretinin
- Metastatic carcinoma with cystic change:
- Adrenal cortical adenoma with cystic change:
- Angiosarcoma with hemorrhage and cystic change (Am J Clin Pathol 2022;157:531):
- Lymphangioma:
- Exceptionally rare in the adrenal gland
- Most are incorrectly classified and are actually adenomatoid tumors (Lack: Tumors of the Adrenal Glands and Extraadrenal Paraganglia, 2007)
- Positive: CD31, CD34, D2-40
- Negative: AE1 / AE3, CK7, CK5/6, calretinin
- Hemangioma:
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
D. Pseudocyst. No distinct lining is present, consistent with a pseudocyst. Careful evaluation of the lining is required because a flat, bland endothelial lining can be difficult to see. Answer A is incorrect because an endothelial lining will be present in an endothelial cyst. Epithelial and parasitic cysts are exceedingly rare. Answer B is incorrect because an epithelial lining will be present in an epithelial cyst. Answer C is incorrect because parasitic cysts usually have a thickened, striated cyst wall and calcified debris in the cyst contents.
Comment Here
Reference: Adrenal cysts
Comment Here
Reference: Adrenal cysts
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
A. Echinococcus. Parasitic cysts in adrenalectomy specimens are exceedingly rare. The most common cause of an adrenal parasitic cyst is Echinococcus. A striated thick cyst wall with cyst contents containing calcified scolices and debris are the characteristic histologic findings. Answer B, C, D and E are incorrect because these are not the most common causes of adrenal parasitic cysts.
Comment Here
Reference: Adrenal cysts
Comment Here
Reference: Adrenal cysts