Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Salahi N, Adeyi O. Caroli disease. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/Livercarolisdisease.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare congenital disorder characterized by multifocal, communicating, cystic dilatation of the large intrahepatic bile ducts (J Hepatol 1986;2:141, Q J Med 1972;41:477)
- Can present as Caroli syndrome when combined with features of congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF)
Essential features
- Multifocal and segmental dilatation of large intrahepatic bile ducts
- Association with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
- Increased risk of cholangiocarcinoma
- Symptomatic presentation can include biliary colic, recurrent cholangitis and jaundice
Terminology
- Discouraged: congenital communicating cavernous ectasia (StatPearls: Caroli Disease [Accessed 26 December 2024])
- Discouraged: congenital saccular dilatation of the intrahepatic bile ducts (HPB (Oxford) 2015;17:278)
Epidemiology
- Caroli disease: prevalence unknown but estimated at ~1 in 1,000,000 individuals (Cureus 2020;12:e11029)
- Caroli syndrome: more common, with a prevalence of ~1 in 100,000 (Cureus 2020;12:e11029)
- Symptoms of Caroli disease usually occur in early adulthood, mostly presenting before age 30
- No significant gender or geographic predilection
Sites
- Large intrahepatic bile ducts
Pathophysiology
- Arrest or derangement in the remodeling of the ductal plate of the larger intrahepatic bile ducts during development (Mayo Clin Proc 1998;73:80, Clin Endosc 2017;50:400)
- PKHD1 gene, present on chromosome 6p21.1p12, which encodes fibrocystin / polyductin, accounts for most cases of Caroli disease / Caroli syndrome, congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF) and autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD) (Nat Genet 2002;30:259)
Etiology
- Autosomal recessive inheritance
- Mutations in the PKHD1 gene, encoding fibrocystin / polyductin
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Biliary colic, recurrent cholangitis, intrahepatic lithiasis, jaundice and cholestasis with an increased risk for cholangiocarcinoma
- Complications of calculi and infections
- In Caroli syndrome, noncirrhotic portal hypertension and upper gastrointestinal bleeding may occur (Semin Liver Dis 1994;14:215)
Diagnosis
- Imaging: ultrasound or magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) showing cystic dilation of large proximal intrahepatic bile ducts with normal common bile duct (Pediatr Radiol 1999;29:463, Am J Gastroenterol 1998;93:109)
- Presence of portal hypertension suggests Caroli syndrome
Laboratory
- Liver enzyme or function test abnormalities: elevated serum alkaline phosphatase (ALP), gamma glutamyl transpeptidase (GGT) and bilirubin
Radiology description
- Ultrasound / CT / MRCP: bile duct ectasia, cystic dilation and central dot sign on imaging (Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 2011;23:578)
Prognostic factors
- Prognosis depends on extent of bile duct dilation and liver involvement
- Higher morbidity / mortality with diffuse lobar involvement, recurrent cholangitis and biliary cirrhosis (StatPearls: Caroli Disease [Accessed 26 December 2024])
- Increase risk of cholangiocarcinoma
Case reports
- 10 year old girl with subcutaneous hemorrhage as the sole clinical manifestation of Caroli disease (Medicine (Baltimore) 2023;102:e36573)
- 13 year old boy with suppurative cholangitis and sepsis caused by Caroli disease (Front Pediatr 2022;10:903285)
- 60 year old woman with Caroli disease (Middle East J Dig Dis 2023;15:289)
Treatment
- General measures: supportive care, antibiotics and biliary drainage for cholangitis (StatPearls: Caroli Disease [Accessed 26 December 2024])
- Surgical: partial hepatectomy in localized disease; liver transplant for recurrent biliary infections and portal hypertension complications (StatPearls: Caroli Disease [Accessed 26 December 2024])
Gross description
- Diffusely nodular liver with intrahepatic cystic dilations are either round or lanceolate, measuring between 1.0 and 4.5 cm in diameter (Burt: MacSween's Pathology of the Liver, 6th Edition, 2012)
- Sometimes lobar or segmental (Burt: MacSween's Pathology of the Liver, 6th Edition, 2012)
- Cystic ducts with fibrous cords (Mayo Clin Proc 1998;73:80)
- Scattered dilated bile ducts filled with bile sludge (StatPearls: Caroli Disease [Accessed 26 December 2024])
- Bile tinged liver surface (StatPearls: Caroli Disease [Accessed 26 December 2024])
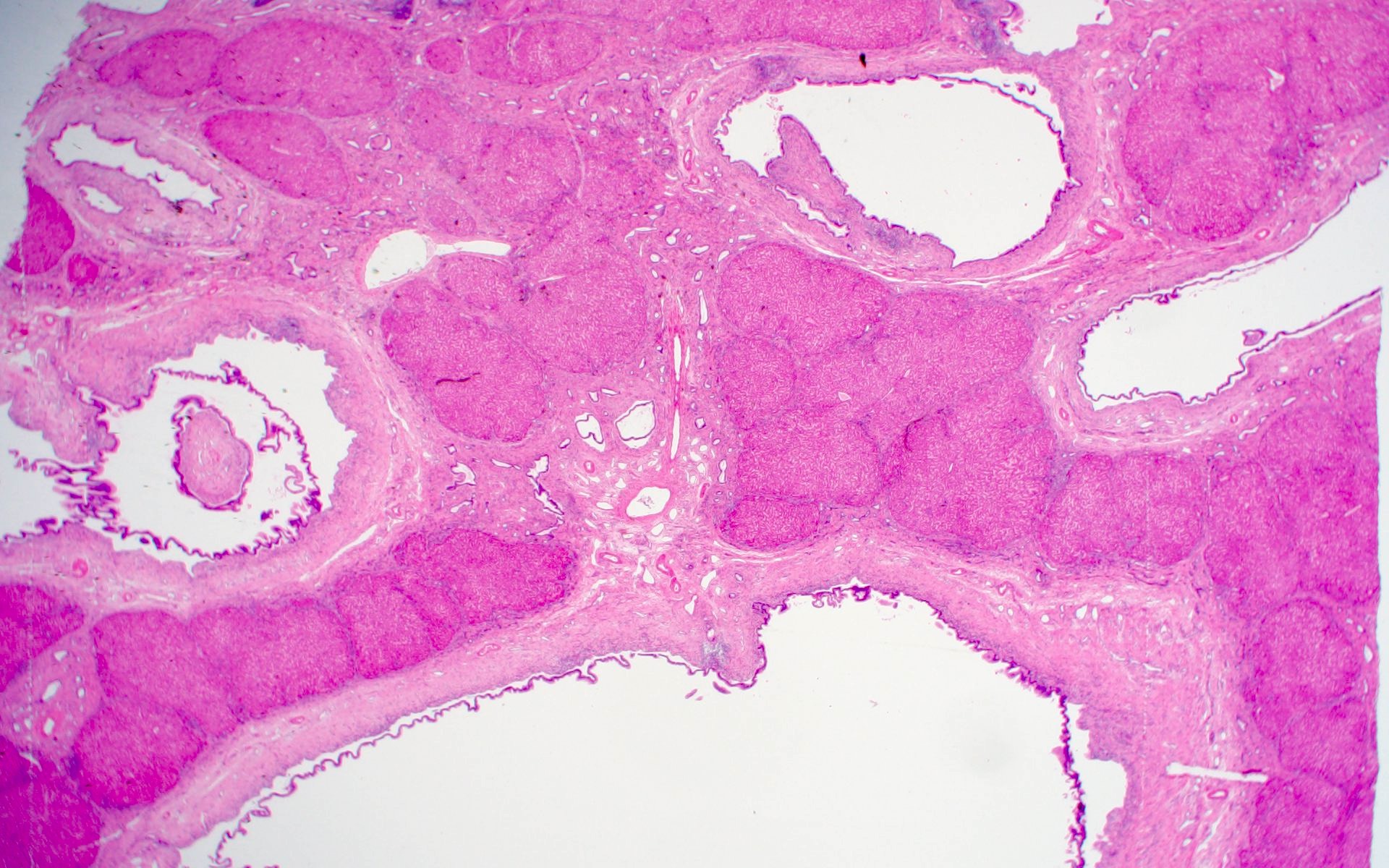
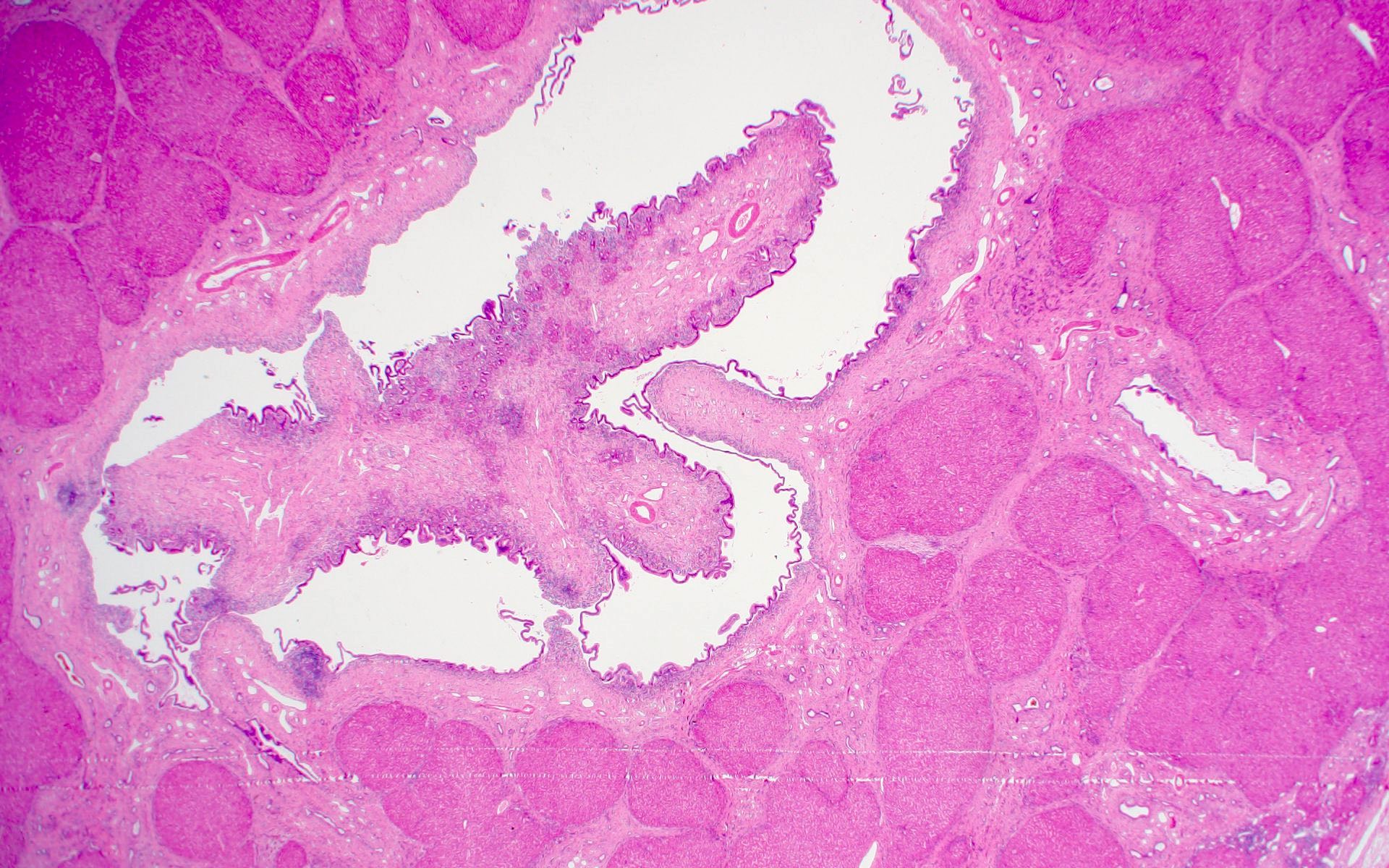
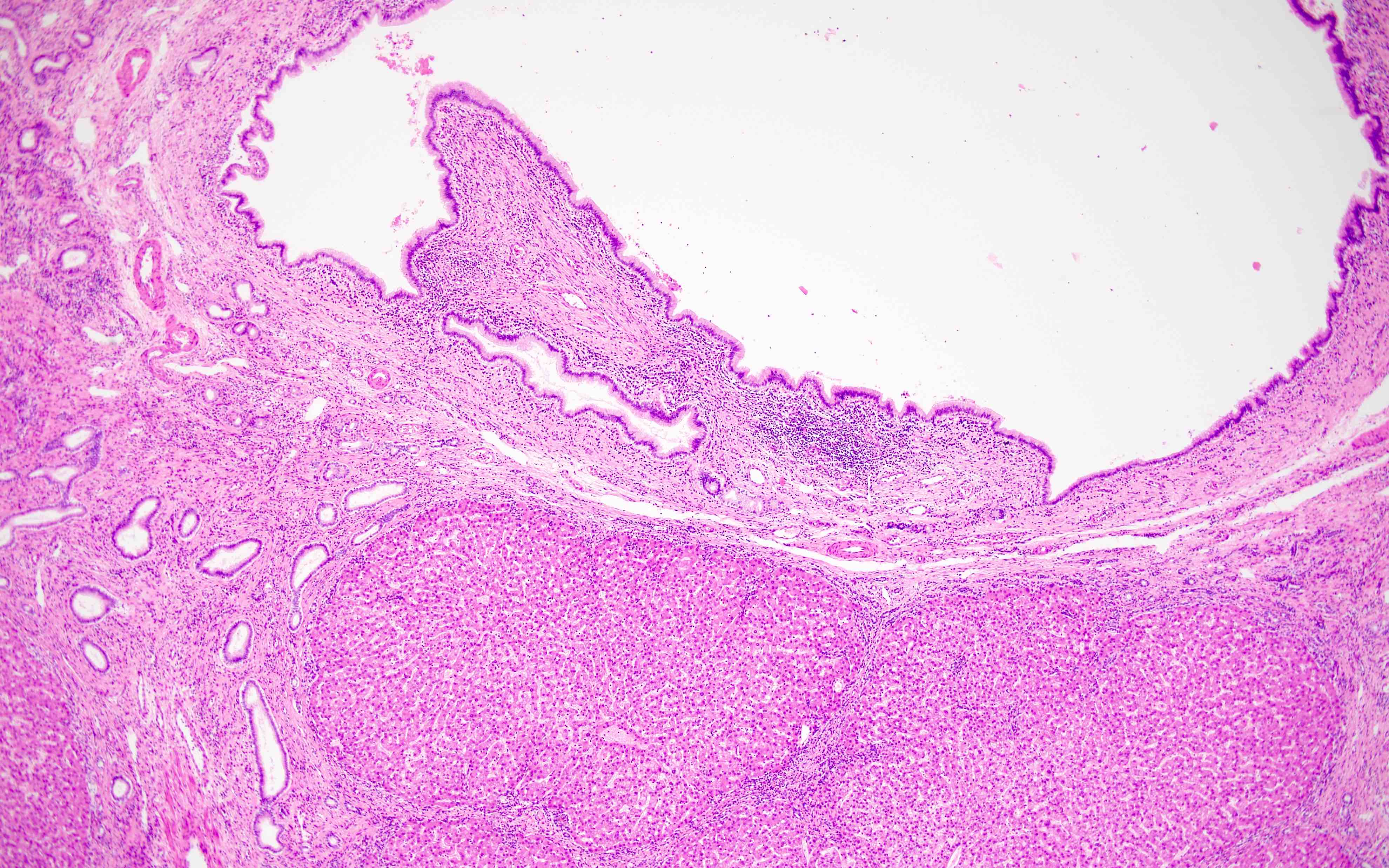
Microscopic (histologic) description
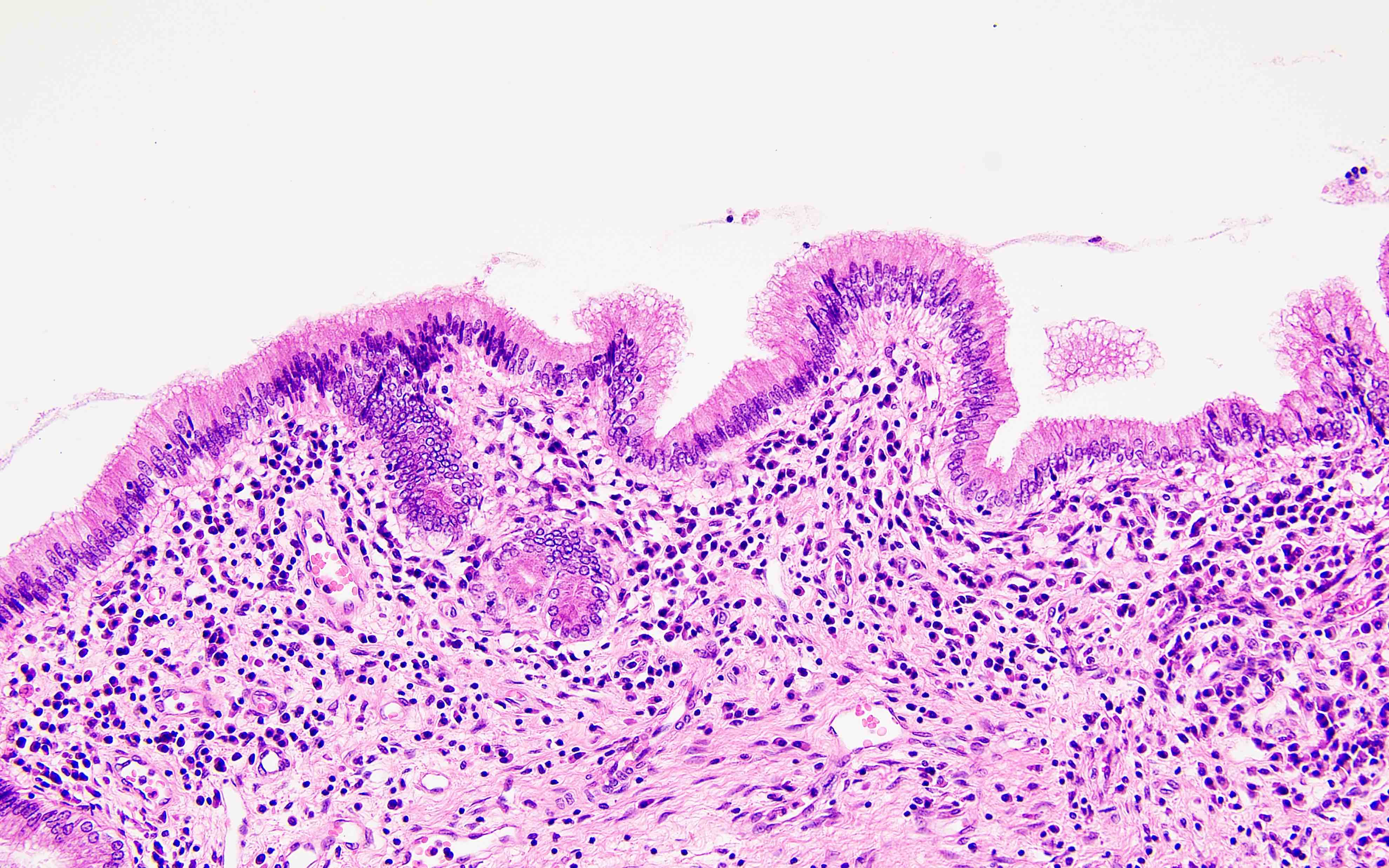
- Large intrahepatic bile ducts dilated and surrounded by acute and chronic inflammation and sometimes superimposed with acute inflammation and varying degrees of fibrosis (Laeknabladid 2007;93:603)
- Ruptured ducts can release bile into parenchyma, causing multinucleated giant cell reaction (Am J Gastroenterol 1997;92:1062)
- Ductal plate malformation manifesting as multiple von Meyenburg complexes are common (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:401)
- Biliary epithelium lining dilated ducts (Int J Hepatol 2012;2012:107945)
- Epithelial lining appearing normal (cuboidal to tall columnar) but sometimes partly or completely ulcerated or focally hyperplastic (Int J Hepatol 2012;2012:107945)
- Dysplasia is rarely observed (Int Surg 1993;78:46, Gut 1990;31:584)
- Associated congenital hepatic fibrosis in Caroli syndrome with bland portal fibrosis and hyperproliferation of interlobular bile ducts of varying shapes and sizes (Int J Hepatol 2012;2012:107945)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Special or immunohistochemical stains are usually not indicated but when stained, the lining epithelium is almost always positive for CK7
Negative stains
- CK20 (usually)
Videos
Caroli disease
Sample pathology report
- Liver, biopsy (or resection):
- Ectatic and dilated large bile ducts; suggestive of Caroli disease (see comment)
- Comment: The excised cyst reveals dilated large bile ducts with mixed surrounding stromal inflammation and papillary projection of the stroma inside the cystic ducts. The background liver lobules show variable amounts of fibrosis and von Meyenburg complexes. Overall, the constellation of histological features are compatible with Caroli disease.
Differential diagnosis
- Polycystic disease of the liver (PCDL) (HPB (Oxford) 2007;9:281):
- Unlike polycystic disease of the liver (PCDL), Caroli disease (CD) is an autosomal recessive, congenital, communicating, cystic dilatation of the large intrahepatic bile duct
- Histologic features of PCDL and CD share similarities, including evidence of ductal plate malformation, which presents as multiple von Meyenburg complexes; these complexes are typically less noticeable in PCDL but are more prominent in congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF) and CD
- Choledochal cyst (CC) (HPB (Oxford) 2007;9:281):
- Traditionally considered as a cystic dilation of the extrahepatic bile ducts
- Congenital hepatic fibrosis (CHF) (HPB (Oxford) 2007;9:281):
- Affects mainly small intrahepatic bile ducts
- Abnormal bile duct proliferation in malformed portal areas
- Portal and periportal fibrosis
- Dilated, tortuous ducts with irregular contours, with or without inspissated bile
- Occurs alone or with autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease (ARPKD)
- Presents early in childhood as portal hypertension
- More likely to occur as Caroli syndrome
Additional references
Board review style question #1
A 20 year old woman presents with jaundice and high alkaline phosphatase. Imaging shows polycystic kidney and polycystic liver diseases with dot signs. The wedge biopsy of the case shows the representative image above. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- Caroli disease
- Choledochal cyst
- Intraepithelial biliary neoplasm
- Mucinous cystic neoplasm
Board review style answer #1
A. Caroli disease. The image demonstrates cystic dilation of intrahepatic bile ducts with background hepatic fibrosis, features usually seen in Caroli disease. Answer B is incorrect as choledochal cyst usually refers to cystic dilation of extrahepatic bile ducts. Answer C is incorrect because these are usually solitary central lesions and lining epithelium is normal biliary epithelium with no dysplasia or atypia. Answer D is incorrect as epithelium of mucinous cystic neoplasm (MCN) has mucin containing cells with ovary type stromal components.
Comment Here
Reference: Caroli disease
Comment Here
Reference: Caroli disease
Board review style question #2
Which of the following genes is mostly associated with Caroli disease?
- EFEMP1
- HLA::DRB1
- MMP7
- PKHD1
Board review style answer #2
D. PKHD1. Caroli disease is associated with mutations in the PKHD1 gene, which is responsible for producing a protein that is essential for kidney and bile duct development during fetal growth. These mutations lead to the characteristic cystic dilation of the intrahepatic bile ducts seen in the disease. Common symptoms include repeated episodes of fever, abdominal discomfort, jaundice and persistent cholangitis. Answer B is incorrect because the HLA::DRB1 gene is mostly linked to primary biliary cholangitis (PBC). Answers A and C are incorrect because EFEMP1 and MMP7 are associated with biliary atresia.
Comment Here
Reference: Caroli disease
Comment Here
Reference: Caroli disease