11 November 2011 - Case #223
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
This case was contributed by Dr. C. Shrinivasan, Sterling Hospital, India.

Case #223
Clinical history:
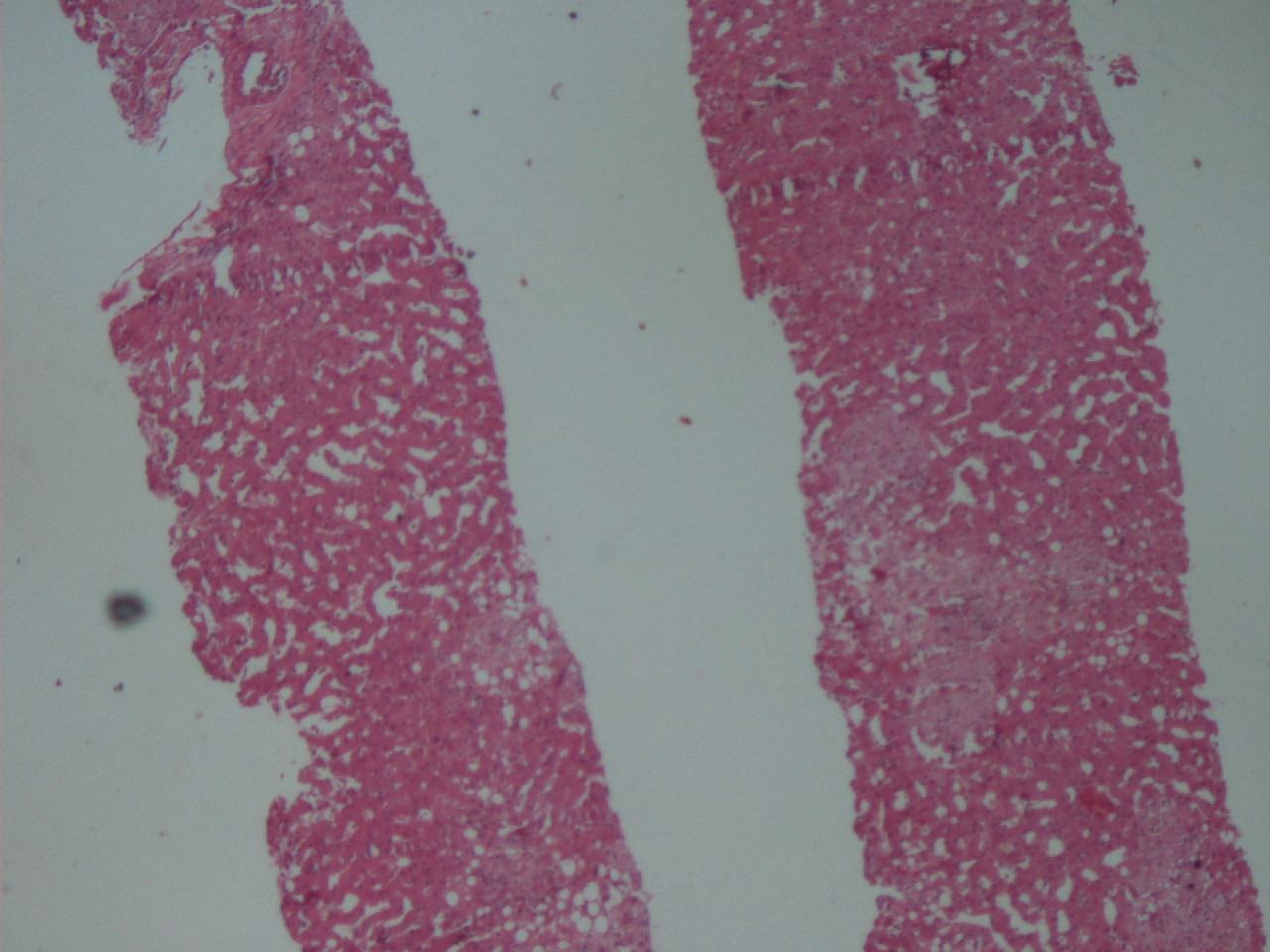
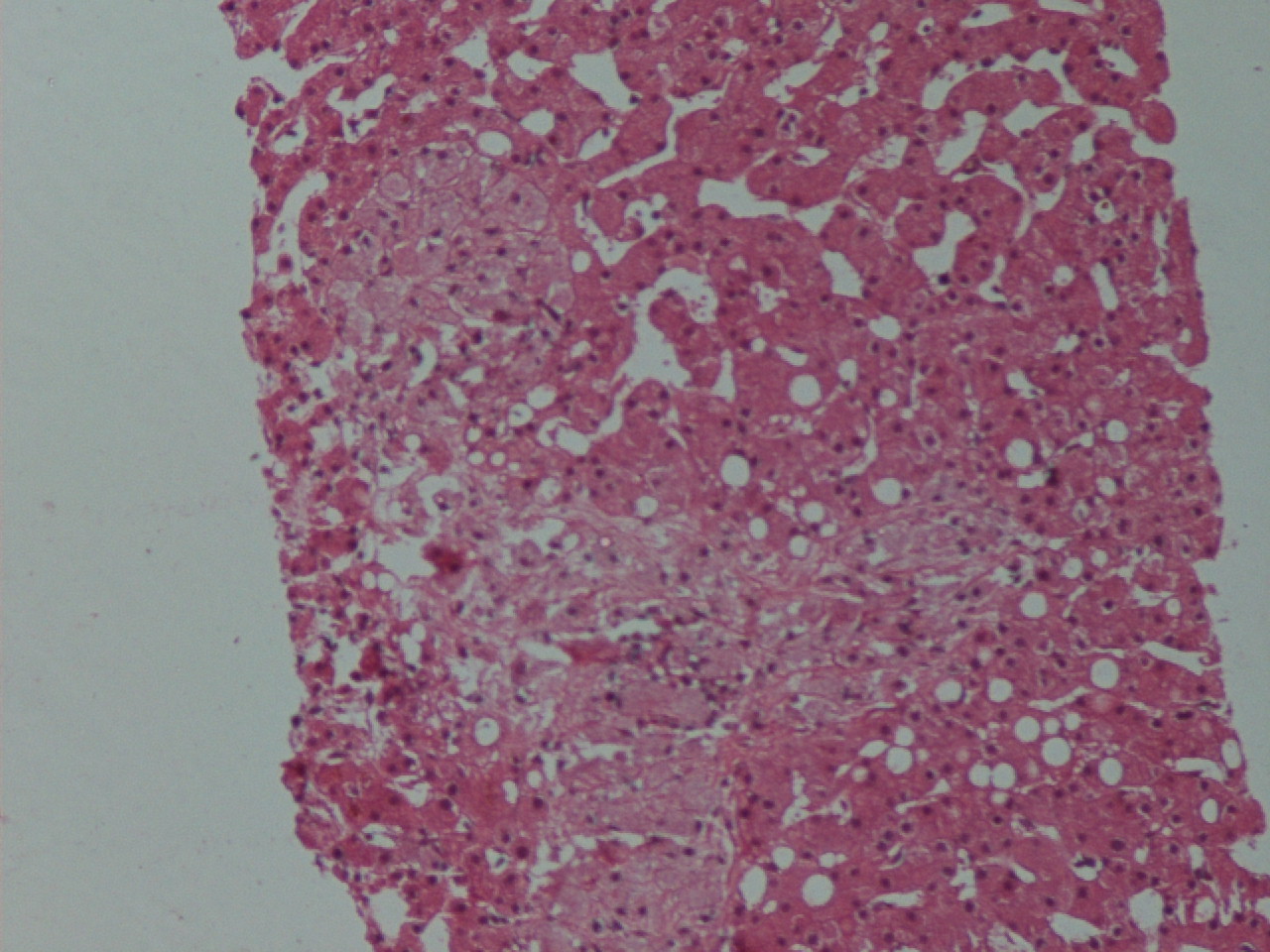
A 55 year old HIV+ man presented with diarrhea and weight loss for one month. He had mildly elevated liver enzymes. Ultrasound showed a granular and enlarged liver, which was biopsied.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
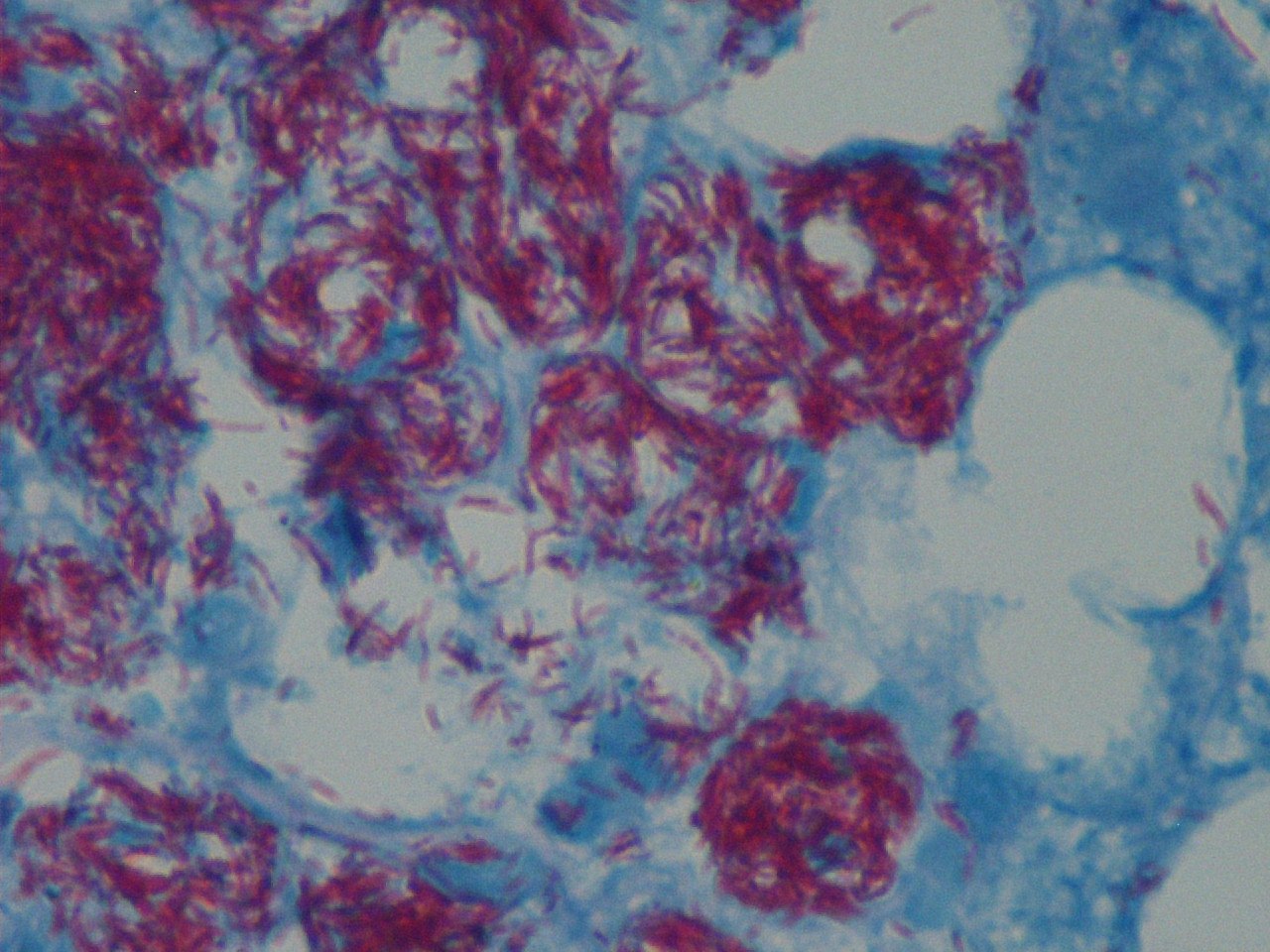
Diagnosis: Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
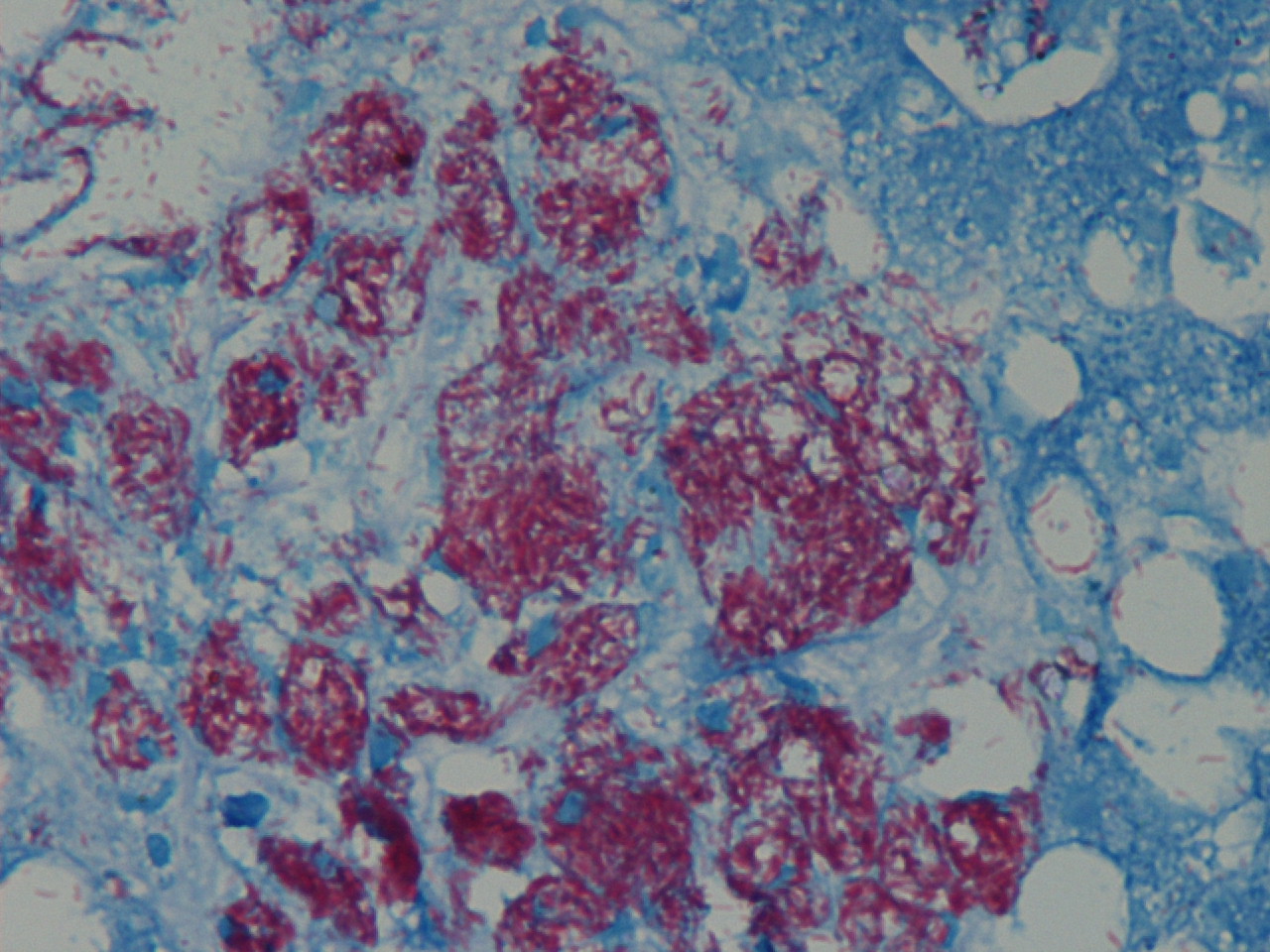
Immunostains:
Discussion:
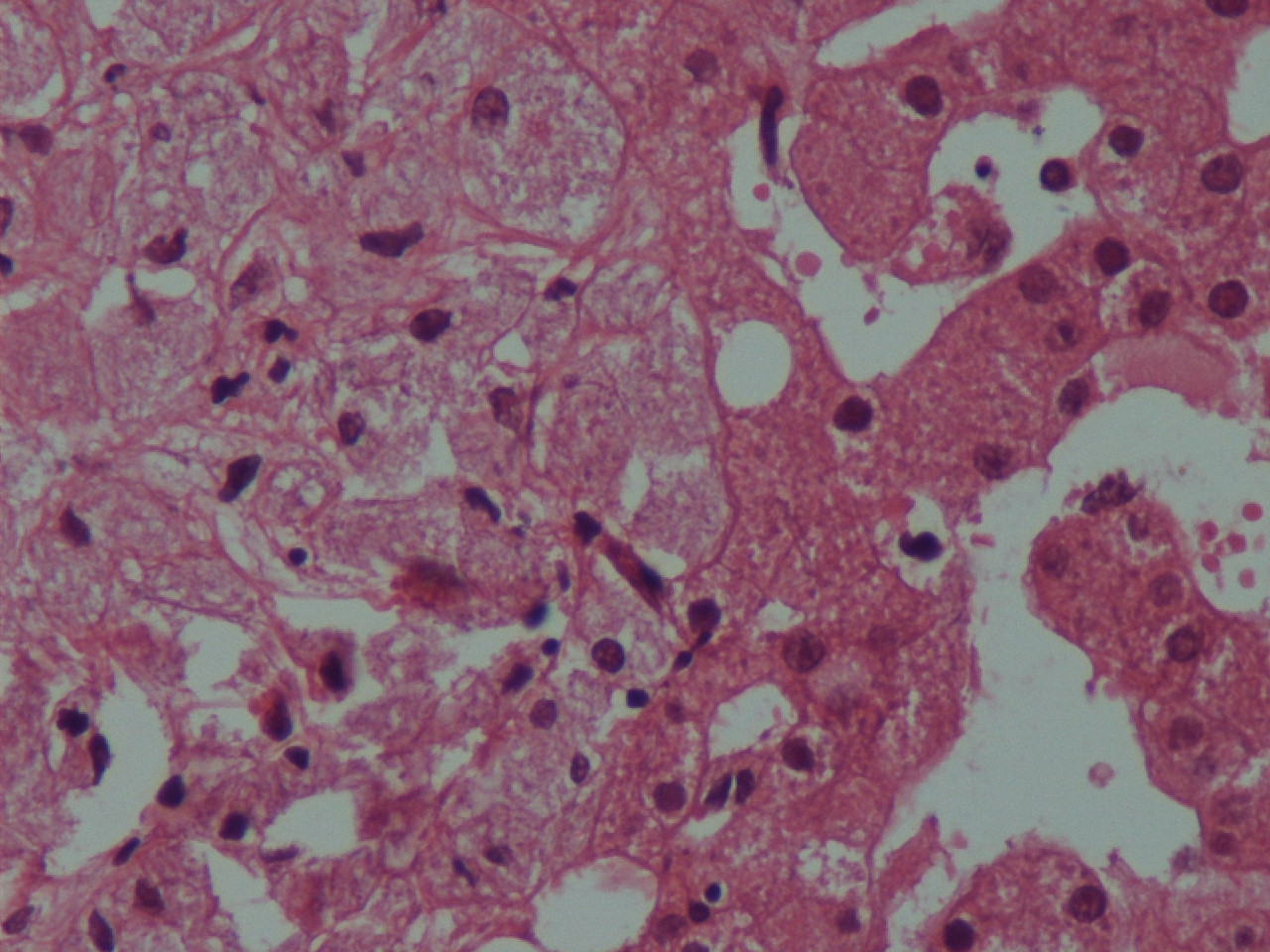
The biopsies showed numerous small aggregates of foamy macrophages distended by dense clusters of rod like structures, highlighted by the Ziehl-Neelsen stain.
Mycobacterium avium complex causes disseminated disease in HIV patients (J Infect Dis 1999;179 Suppl 3:S461). Mycobacterium organisms are commonly found worldwide in soil, water, animals, birds and food. Ingested organisms penetrate the GI mucosa and are phagocytosed by lamina propria macrophages, which are unable to kill them. The bacteria then enter submucosal lymphatics, are transported to abdominal lymph nodes and enter the bloodstream. In immunocompromised patients, they are disseminated widely, including to liver, spleen and bone marrow. Acid fast stains are recommended for liver biopsies in HIV+ patients (Suriawinata: Liver Pathology, 1st Edition, 2011). Fungal stains help rule out coinfections.
Treatment consists of multidrug regiments, such as clarithromycin 500 mg BID plus ethambutol 15 mg/kg once daily. Patients should also be started on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
In patients with subclinical or incompletely treated MAC who have recently started ART, an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) may occur with localized lymphadenitis or paradoxically worsening symptoms (Int J STD AIDS 2009;20:221).
All cases are archived on our website. To view them sorted by case number, diagnosis or category, visit our main Case of the Month page. To subscribe or unsubscribe to Case of the Month or our other email lists, click here.
This case was contributed by Dr. C. Shrinivasan, Sterling Hospital, India.

Website news:
(1) We are looking for more Cases. We are also looking for authors with expertise in AP computer systems and LIS systems, to add content to these pages. Click here for more information.
(2) Our Feature Page for November 2011 highlights Consumable Lab Products / Clinical Lab Analyzers, and includes Biogenex, Leica Microsystems, Sakura Finetek USA and Ventana Medical.
(3) Last month, we again had record traffic, with 359,051 visits (85 million "hits"). We continue to update topics daily. We update each chapter as we get topics back from reviewers, so the topics in a chapter are not all updated at the same time.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
(1) We are looking for more Cases. We are also looking for authors with expertise in AP computer systems and LIS systems, to add content to these pages. Click here for more information.
(2) Our Feature Page for November 2011 highlights Consumable Lab Products / Clinical Lab Analyzers, and includes Biogenex, Leica Microsystems, Sakura Finetek USA and Ventana Medical.
(3) Last month, we again had record traffic, with 359,051 visits (85 million "hits"). We continue to update topics daily. We update each chapter as we get topics back from reviewers, so the topics in a chapter are not all updated at the same time.
Visit and follow our Blog to see recent updates to the website.
Case #223
Clinical history:
A 55 year old HIV+ man presented with diarrhea and weight loss for one month. He had mildly elevated liver enzymes. Ultrasound showed a granular and enlarged liver, which was biopsied.
Microscopic images:
What is your diagnosis?
Click here for diagnosis and discussion:
Diagnosis: Mycobacterium avium complex (MAC)
Immunostains:
Discussion:
The biopsies showed numerous small aggregates of foamy macrophages distended by dense clusters of rod like structures, highlighted by the Ziehl-Neelsen stain.
Mycobacterium avium complex causes disseminated disease in HIV patients (J Infect Dis 1999;179 Suppl 3:S461). Mycobacterium organisms are commonly found worldwide in soil, water, animals, birds and food. Ingested organisms penetrate the GI mucosa and are phagocytosed by lamina propria macrophages, which are unable to kill them. The bacteria then enter submucosal lymphatics, are transported to abdominal lymph nodes and enter the bloodstream. In immunocompromised patients, they are disseminated widely, including to liver, spleen and bone marrow. Acid fast stains are recommended for liver biopsies in HIV+ patients (Suriawinata: Liver Pathology, 1st Edition, 2011). Fungal stains help rule out coinfections.
Treatment consists of multidrug regiments, such as clarithromycin 500 mg BID plus ethambutol 15 mg/kg once daily. Patients should also be started on antiretroviral therapy (ART).
In patients with subclinical or incompletely treated MAC who have recently started ART, an immune reconstitution inflammatory syndrome (IRIS) may occur with localized lymphadenitis or paradoxically worsening symptoms (Int J STD AIDS 2009;20:221).