Cite this page: Islam S. Radiation thyroiditis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/thyroidradiationthyroiditis.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Histologic changes vary with dose and type of radioactive isotope
- Low doses to tonsils cause nodular hyperplasia of thyroid, follicular disruption, focal hemorrhagic necrosis, neutrophil infiltration
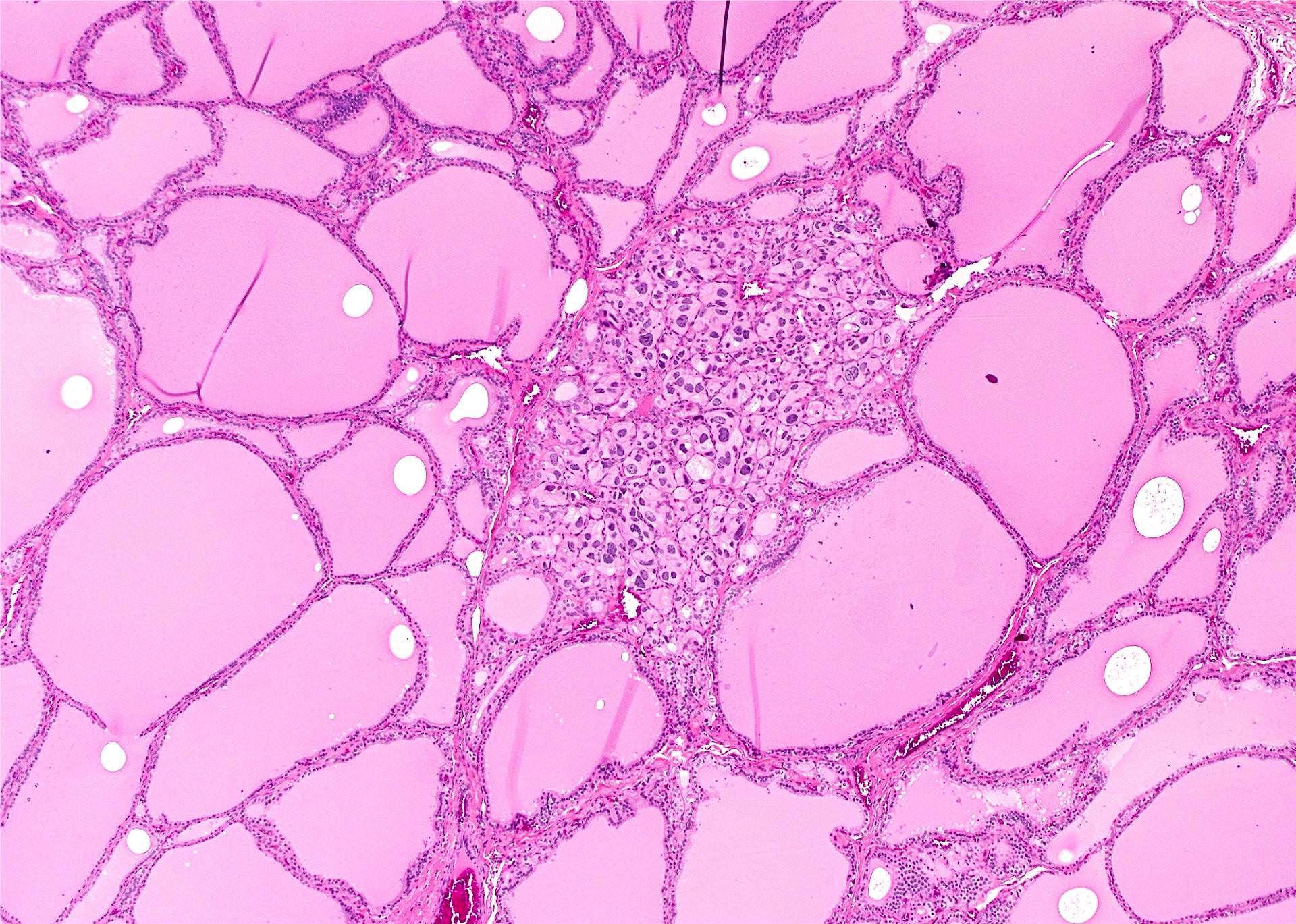
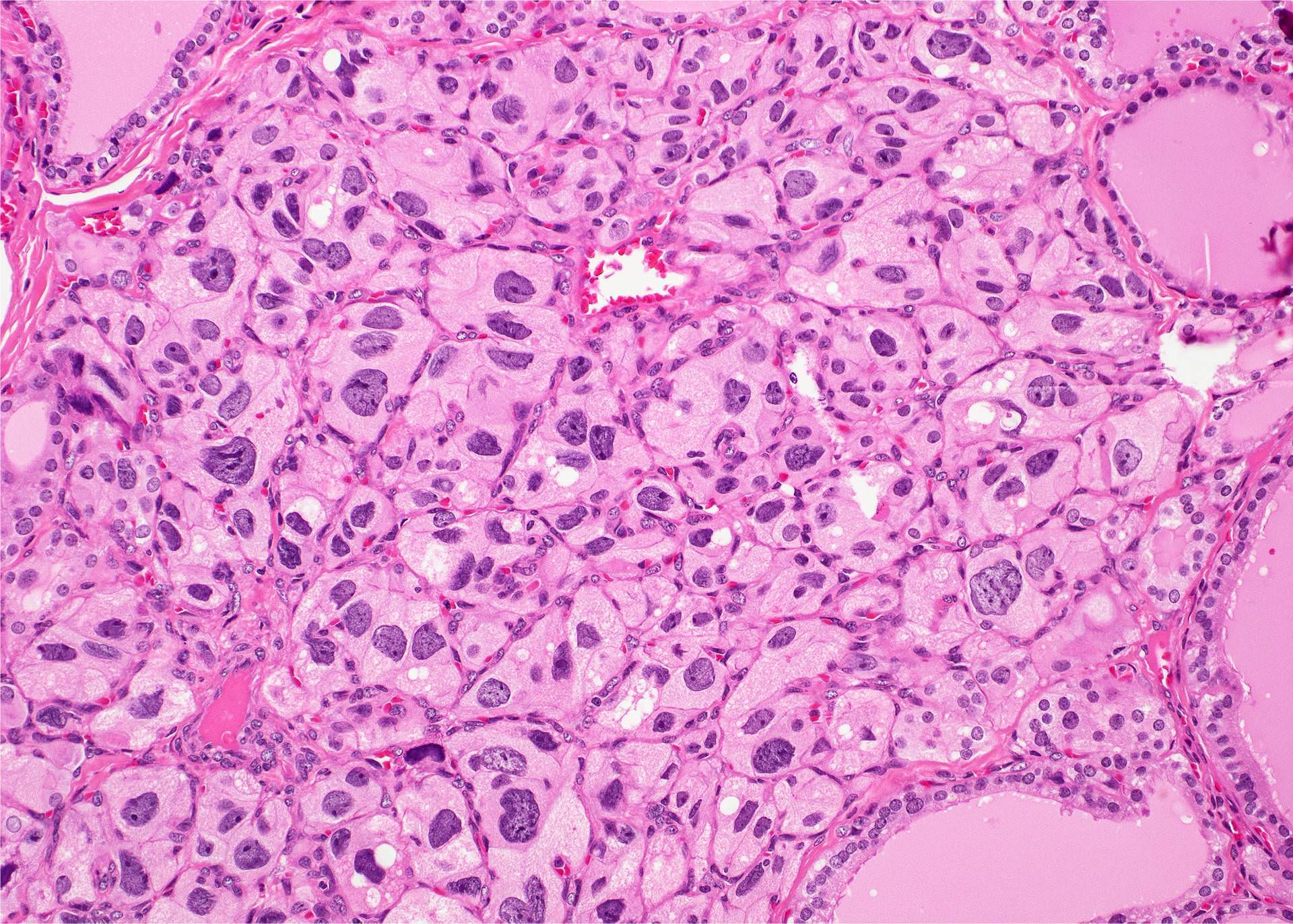
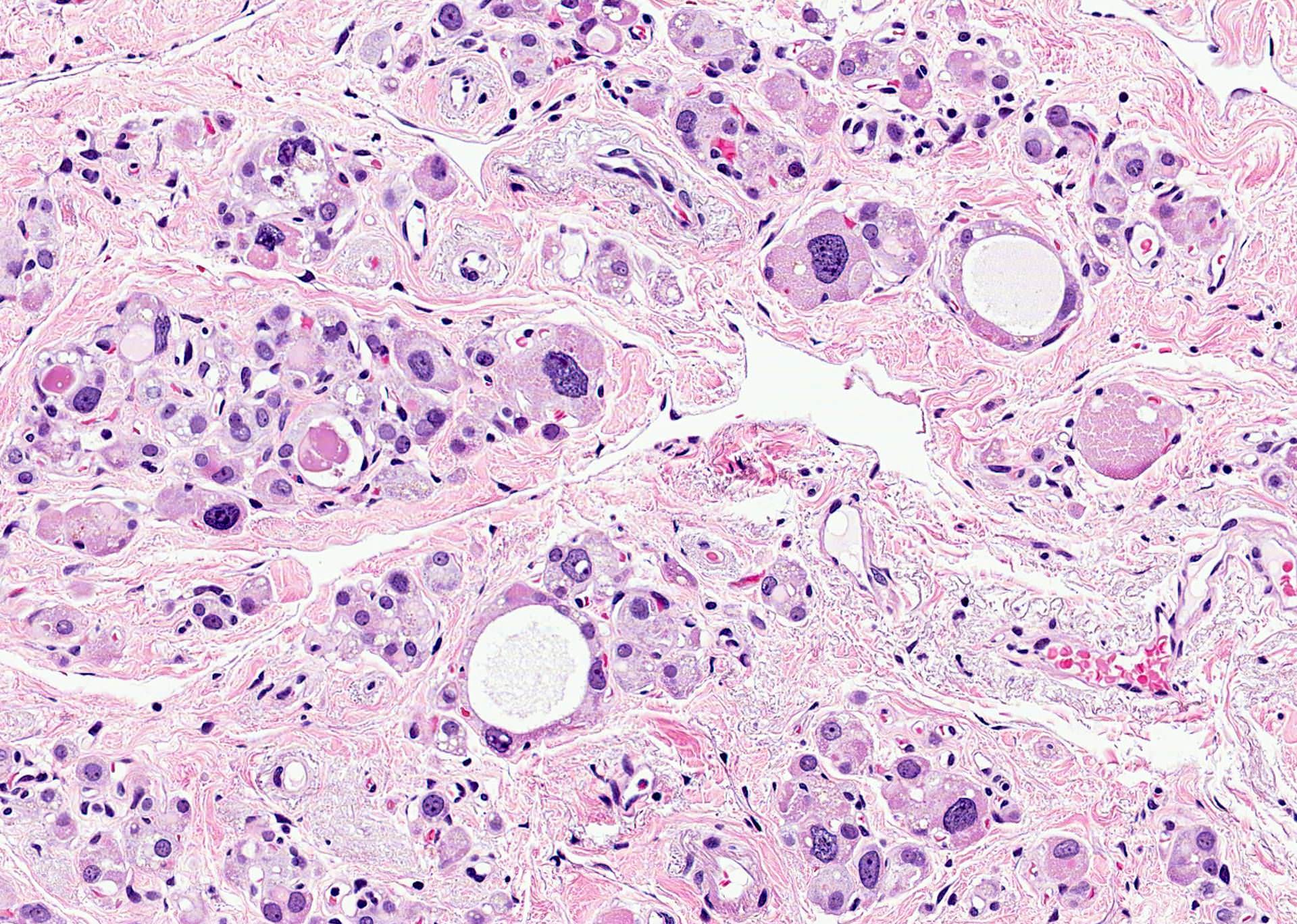
- Radioactive iodine may cause large bizarre cells with hyperchromatic nuclei and prominent nucleoli or nuclear features of papillary carcinoma; cells are in clusters and sheets accompanied by lymphocytes, histiocytes and Hürthle cells (Am J Clin Pathol 1997;107:20)
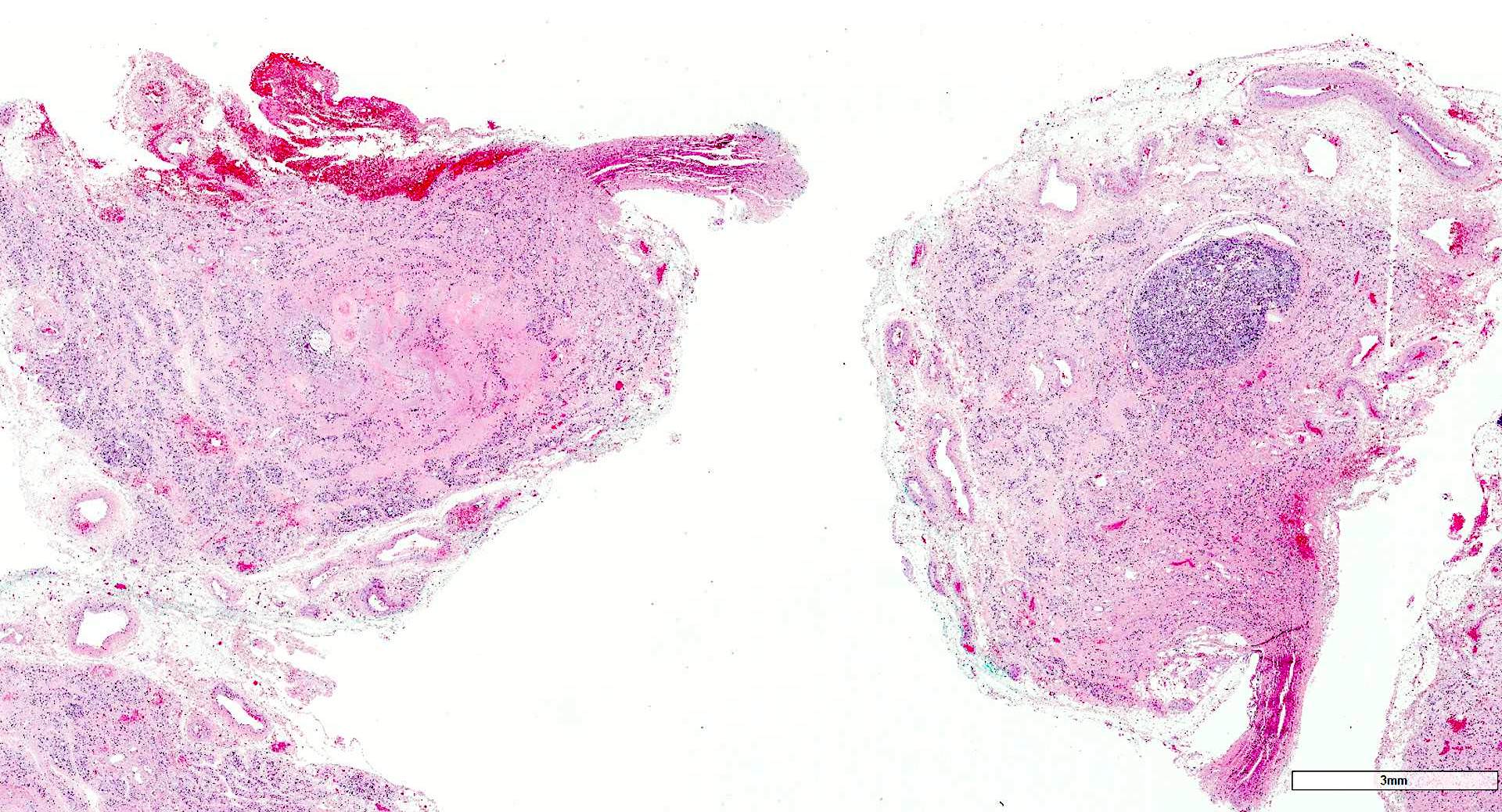
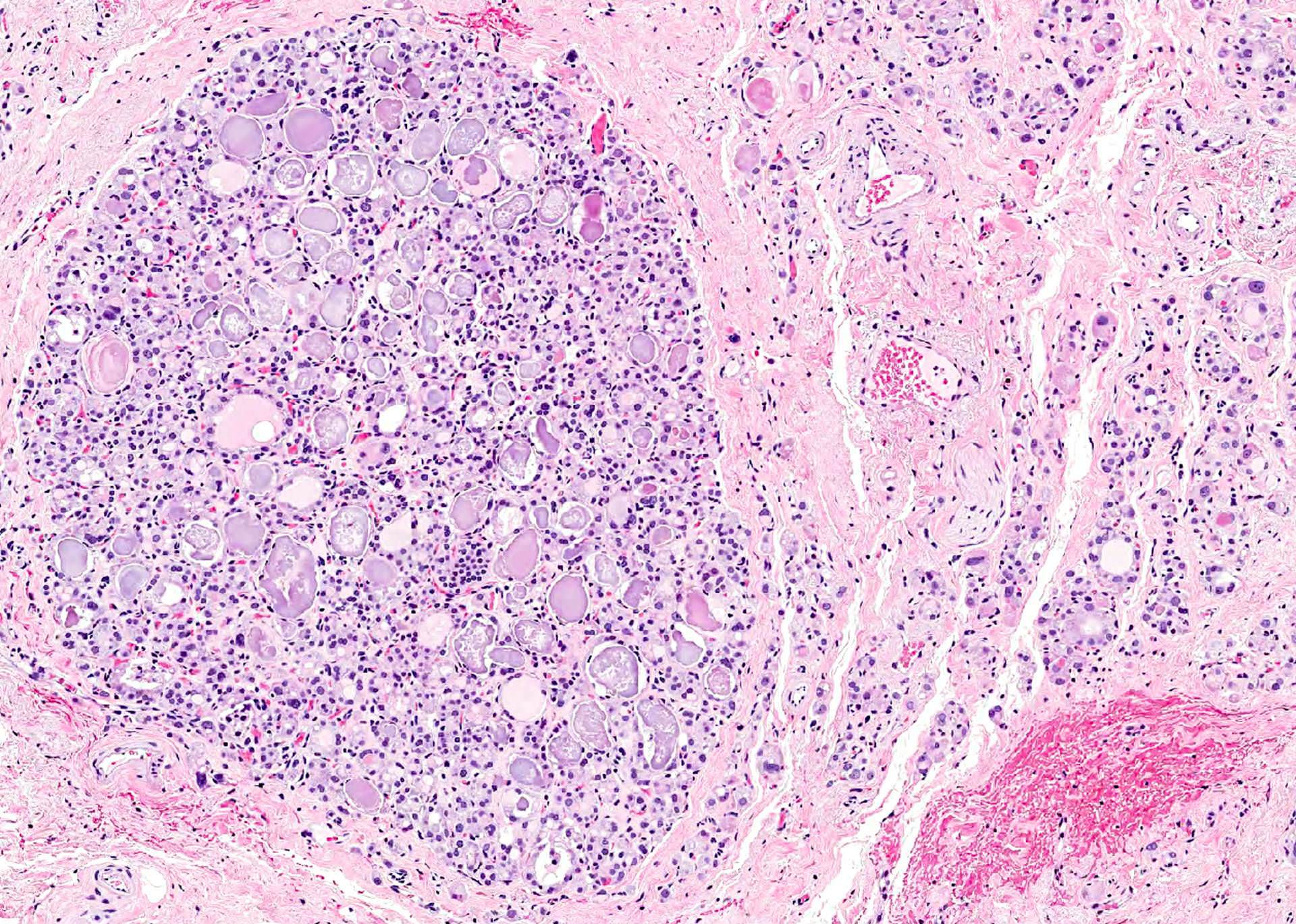
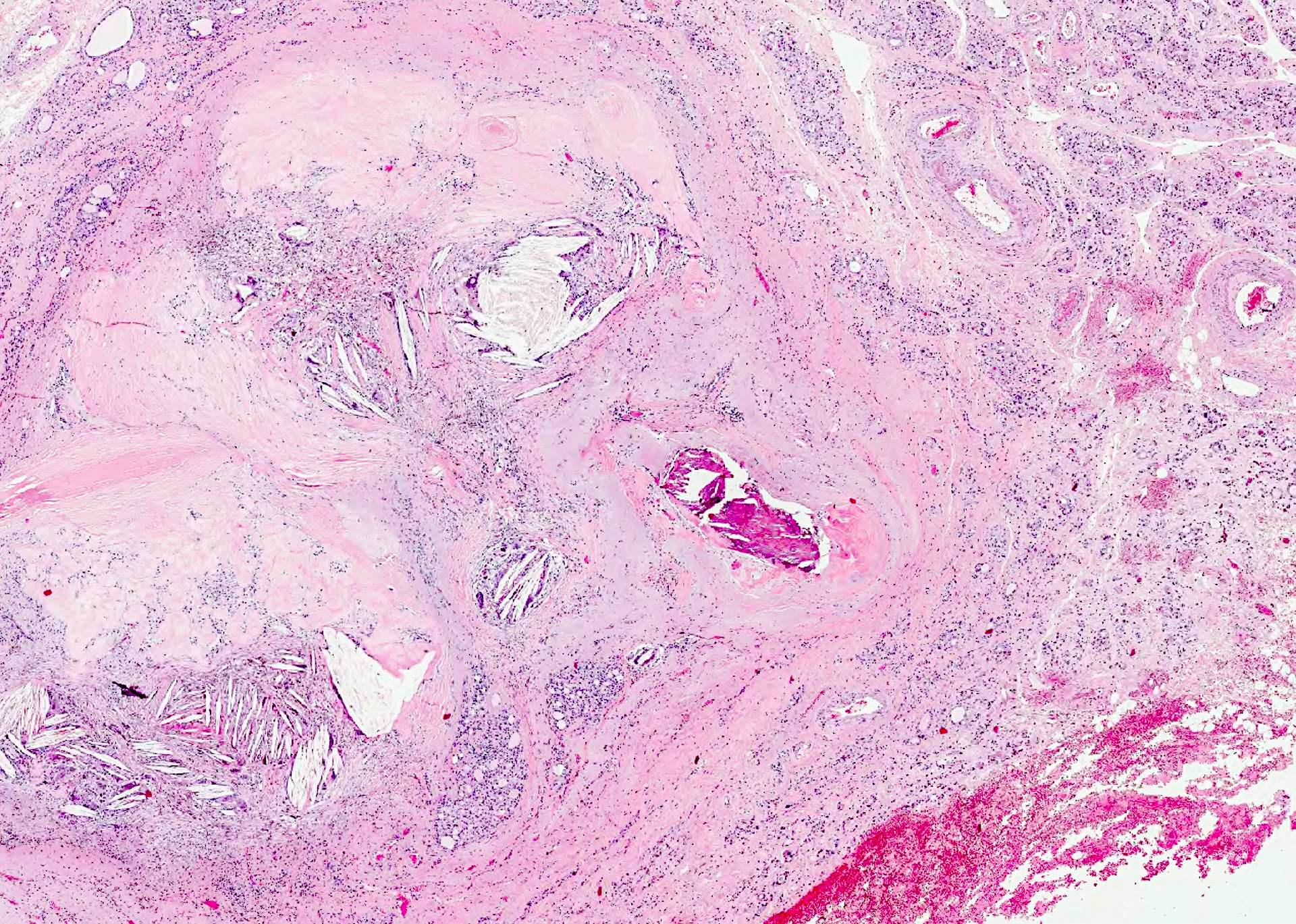
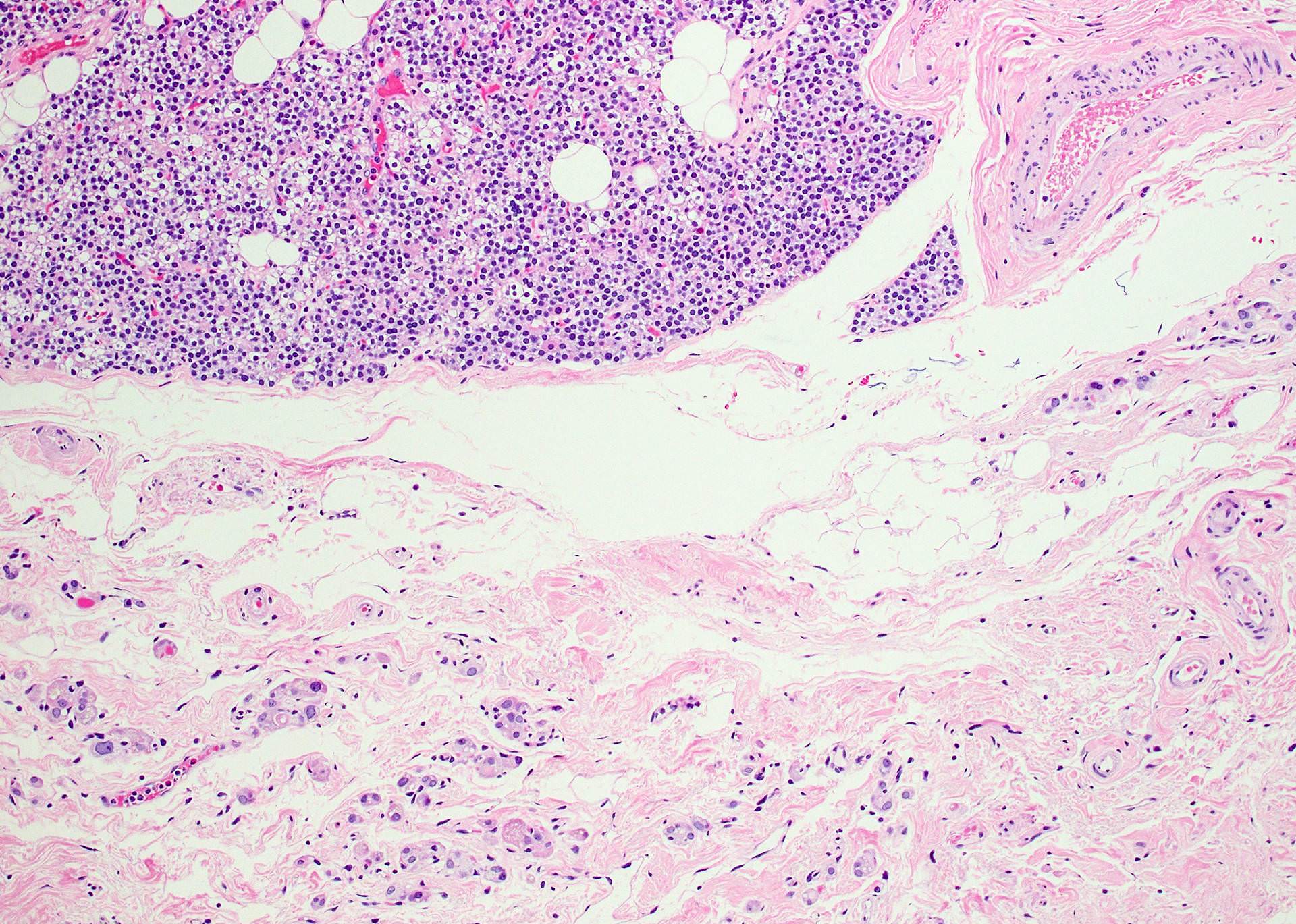
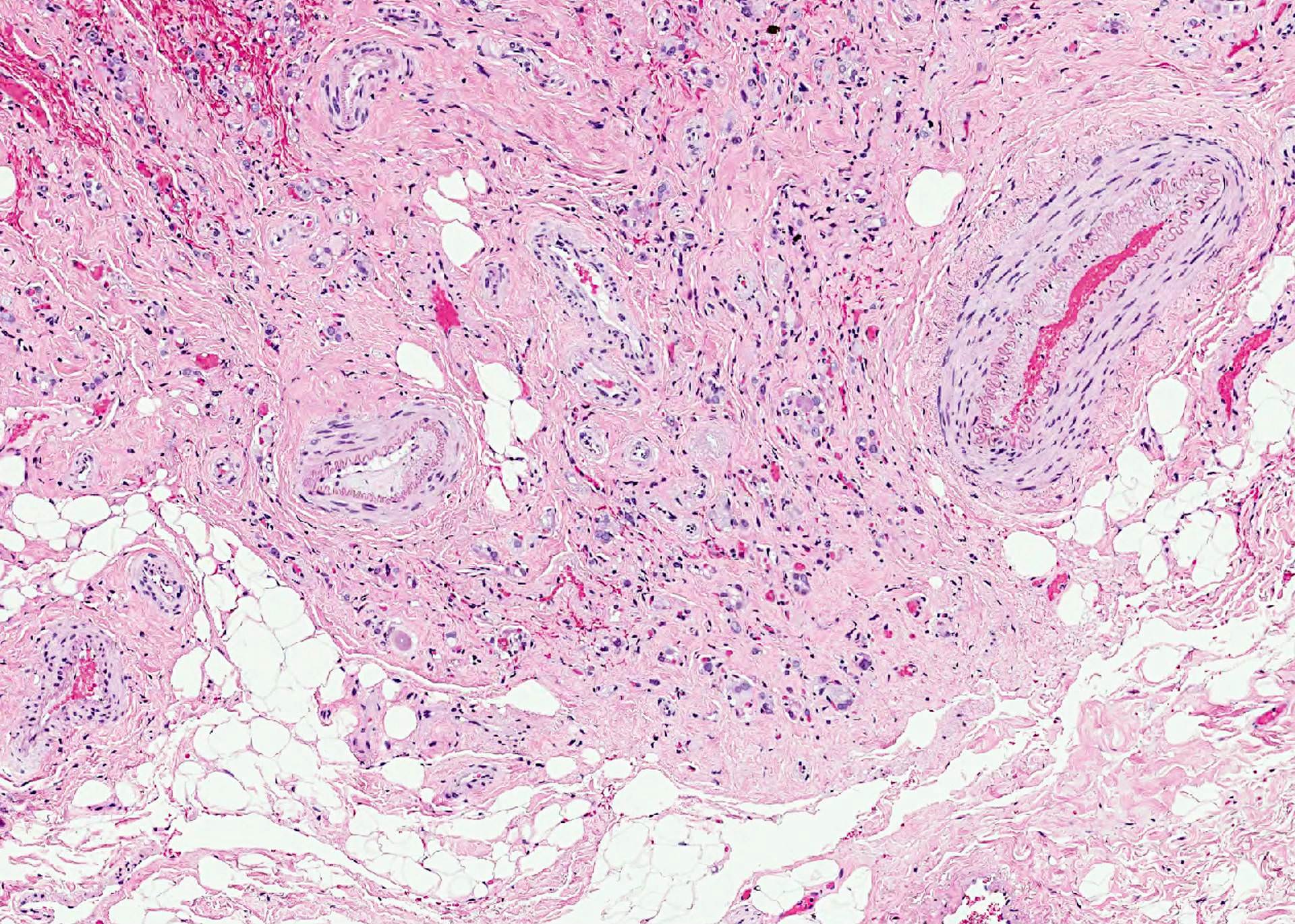
- External radiation (for lymphoma) causes hypercellularity, lymphocyte infiltration, adenomatous nodules, oncocytic metaplasia, fibrosis and atypia; chronic changes include fibrosis, atrophy and vascular change
- Post Chernobyl changes include antithyroperoxidase antibodies, but no thyroid dysfunction (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 2008;93:2729)
- Childhood radiation is associated with high frequency of allelic loss (Mod Pathol 2008;21:1176)
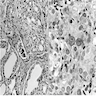
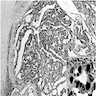
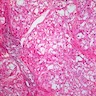
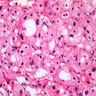
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Andrey Bychkov, M.D., Ph.D. and AFIP
Images hosted on other servers: