Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Assarzadegan N, Gonzalez RS. Fundic gland polyp. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stomachfundicgland.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign cystic hyperplastic proliferation of oxyntic gland
- Traditionally regarded as hamartomatous lesions; however, studies have shown alterations in the APC beta catenin pathway in both sporadic and syndromic cases, supporting a neoplastic nature of these polyps (Mod Path 2002;15:718)
Essential features
- Can be sporadic, associated with familial adenomatous polyposis (FAP) or arise as part of a familial condition confined to the stomach without polyposis coli
Terminology
- Also known as Elster glandular cysts and cystic hamartomatous epithelial polyps
Sites
- Typically restricted to the fundus and body of the stomach
Etiology
- Sporadic cases are usually secondary to use of proton pump inhibitors and are usually solitary but may be multiple (Hum Pathol 2000;31:684)
- Syndromic cases can arise from FAP or gastric adenocarcinoma and proximal polyposis of the stomach (GAPPS) (Gut 2012;61:774)
Clinical features
- Most commonly encountered form of gastric polyps
- Peak incidence in fifth or sixth decade of life in sporadic cases and second and third decade in FAP patients
- Sporadic cases rarely harbor dysplasia (Gasteroenterol Hepatol 2009;7:849)
- Progression to carcinoma is vanishingly rare (Am Surg 2008;74:79)
- FAP associated fundic gland polyps arise at younger ages, are more numerous and are more likely to show low grade dysplasia
- Patients with GAPPS present with fundic gland polyposis and gastric adenocarcinoma at a young age
Case reports
- 42 year old woman with diffuse polyps after taking proton pump inhibitor Korean J Intern Med 2017;32:197
- 51 year old woman with multiple polyps after taking proton pump inhibitor Intern Med 2019;58:1871
Treatment
- Current guidelines do not recommend polypectomy or surveillance endoscopy for sporadic cases
- Findings of multiple fundic gland polyps in a younger patient or fundic gland polyp with dysplasia should prompt colonic investigation for the possibility of familial adenomatous polyposis
- In GAPPS, gastrectomy may be indicated
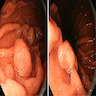
Gross description
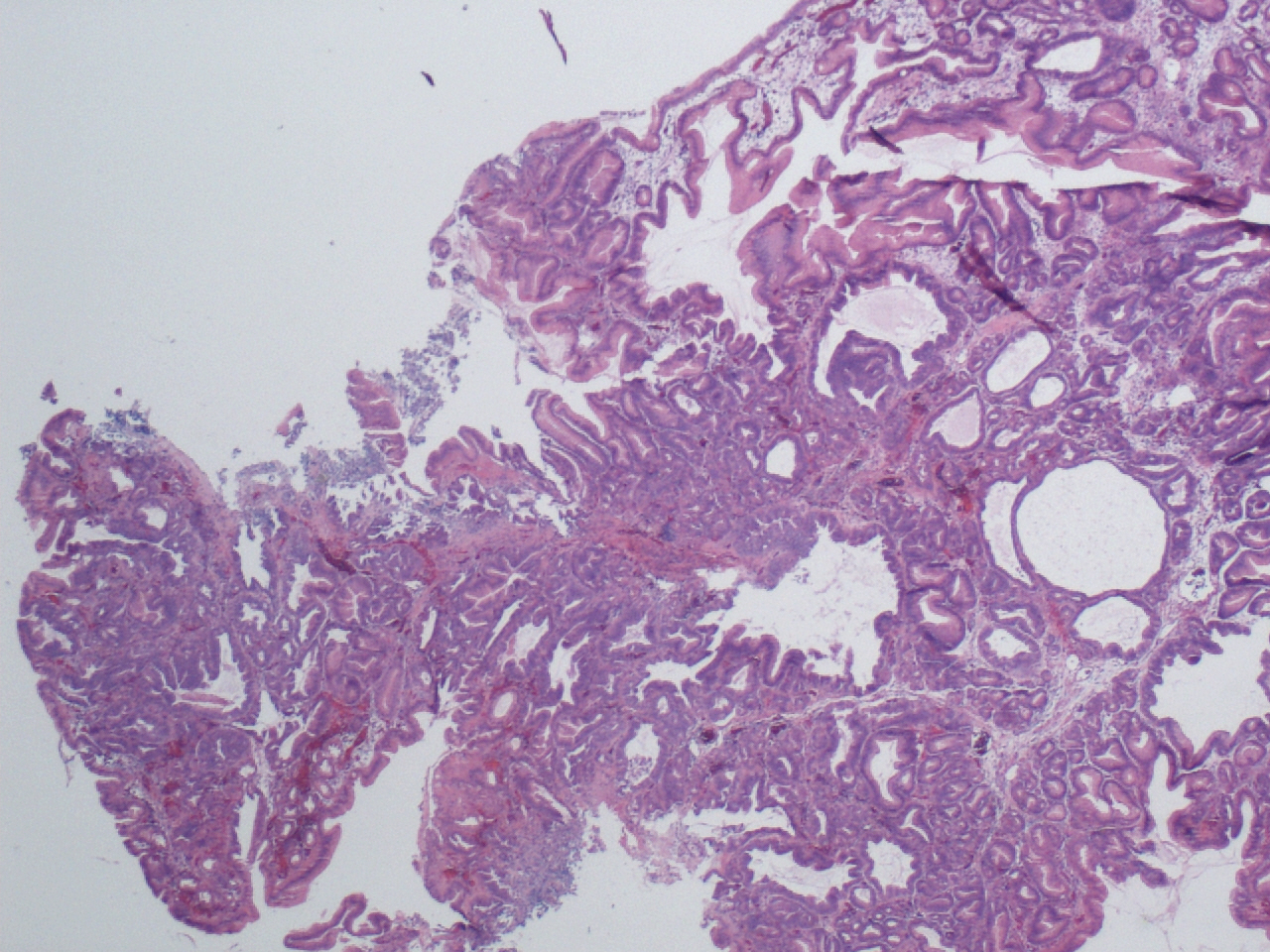
- Typically small and sessile, with a glassy surface, usually less than a centimeter
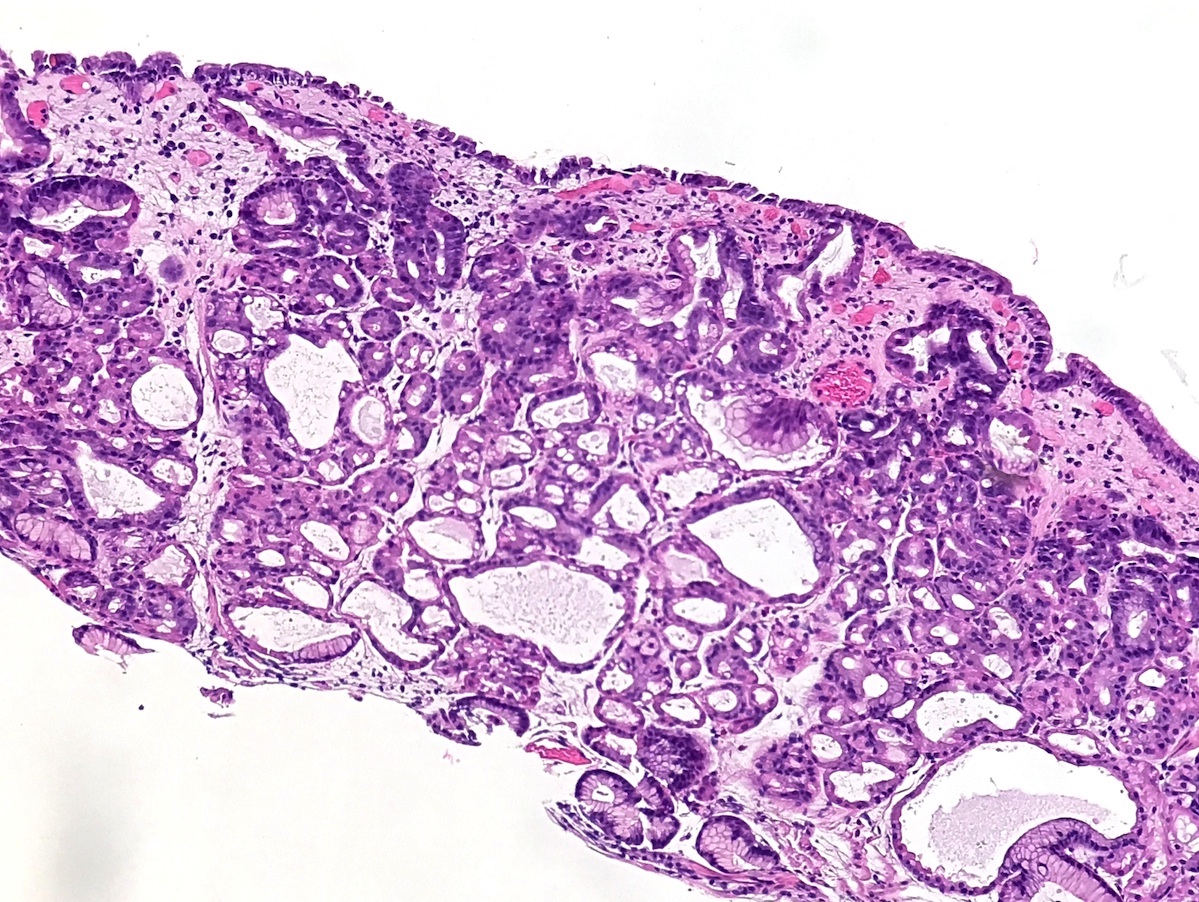
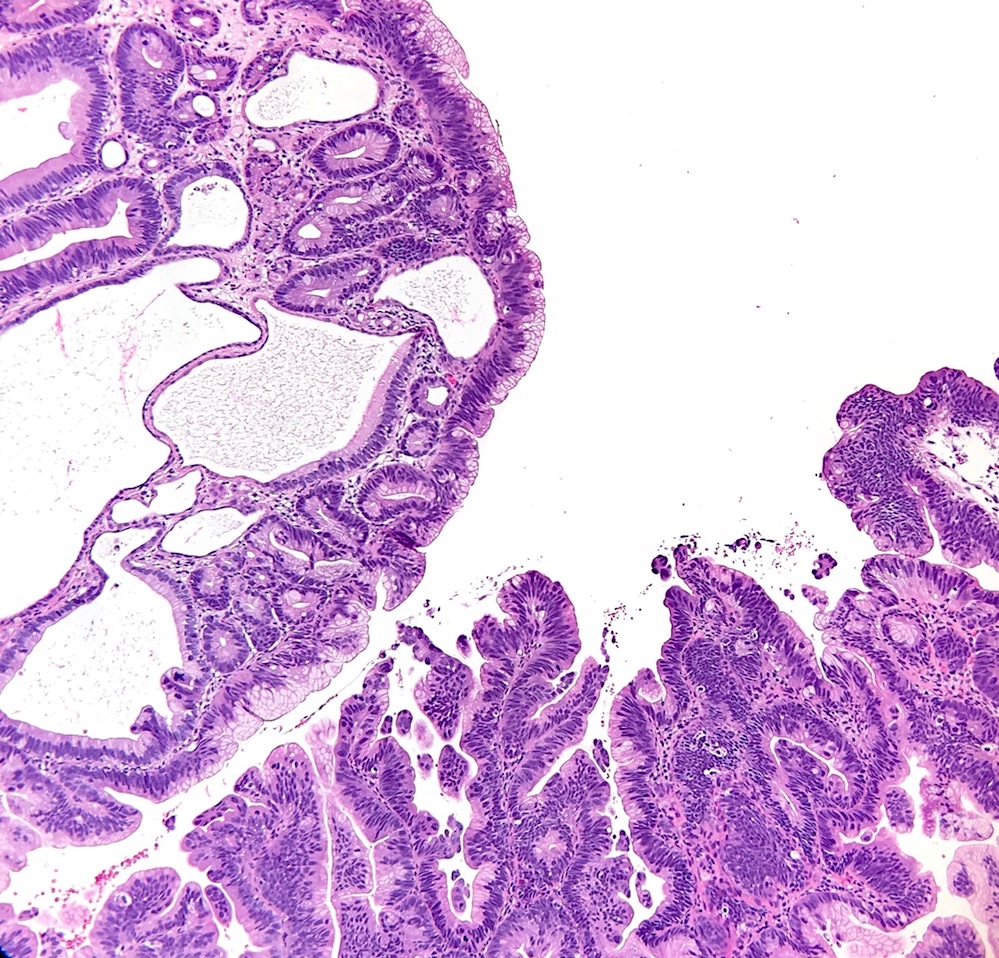
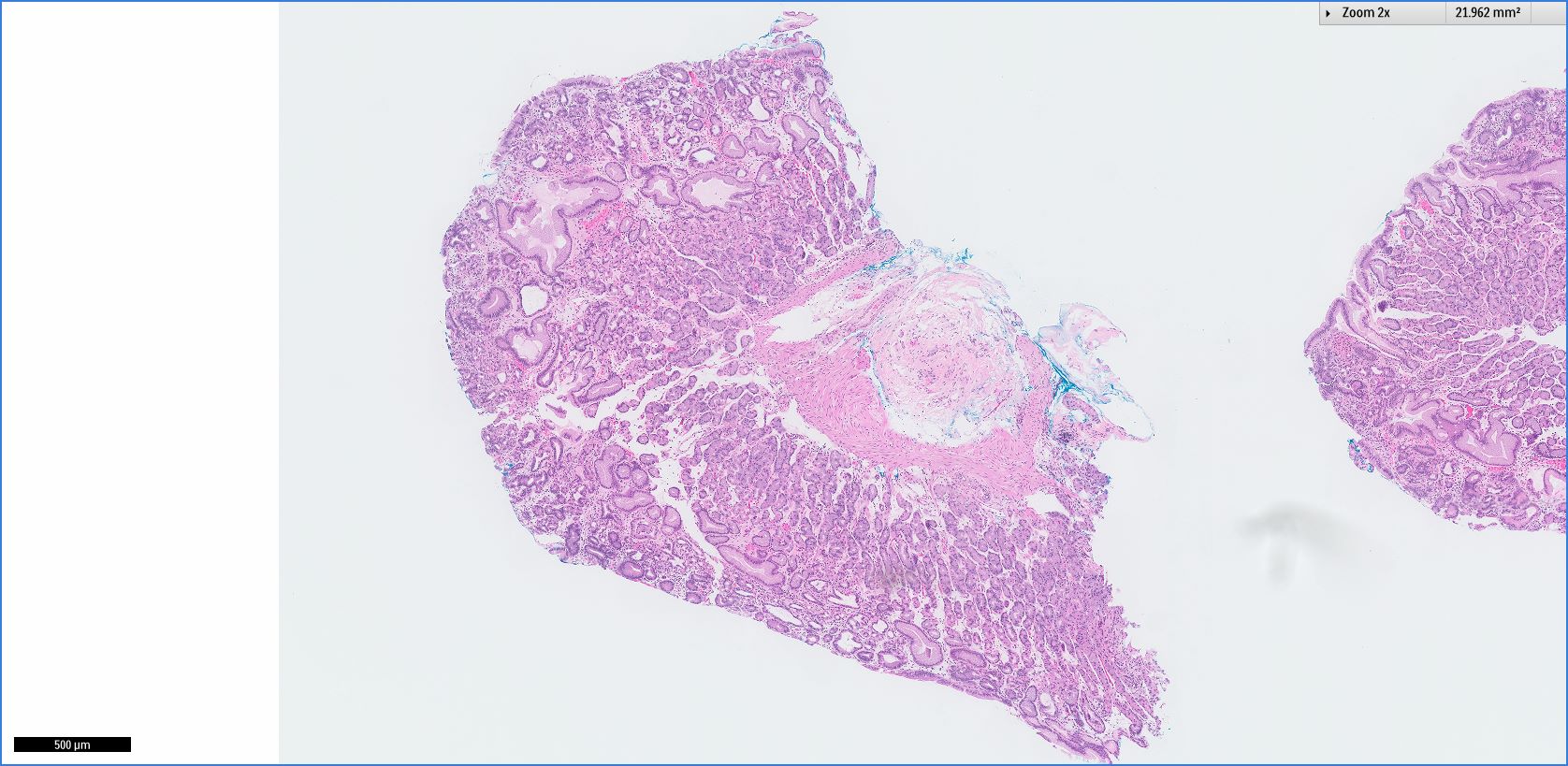
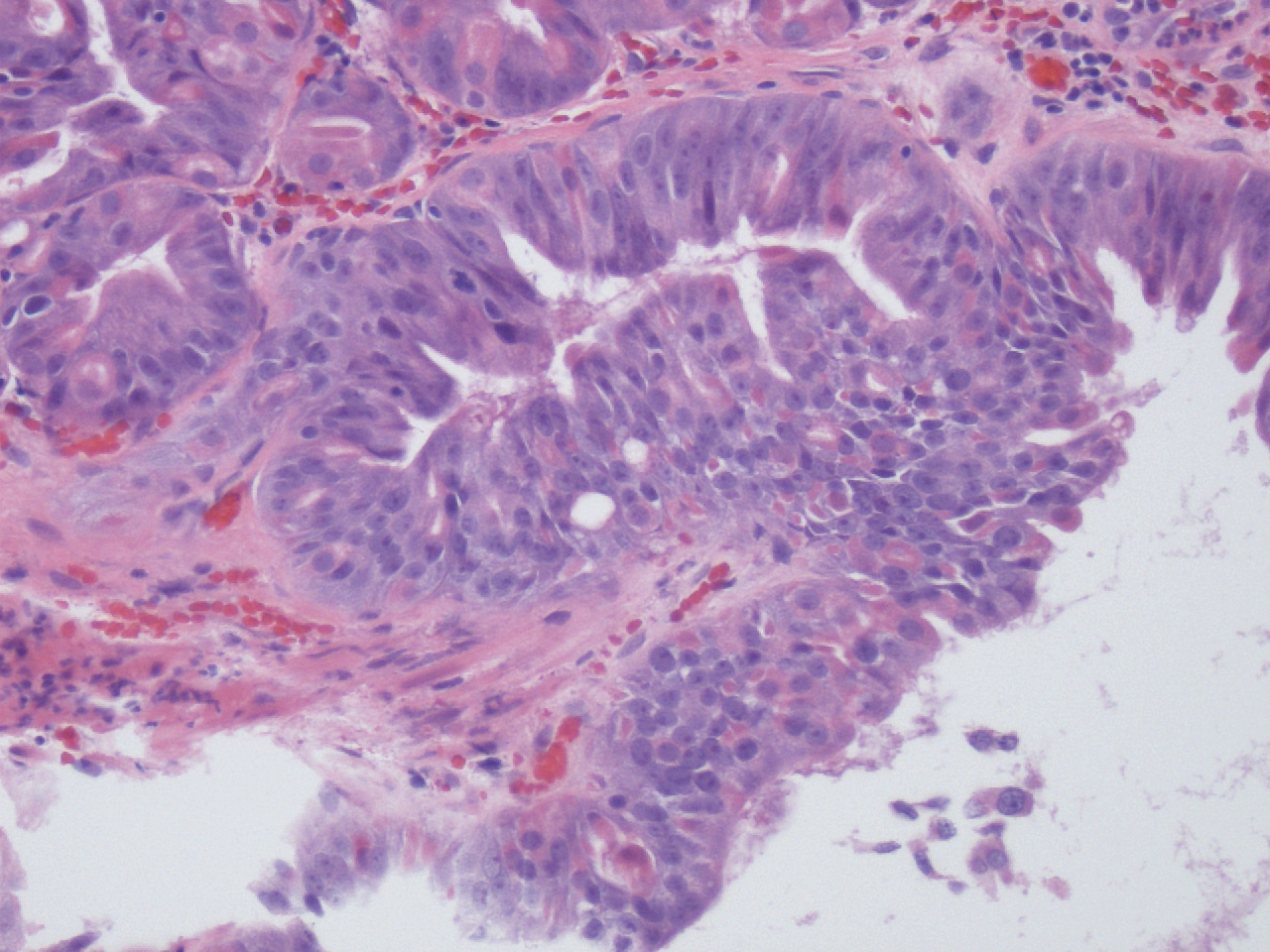
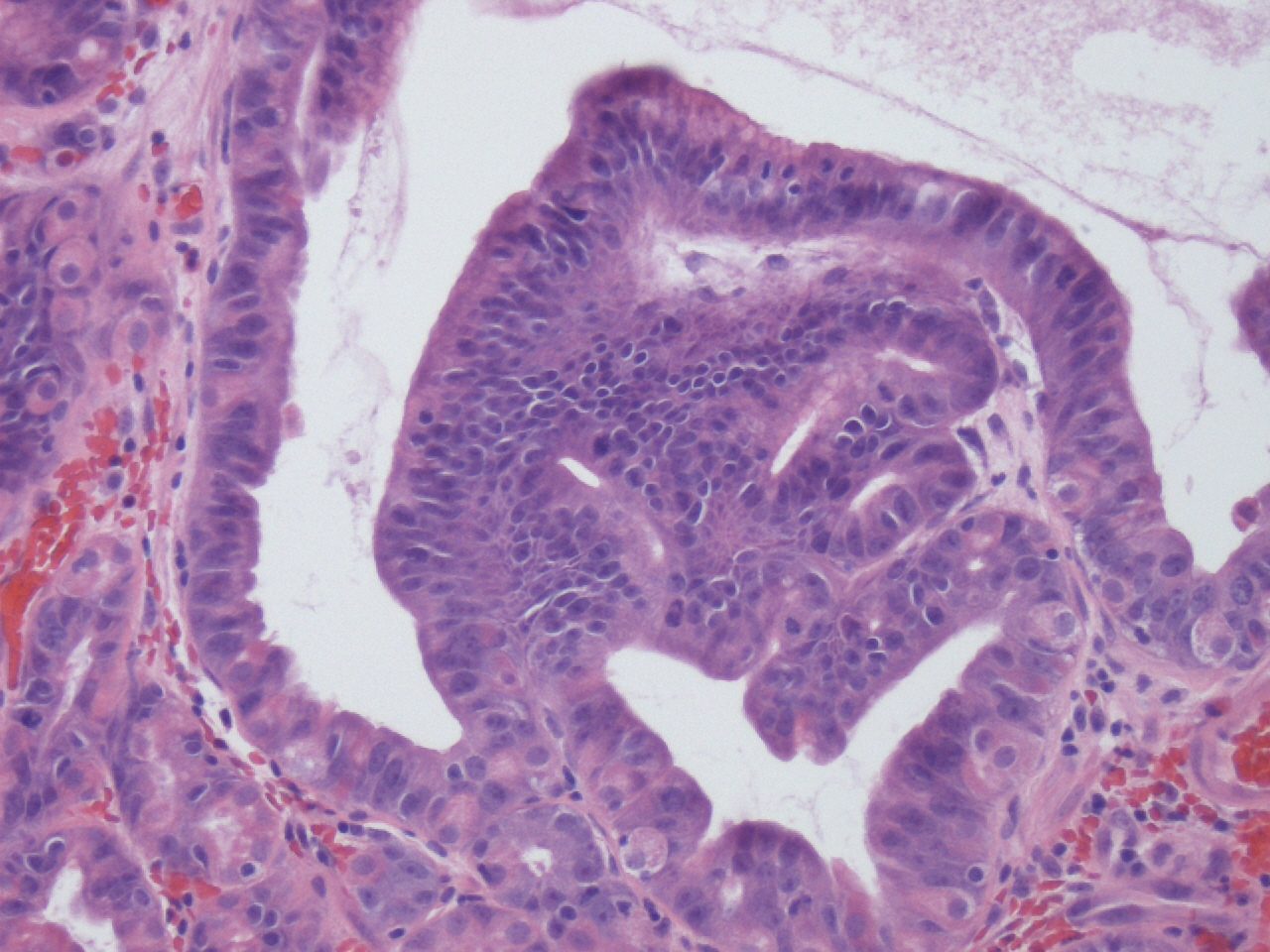
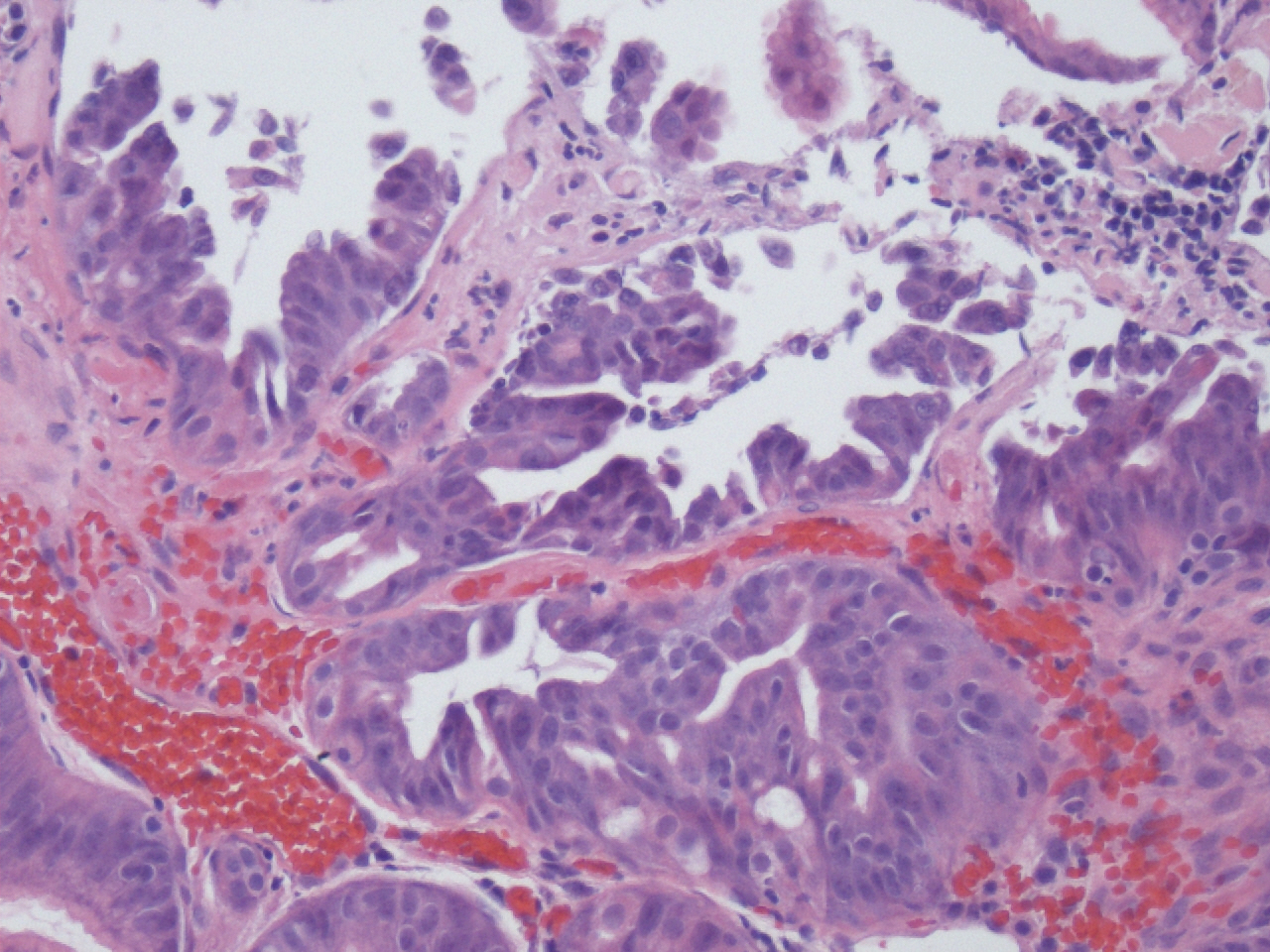
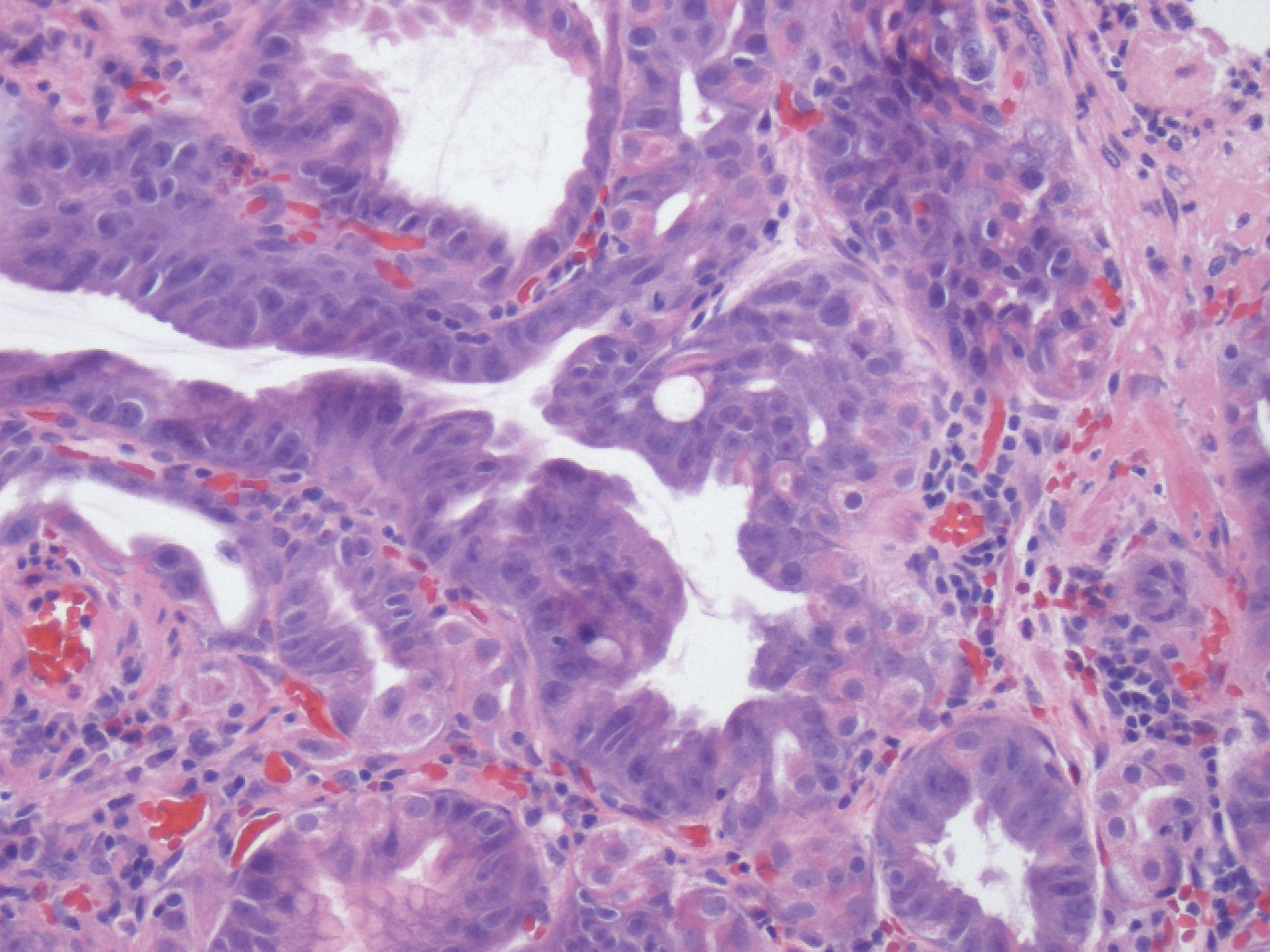
Microscopic (histologic) description
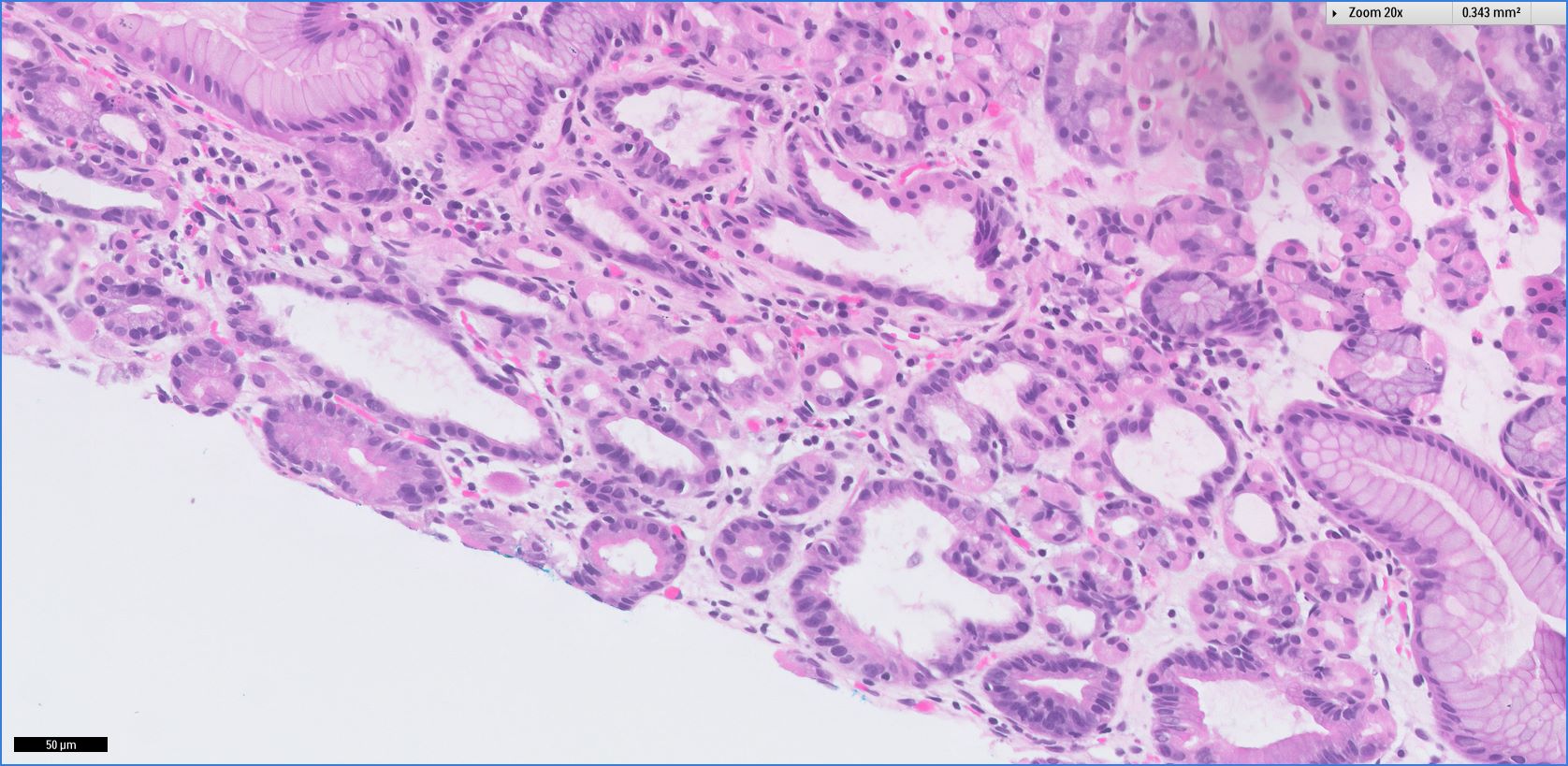
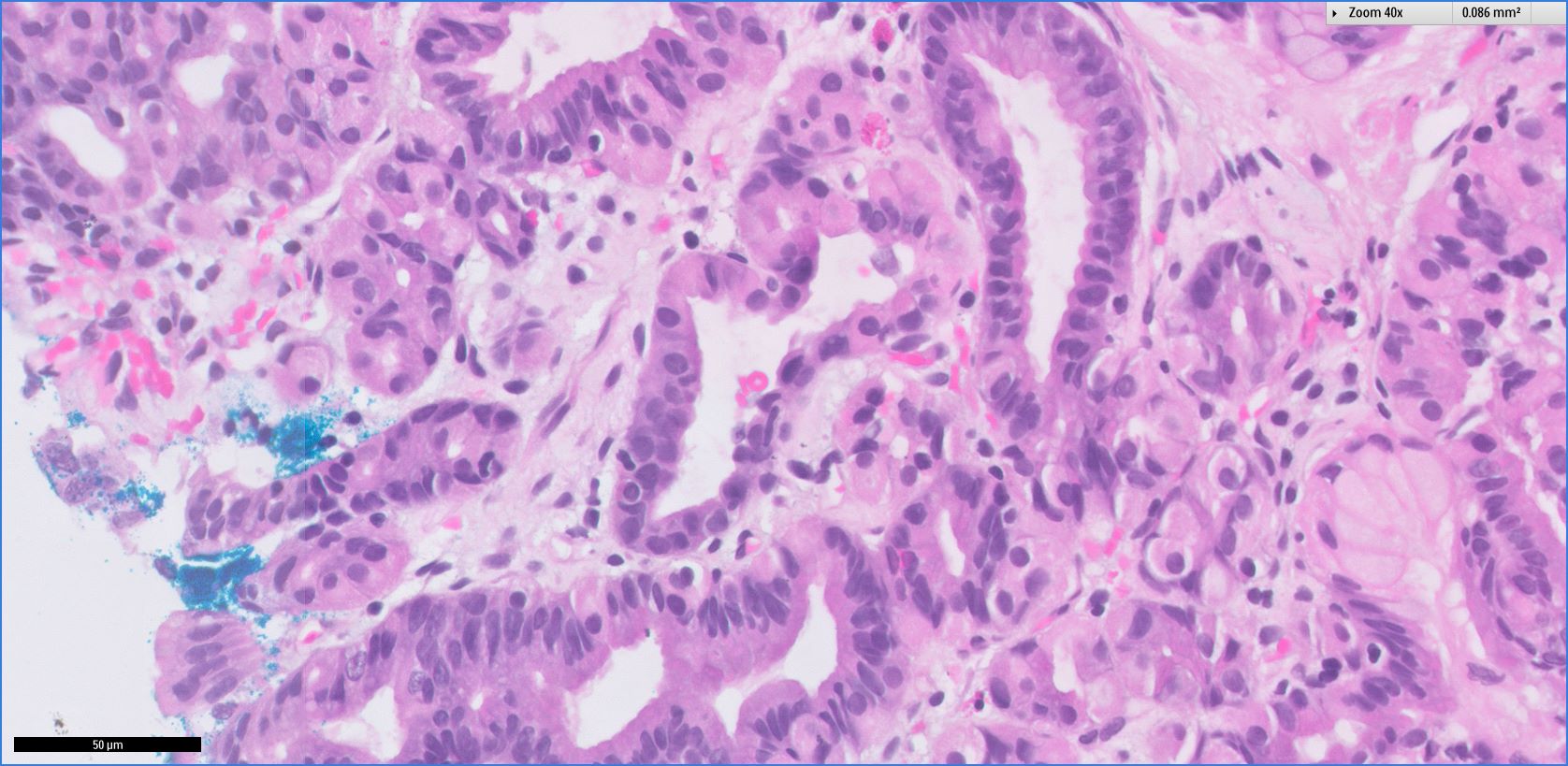
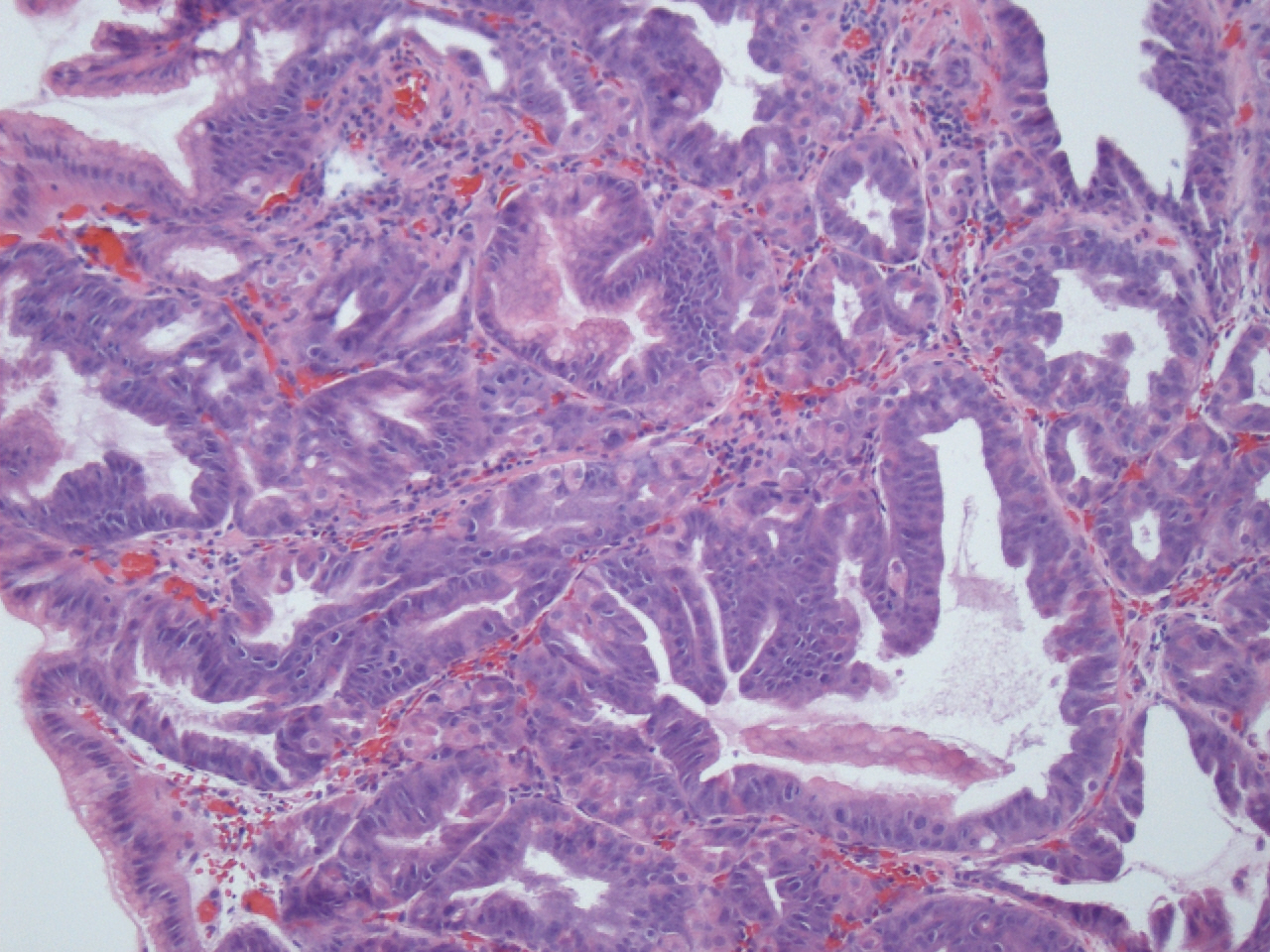
- Cystically dilated glands lined by chief cells, parietal cells and mucinous foveolar cells
- Hyperplastic parietal cells with apocrine snouting is seen in patients on proton pump inhibitors
- May rarely contain morules (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2014;7:1241)
- May harbor dysplasia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Nuclear beta catenin positivity in some foci of dysplasia (Scand J Gastroenterol 2003;38:916)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Associated with APC beta catenin alteration in both sporadic and syndromic cases
Sample pathology report
- Stomach, fundus, polypectomy:
- Fundic gland polyp
- Stomach, fundus, resection:
- Portion of stomach with numerous fundic gland polyps, some with focal low grade dysplasia (see comment)
- Negative for high grade dysplasia or malignancy
- Margins of resection unremarkable
- Comment: Multiple fundic gland polyps can arise in several settings, including proton pump inhibitor use, familial adenomatous polyposis and gastric adenocarcinoma and proximal polyposis of the stomach.
Differential diagnosis
- Oxyntic gland adenoma:
- Anastomosing cords of oxyntic cells rather than dilated cysts
- Contain mucous neck cells rather than foveolar cells (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1030)
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following statements is true about gastric fundic gland polyps?
- Alterations of APC beta catenin pathway is seen in both sporadic and syndromic fundic gland polyps
- Dysplasia is a common finding in fundic gland polyps
- Only familial forms are associated with alteration in APC beta catenin pathway
- They are unequivocally benign and nonneoplastic
Board review style answer #1
A. Alterations of APC beta catenin pathway is seen in both sporadic and syndromic fundic gland polyps
Comment Here
Reference: Fundic gland polyp
Comment Here
Reference: Fundic gland polyp