Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Interpretation | Uses by pathologists | Prognostic factors | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive staining - normal | Positive staining - disease | Negative staining | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Yan S. GLUT1. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/stainsglut1.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Glucose transporter isoform 1, GLUT1, is a member of a family of glucose transporters, proteins that catalyze bidirectional transfer of substrates, particularly glucose, across cell membranes
- GLUT are key rate limiting factors for glucose metabolism (Melanoma Res 2019;29:603)
Essential features
- GLUT are proteins that catalyze bidirectional transfer of substrates, particularly glucose, across cell membranes
- GLUT1 is highly expressed in microvascular endothelia at sites of blood tissue barriers, such as in the central nervous system, retina, placenta, ciliary muscle and endoneurium of peripheral nerves (J Neurosci 1990;10:3862, J Neurocytol 1988;17:173, Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:163, Exp Eye Res 1998;66:747, J Histochem Cytochem 1992;40:193)
- GLUT1 immunoreactivity has been found useful in supporting the diagnosis of infantile hemangioma and perineurioma (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:591, Hum Pathol 2000;31:11, Mod Pathol 2003;16:293, Virchows Arch 2003;443:159)
- Tumor cells differ from their benign counterparts in energy metabolism by converting glucose into lactate
- Tumor cells rely mostly on aerobic glycolysis despite the presence of adequate oxygen to support aerobic mitochondrial oxidation (Warburg effect) (Nat Rev Cancer 2011;11:325)
- Upregulation of GLUT1, an important glucose transporter, has been identified in various neoplastic processes and may be a useful diagnostic and prognostic factor
Terminology
- Glucose transporter isoform 1, GLUT1, GLUT-1
Pathophysiology
- GLUT are proteins that catalyze bidirectional transfer of substrates, particularly glucose, across cell membranes
- GLUT1 antibody highlights the membrane expression of glucose transporter isoform 1
- Glucose is the primary energy source of malignant neoplasms (Int J Oncol 1995;7:701)
- Increased expressions of glucose transporters have been identified in various tumors, including
- Pancreatic carcinoma (J Nucl Med 1997;38:1337)
- Thyroid carcinoma (Surgery 2017;161:188)
- Colorectal carcinoma (Oncotarget 2017;8:11788)
- Breast carcinoma (Hell J Nucl Med 2018;21:35)
- Lung carcinoma (Lung Cancer 2015;88:310)
- Ovarian carcinoma (Cancer Invest 2013;31:607)
- Squamous cell carcinoma (Medicine (Baltimore) 2016;95:e5324)
- Melanoma (Anticancer Res 2016;36:2871)
- GLUT1 may serve as a potential diagnostic and prognostic marker
Clinical features
- Upregulation of GLUT1 has been identified in various neoplastic processes
Interpretation
- Membrane staining pattern
Uses by pathologists
- Differentiate infantile hemangioma from vascular malformation or other vascular neoplasms (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:591, Hum Pathol 2000;31:11)
- Highlights perineurium and is useful to differentiate perineurioma (or sclerotic perineurioma) from other neoplasms such as neurofibroma (Mod Pathol 2003;16:293, Virchows Arch 2003;443:159)
- Diagnosis should be made through interpretation of all clinical and diagnostic features, not based on GLUT1 immunostaining alone
Prognostic factors
- Overexpression of GLUT1 has been found to predict poor prognosis in multiple tumors and may serve as a useful prognostic factor (Anticancer Res 2016;36:2871, Cancer Invest 2013;31:607, Oncotarget 2017;8:11788)
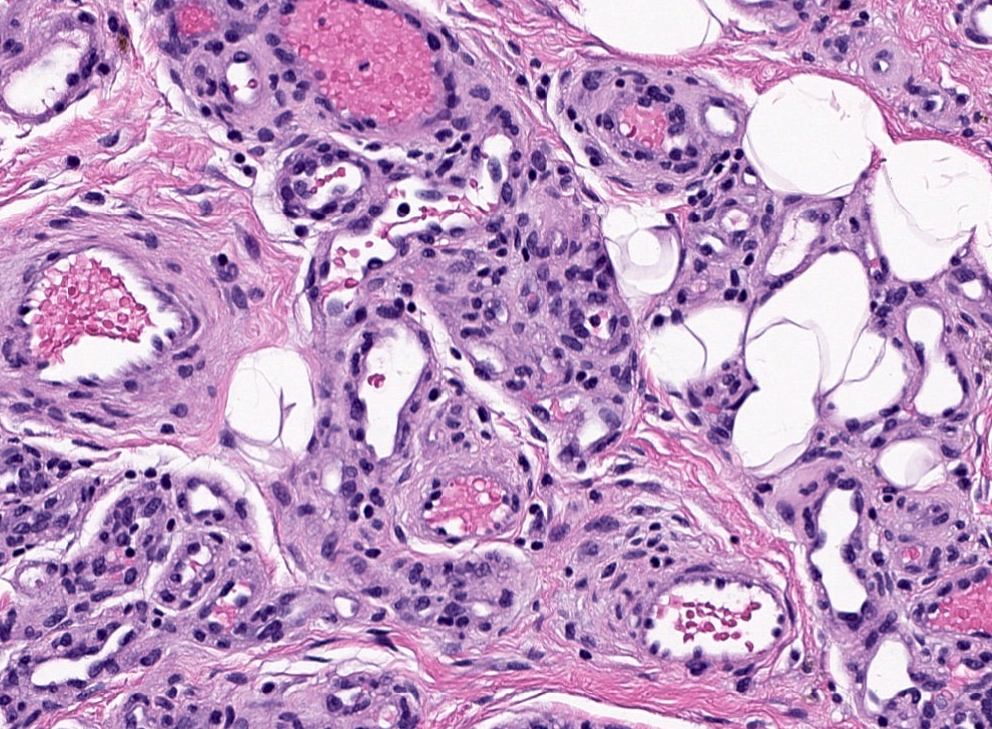
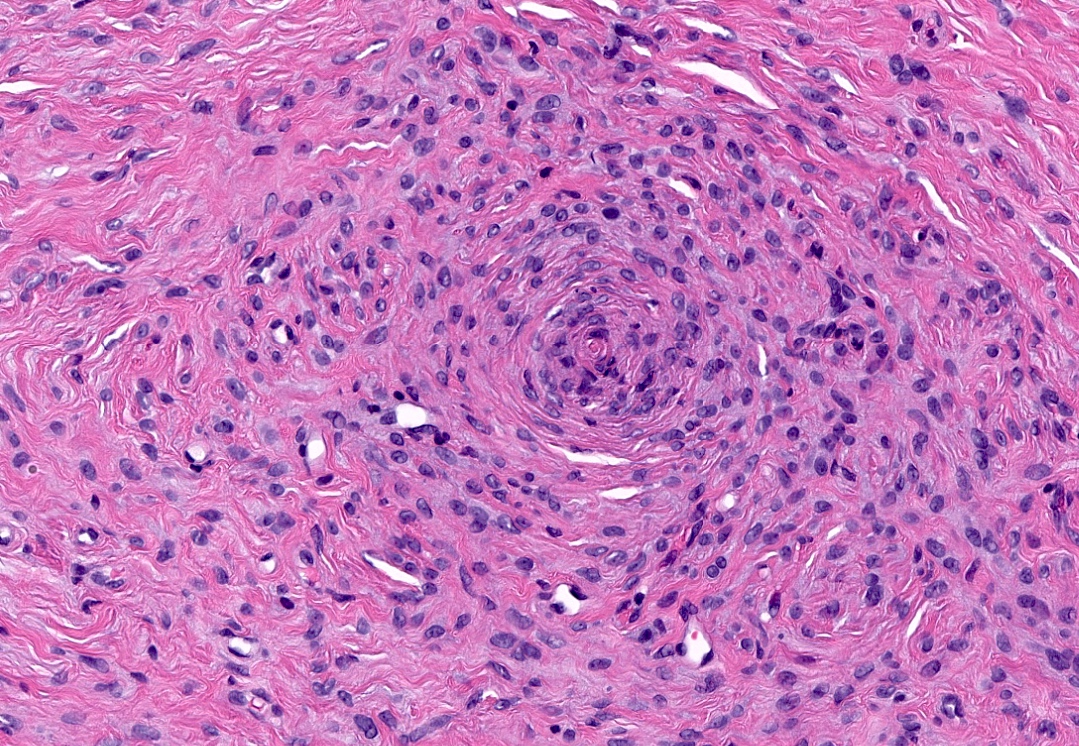
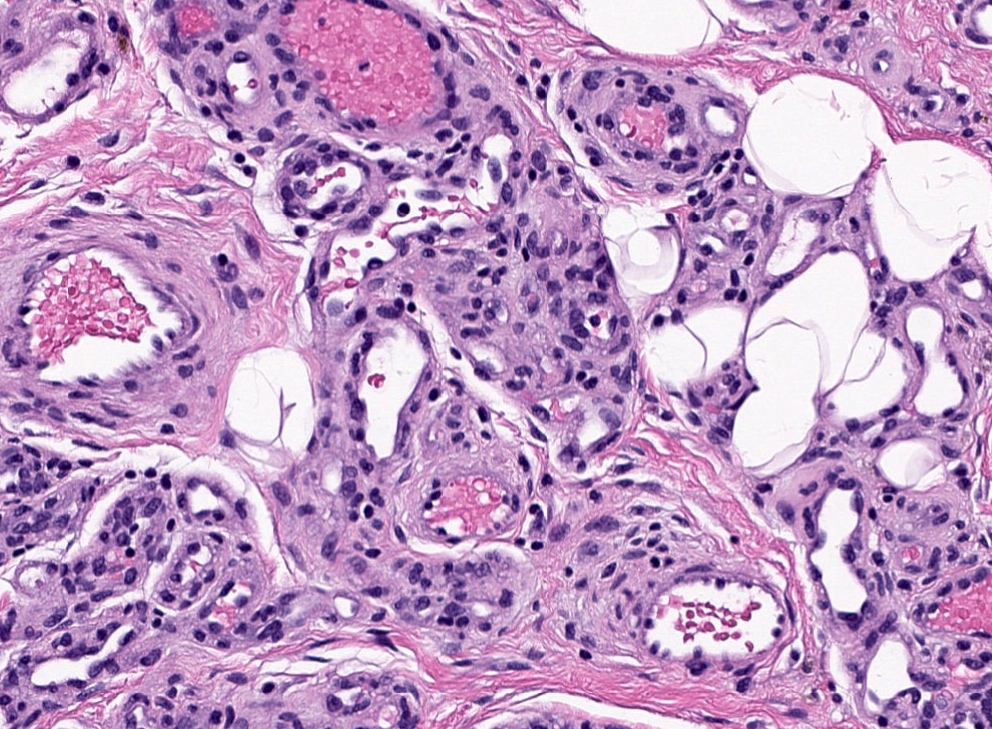
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive staining - normal
- Red blood cell, blood-brain barrier, perineurium, cutaneous keratinocytes, placenta tissue (J Neurosci 1990;10:3862, J Neurocytol 1988;17:173, Am J Obstet Gynecol 1999;180:163, Exp Eye Res 1998;66:747, J Histochem Cytochem 1992;40:193)
Positive staining - disease
- Infantile hemangioma (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:591)
- Perineurioma (Virchows Arch 2003;443:159)
Negative staining
- Vascular malformation (Pathol Res Pract 2017;213:591, Hum Pathol 2000;31:11)
- Neurofibroma (Mod Pathol 2003;16:293)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1