Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Shankar V. Hemangioma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/spleenhemangioma.html. Accessed April 27th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Nonencapsulated benign proliferation of vascular channels that range from capillary to cavernous in size
- Most common primary tumor of spleen
Epidemiology
- Average age is 63 years (range 23 - 94 years) (J Gastrointest Surg 2000;4:611)
Clinical features
- Usually < 2 cm, incidental mass, asymptomatic
- May present with a palpable mass or abdominal pain / discomfort
- May be associated with hemangiomas at other sites
- May be associated with anemia, thrombocytopenia, Kasabach-Merritt syndrome (thrombocytopenia caused by platelet sequestration and destruction in large cavernous hemangiomas, usually infants, rarely adults) (Srp Arh Celok Lek 2012;140:777)
- Rarely is large, multiple or involves entire spleen (angiomatosis)
- Rarely presents with splenic rupture and massive hemorrhage
Diagnosis
- By ultrasound examination and CT, confirmation by histopathology
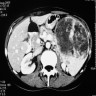
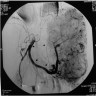
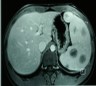
Radiology description
- At CT, hemangiomas appear as hypodense well circumscribed masses with marked homogeneous enhancement of solid components
Radiology images
Case reports
- 18 year old man with elective laparoscopic splenectomy for giant hemangioma (Cases J 2009;2:10)
- 42 year old woman with coexisting giant splenic hemangioma and multiple hepatic hemangiomas (J Med Case Rep 2008;2:147)
- 68 year old man with noncalcified splenic hemangioma identified by radionuclide bone scan (J Nucl Med 1989;30:1111)
Treatment
- Splenectomy
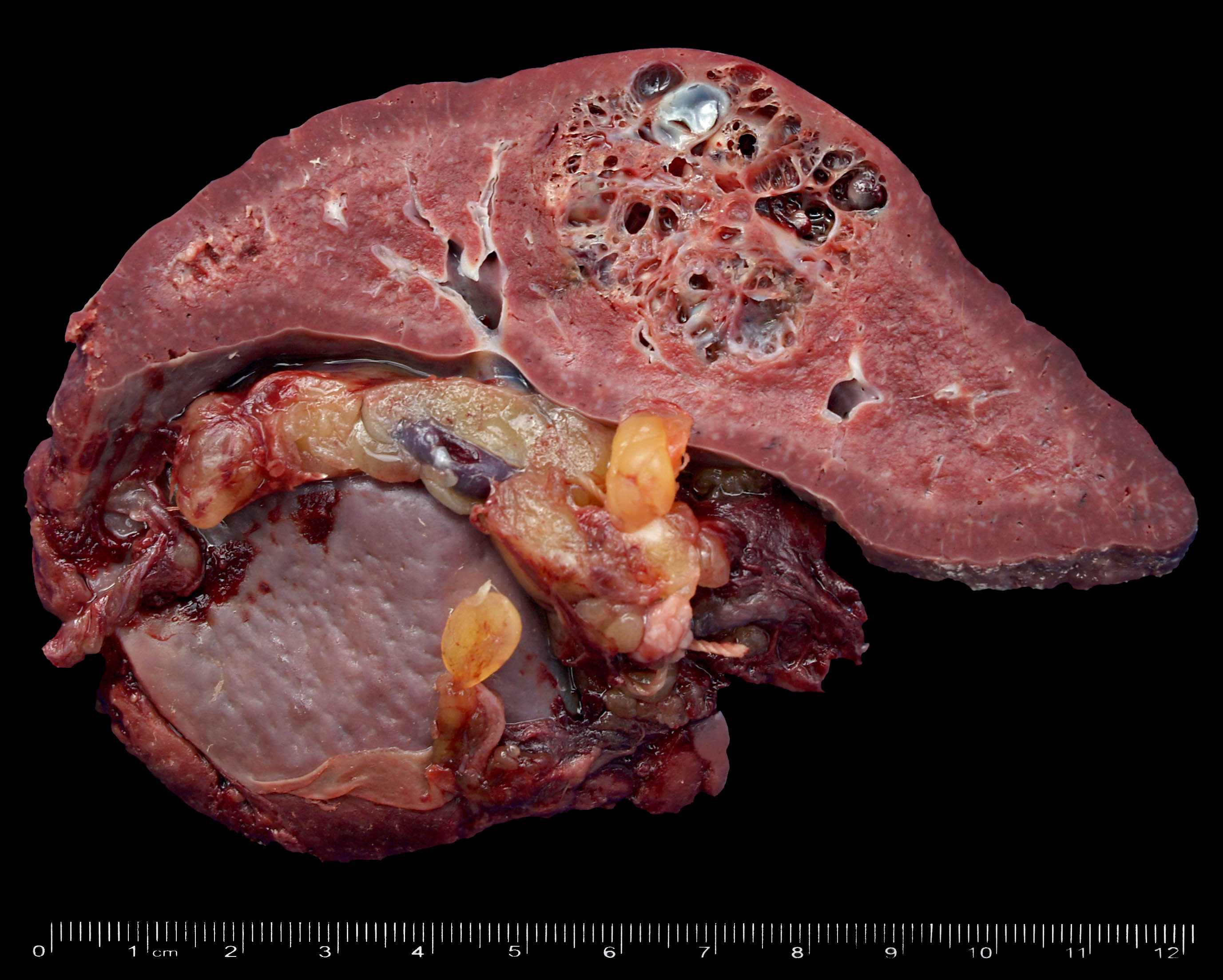
Gross description
- Well defined lesions, 0.3 - 7 cm, rarely diffuse
- Usually solid, larger lesions can be partly cystic
- Large lesions may have calcifications
Gross images
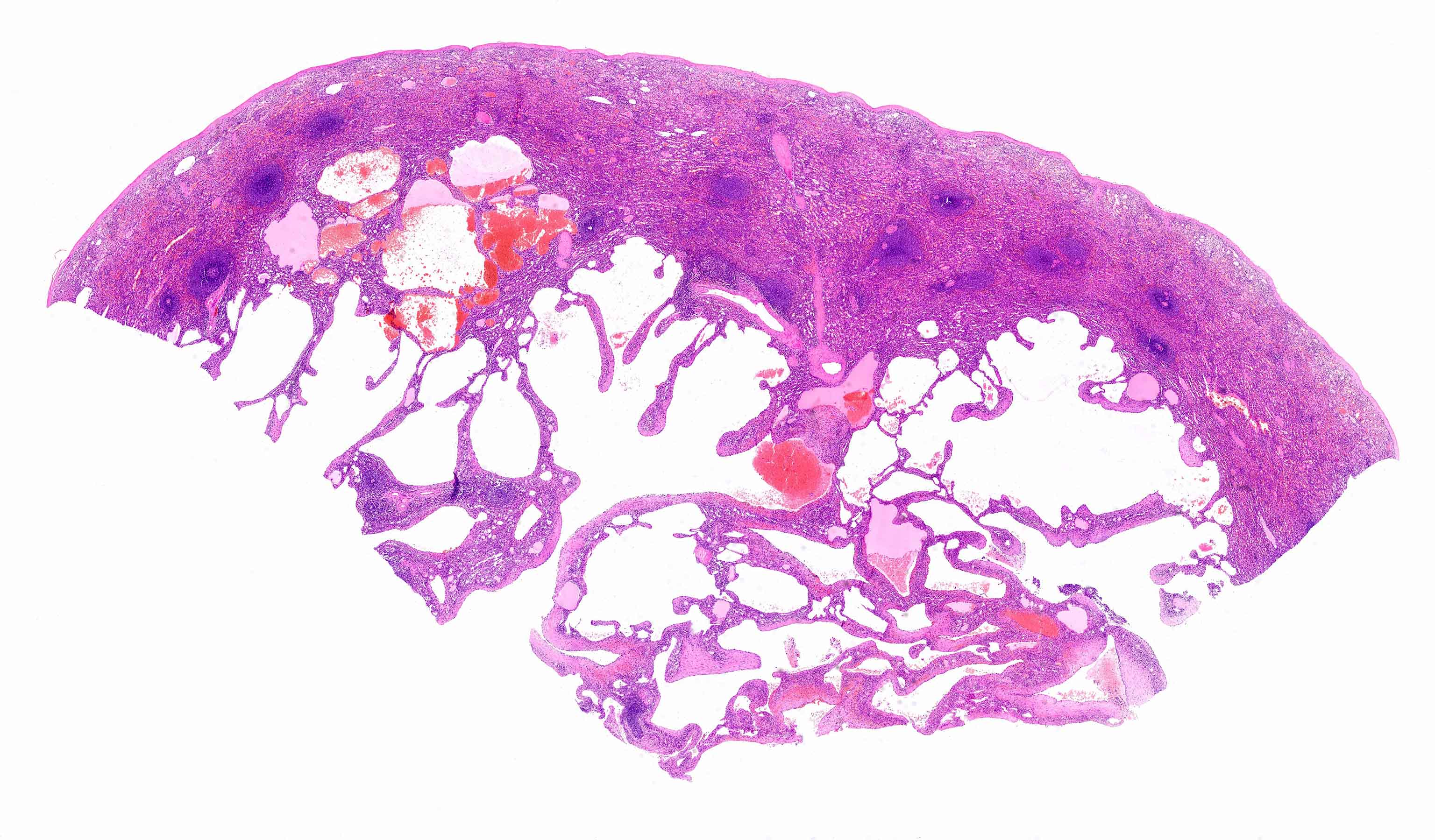
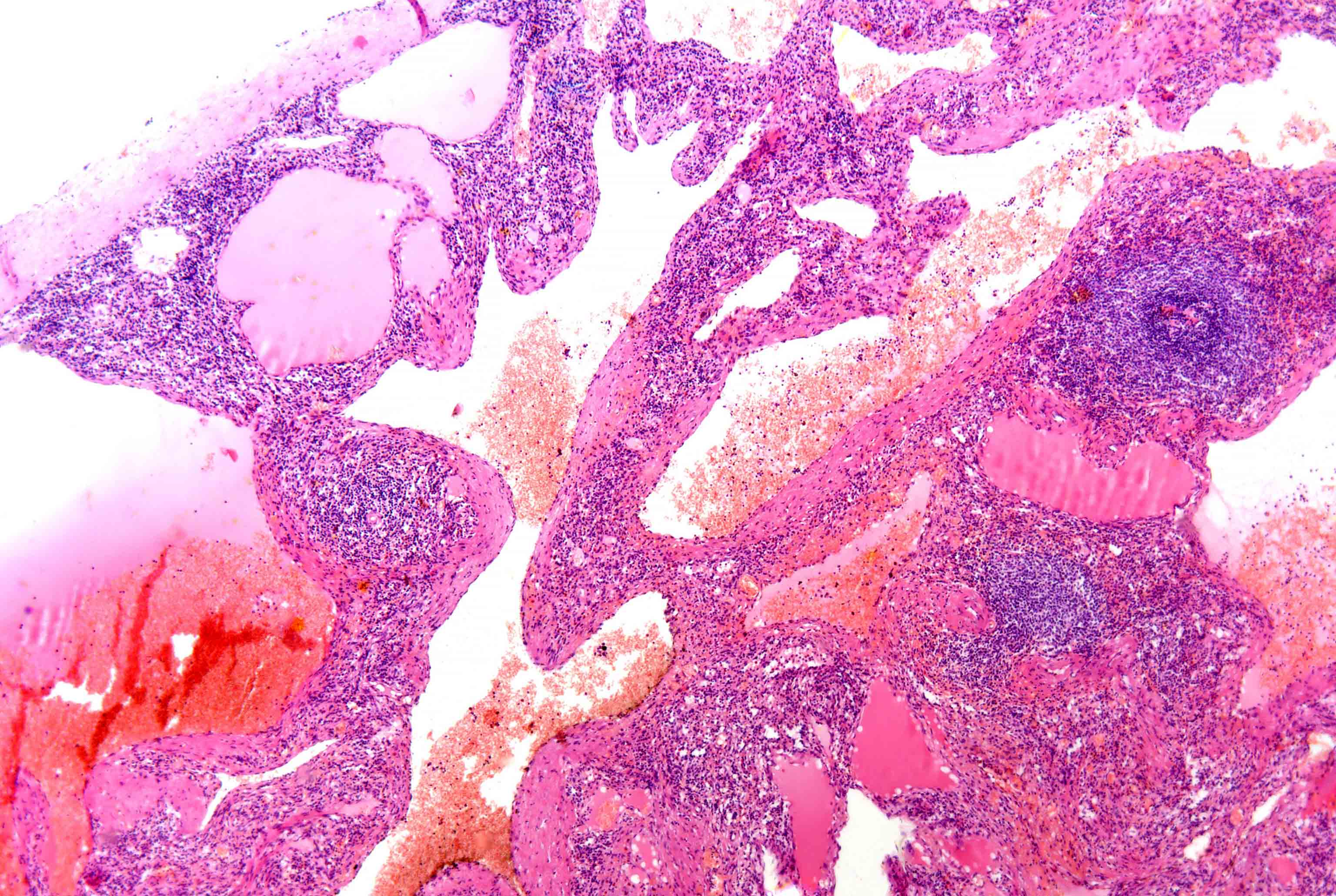
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Capillary or cavernous
- Vascular spaces lined by single layer of bland endothelial cells, without mitoses
- Thrombosis and infraction can be seen
- When organized, infarcted hemangioma may resemble leiomyoma
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Factor VIII, CD31, CD34
- CD68 (diffuse hemangiomas)
Differential diagnosis
- Angiosarcoma: marked atypia, anastomosing vascular spaces
- Splenic hamartoma: well circumscribed lesion with disorganized blood vessels of varying sizes intermingled with splenic red pulp element; also entrapped adipocytes, focal extramedullary hematopoiesis; CD8+