Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Jabcuga C, Gardner JM. Nuchal type fibroma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissuenuchaltypefibroma.html. Accessed January 5th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Bundles of thick collagen fibers in posterior neck
- Also called collagenosis nuchae, nuchal fibrocartilaginous pseudotumor, nuchal fibroma
- Nuchal: nape (posterior) of neck
- Related entities: Gardner associated fibroma (extra-nuchal location but essentially identical histology)
Epidemiology
- Rare benign lesion of dermis and subcutis in posterior neck (70%), upper back or other regions
- More common in men, mean age 40 years (age range 3 - 74 years)
- Associated with diabetes mellitus in 44% (Cancer 1999;85:156)
Case reports
- 43 year old man with case associated with dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans (DFSP, J Cutan Pathol 2004;31:62)
- Cases at extranuchal sites may be associated with Gardner’s syndrome (familial adenomatous polyposis; adenomatous polyposis coli):
- 2 cases: 13 year old boy and his 60 year old grandfather (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:1563)
- 45 year old man with a painless forehead lump (Case of the Week #469)
- 51 year old man (J Cutan Pathol 2011;38:911)
- Fibromatosis (desmoid tumor) occurring in excision site of nuchal type fibroma (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:828)
Treatment
- Excision, may recur locally but does not metastasize
Gross description
- Usually 3 cm or less, hard and white, unencapsulated, poorly circumscribed
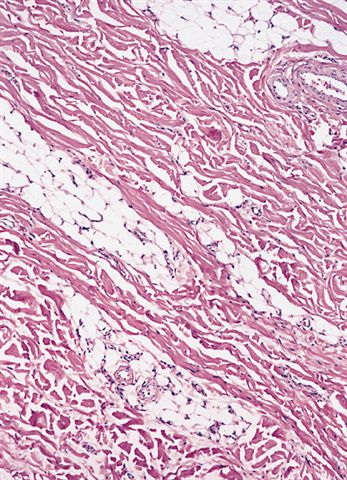
Microscopic (histologic) description
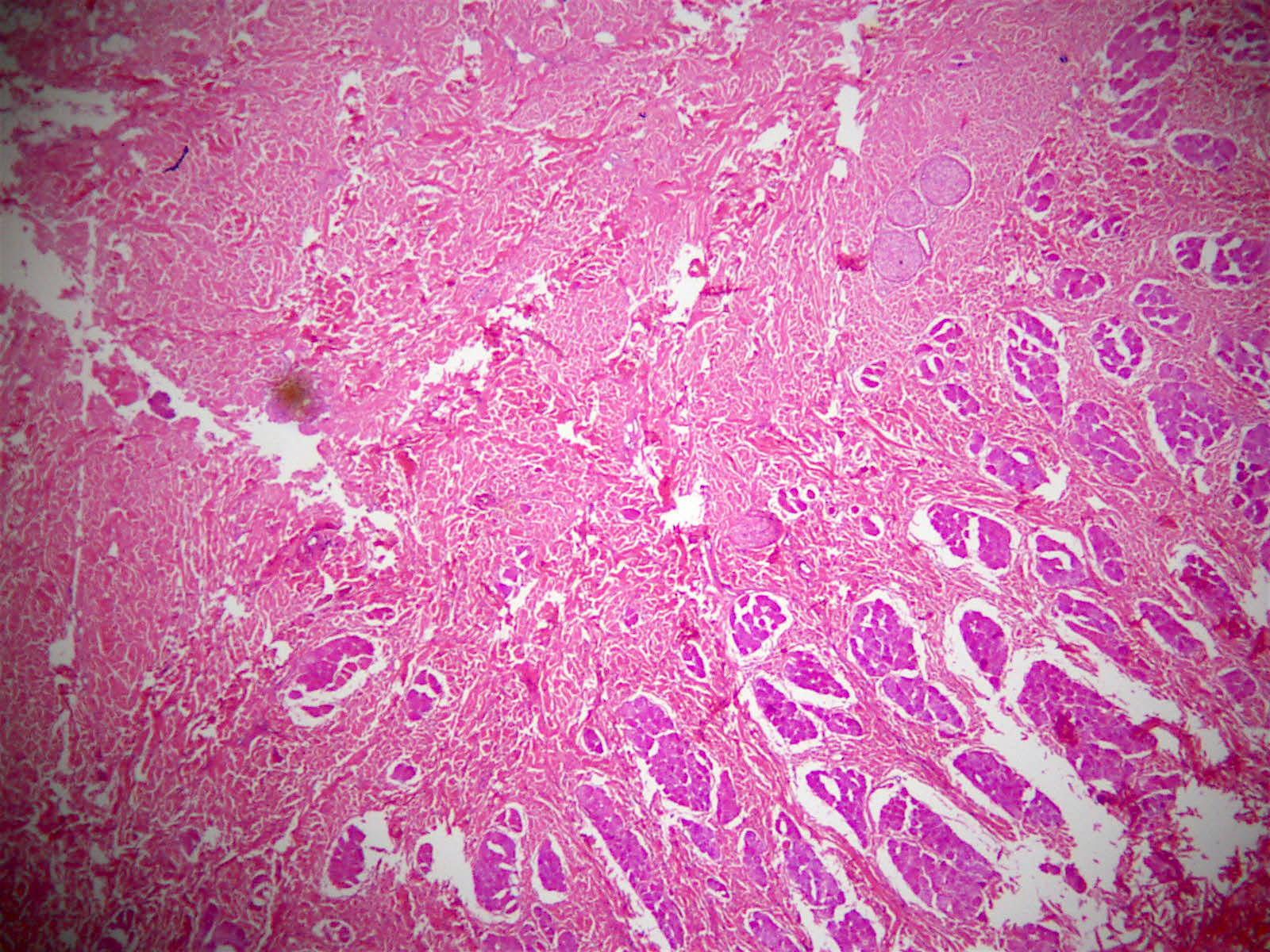
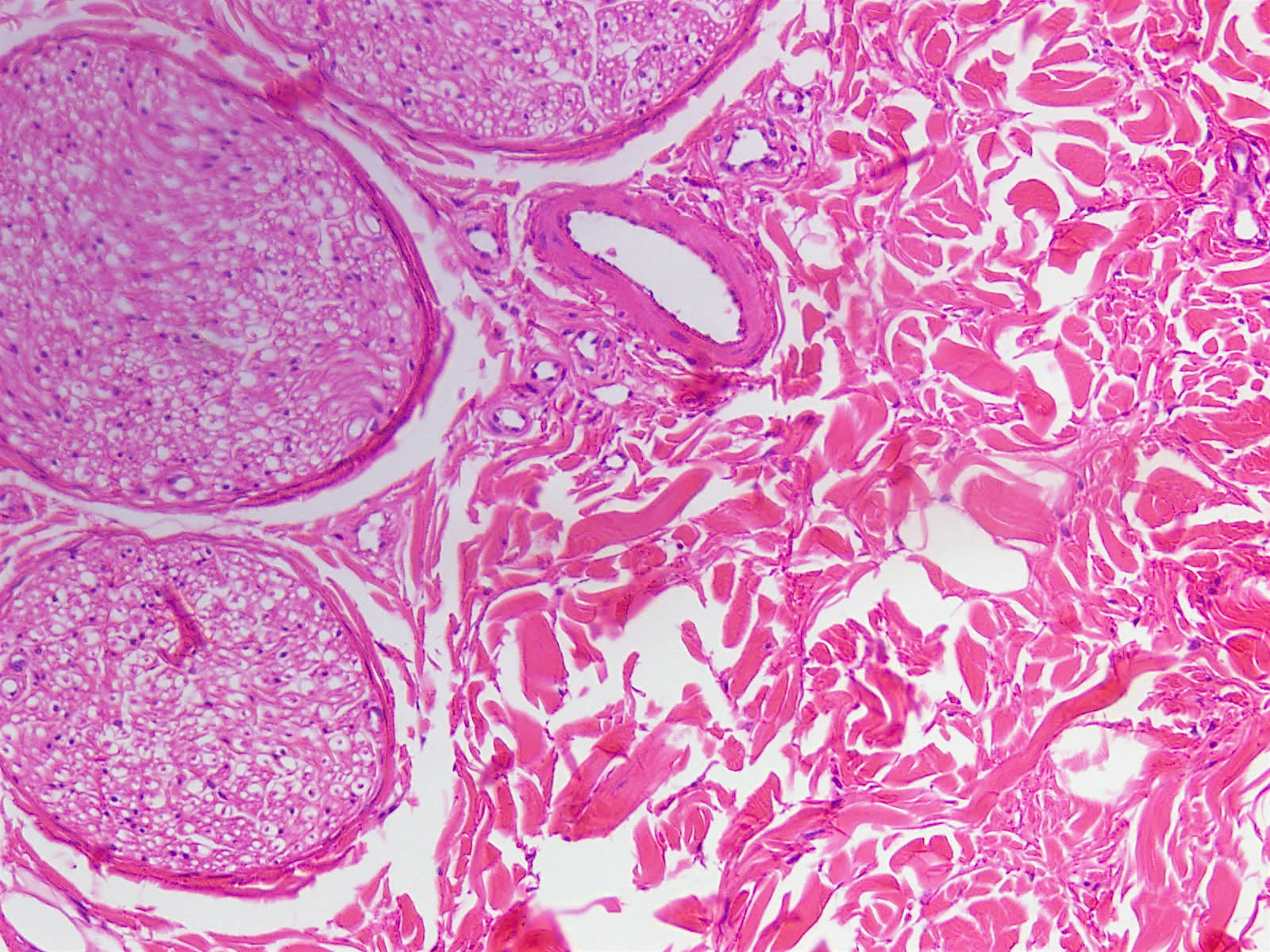
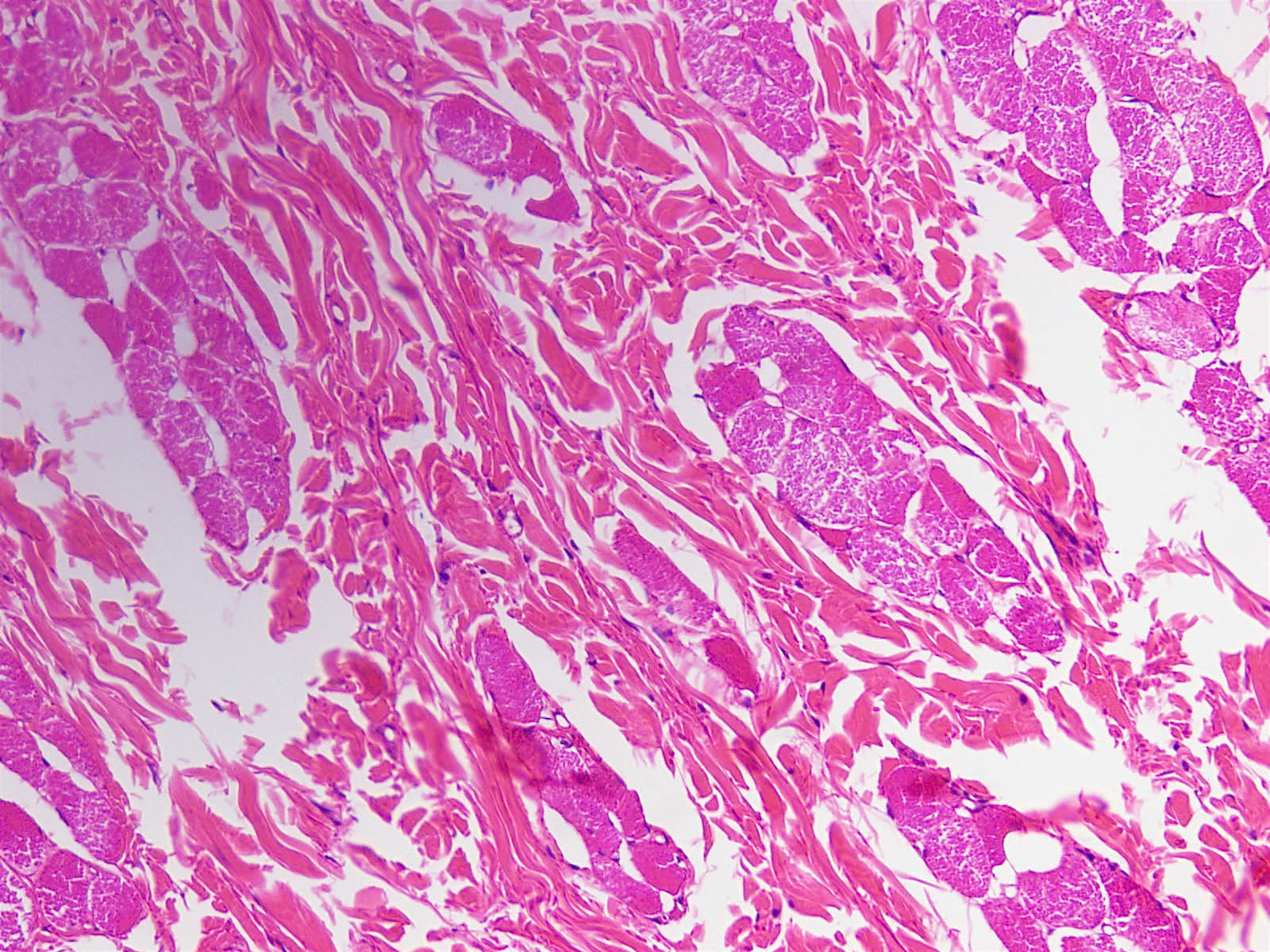
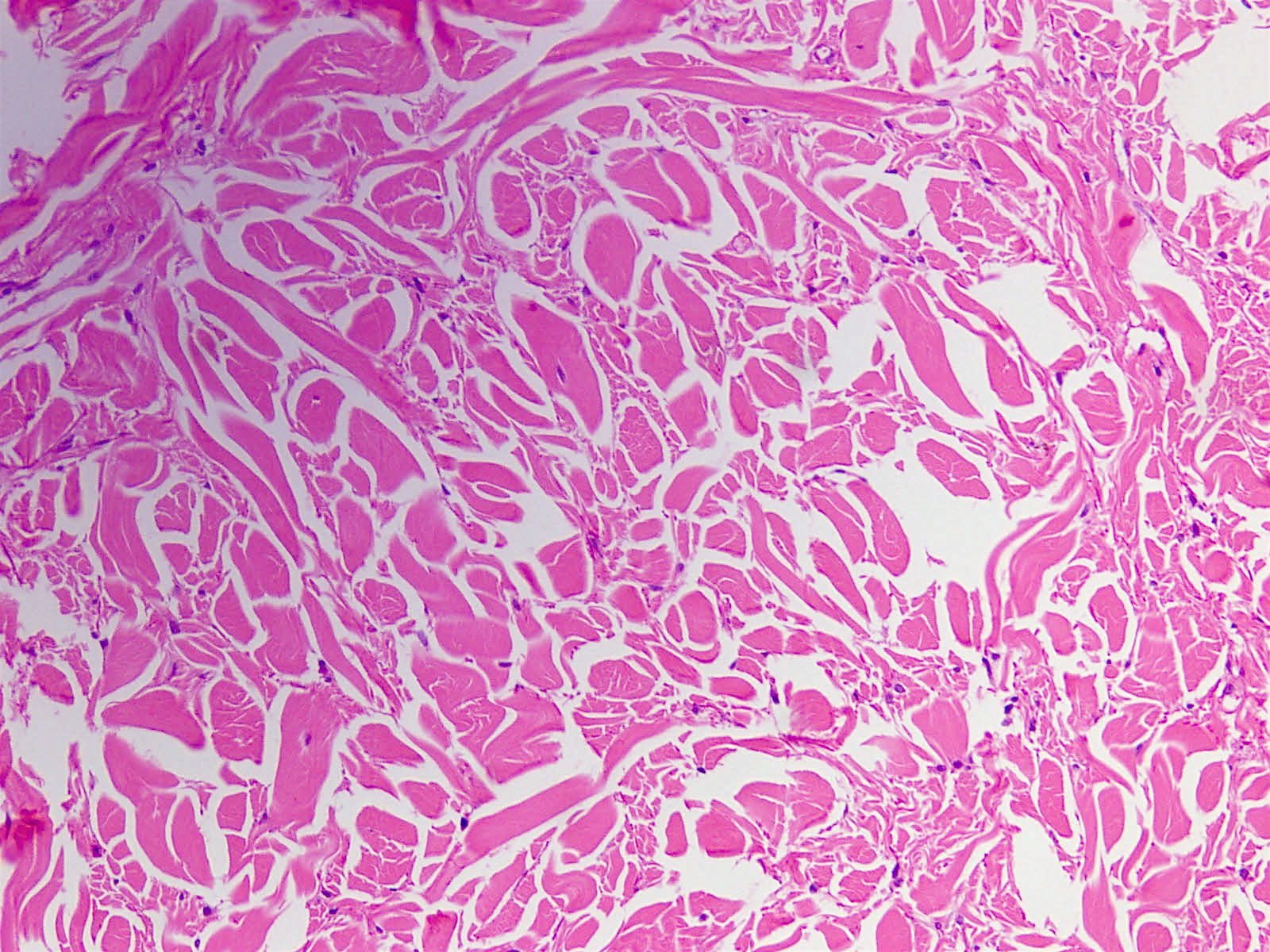
- No capsule, hypocellular, thick collagen fibers with delicate elastic fibers (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:313, Stanford University)
- Entrapped adipose tissue and entrapped nerves (may resemble traumatic neuroma)
- May infiltrate into skeletal muscle and adipose tissue, may have scattered lymphocytes
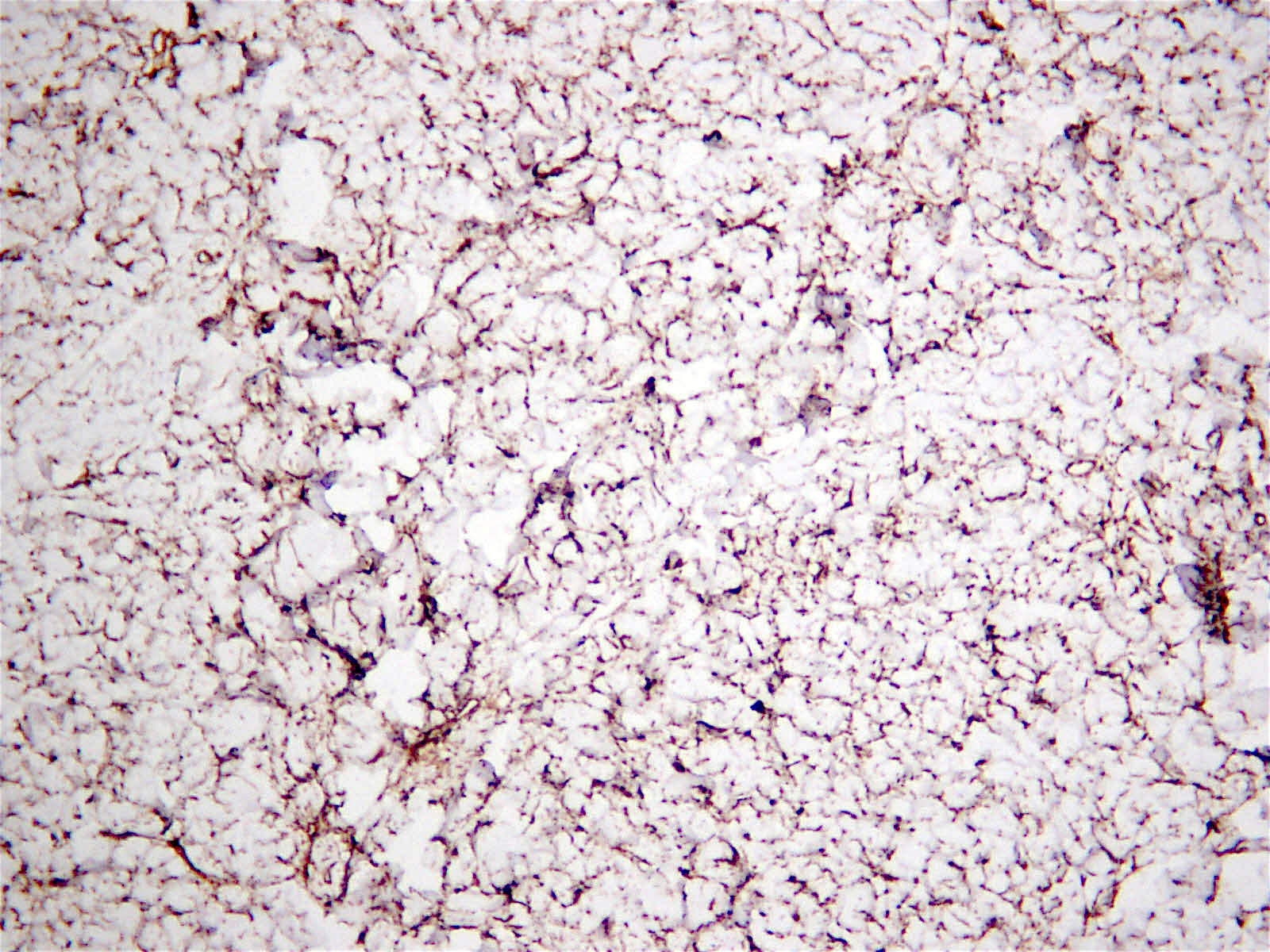
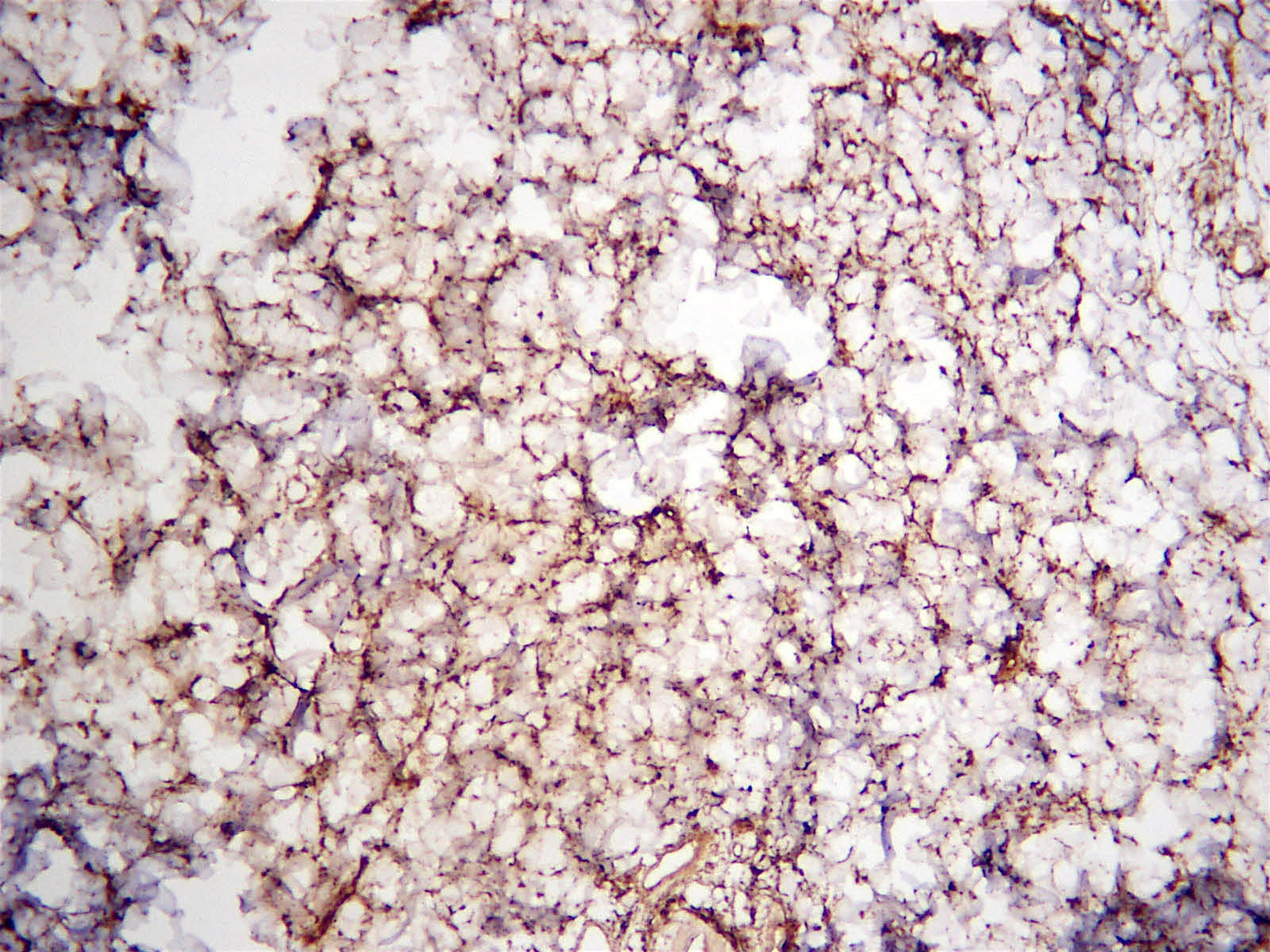
Microscopic (histologic) images
Negative stains
Differential diagnosis
- Elastofibroma: prominent abnormal elastic fibers, subscapular location and often bilateral
- Fibrolipoma: circumscribed, different location
- Fibromatosis: deep soft tissue, not back of neck, more cellular with broad fascicles of fibroblasts
- Gardner fibroma: same histologic features but extra-nuchal location (may be related or identical entity)
- Solitary fibrous tumor: patternless pattern, more cellular, staghorn type vessels
Board review style question #1
Nearly half of patients with nuchal type fibroma will also carry what diagnosis?
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Hypertension
C. Proteinuria
D. Turcot syndrome
A. Diabetes mellitus
B. Hypertension
C. Proteinuria
D. Turcot syndrome
Board review style answer #1