Table of Contents
Definition / general | Sites | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Arora K. Inclusion body fibromatosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueinfantiledigitalfibromatosis.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
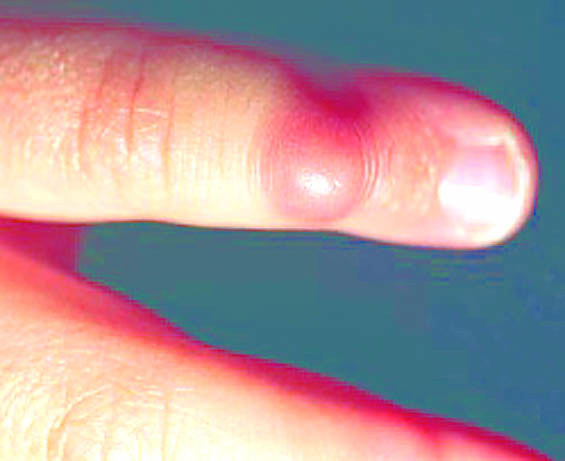
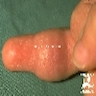
- Dermal fibroblastic and myofibroblastic lesion with cytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusions, usually in digits of infants
- Also called infantile digital fibromatosis, infantile digital fibroma (J Hand Surg Am 1995;20:1014)
- Distinct lesion from classic fibromatosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1)
Sites
- Usually exterior surface of distal phalanges of fingers and toes, but not thumb or great toe, also oral cavity and breast
- 50% recur, do not metastasize
- Similar inclusions reported in breast fibroadenoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:1126), breast phyllodes tumor (Am J Surg Pathol 1994;18:506, Breast J 2008;14:198), cervical polyp (Pathology 1998;30:215), GI leiomyomas (Cesk Patol 2006;42:139)
Clinical features
- Rare; lesions usually present at birth or in first 2 years
- Similar lesions in adults
- Often are multiple
Case reports
- 6 month old girl (Indian J Pathol Microbiol 2010;53:827)
- 1 year old boy with spontaneous regression (J Dermatol 1998;25:523)
- 2 year old with post-surgical involvement of all 4 extremities (Ann Plast Surg 2008;61:472)
Treatment
- Conservative excision (preserve function because recurrences are not destructive and tumors do not metastasize) or watchful waiting (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1, Pediatr Dermatol 2008;25:72)
Gross description
- Nodules with stretched overlying skin, lesions are ill defined, white-tan, usually 2 cm or less
- No hemorrhage or necrosis
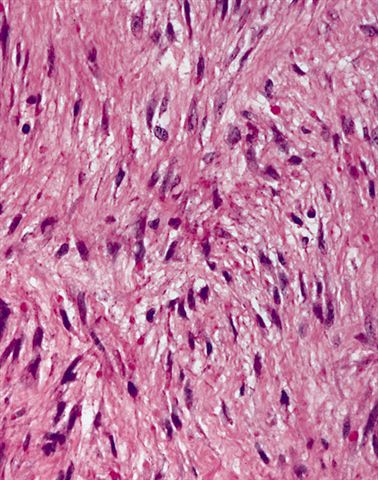
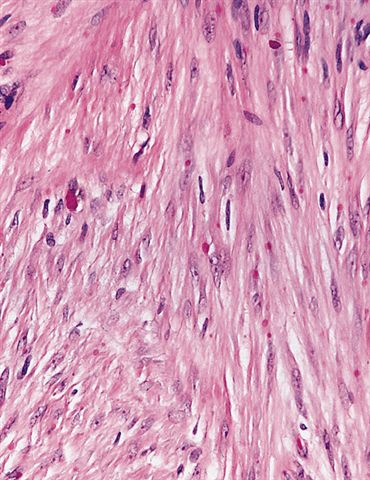
Microscopic (histologic) description
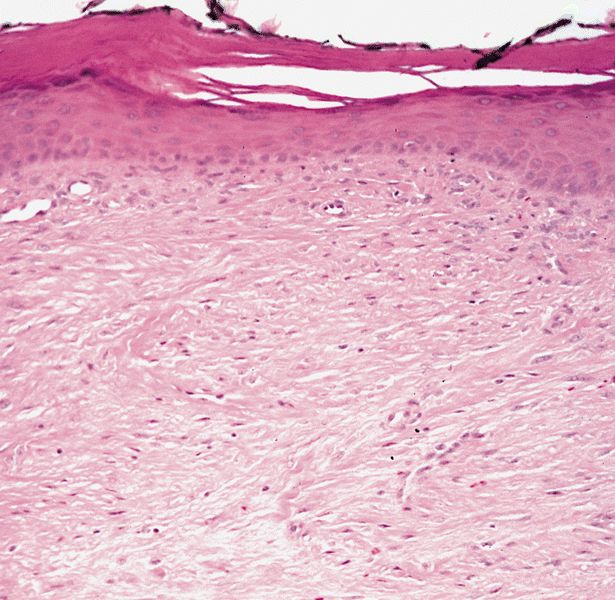
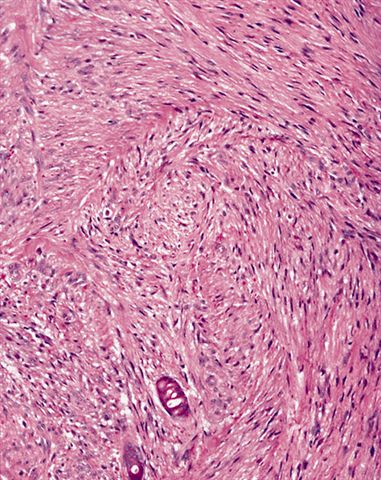
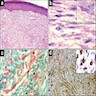
- Nonencapsulated, dermal proliferation of hypocellular sheets or fascicles of fibroblasts and myofibroblasts with variable collagen
- Some spindle cells have peculiar eosinophilic (hyaline) cytoplasmic inclusions the size of a lymphocyte nucleus
- Usually mitotic figures
- May infiltrate into adjacent tissue
- No atypia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
Positive stains
Negative stains
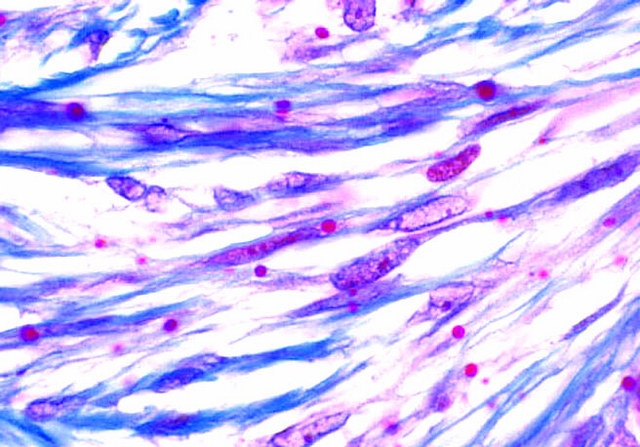
- Inclusions: PAS
- Spindle cells: keratin, ER, PR, beta-catenin
Electron microscopy description
- Spindle cells are myofibroblasts with rough endoplasmic reticulum and free lying inclusions composed of compact masses of actin granules and filaments without a limiting membrane (Am J Pathol 1979;94:19)
Differential diagnosis
- Infantile fibrosarcoma:
- Not digits, usually > 2 cm, more cellular, chromatin is denser and more irregular, more mitotic figures, no inclusions
- Infantile desmoid fibromatosis:
- Rare on hand, usually > 2 cm, more cellular, no inclusions