Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Singh C. Lipomatosis of nerve. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/softtissueadiposelipomatosisnerve.html. Accessed April 2nd, 2025.
Definition / general
- Infiltration of epineurium of a major nerve by adipose and fibrous tissue
Terminology
- Also called fibrolipoma of nerve, fibrolipomatous hamartoma of nerve, macrodystrophia lipomatosa
Epidemiology
- May be noted at birth
- Almost always age 30 years or less
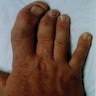
- Associated with macrodactyly (abnormal enlargement of digits) innervated by affected nerve in 30 - 67%
Sites
- 85% have involvement of median nerve and its digital branches in hand, wrist and forearm (Histopathology 1994;24:391)
- Also ulnar nerve
Radiology description
- T1 weighted images on MR imaging reveal a fatty mass that is evenly distributed between nerve bundles and is seen running along individual nerves
- Often described as having a "coaxial cable-like" appearance on axial scans (Acta Radiol 2003;44:326)
Case reports
- 26 year old man with sciatic nerve involvement (Microsurgery 2009;29:66)
- 26 year old man with mass on palm of hand (Case of the Week #158)
- 32 year old woman (J Orthop Surg (Hong Kong) 2011;19:123)
- 46 year old man with bilateral involvement (Muscle Nerve 1998;21:656)
Treatment
- Benign but often no effective treatment as resection causes sensory and motor deficits (J Neurosurg 1998;89:683)
- Carpal tunnel release may relieve symptoms of median nerve involvement
- Amputation if severe deformity
- May recur in 33 - 60% if incomplete resection
Gross description
- Fusiform enlargement of nerve by yellow adipose tissue, confined within epineurium
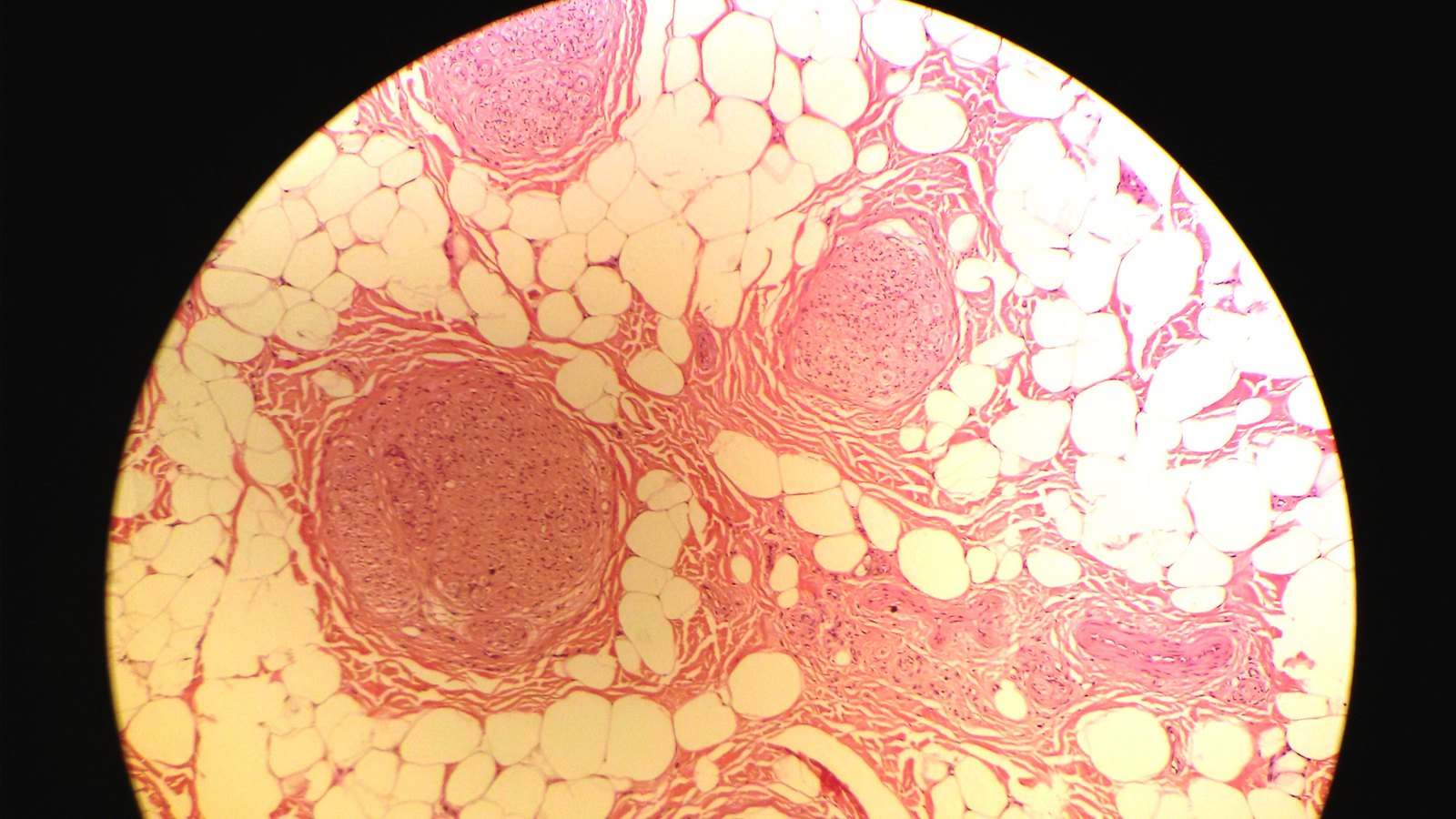
Microscopic (histologic) description
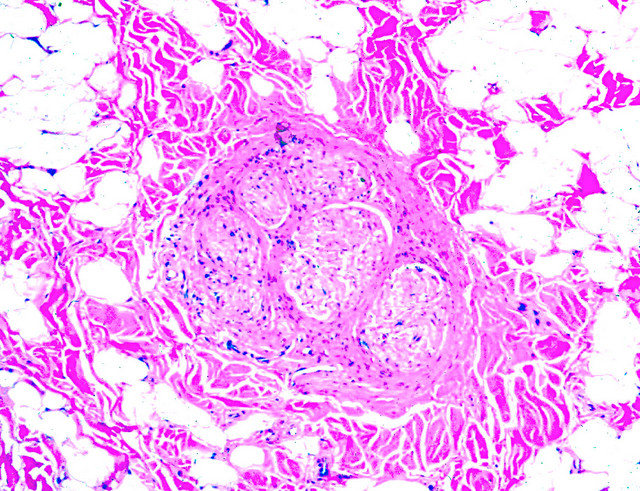
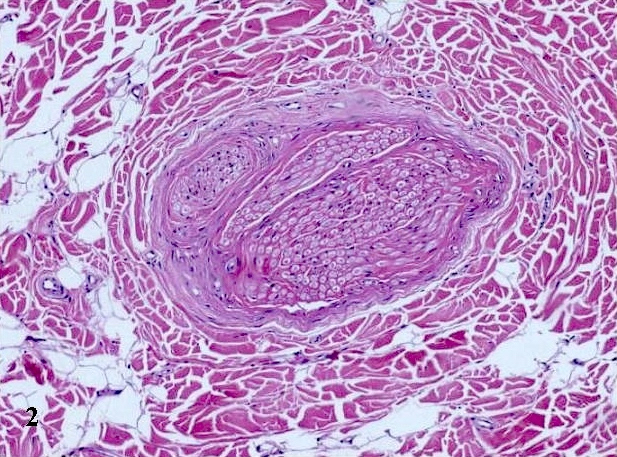
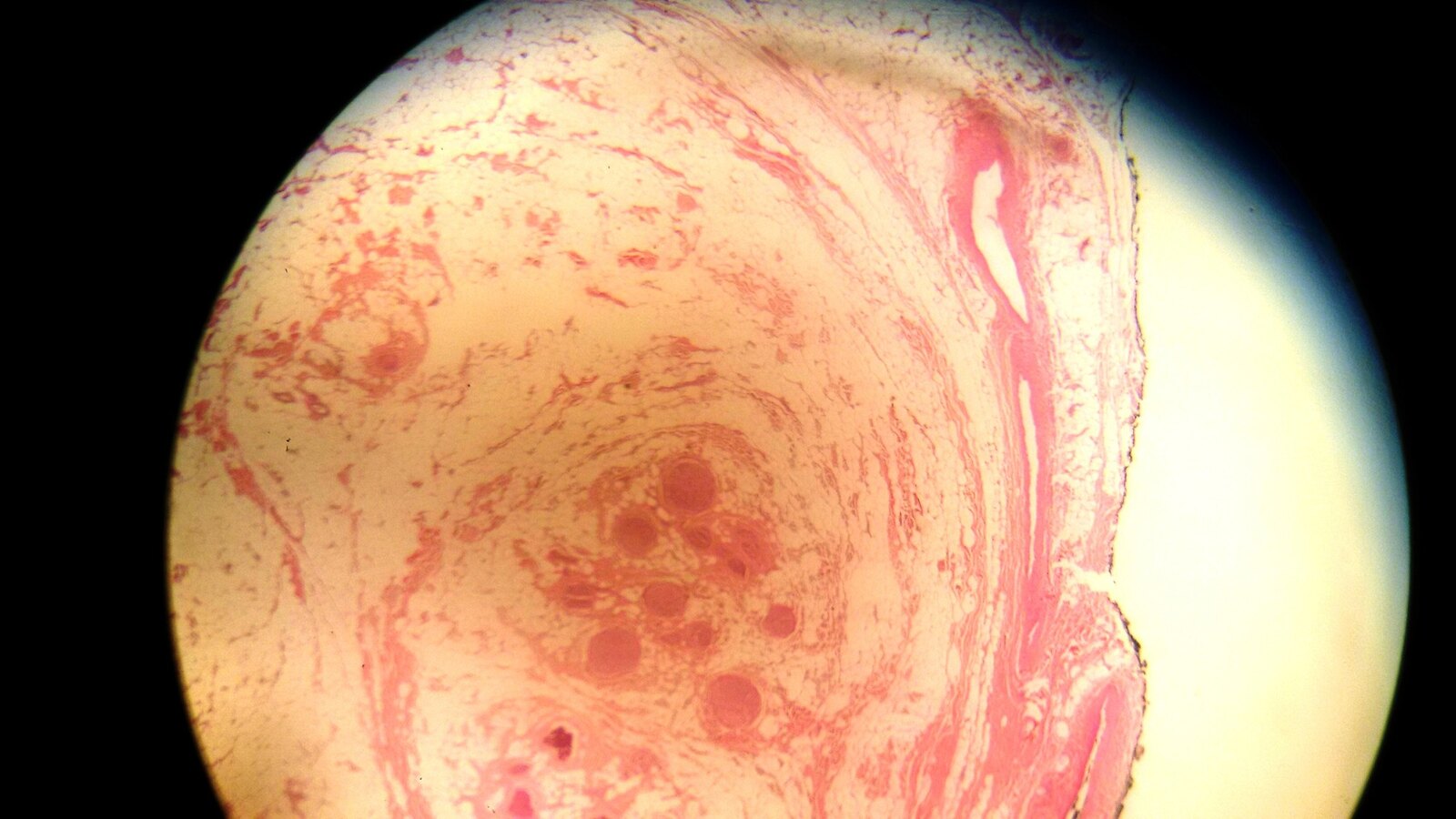
- Infiltration of epineurium and perineurium by adipose and fibrous tissue (collagen), causing enlargement of nerve
- Concentric perineurial fibrous tissue and pseudo-onion bulb formation
- Occasionally metaplastic bone
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Charanjeet Singh, M.D., Mark R. Wick, M.D., Saroona Haroon, M.D. and Geoffrey A. Talmon, M.D. (Case #158)
Differential diagnosis
- Diffuse lipomatosis: not confined to epineurium
- Intraneural lipoma: mass of fatty tissue displaces nerve bundles, but does not separate them
- Traumatic neuroma: onion bulb formation, usually lacks concentric perineural fibrosis, has high T2 signal density on magnetic resonance imaging
- Differential diagnosis of macrodactyly:
- Angiomatosis
- Klippel-Trenaunay-Weber syndrome (eMedicine)
- Neurofibromatosis type 1
- Proteus syndrome (Wikipedia)