Table of Contents
Definition / general | Ampulla | Duodenum | Jejunum | Ileum | Ileocecal valve | Lymph nodes | Intestinal immune system | Neuromuscular function | Diagrams / tables | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Gulwani H. Anatomy. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/smallbowelnormalanatomy.html. Accessed December 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
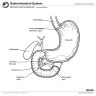
- Small intestine extends from gastric pylorus to ileocaecal valve
- 6 meters long, divided into duodenum, jejunum, ileum
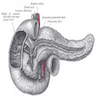
Ampulla
- Ampulla means flask like dilatation (spreading or stretching) of a tubular structure
- May refer to Ampulla of Vater or portion of fallopian tube, vas deferens, semicircular canal or colon
- Vater ("fah-ter") is German anatomist Abraham Vater (1684-1751) who first described this structure
- Usually refers to confluence of distal common bile duct and main pancreatic duct in second portion of duodenum near pancreatic head, although in 42% of patients, ampulla is termination of common bile duct only as the pancreatic duct enters the duodenum separately next to ampulla; in these cases, ampulla may be difficult to locate or nonexistent
- Ampulla is 1.5 cm long or less, traverses duodenal wall, opens into the duodenal lumen through (major) duodenal papilla (papilla of Vater), a 0.5 cm in diameter mucosal elevation with mucosal reduplications (valves of Santorini) that probably prevent regurgitation
- Minor papilla, also called accessory pancreatic duct (APD) of Santorini, is 2 cm proximal and slightly anterior to major papilla
- APD is Patent in 50% cases, pancreatic tissue is noted in 80% of cases in minor papilla (Dig Surg 2010;27:137)
- Ampulla is surrounded by muscular fibers of sphincter of Oddi
- Reference: Dig Surg 2010;27:90
Duodenum
- 25 cm long, from pyloric sphincter to ligament of Treitz, mostly retroperitoneal, fixed in position
- Common bile duct (CBD) and pancreatic duct enter second part of duodenum posteromedially at ampulla of Vater (eMedicine: Duodenal Anatomy [Accessed 9 February 2018)
Jejunum
- 240 cm long, 40% of remainder of bowel, begins at ligament of Treitz
- Has prominent circular mucosal folds (folds of kerckring) that increase absorptive surface
Ileum
- 360 cm long, distal 60% of postduodenal bowel
- Mucosa has transverse folds, prominent in proximal ileum, flat / absent at terminal ileum
Ileocecal valve
- At end of small bowel
- 2 lip structure containing adipose tissue and lymphoid tissue
Lymph nodes
- Duodenum drains to portal and pyloric nodes
- Jejunum and proximal ileum drain to mesenteric nodes and nodes around superior mesenteric artery, terminal ileum drains to ileocolic nodes
- Lacteals are lymphatic channels in villi for chylomicrons
Intestinal immune system
- Peyer patches in ileum (ovoid lymphoid follicles, partly mucosal and partly submucosal, in antimesenteric side of terminal ileum)
- Small intestinal goblet cells, which deliver low molecular weight soluble antigens from intestinal lumen to CD103+ lamina propria dendritic cells, which regulates development of T cells (Nature 2012;483:345)
- M (membranous) cells, part of follicle associated epithelia (MALT) in small bowel and colon, which transfer antigen macromolecules from lumen to lymphocytes
- T cells, usually CD8+ and scattered in surface epithelium
- Lamina propria contains CD4+ T cells and B cells
- Mucosa associated lymphoid tissue: lymphoid nodules, mucosal lymphocytes, appendiceal lymphoid follicles and mesenteric nodes (Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 2000;16:301)
Neuromuscular function
- Anterograde and retrograde peristalsis mixes food and promotes maximal contact of nutrients with mucosa
- Colonic peristalsis prolongs contact with mucosa
- Peristalsis is mediated via myenteric plexus and autonomic innervation (sympathetic thoracolumbar, parasympathetic vagal)
- Also through interstitial cells of Cajal (pacemaker cells) and smooth muscle cells
- Vagal receptors are abundant in duodenum and scattered throughout wall
Diagrams / tables