Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Asgari M, Chen S. Papillary eccrine adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticpapillaryeccrineadenoma.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- A cutaneous glandular neoplasm
- Eccrine or apocrine in origin
- First described by Rulon and Helwig in 1977 (Arch Dermatol 1977;113:596)
- A benign neoplasm (by some) and papillary adenocarcinoma in situ (by others) (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
- May be an analogue of micropapillary ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast
Essential features
- Solitary nodule, mostly in lower extremity of young black women
- Well circumscribed in the dermis, composed of tubules with intraluminal papillary, micropapillary or cribriform and peripheral flat myoepithelial cells
- Nuclear hyperchromasia, single cell necrosis and mitotic figures present
Terminology
- Called tubulopapillary hidradenoma by Falck and Jordaan in 1986 (Am J Dermatopathol 1986;8:64)
- Considerable overlap with apocrine tubular adenoma; may be part of the same spectrum (Am J Dermatopathol 1992;14:149, Am J Dermatopathol 1993;15:482)
- Significant similarities with nipple adenoma (Hum Pathol 2018;73:59)
- Papillary adenocarcinoma in situ was proposed in 2014 (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Usually occurs in young people
- Blacks > whites
- Women > men
Sites
- Usually extremities, lower more than upper
Pathophysiology
- Poorly understood; may be associated with nevus sebaceus
- Similar to nipple adenoma, BRAF V600E and KRAS mutations were frequently reported (Hum Pathol 2018;73:59)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Solitary (almost always)
- Flesh-colored papule or nodule
- Dermal based neoplasm
- May mimic a basal cell carcinoma (J Am Acad Dermatol 2014;71:e45)
Diagnosis
- Incisional or excisional biopsy should be performed with histologic examination for a definite diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- Excellent prognosis; no recurrence following simple conservative complete excision
- Can have recurrence / persistence after incomplete removal
Case reports
- 35 year old Caucasian man with heel tumor (J Foot Ankle Surg 2000;39:249)
- 45 year old African American man with papillary eccrine adenoma (J Dermatol Sci 1990;1:65)
- 52 year old woman with foot lesion (Am J Dermatopathol 1993;15:150)
- 63 year old woman with thigh tumor (Dermatologica 1991;182:47)
- 4 cases of papillary adenocarcinoma in situ of the skin (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
Treatment
- Simple surgical excision
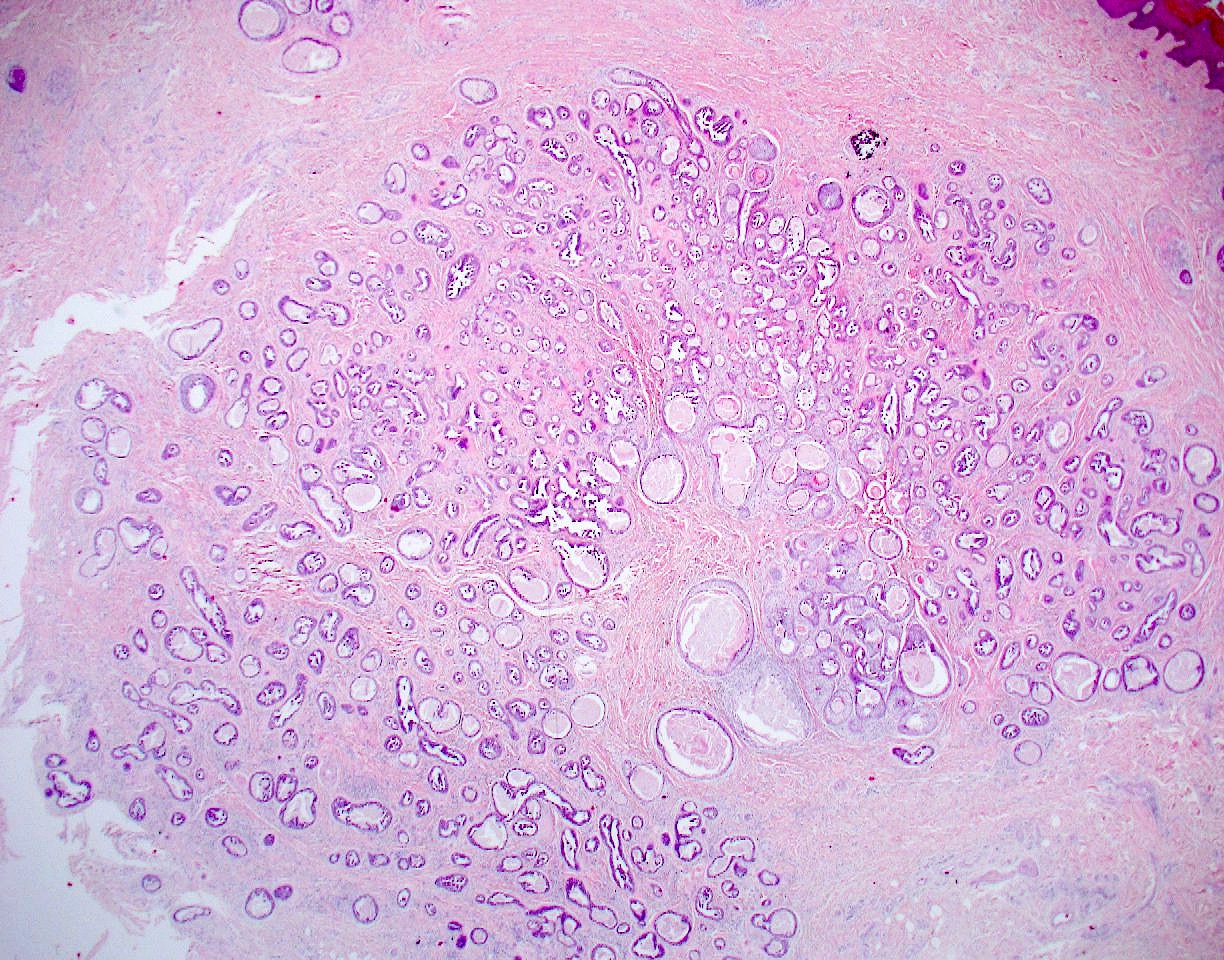
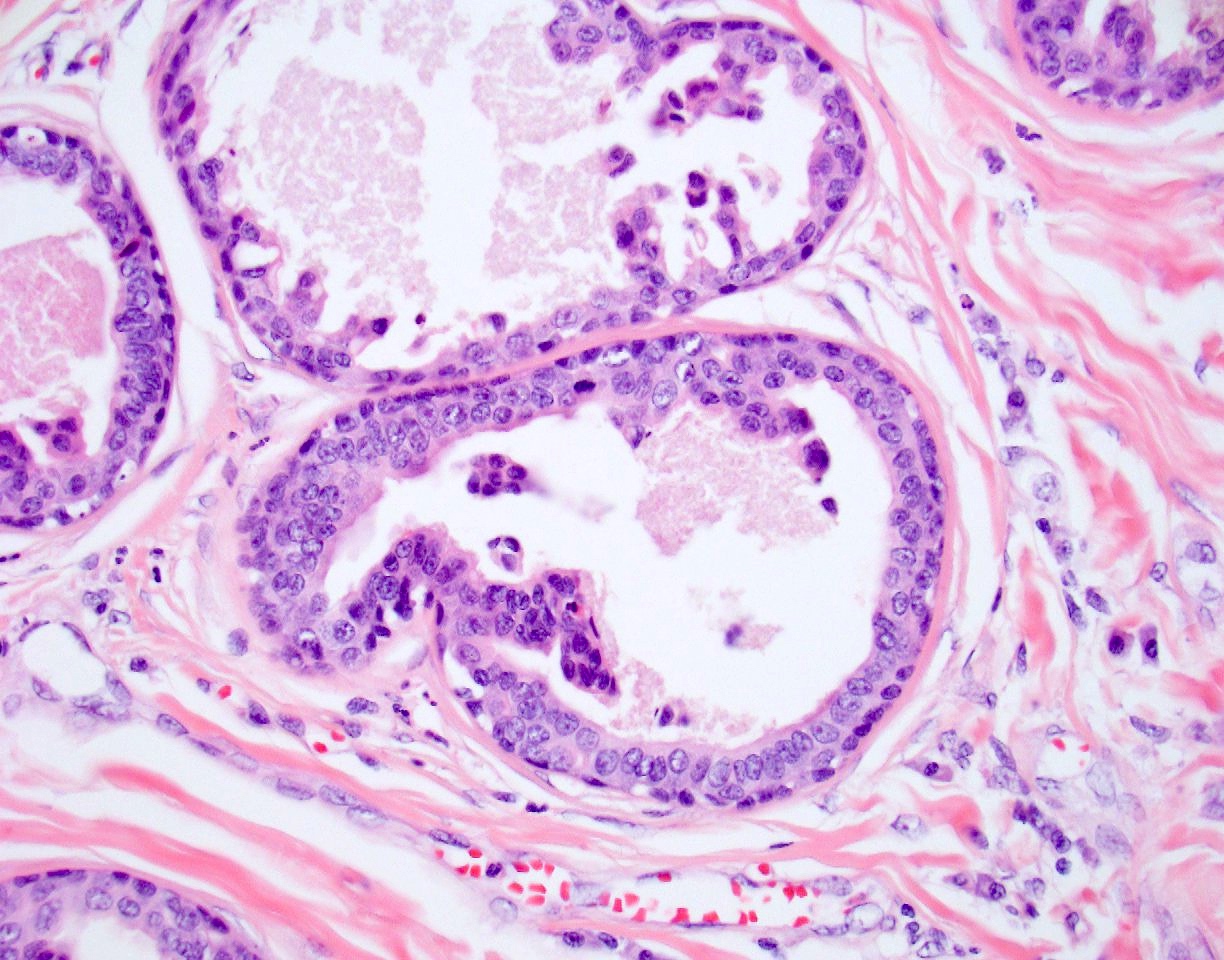
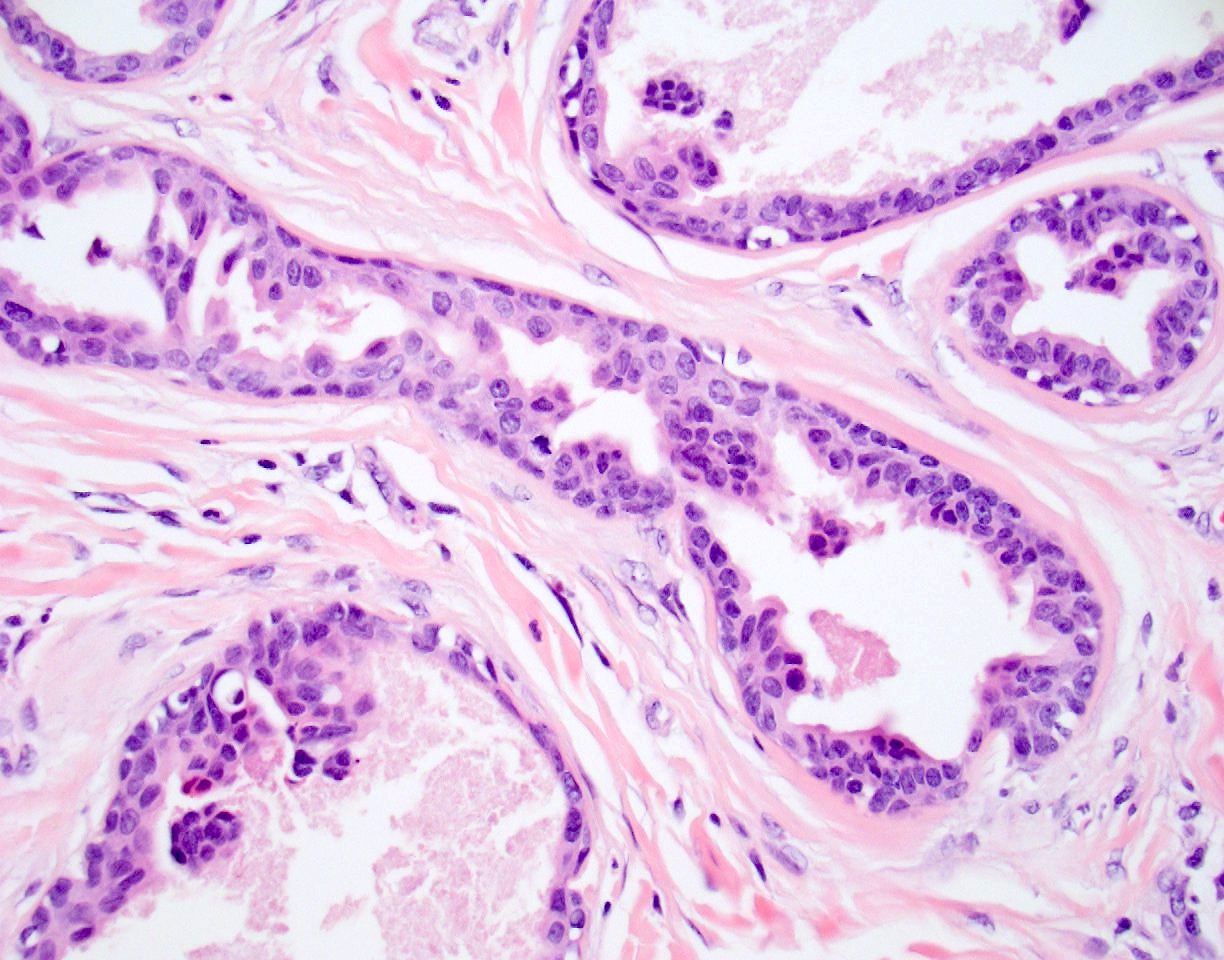
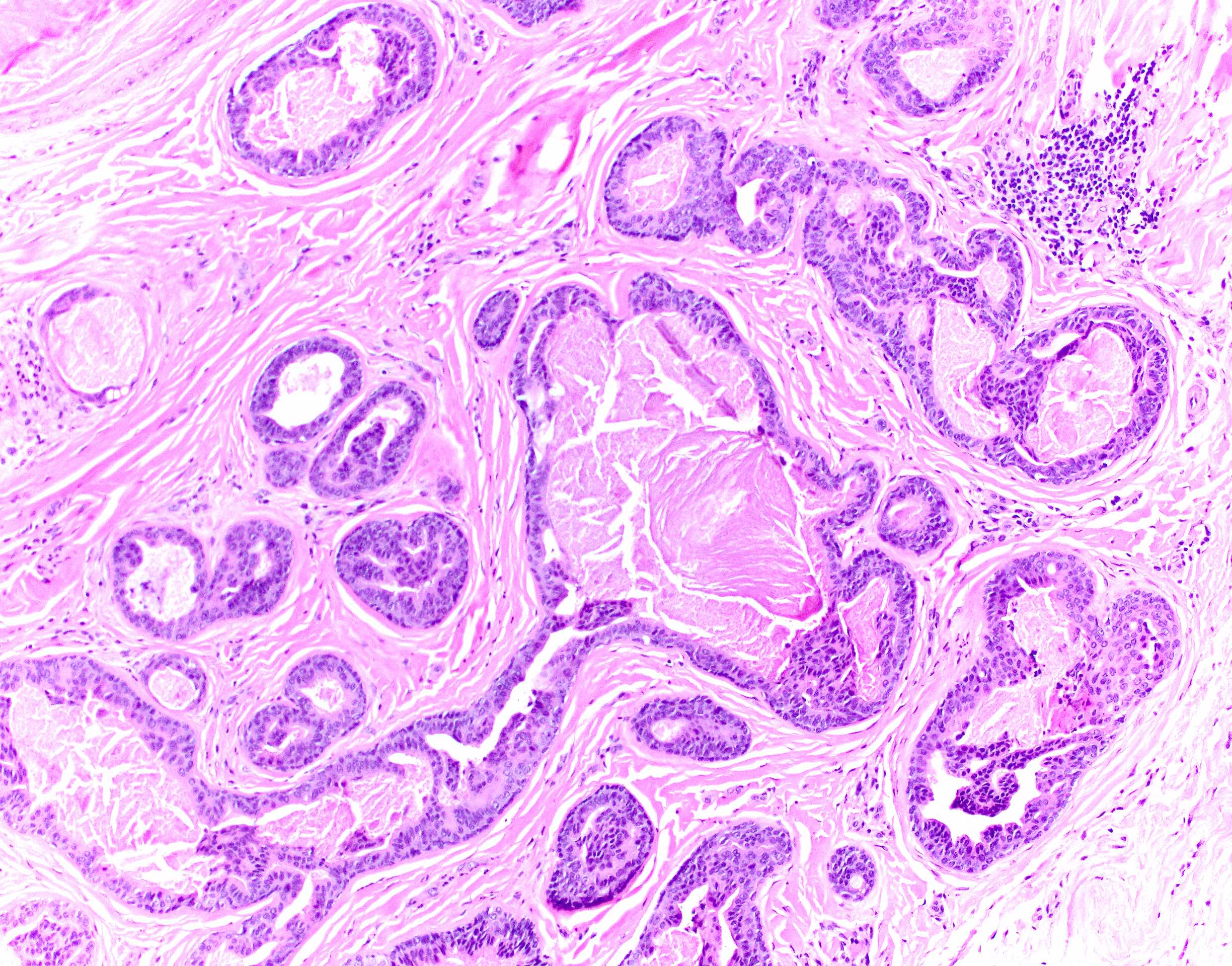
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nodular, well circumscribed and often asymmetrical from scanning magnification
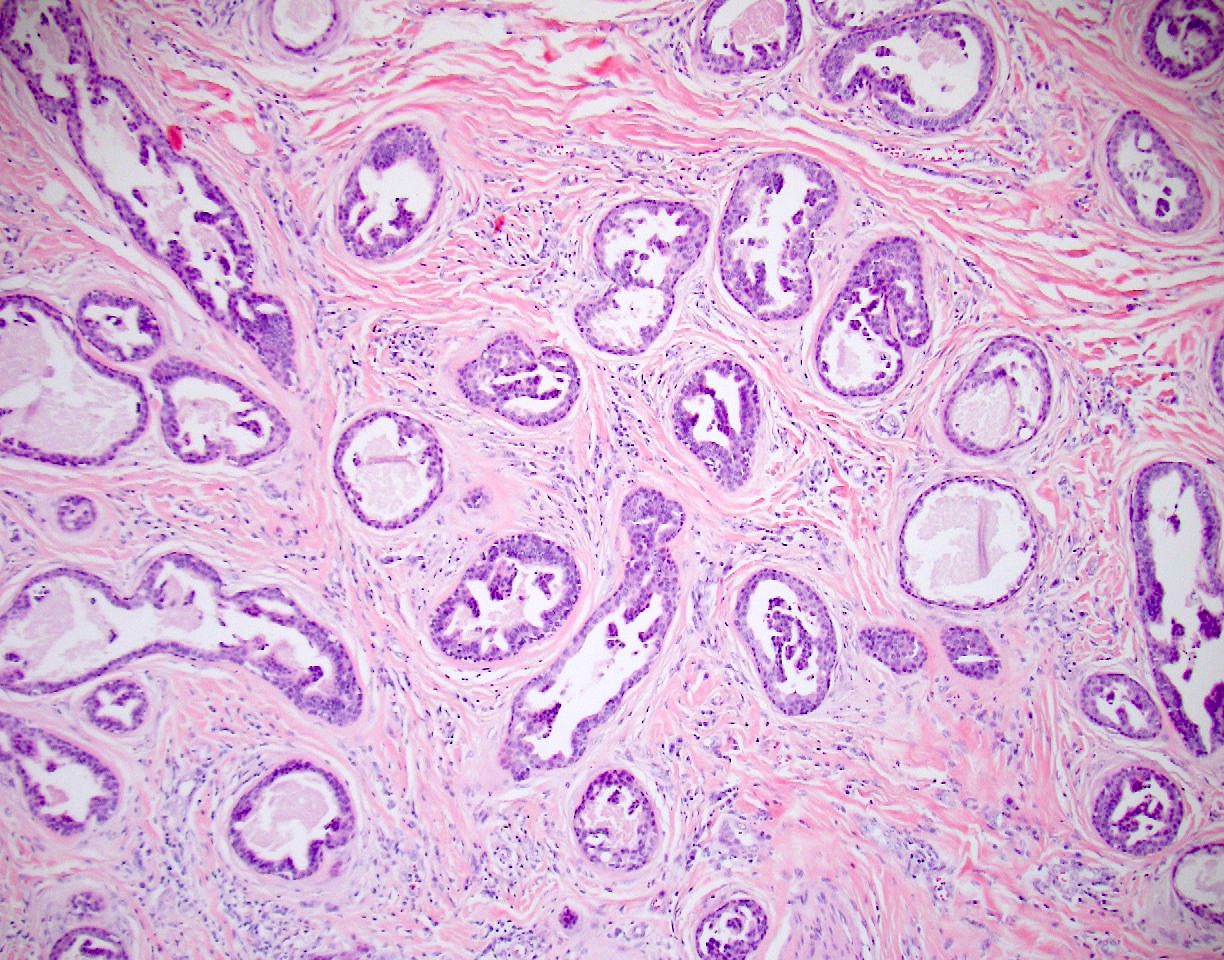
- Tubular or cystic structures with intraluminal papillary, micropapillary or cribriform growth (common)
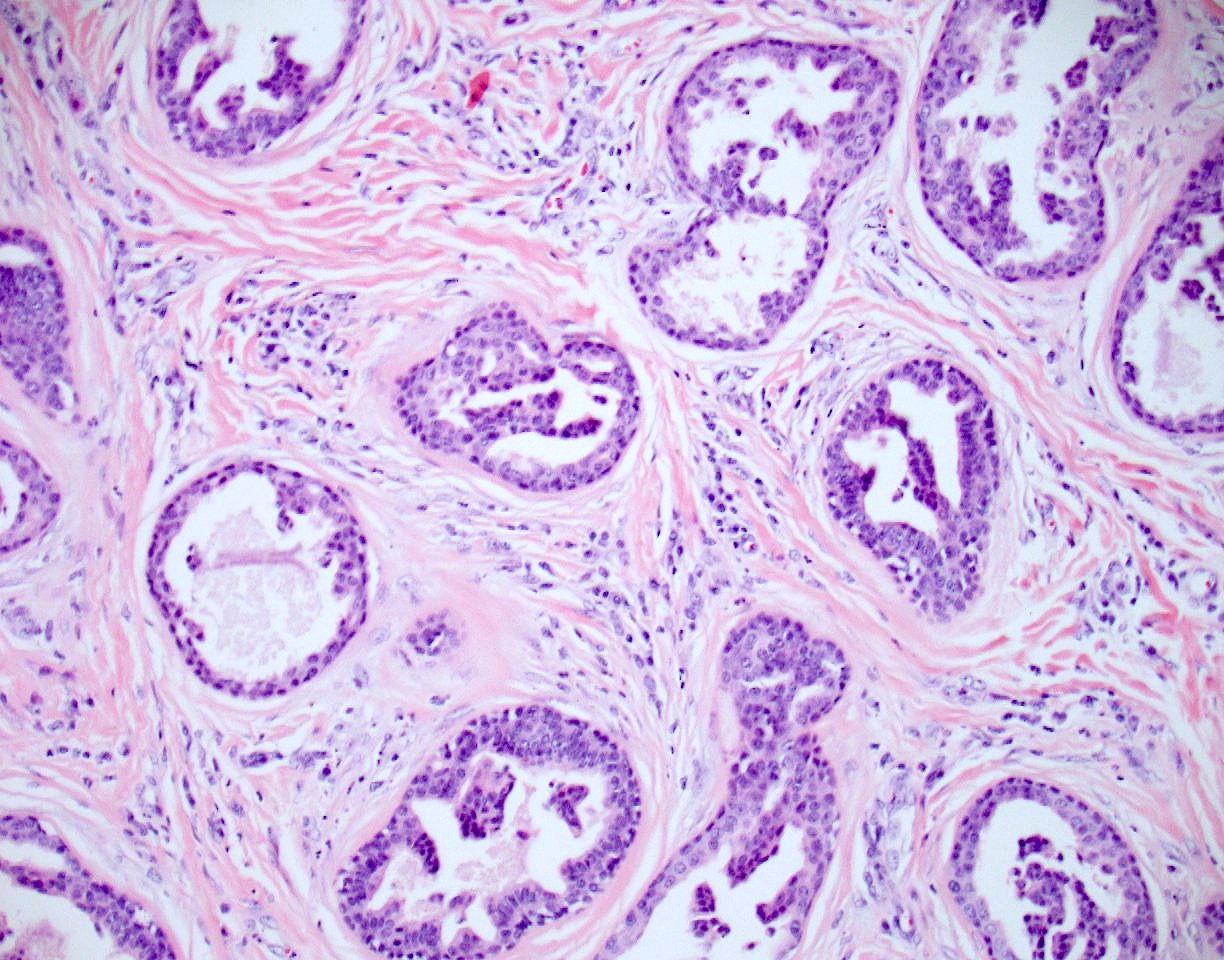
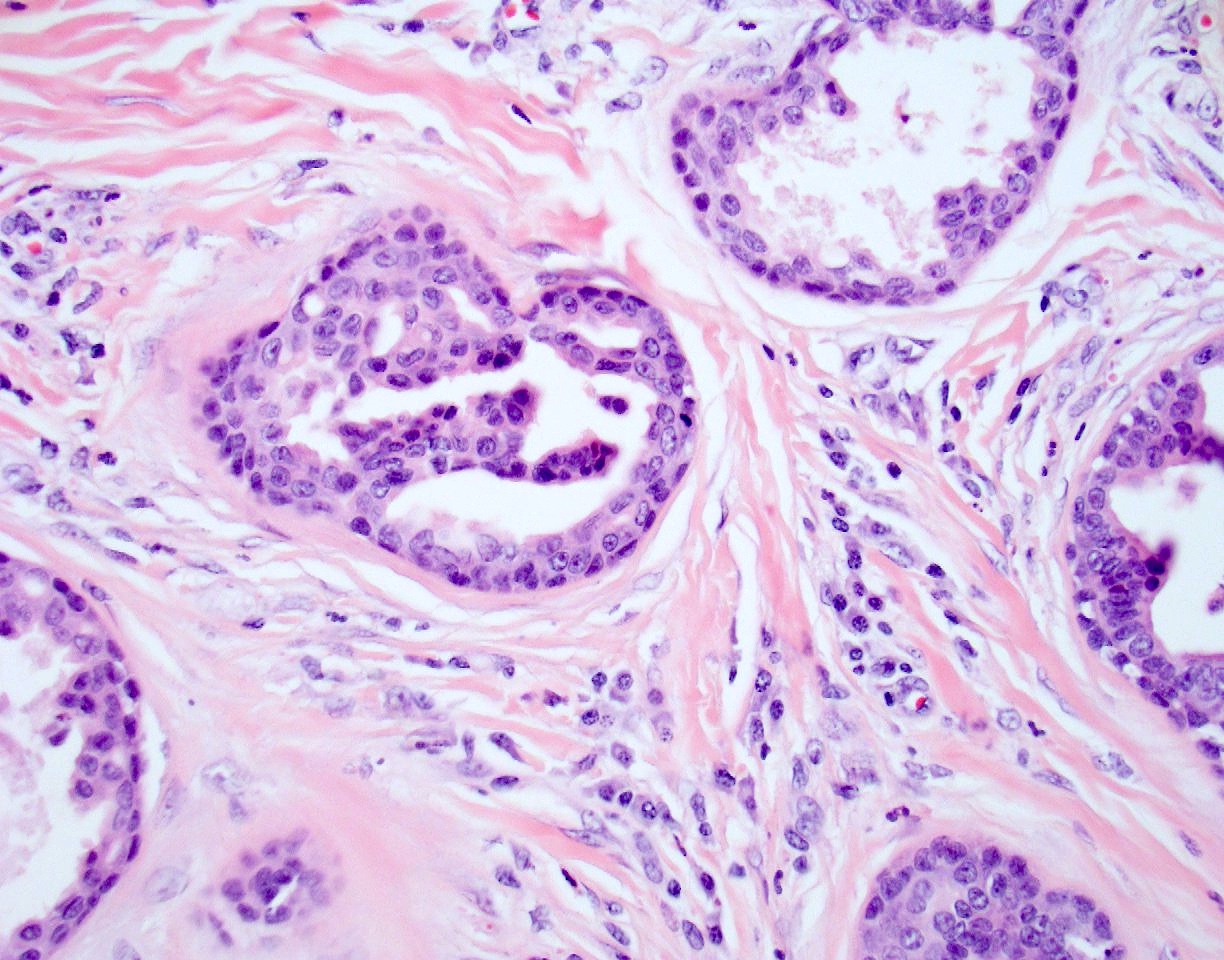
- Ductal lining is bilayered with luminal cuboidal cells and peripheral flat myoepithelial cells
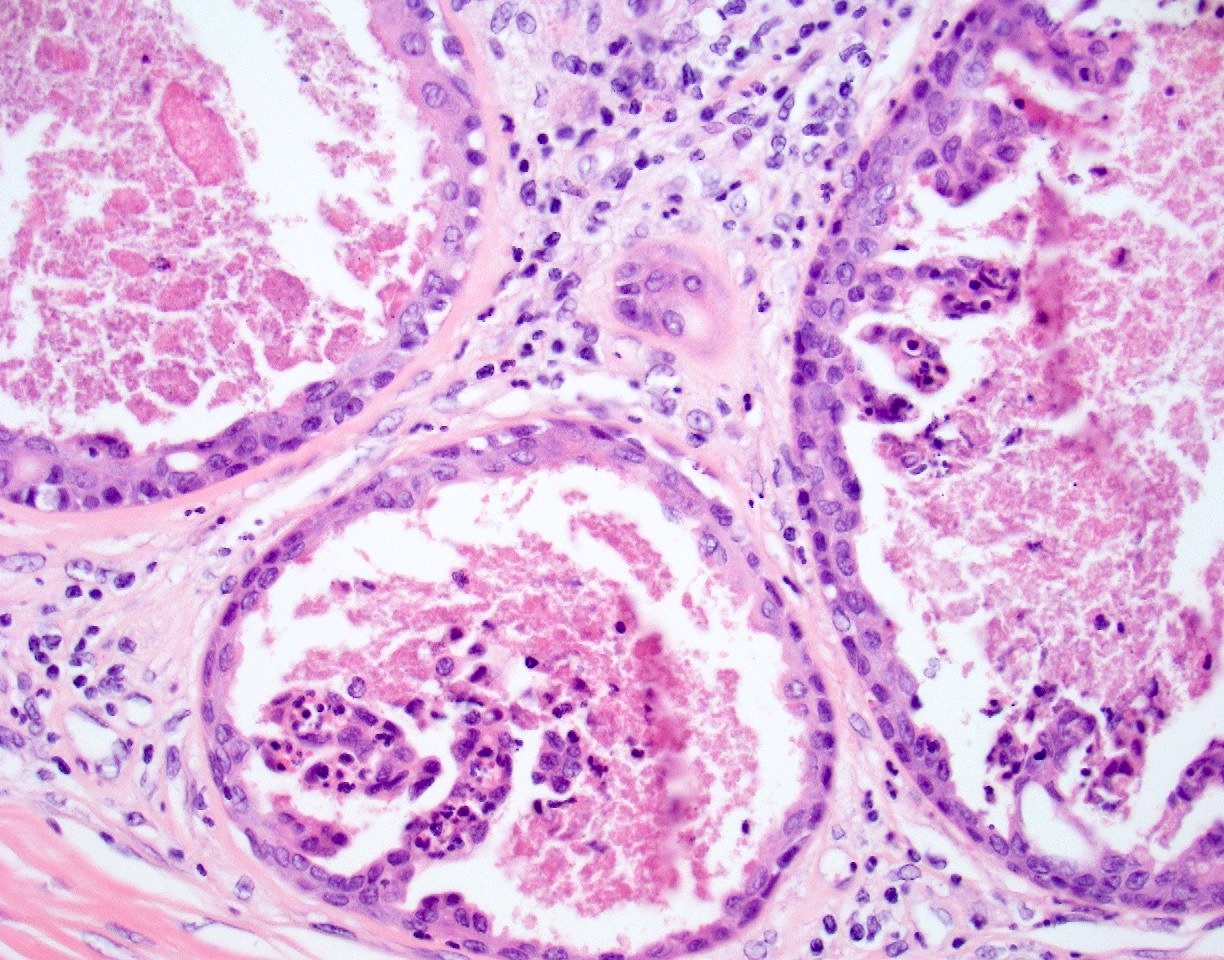
- Occasional findings
- Variable clear cell change and squamous differentiation
- Nuclear hyperchromasia (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
- Mitotic figures (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
- Necrosis of single cells or necrosis en masse (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
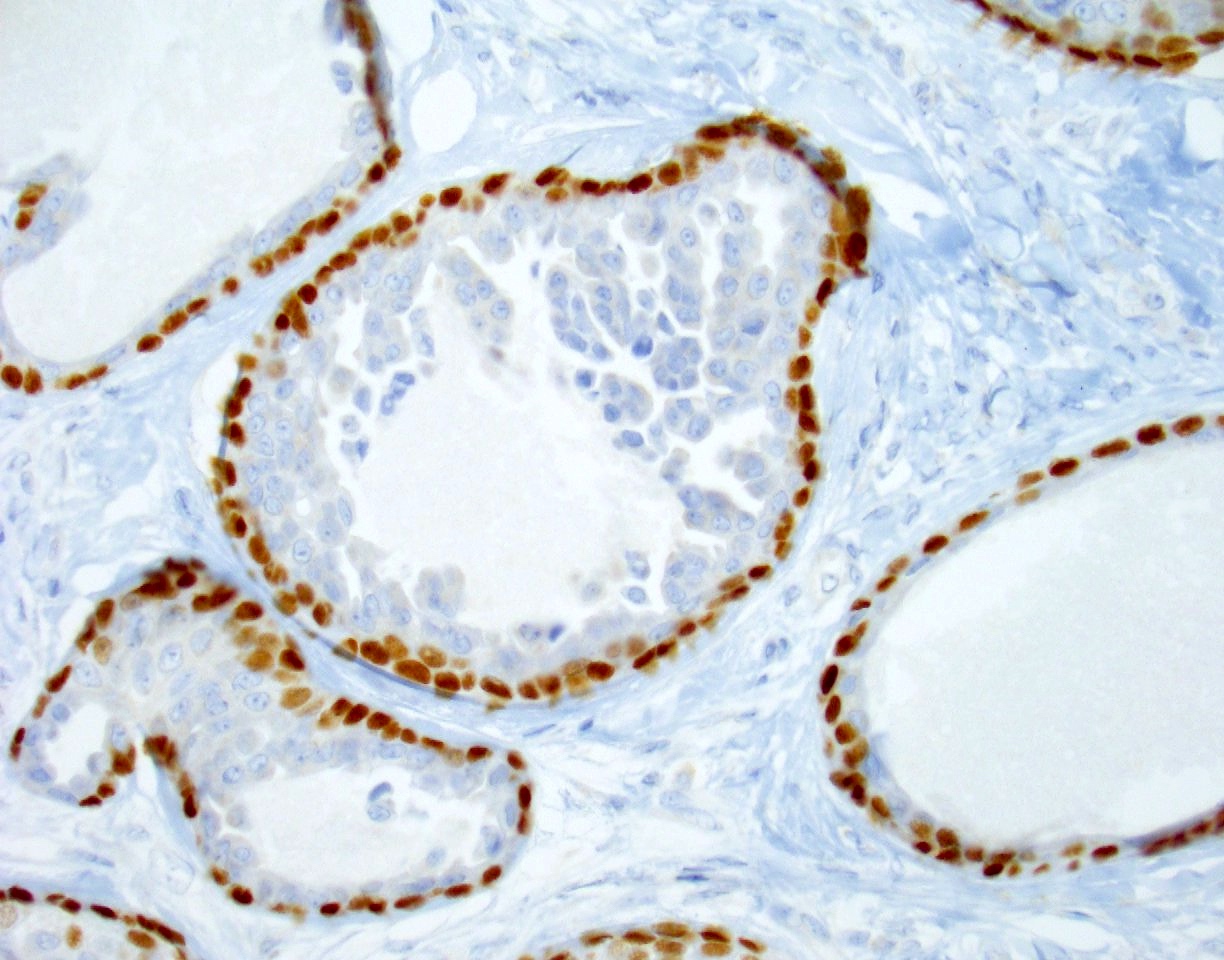
- Inner epithelial cells: EMA, CAM 5.2, CK7, CK8, CEA (Clin Exp Dermatol 1990;15:425, J Cutan Pathol 1998;25:59)
- Outer myoepithelial cells: S100, calponin, p63, CK14 and SMA (J Cutan Pathol 1998;25:59)
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Cells of the inner layer have features of eccrine secretory (clear) cells
- Cells of the outer layer have characteristics of both ductal basal cells and glandular myoepithelial cells (J Dermatol Sci 1990;1:65)
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right foot, excision:
- Papillary glandular neoplasm (see comment)
- Margins negative for tumor
- Comment: The findings are consistent with a papillary eccrine adenoma (also called papillary adenocarcinoma in situ).
Differential diagnosis
- Aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma:
- Digit predilection, more cellularity, solid growth, proliferation of both epithelial and myoepithelial cells (epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma) (Clin Exp Dermatol 2014;39:223, J Cutan Pathol 2017;44:410, Am J Dermatopathol 2018;40:152)
- Microcystic adnexal carcinoma:
- Face predilection, infiltrative, deep involvement, multiple keratin cysts, perineural invasion
- Syringocystadenoma papilliferum:
- Face predilection, squamous and glandular epithelium, decapitation secretion, many plasma cells, usually associated with nevus sebaceus
- Hidradenoma papilliferum:
- Female genital predilection, packed elongated tubular structures, decapitation secretion
- Nipple adenoma:
- Nipple location, fundamentally the same
- Papillary adenocarcinoma:
- Infiltrative, loss of myoepithelial cells at least in some foci (Dermatol Pract Concept 2014;4:23)
Board review style question #1
A 41 year old African American woman with a solitary, 1 cm nodule localized on the right leg comes to the office. Incisional biopsy was performed and the findings are illustrated above. Which of the following statements regarding this neoplasm is correct?
- Identical features may be seen in nipple adenoma
- It is composed of solid proliferation of both myoepithelial cells and epithelial cells
- Many plasma cells are present
- Myoepithelial cell layer may be absent at the periphery of some tubular structures
- This is an aggressive neoplasm with a high rate of metastasis (15%)
Board review style answer #1
A. Identical features may be seen in nipple adenoma. This is a papillary eccrine adenoma. Nipple adenoma and papillary eccrine adenoma have identical histopathologic features and therefore choice A is correct. So called papillary eccrine adenoma is not an aggressive neoplasm (choice E) but it may recur if it is not completely excised. The lesion was initially considered benign and called adenoma by Rulon and Helwig on the basis of available follow up information. However, adenocarcinoma in situ, when completely removed, behaves in the same way, namely, no recurrence or metastasis. Choice B is a cardinal feature of so called aggressive digital papillary adenocarcinoma. Choice C is a feature of syringocystadenoma papilliferum. Choice D may suggest an invasive focus within the neoplasm, given the absence of myoepithelial layer around some tubular structures.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary eccrine adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary eccrine adenoma
Board review style question #2
Which of the following gene mutations is usually seen in papillary eccrine adenoma?
- BRAF V600E
- CYLD1
- FLCN
- MLH1
- PTCH
Board review style answer #2
A. BRAF V600E. Mutation in BRAF V600E is frequently seen in papillary eccrine adenoma, similar to its analogue nipple adenoma. Mutation in CYLD1 is usually seen in cylindroma. Mutation in PTCH is usually seen in adenoid basal cell carcinoma. Mutations in MMR genes (such as MLH1, MSH2, MSH6 and PMS2) are associated with sebaceous carcinoma. FLCN may be mutated in fibrofolliculoma / trichodiscoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary eccrine adenoma
Comment Here
Reference: Papillary eccrine adenoma