Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Regmi A, Speiser J. Dermoid cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skintumornonmelanocyticdermoidcyst.html. Accessed December 22nd, 2024.
Definition / general
- Benign cutaneous developmental anomaly
- Arises from the entrapment of ectodermal elements along the lines of embryonic closure
Essential features
- Derived from both ectoderm (stratified squamous epithelium) and mesoderm (cutaneous adnexal structures)
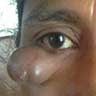
- Most commonly on the lateral aspect of the upper eyelid
- Can be complicated by intracranial involvement
- Total resection of the cyst, along with the adhesions and sinuses, is crucial
Terminology
- Cystic teratoma (not true teratoma), nasal dermoid sinus cyst (when located in sinus)
ICD coding
- ICD-10: D23.9 - other benign neoplasm of skin, unspecified
Epidemiology
- One of the most common pediatric skull tumors
- Accounts for about 15.4 - 58.5% of all scalp and skull masses in pediatric patients (World Neurosurg 2018;120:119)
- Incidence roughly 3 per 10,000 pediatric patients
- Mostly are congenital (40%) but not all of them are diagnosed at birth
- About 60% of cases discovered in children 5 years old or younger (World Neurosurg 2018;120:119, Pediatr Dermatol 2013;30:706)
- Cases in adulthood have also been reported (World Neurosurg 2018;120:119)
- No significant predominance for sex and race
Sites
- Most common: lateral aspect of the upper eyelid (Pediatr Dermatol 2019;36:999)
- Other: midline of neck, nasal root, nose, forehead, the mastoid area, anterior chest and scalp (J Pediatr Surg 1990;25:294)
- Rare: mid chest, sacrum, perineum, scrotum, penis and ear (Pediatr Dermatol 2013;30:706)
Pathophysiology
- Results from incomplete closure of the neural tube during the third to fifth week of fetal development (Case Rep Neurol Med 2021;2021:9917673)
- Arises from traumatic sequestration of cutaneous tissues along the embryonal lines of closure (Pediatr Dermatol 2019;36:999)
- Derived from both ectoderm (stratified squamous epithelium) and mesoderm (cutaneous adnexal structures)
- Trichilemmal differentiation rarely seen in the lining of the cyst (Ophthalmic Plast Reconstr Surg 2017;33:e116)
- Some authors propose an embryological origin for these cysts, particularly in the nasal form (Cleft Palate Craniofac J 2005;42:51)
Etiology
- Mostly unknown
Clinical features
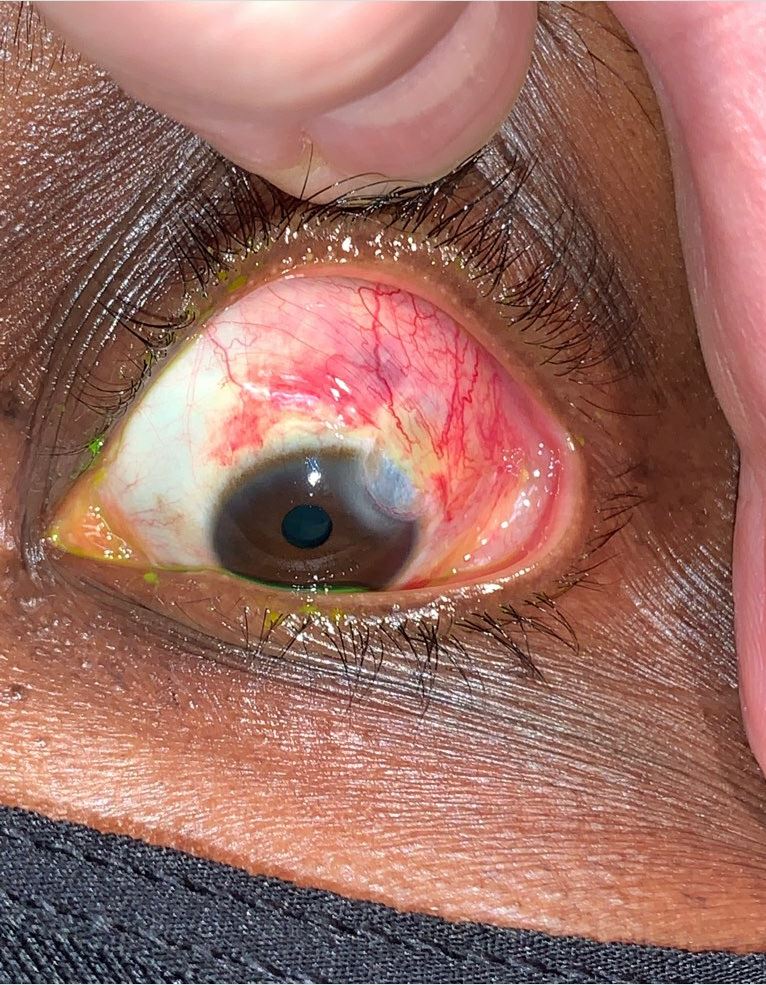
- Usually a solitary, pale to flesh colored, nontender, noncompressible, firm, nonpulsatile, deep seated, predominantly subcutaneous nodule (Pediatr Dermatol 2019;36:999)
- Hair protruding from a cyst is pathognomonic (Cleft Palate Craniofac J 1991;28:87)
- May lie dormant for a period of time and then grow and become clinically manifest because of enlargement, rupture or sometimes extension to surrounding structures (World Neurosurg 2018;120:119)
Diagnosis
- Based on clinical features, imaging modalities and histopathological findings
Radiology description
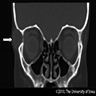
- CT imaging is better at delineating the changes in bony erosions
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is the preferred means of revealing evidence of intracranial extension
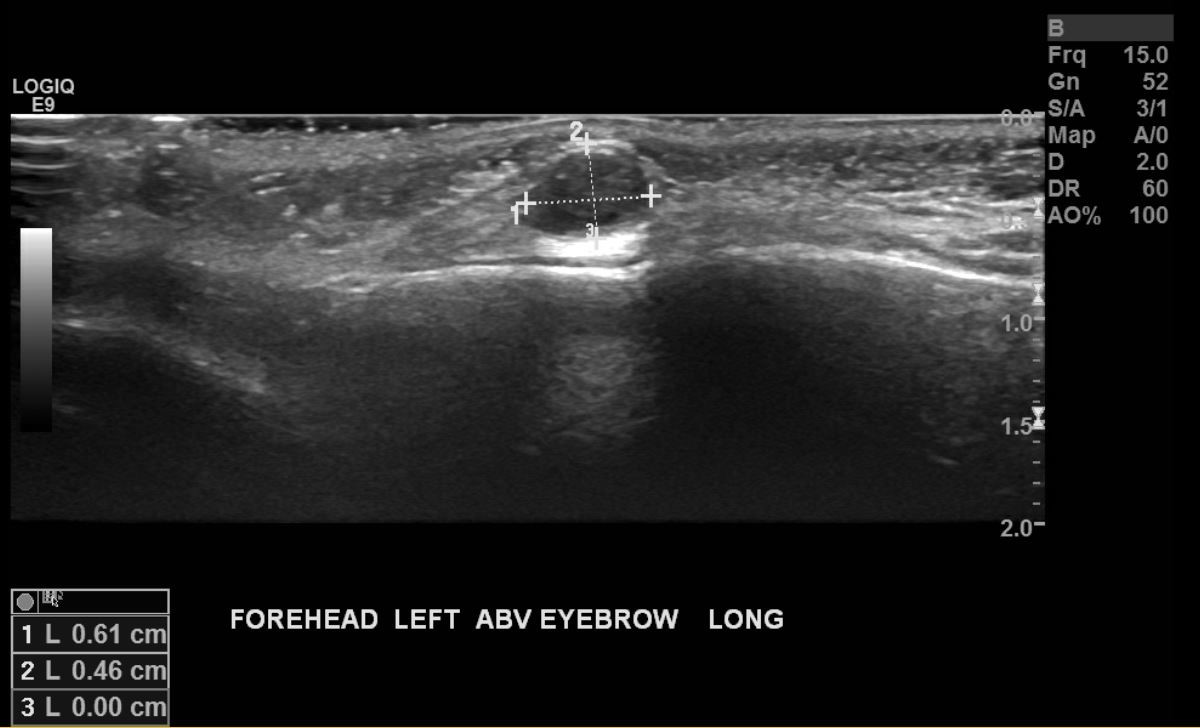
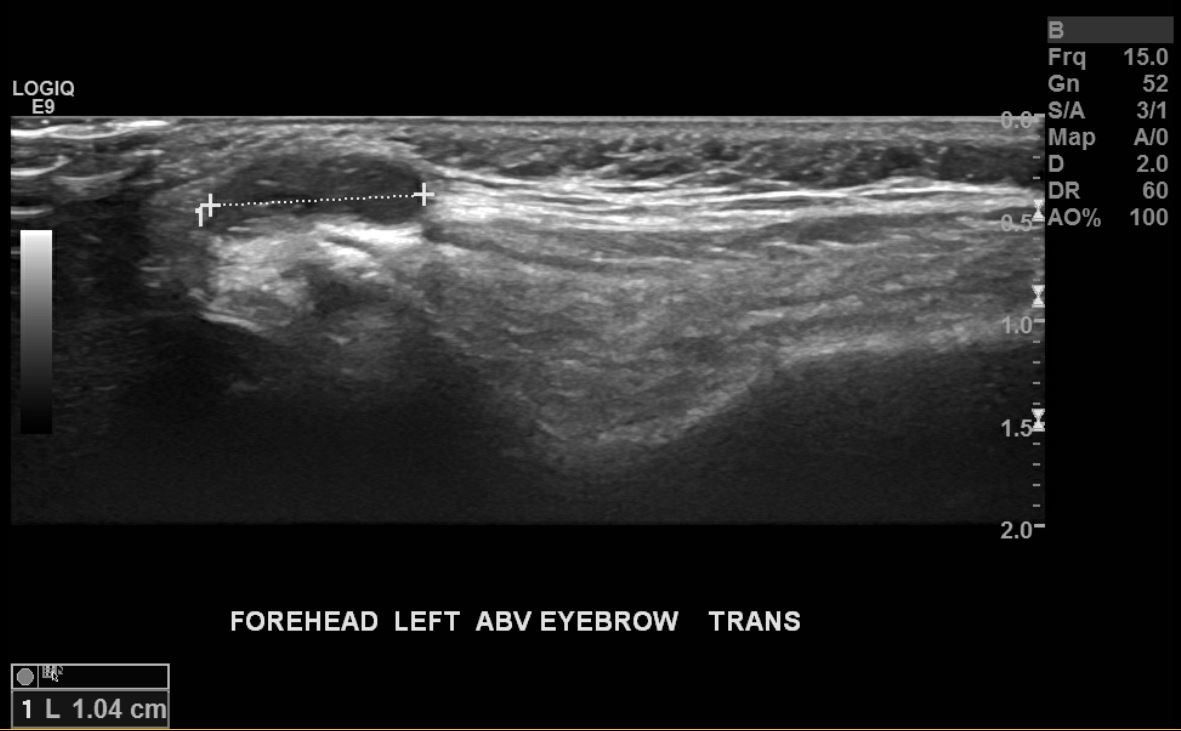
- Ultrasound (USG) demonstrates a well defined homogenous and hypoechoic cystic lesion
- Radiological features include characteristic signal intensities, absence of perilesional edema and the presence of well defined margins to the cyst (Case Rep Neurol Med 2021;2021:9917673)
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Overall prognosis good, especially when there is no intracranial or intraspinal extension (Pediatr Dermatol 2013;30:706)
- Aspiration or biopsies have the potential to cause infection, further leading to osteomyelitis, meningitis or cerebral abscess (Case Rep Neurol Med 2021;2021:9917673, J Pediatr Surg 1990;25:294)
- Squamous cell carcinoma very rarely develops in the wall of the cyst (Int Orthop 1995;19:185)
- Rarely, the development of carcinosarcoma has been described (J Med Case Rep 2017;11:11)
Case reports
- 14 year old boy with a painless swelling in left upper part of chest wall of 2 years' duration (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e228831)
- 22 year old woman with a gradually enlarging mass in the right retroauricular region (Acta Biomed 2021;92:e2021075)
- 40 year old woman with a painless swelling of the lower eyelid of 20 years' duration (BMJ Case Rep 2013;2013:bcr2013200686)
- 42 year old Sri Lankan Tamil man presented with a large cystic swelling in his submental region (J Med Case Rep 2017;11:11)
- 75 year old man presented with a soft, painless mass on his left upper back (Radiol Case Rep 2021;16:1127)
- 15 cases of orbital dermoids representing 6% of orbital tumors (Br J Ophthalmol 1984;68:642)
Treatment
- Complete surgical resection is the treatment of choice
- Imaging done prior to determine the extent of underlying tissue involvement
- Resected carefully to avoid spilling of contents intracranially
- Recurrences have been reported in case of incomplete excision (Pediatr Dermatol 2013;30:706)
Clinical images
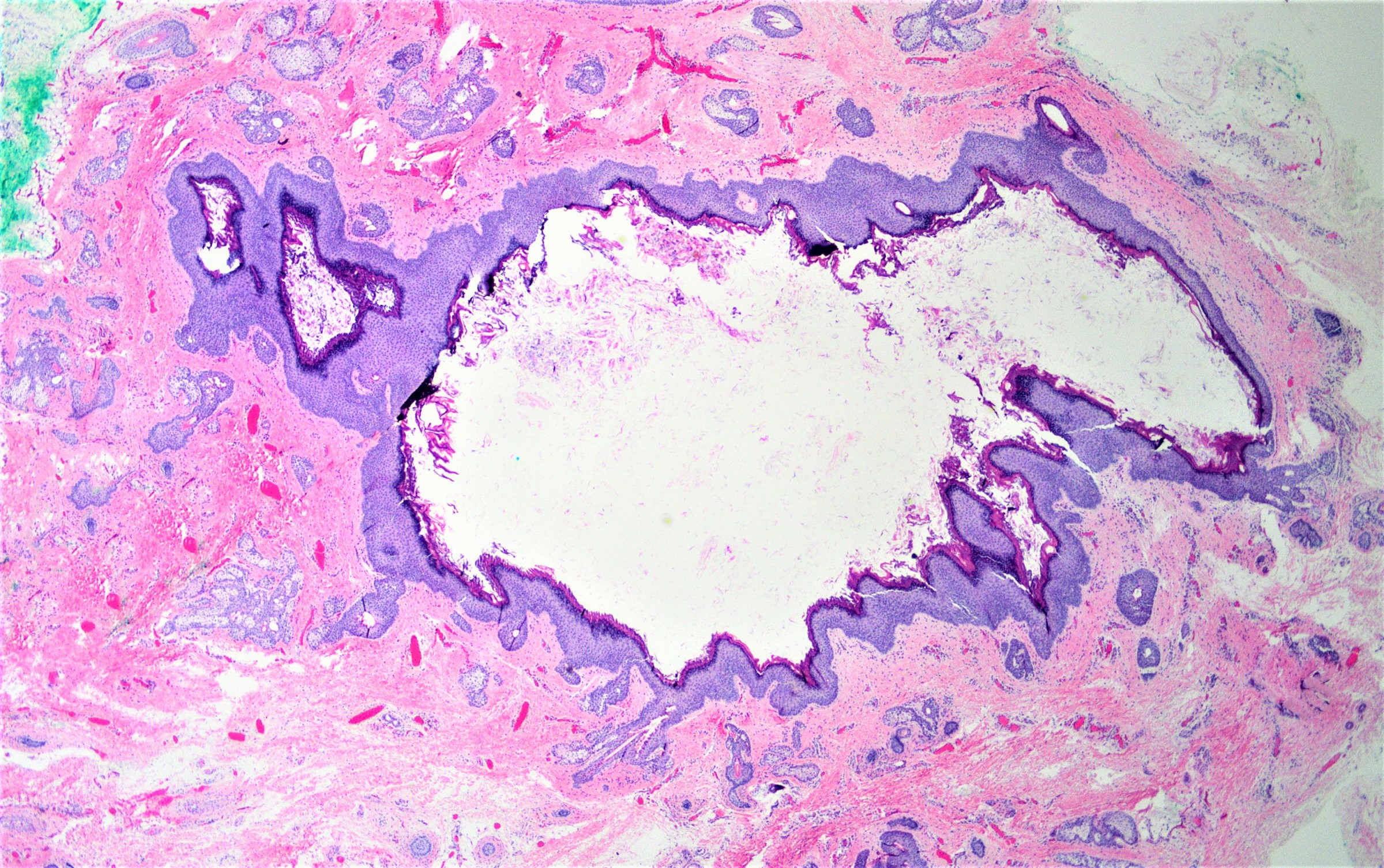
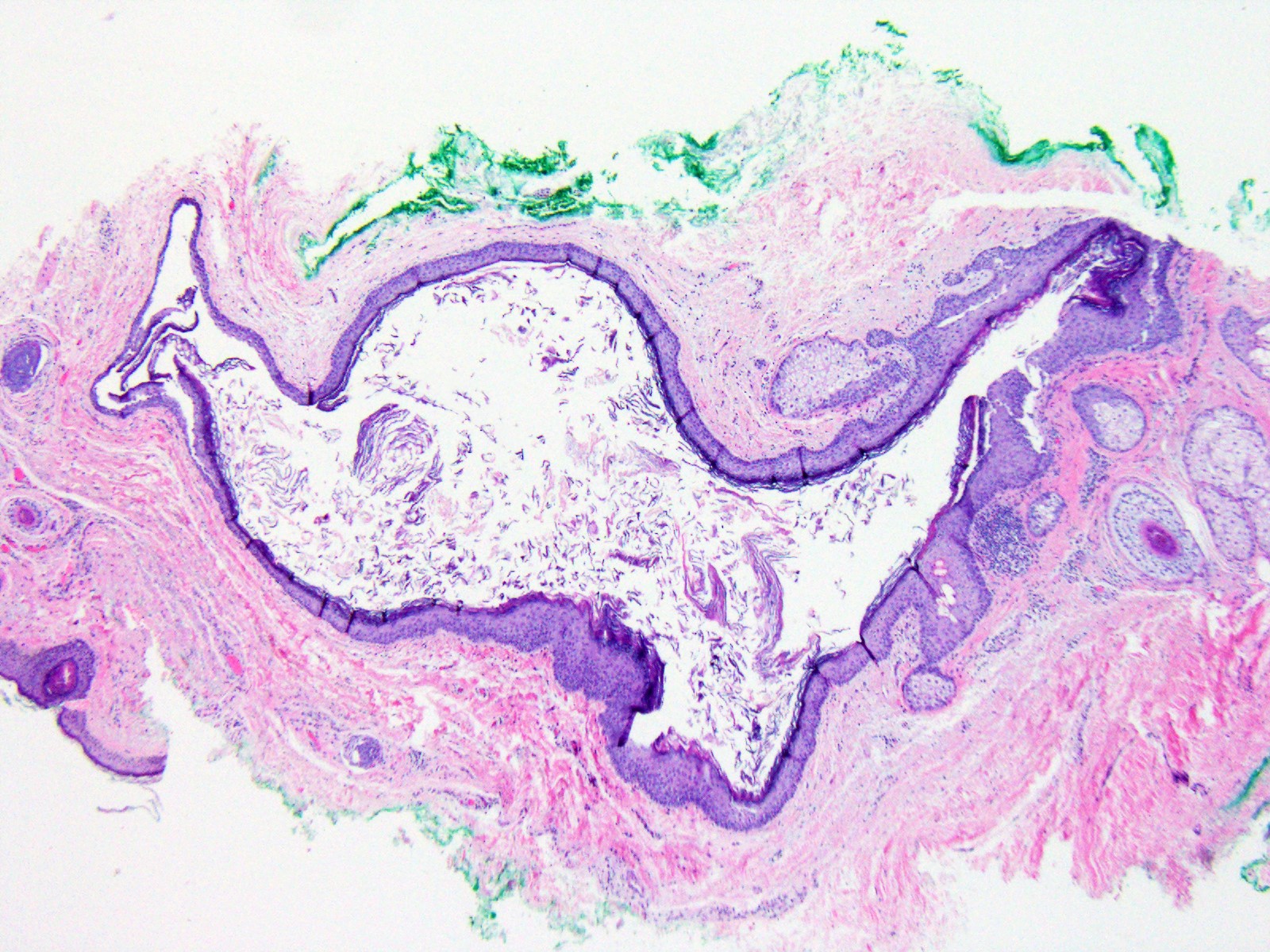
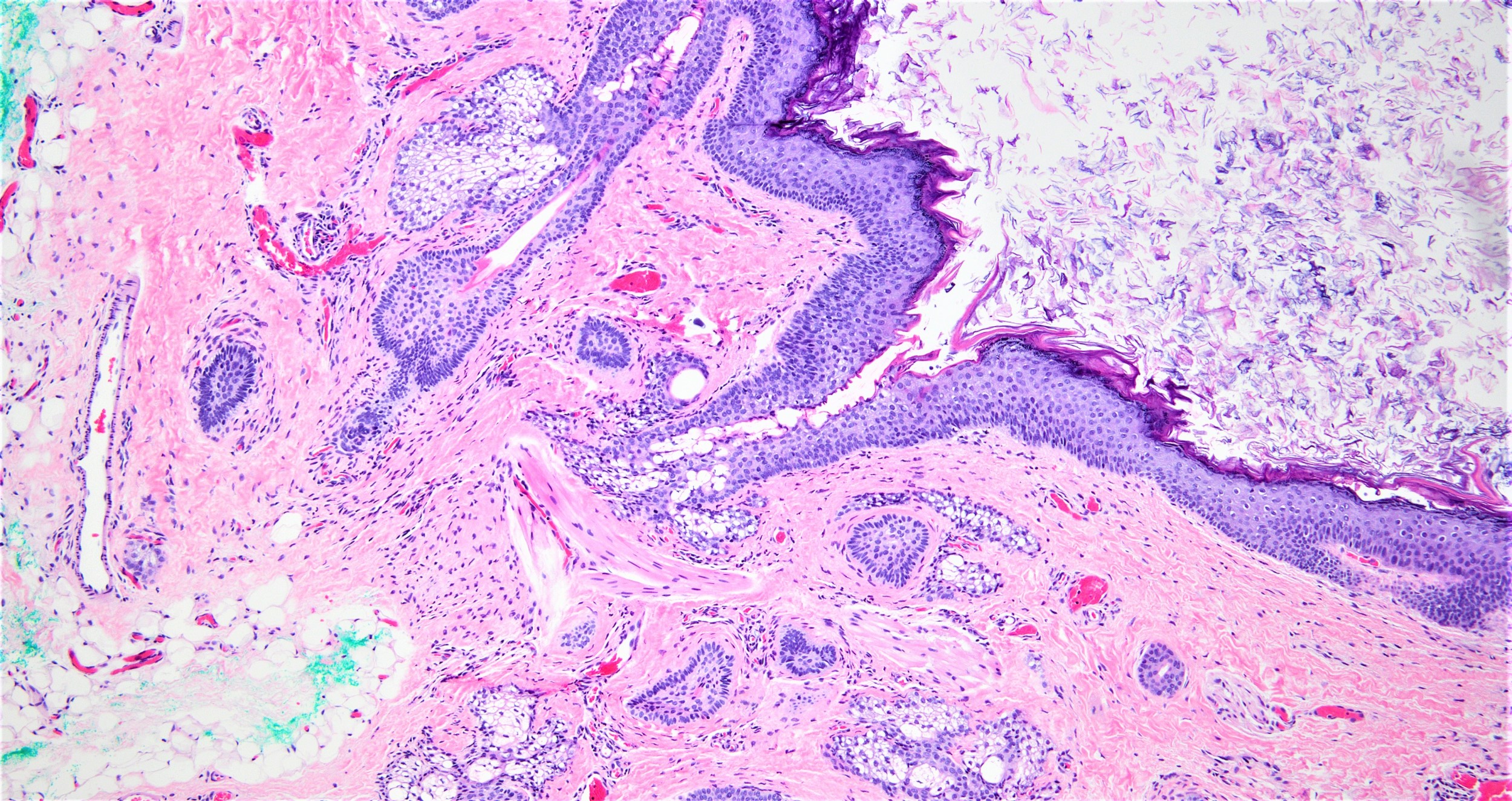
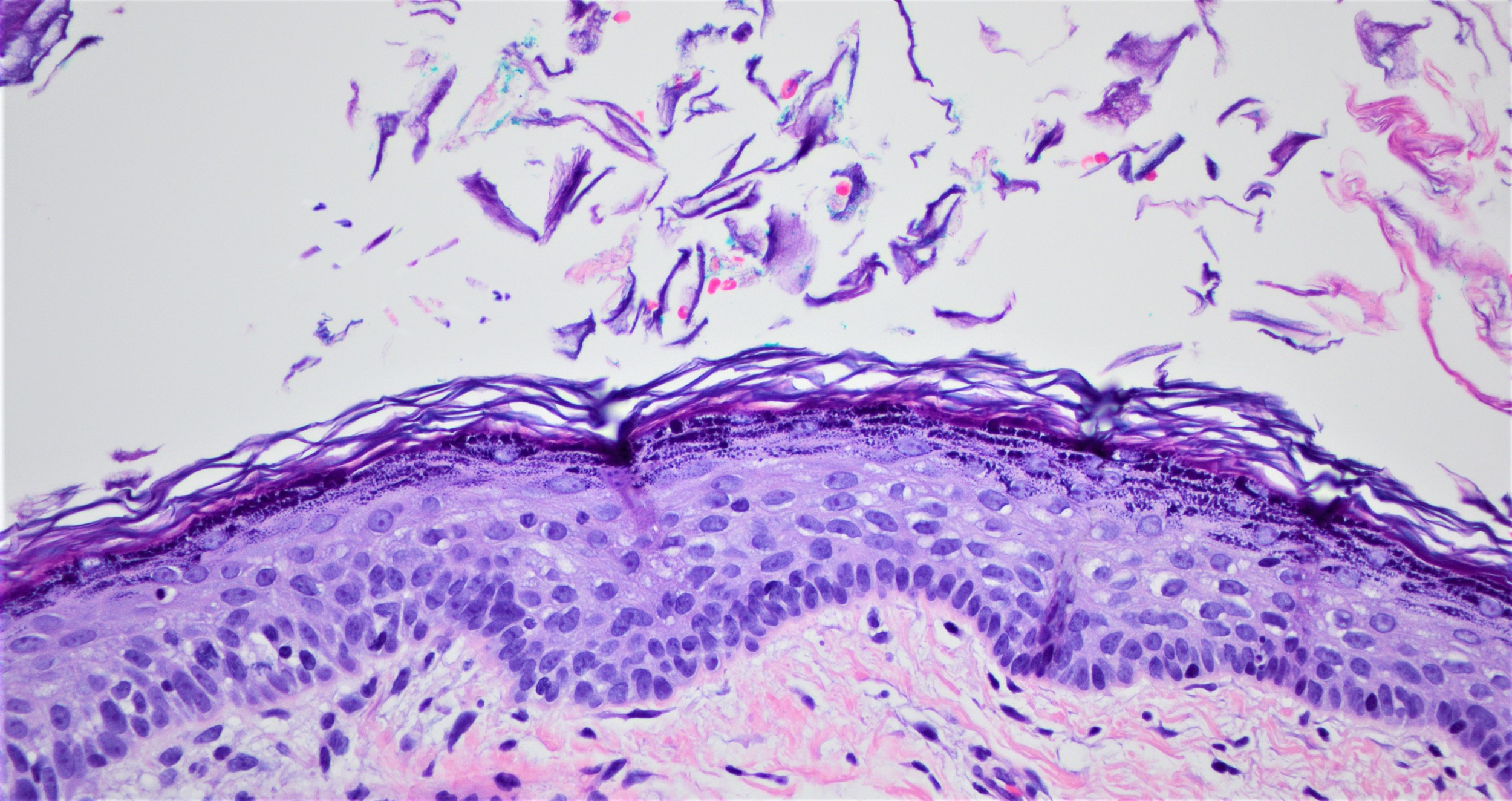
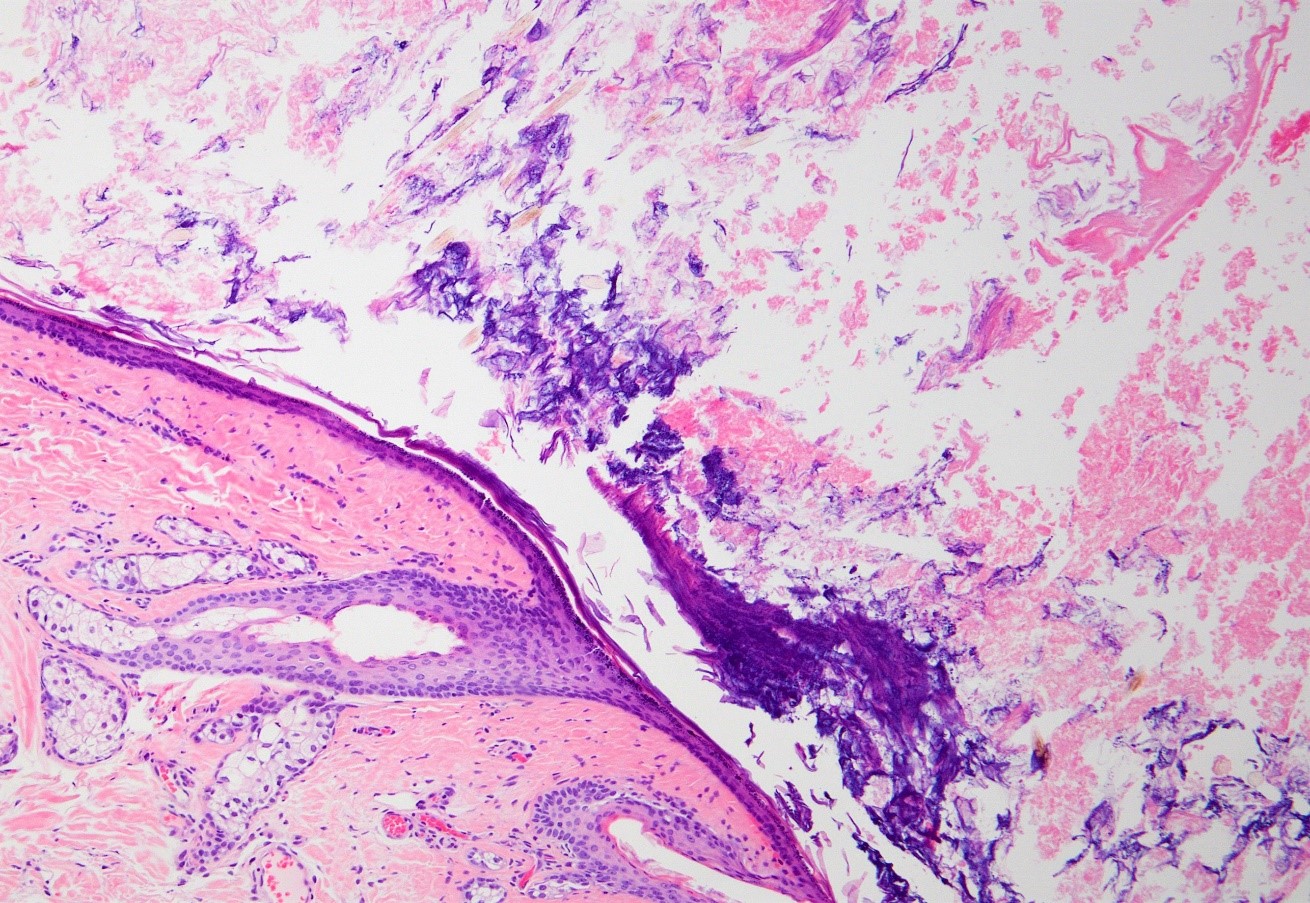
Microscopic (histologic) description
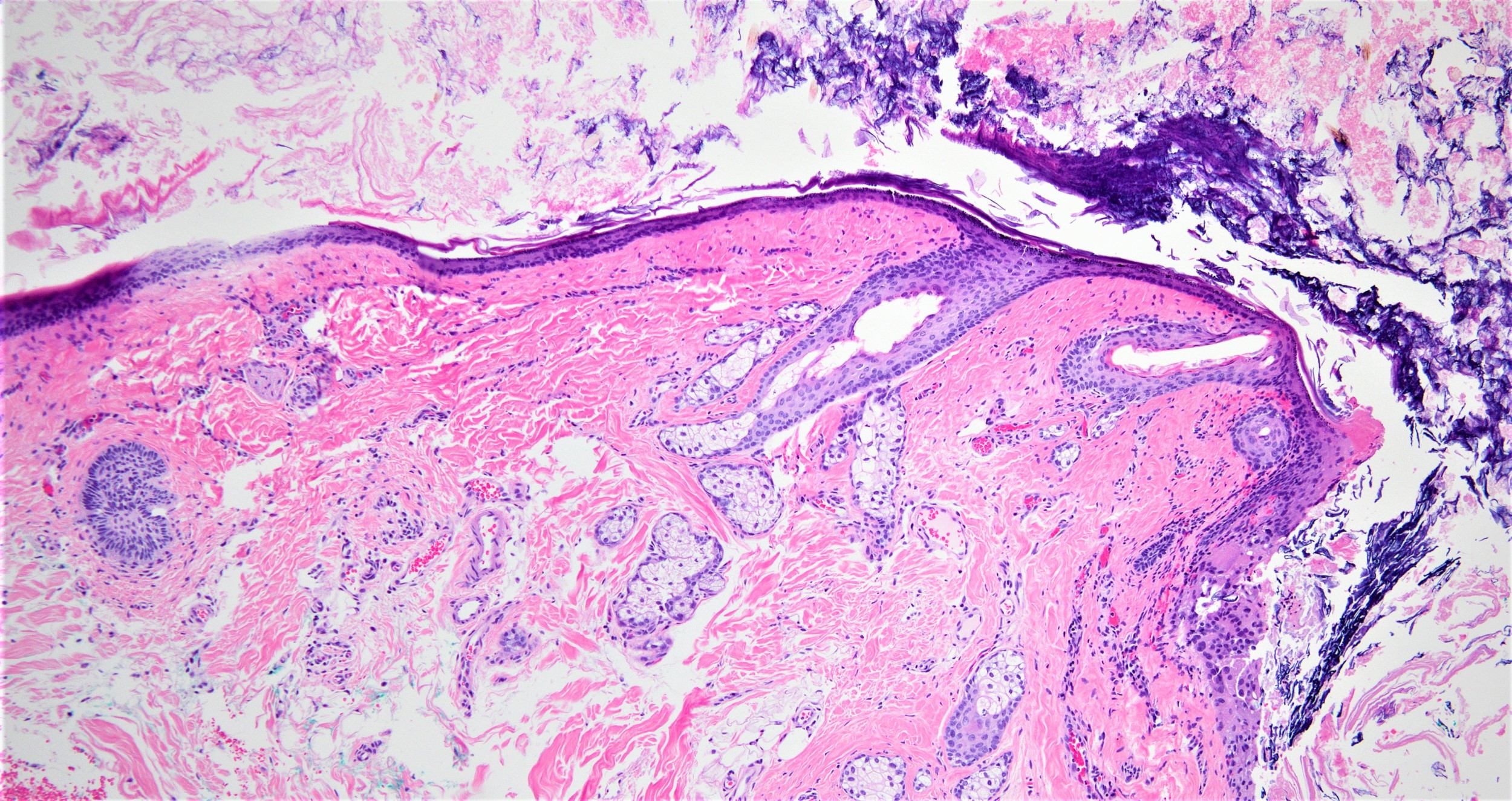
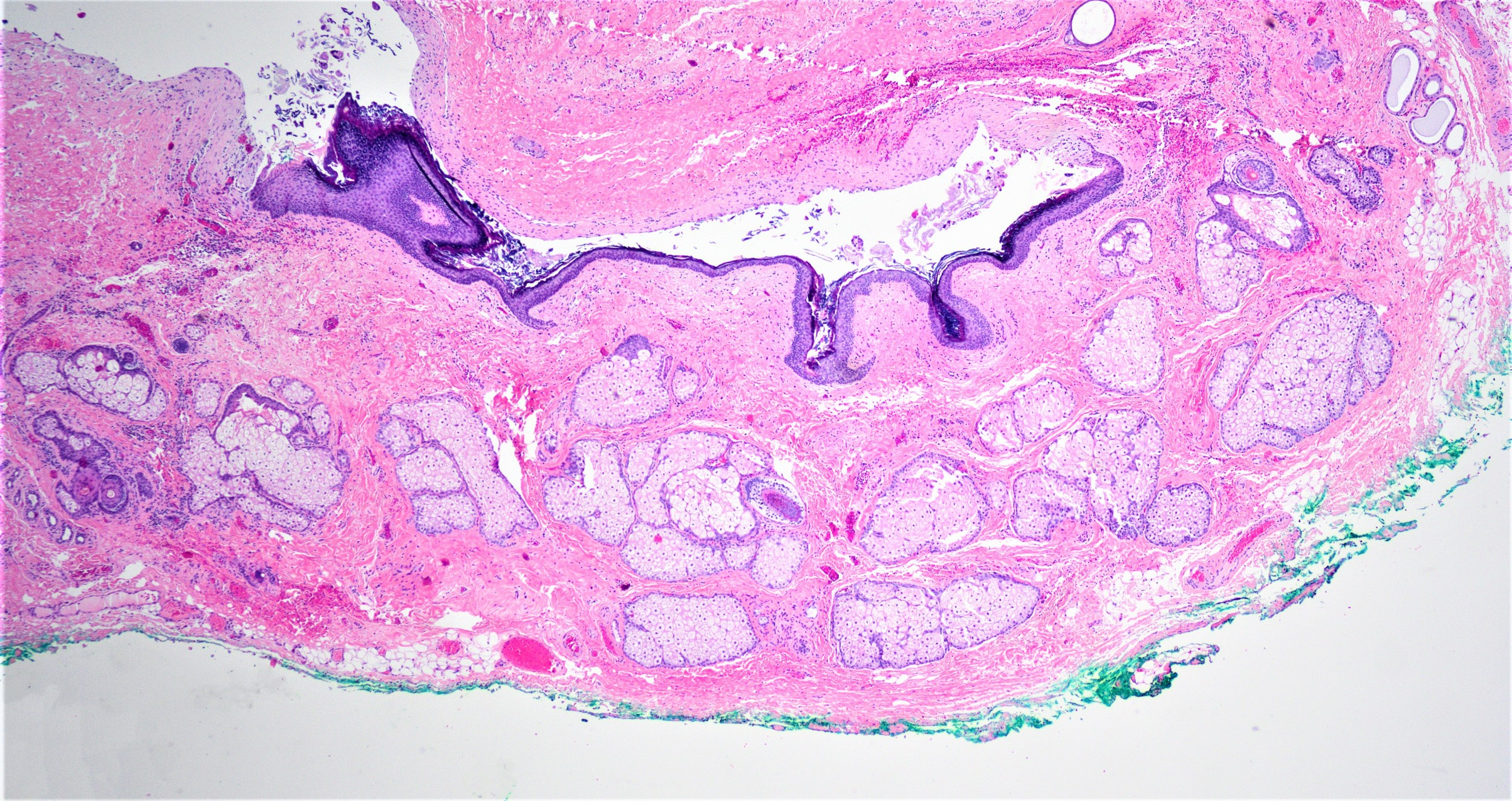
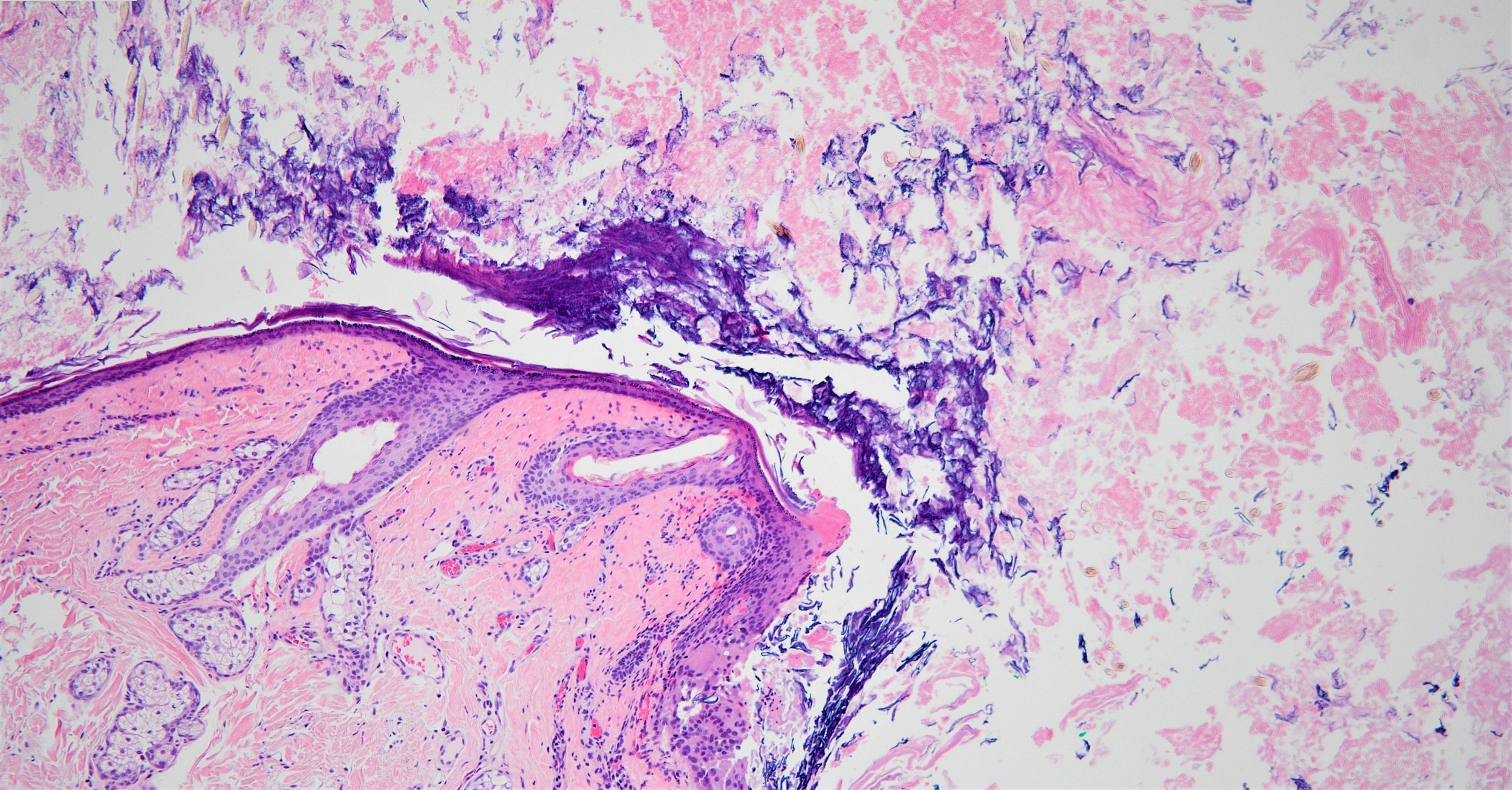
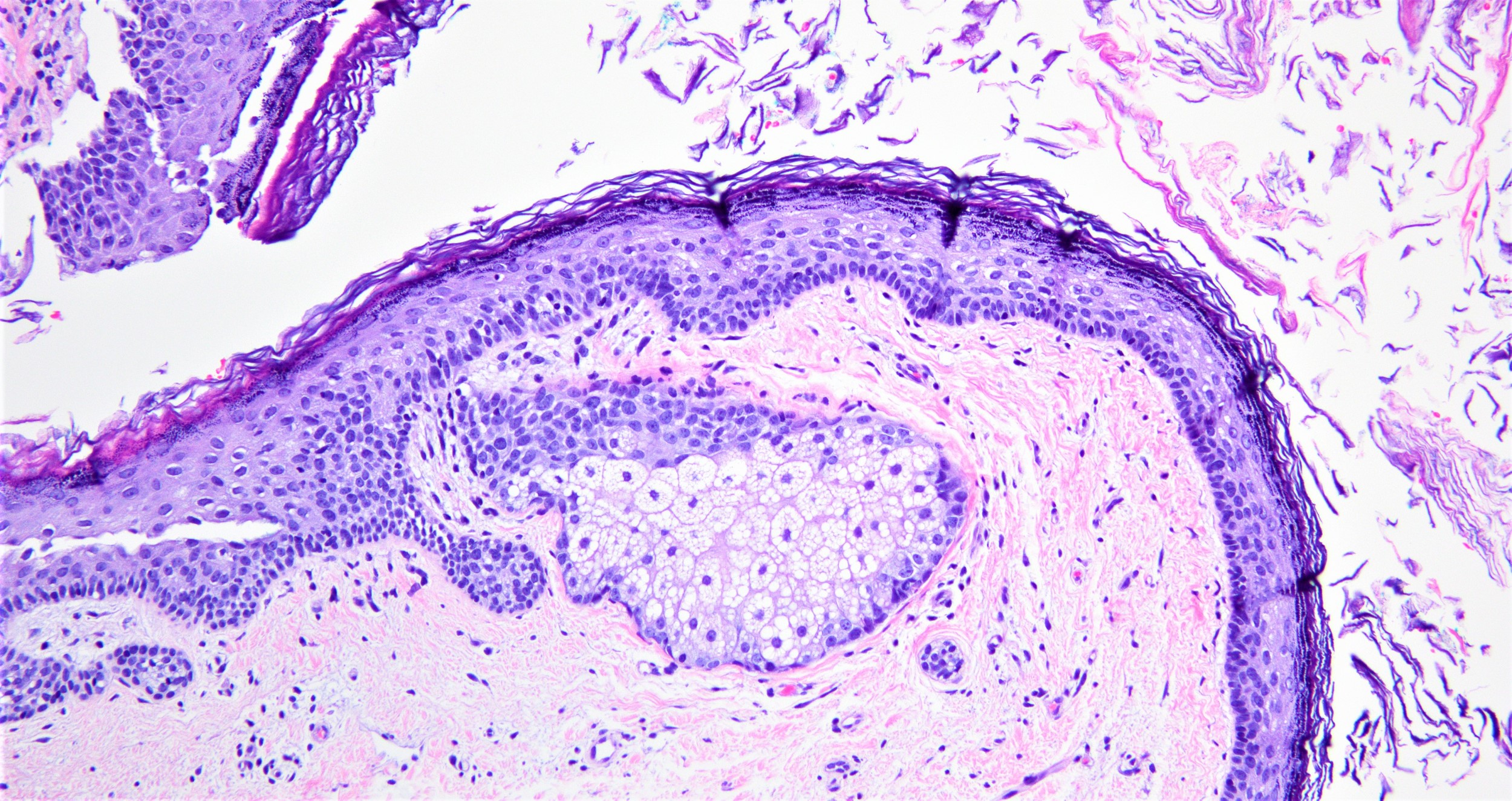
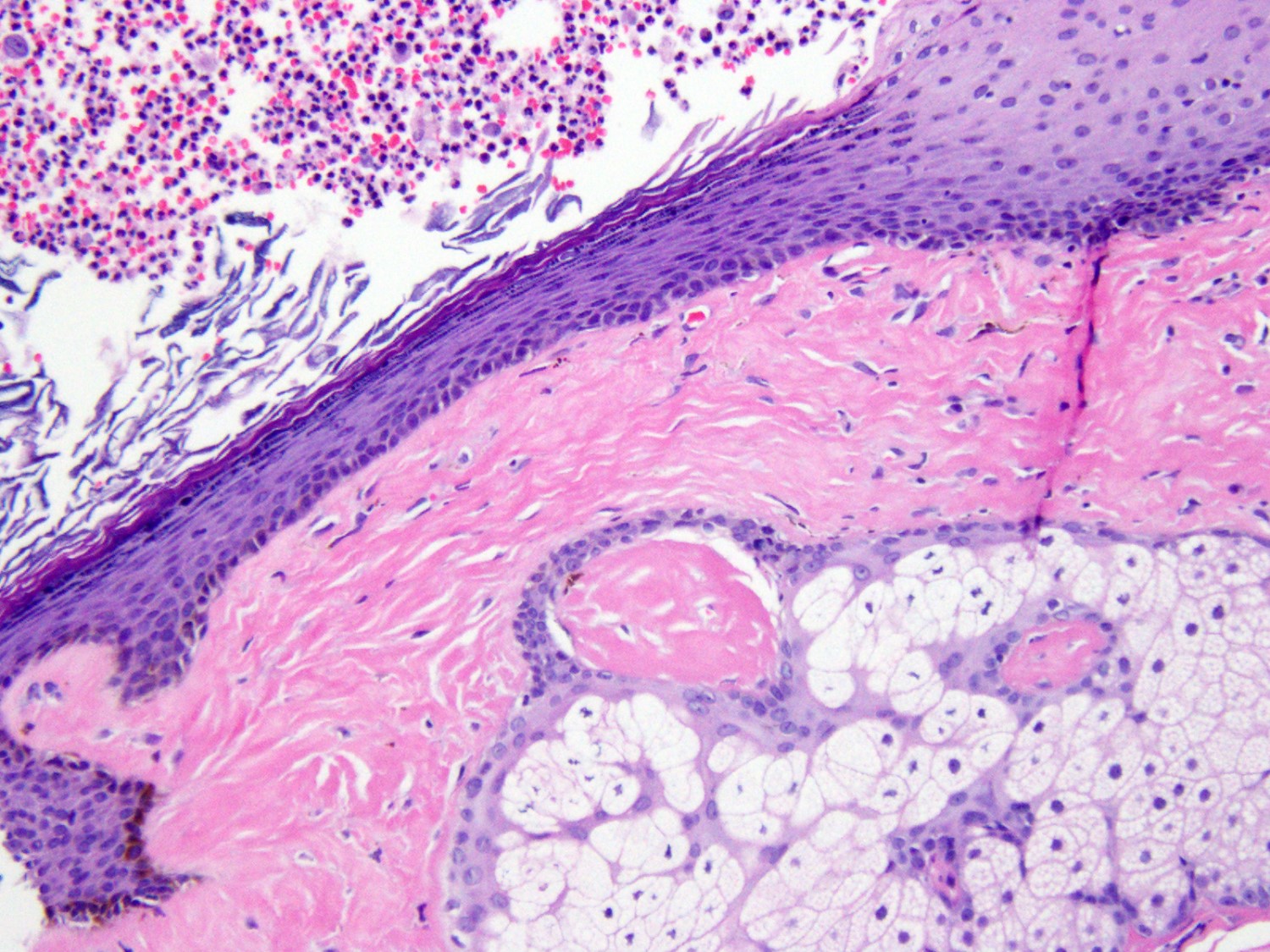
- Well defined wall lined by stratified squamous epithelium with mature skin appendages (hair follicles and sebaceous glands) and a lumen filled with keratin and hair shafts (Yale J Biol Med 2014;87:349, Pediatr Dermatol 2013;30:706)
- Occasionally, smooth muscle may be present but in contrast to benign cystic teratoma, cartilage and bone has not been described (Yale J Biol Med 2014;87:349)
- Eccrine sweat glands present in 35% of cases and apocrine glands in 15%
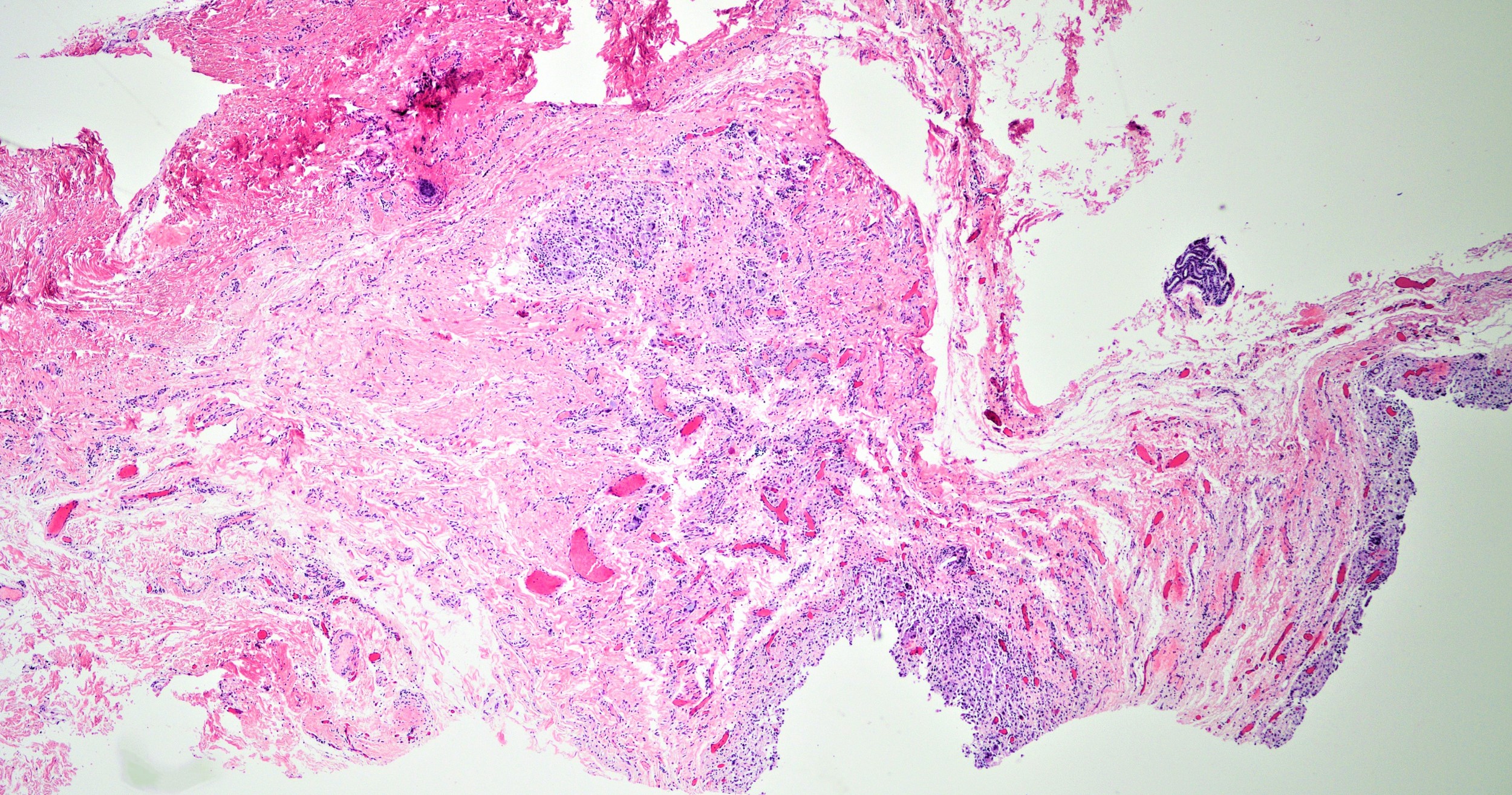
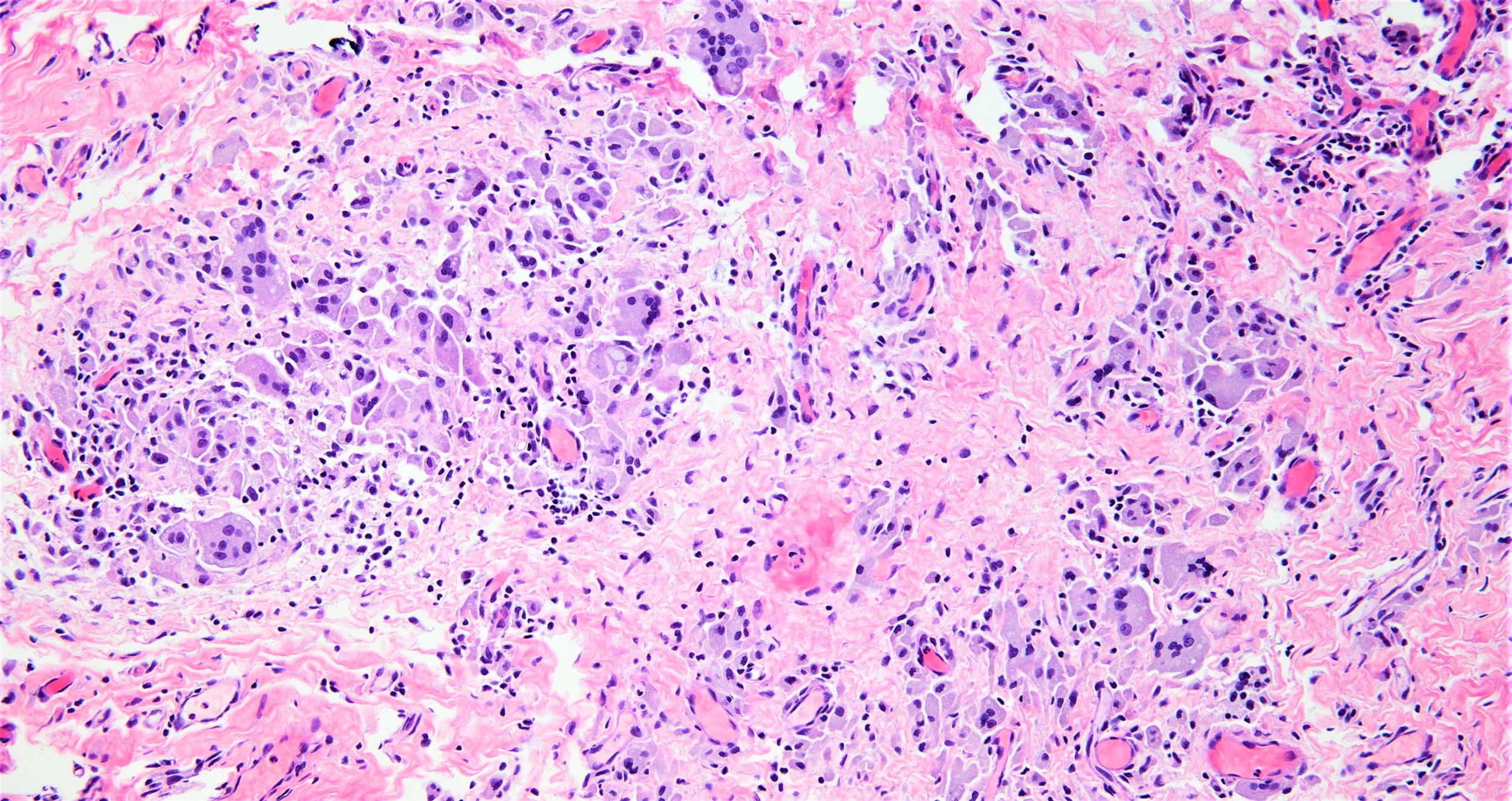
- Ruptured cyst with evidence of granulomatous inflammation with giant cells, most concentrated around exposed hair follicles
- Implantation dermoid cysts have no adnexal structures and therefore, they are easily distinguished from congenital forms on histology (BMJ Case Rep 2019;12:e228831)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
Negative stains
- CK6 (positive in epidermoid cyst, indicating cell hyperproliferation)
Videos
Cutaneous dermoid cyst
Sample pathology report
- Skin, right lower eyelid, excision:
- Dermoid cyst
- Skin, left shin, excision:
- Dermoid cyst (see comment)
- Comment: The sections show a dermal cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium with attached sebaceous gland and hair follicle. The lumen contains loose keratin flakes and scattered hair shafts.
Differential diagnosis
- Epidermal inclusion cyst / epidermoid cyst:
- Smooth, dome shaped firm, skin colored nodule that is freely movable on palpation and sometimes has a small, dilated punctum
- Lined only by stratified squamous epithelium; no adnexal structures identified
- Lumen contains abundant keratin flakes
- Vellus hair cyst:
- Multiple, small, smooth, skin colored, reddish, bluish, yellowish, brown, violaceous or grayish papules
- Mid dermal cyst containing laminated keratin and many vellus hairs
- Epithelial lining consists of several layers of squamous epithelium, often with a granular cell layer
- Steatocystoma:
- Skin colored to yellowish dermal cystic papules or nodules
- Cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium without a granular layer with attached sebaceous gland
- Diagnostic, corrugated eosinophilic layer lining luminal surface
- Congenital dermoid fistula:
- Presents at birth as a superficial fistula tract
- Pilomatrixoma:
- Benign tumor arising from hair matrix
- Solid nests of basaloid cells undergoing abrupt trichilemmal type keratinization
- Ghost cells, calcification or ossification with extramedullary hematopoiesis and frequent rupture leading to giant cell reaction
- Encephalocele:
- Can also be found in glabella area
- Compressible / soft and bluish in color
- Typically transilluminate
- Nasal glioma:
- Pilar / trichilemmal cyst:
- Firm and well circumscribed nodule on palpation
- Lined by stratified squamous epithelium, which lacks granular layer
- Contains dense eosinophilic keratin
- Teratoma:
- Represents true neoplasm comprised of tissues from all 3 germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm
Board review style question #1
A 5 year old girl with no significant past medical history presents with a slowly growing, nontender mass on the lateral third of her eyebrow. The mass is a firm, nonpulsatile, pale to flesh colored, subcutaneous nodule. Which of the following is the next best step in the management of this condition?
- Biopsy
- Excision
- MRI
- Radiograph (Xray)
Board review style answer #1
C. MRI. Before doing therapeutic excisional biopsy, proper imaging should be done due to risk of possible bony deformities, intracranial extension or intraspinal extension. Biopsy may lead to further complications worsening the infection due to rupture / spill of the content of the cyst. MRI is better than radiograph (Xray) as it evaluates the extent of intracranial and intraspinal extension, whereas Xray may detect the bone deformities.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermoid cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Dermoid cyst
Board review style question #2
What findings in the above picture are specific to dermoid cyst?
- Cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium and abundant keratin flakes
- Cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium and sebaceous glands
- Cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium with multiple hair shafts
- Cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium with retained the granular layer
- Cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium, sebaceous glands and hair follicle
Board review style answer #2
E. Dermoid cyst is lined by stratified squamous epithelium, sebaceous glands and hair follicles and is composed of abundant keratin flakes. Pilar cyst is lined by stratified squamous epithelium lacking the granular layer and contains dense laminated eosinophilic keratin. Epidermoid cyst is lined by stratified squamous epithelium with retained the granular layer and keratin flakes. Vellus hair cyst is lined by stratified squamous epithelium with multiple hair shafts. Steatocystoma is a cyst lined by stratified squamous epithelium and sebaceous glands.
Comment Here
Reference: Dermoid cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Dermoid cyst