Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Clinical features | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Hamodat M. Pancreatic panniculitis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorpancreaticfatnecrosis.html. Accessed January 17th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Due to acute pancreatitis or pancreatic carcinoma
- Lesions may be widespread, may drain chalky material
- Associated with elevated serum amylase and lipase
Epidemiology
- Males are affected more than females
Clinical features
- Tender violaceous and erythematosus nodules, usually in trunk, buttocks and lower extremities
- Also joint involvement, pleural effusion, ascitis and pericardial effusion
- Peripheral blood eosinophilia is quite common
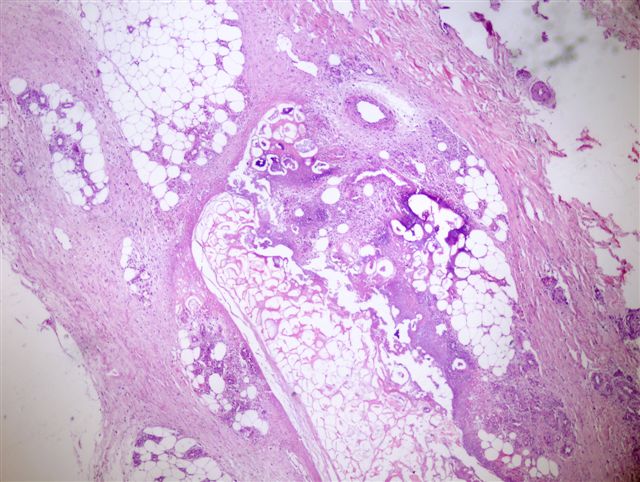
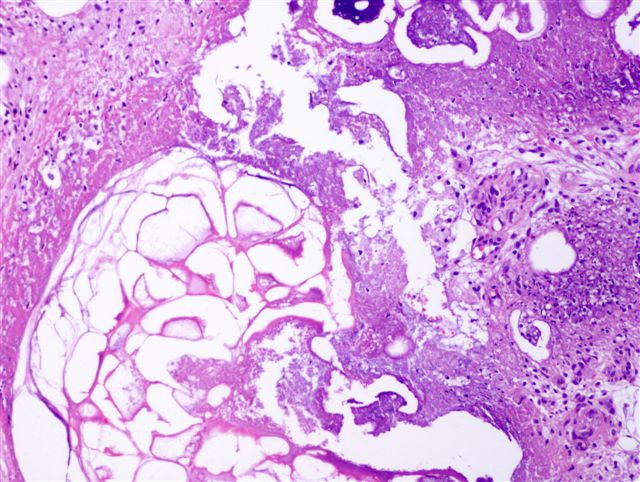
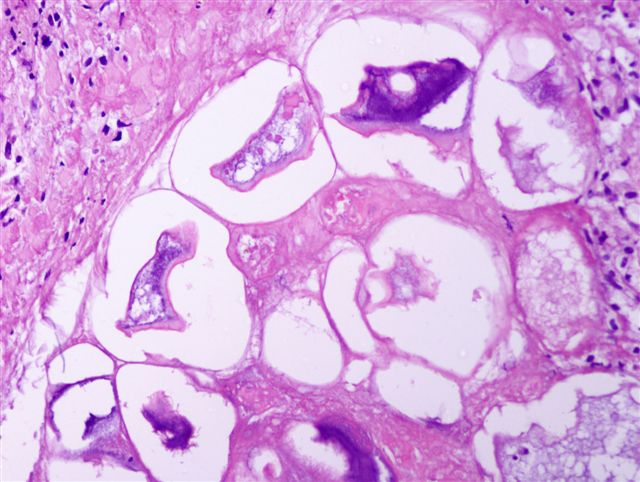
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Changes are lobular in distribution and characterized by ghost cells, which are anucleate cells composed of amorphous granular debris and a rim of eosinophilia; also stippled basophilia due to calcification
- Usually neutrophils around foci of fat necrosis and hemorrhage
- Uninvolved surrounding fat is heavily infiltrated by acute and chronic inflammatory cells including large numbers of macrophages, many with foamy cytoplasm due to ingested lipid, and occasional multinucleated giant cells
- No evidence of vasculitis
- Birefringent crystals have been described in the mesenteric fat and within affected joints, but not in subcutaneous fat