Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Carrasquillo OY, Sánchez JL. Molluscum contagiosum. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumormolluscum.html. Accessed January 11th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Self limited infectious dermatosis caused by molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) of the Poxviridae family (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
Essential features
- Infectious dermatosis most commonly affecting children and immunocompromised patients
- Majority of infections are caused by MCV1 (98% of cases)
- In contrast to most double stranded DNA viruses, poxvirus replicates in the cytoplasm
- Henderson-Paterson bodies, also known as molluscum bodies, are large (up to 35 microns) intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusion on keratinocytes
ICD coding
- ICD-10: B08.1 - Molluscum contagiosum
Epidemiology
- Most common in children aged 2 - 5 (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
- ~8.3% prevalence among children (Fam Pract 2014;31:130)
- M = F (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
- Higher frequency in areas with warm climates (Fam Pract 2014;31:130)
- 18% prevalence in adults with HIV (Pediatr Dermatol 2017;34:504)
Sites
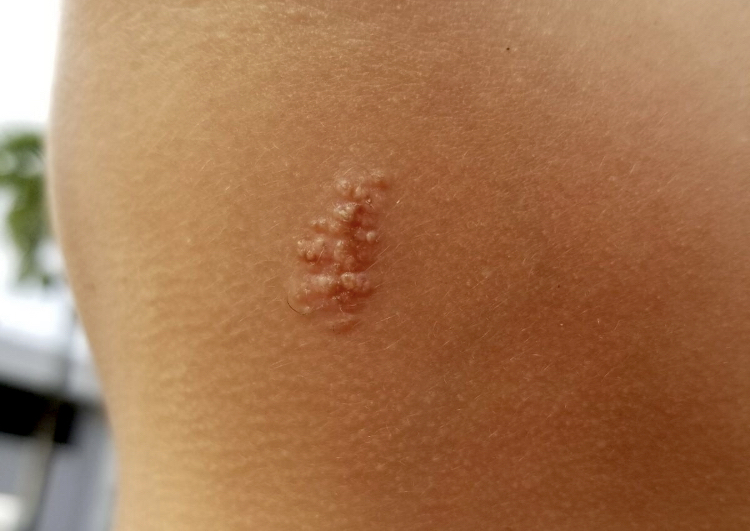
- In children: trunk, extremities, neck, axilla, genitals and face (JAMA Dermatol 2016;152:1072)
- In adults: lower abdomen, thighs, genitals and perianal area (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
Pathophysiology
- Double stranded DNA poxvirus that infects keratinocytes (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
- Replicates in the cytoplasm (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
- Incubation period: 2 weeks to 6 months (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
Etiology
- In adults, most commonly transmitted by sexual contact (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
- MCV1 (98% of cases) most common in children (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
- MCV2 most common in HIV patients (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
Clinical features
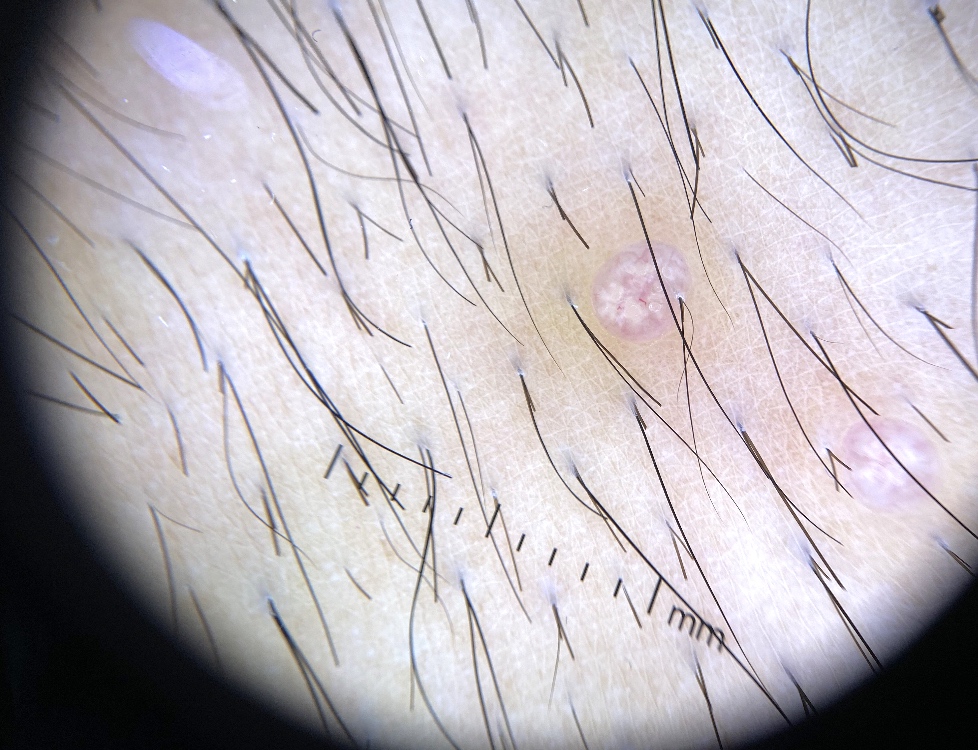
- Firm, white to flesh colored, dome shaped, pearly, umbilicated papules (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
- Spares palms and soles (JAMA Dermatol 2016;152:1072)
- Involvement of the oral mucosa is rare (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
Diagnosis
- Clinical, dermoscopy, biopsy or reflectance confocal microscopy (Recent Pat Inflamm Allergy Drug Discov 2017;11:22)
Prognostic factors
- Usually self limiting (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
Case reports
- 37 year old man with HIV with generalized nodular cutaneous lesions (Afr J Lab Med 2019;8:747)
- 50 year old healthy woman with asymptomatic lesions on her genital area (Dermatol Online J 2019;25)
- 50 year old man with infiltrated plaques in the head and neck area (Case Rep Dermatol 2019;11:52)
Treatment
- Self limited
- Mechanical methods: cryotherapy, curettage, pulse dye laser
- Chemical methods: potassium hydroxide, podophyllotoxin, trichloroacetic acid, salicylic acid, lactic acid, glycolic acid, benzoyl peroxide and tretinoin
- Immunomodulatory methods: imiquimod, oral cimetidine, interferon alfa, candidin and diphencyprone
- Antivirals: cidofovir (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
Clinical images
Microscopic (histologic) description
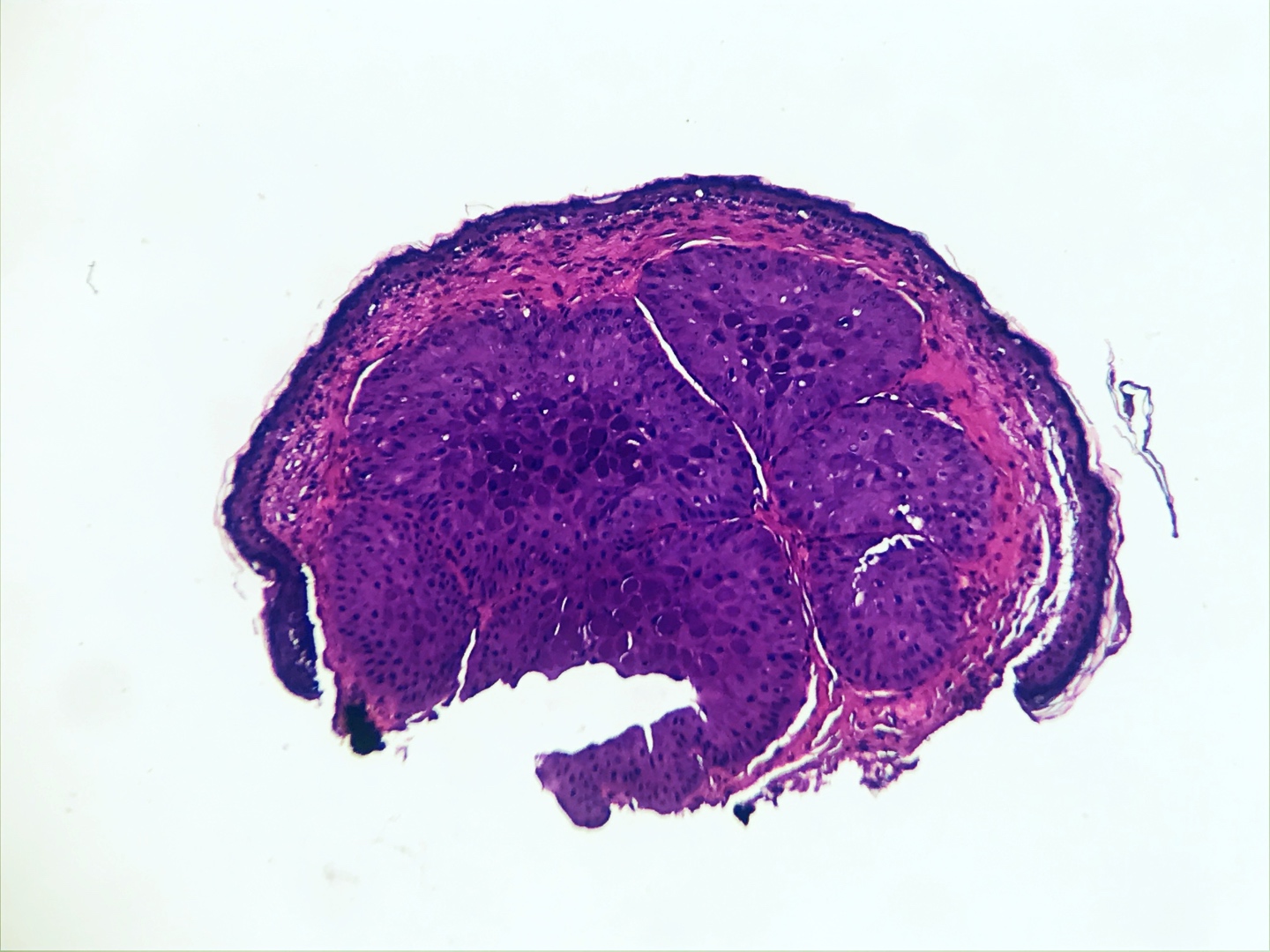
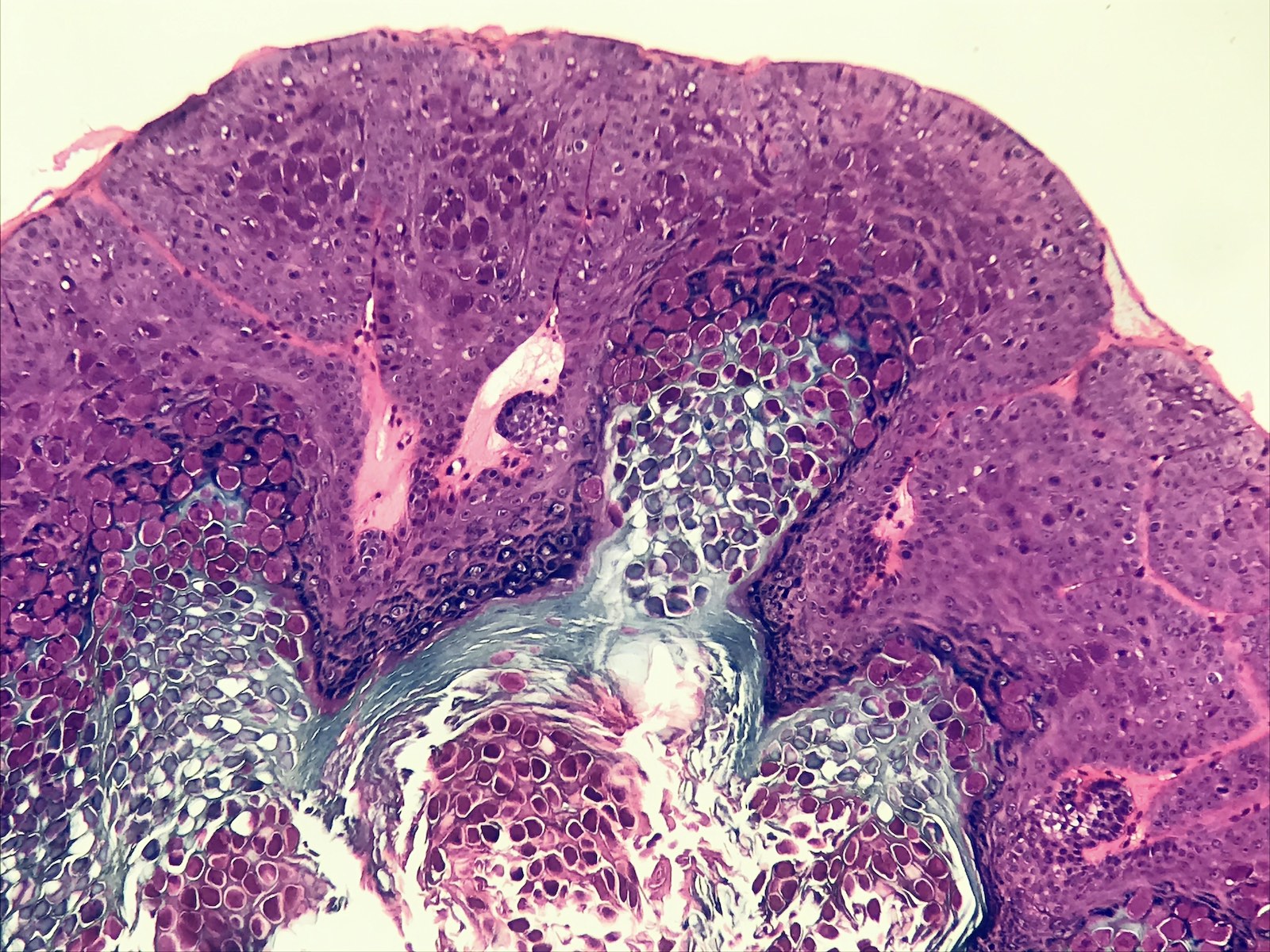
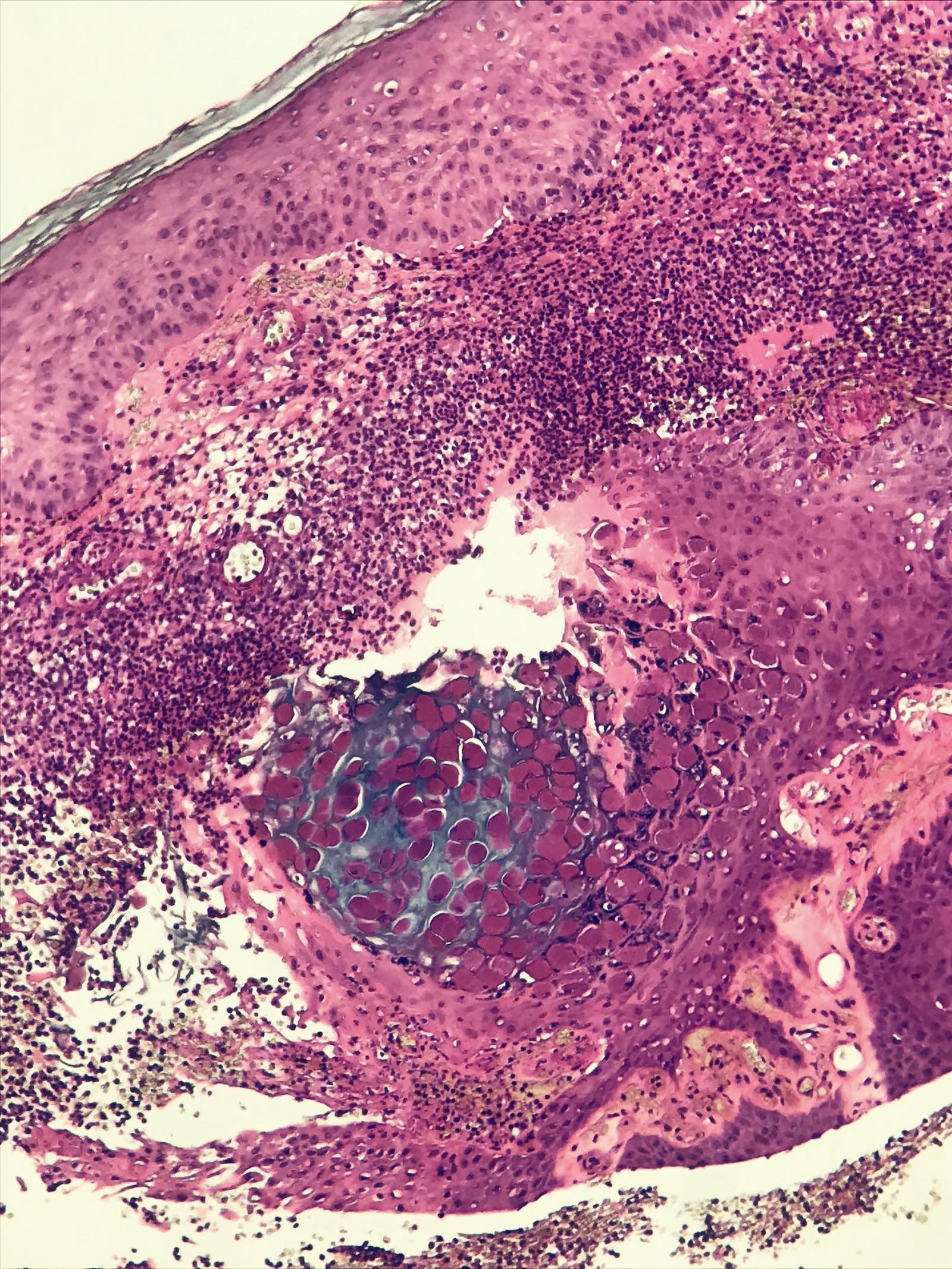
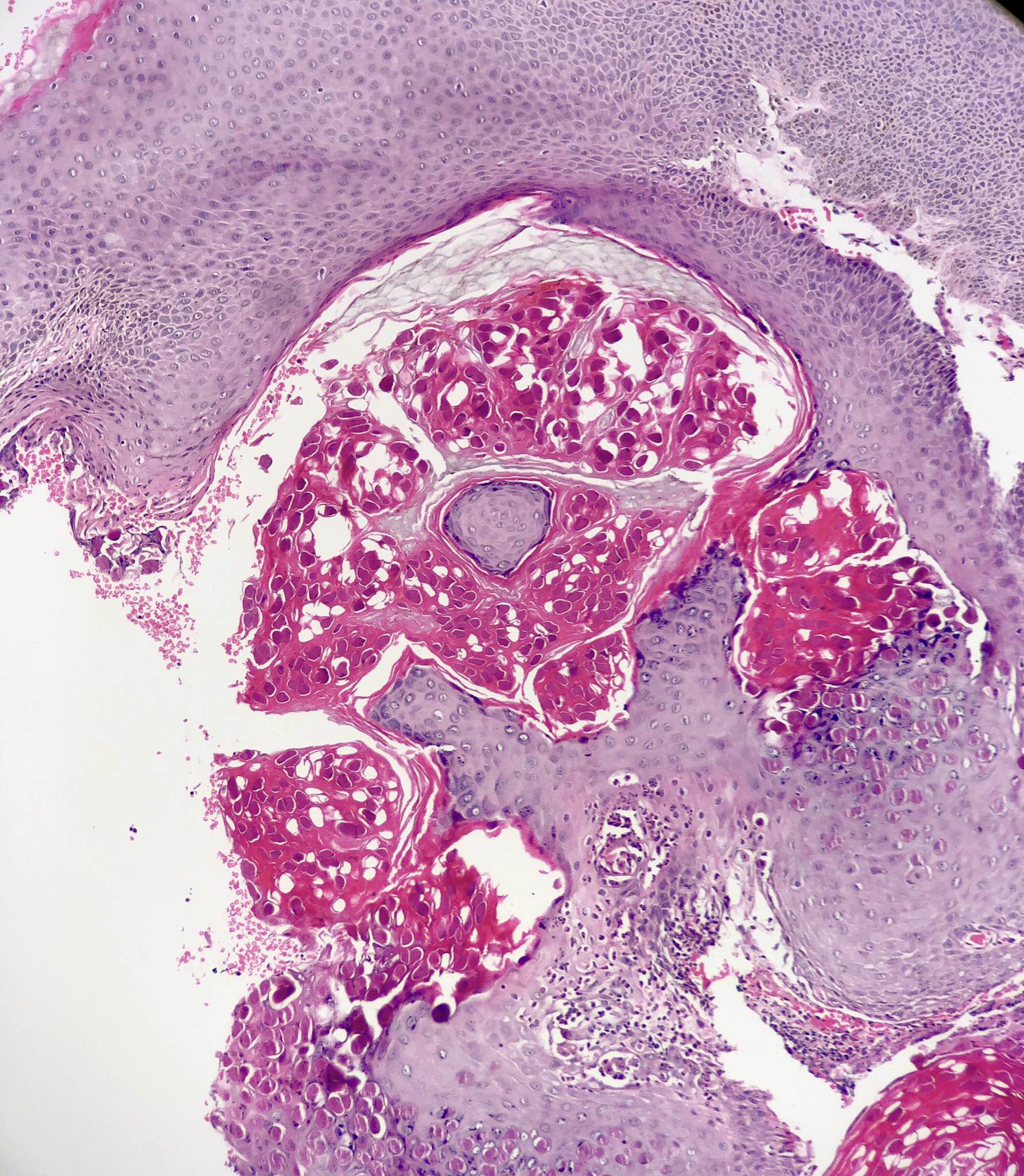
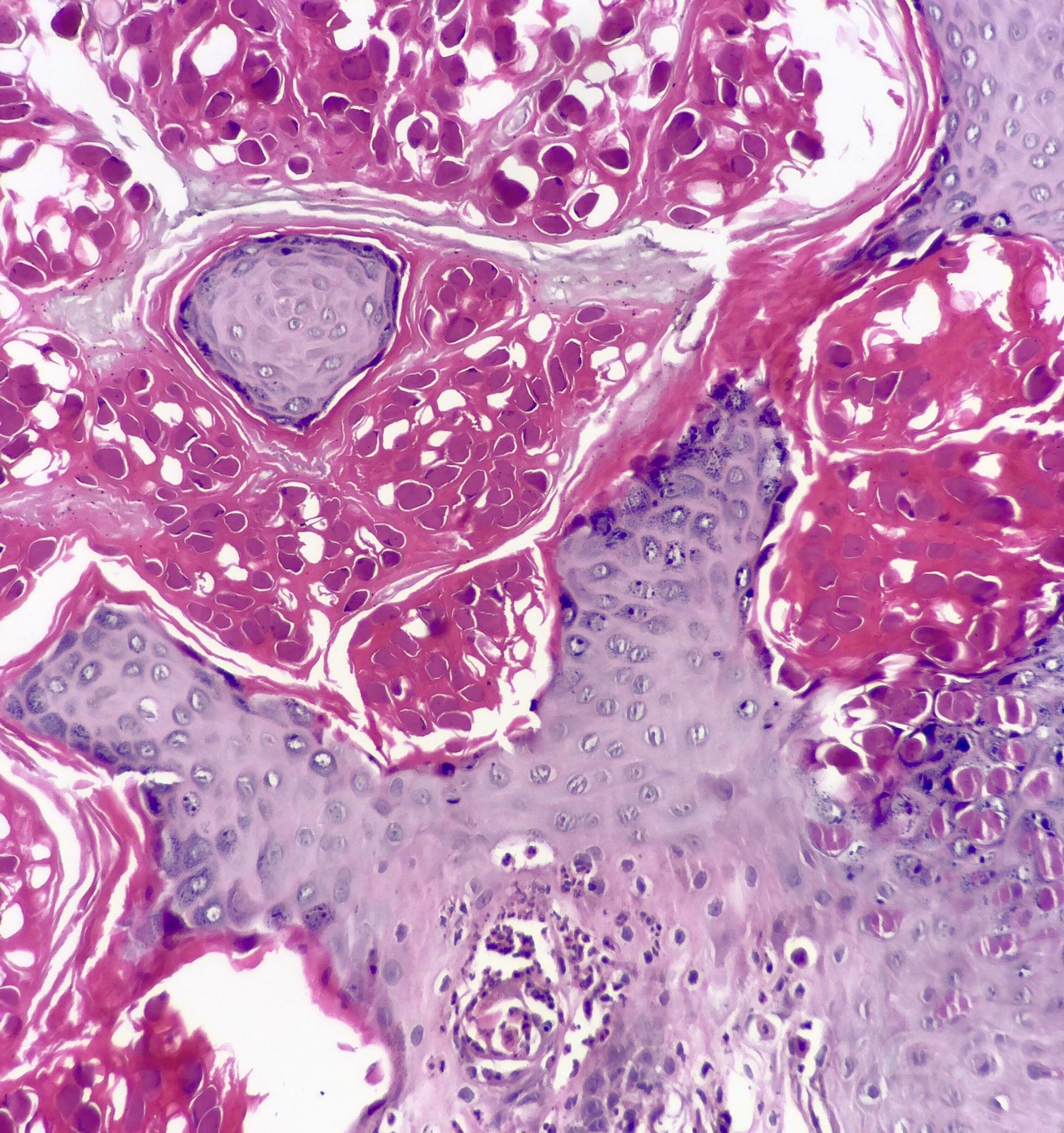
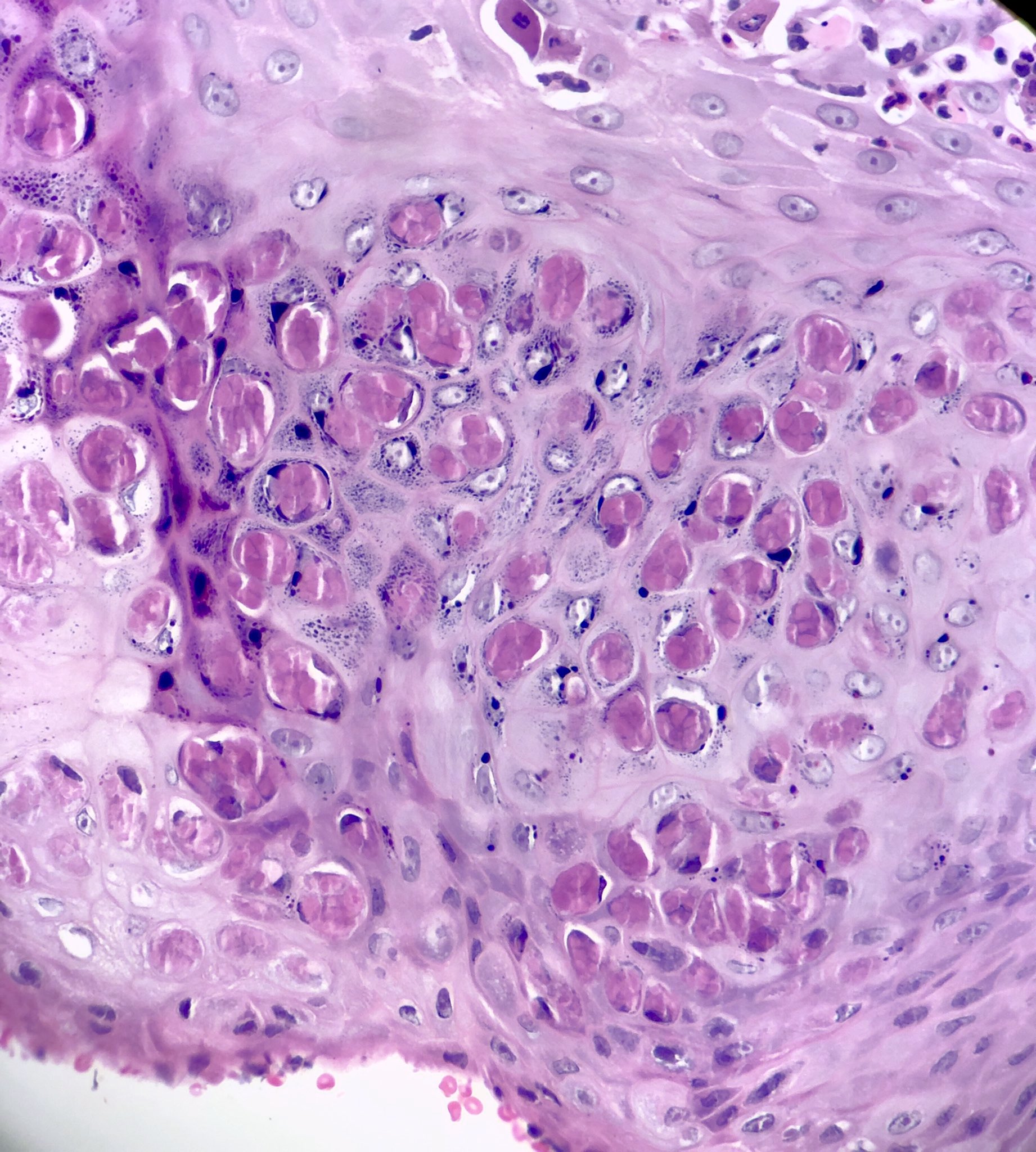
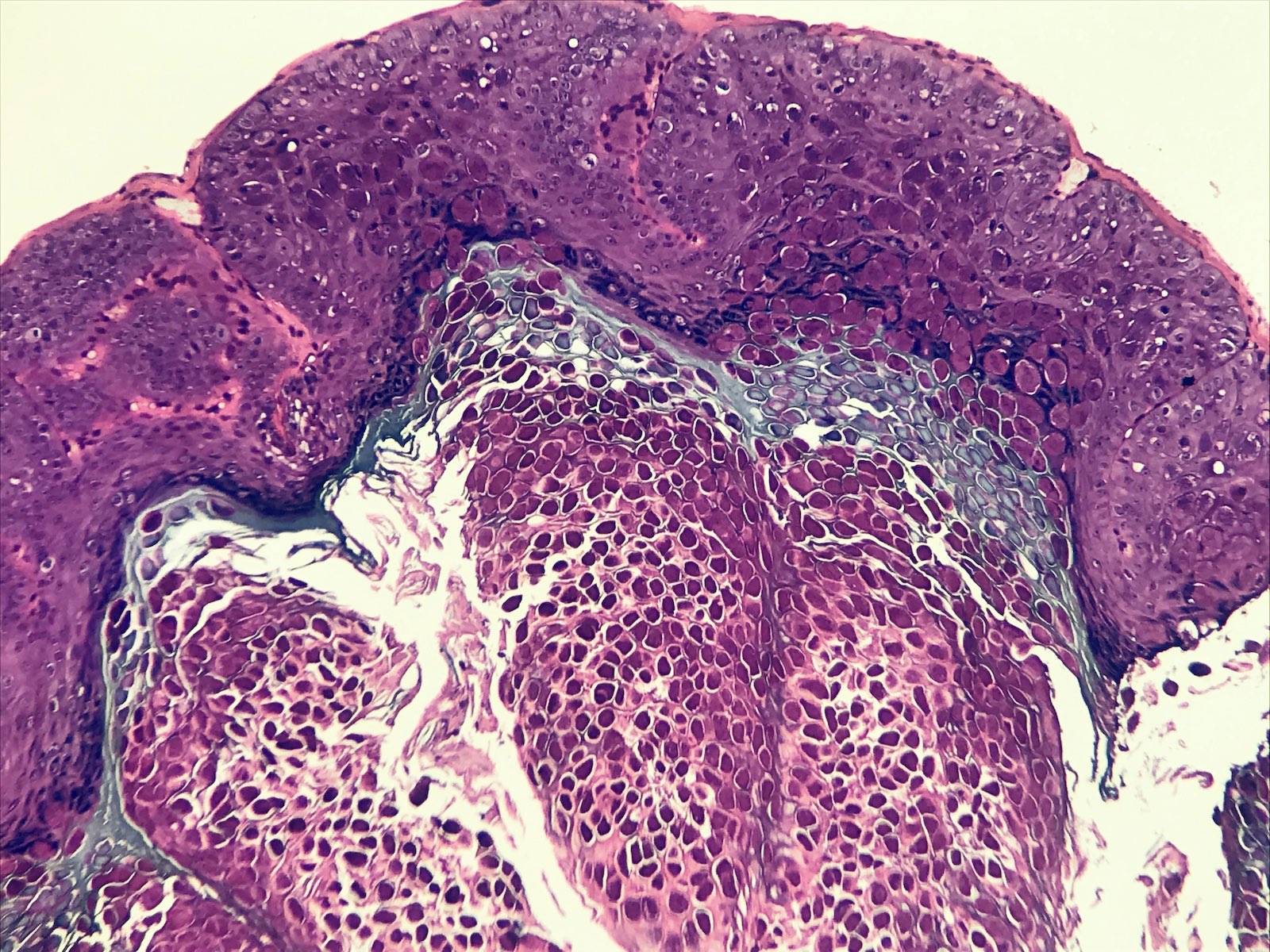
- Cup shaped lesion with inverted lobules of hyperplastic squamous epithelium which expand into the underlying dermis (StatPearls: Molluscum Contagiosum [Accessed 29 June 2020])
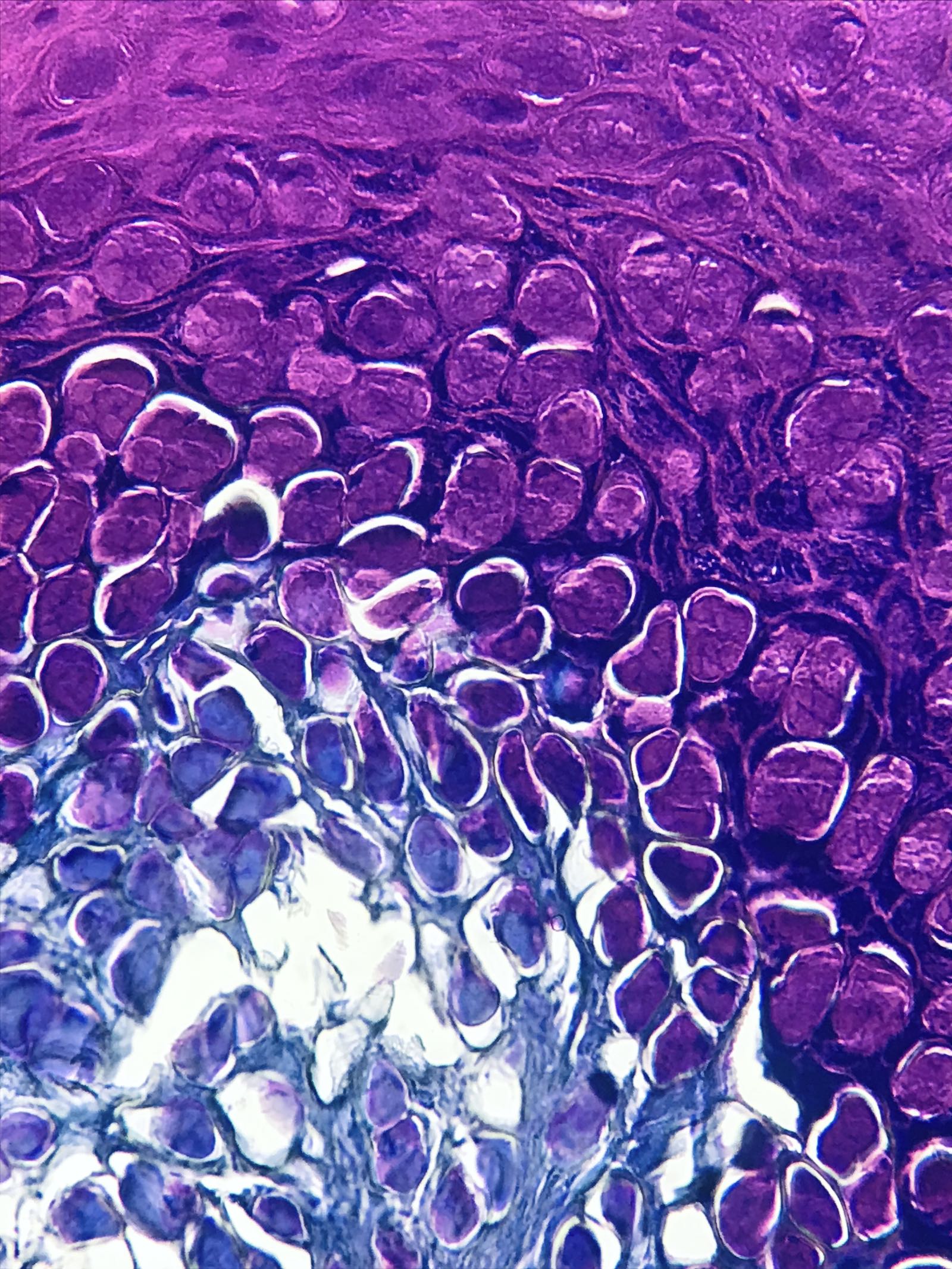
- Henderson-Paterson or molluscum bodies: large (up to 35 microns) intracytoplasmic eosinophilic inclusion bodies (Clin Cosmet Investig Dermatol 2019;12:373)
- At the granular layer, the bodies become increasingly hematoxyphilic and occupy the entire cell
- Chronic inflammatory infiltrate seen in regressing lesions
Microscopic (histologic) images
Videos
Molluscum versus myrmecia wart - dermpath lookalikes
Sample pathology report
- Left superior eyelid skin, biopsy:
- Molluscum contagiosum (see comment)
- Comment: There is epidermal hyperplasia with large eosinophilic cytoplasmic bodies within keratinocytes.
Differential diagnosis
- Common wart:
- Verrucous or filliform flesh colored papules
- Herpes simplex:
- Grouped vesicles that rupture quickly, leading to painful ulcerations with scalloped borders
- Nuclear viral inclusions (multinucleation, nuclear molding, margination of chromatin)
- Juvenile xanthogranuloma:
- Dome shaped, yellowish orange papules or nodules
- Triple association between juvenile xanthogranuloma, neurofibromatosis type 1 and juvenile promyelomonocytic leukemia has been reported
- Touton giant cells, histiocytes, lymphocytes and eosinophils in reticular and papillary dermis
- Spitz nevi:
- Lesions typically located in face and extremities
- Melanocytic nests with epithelioid cells at the dermal-epidermal junction
- Kamino bodies within the epidermis
- Basal cell carcinoma:
- Most common in chronically sun exposed areas
- Nest of basaloid cells with peripheral palisading and retraction artifact
Board review style question #1
A 6 year old boy presents with multiple scattered, flesh colored, small skin papules on the trunk and upper extremities. His medical history was unremarkable and his older sister had similar lesions in the past. A skin biopsy of one of the lesions is shown. Which of the following is the most likely cause of his condition?
- Human papillomavirus type 1 (HPV1)
- Human papillomavirus type 2 (HPV2)
- Human papillomavirus type 3 (HPV3)
- Molluscum contagiosum virus type 1 (MCV1)
- Molluscum contagiosum virus type 2 (MCV2)
Board review style answer #1
D. Molluscum contagiosum virus type 1 (MCV1). The histology shows molluscum contagiosum, which is caused by the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV) of the Poxviridae family (double stranded DNA). There are several types of MCV but the most common by far is MCV1 (98% of cases). MCV1 most commonly affects children, whereas MCV2 is usually seen in patients with HIV. Although verruca vulgaris from HPV (especially type 1) is common in children, the specimen is characteristic for molluscum contagiosum as it shows epidermal hyperplasia with large eosinophilic inclusion bodies on the keratinocytes (Henderson-Patterson bodies).
Comment Here
Reference: Molluscum contagiosum
Comment Here
Reference: Molluscum contagiosum
Board review style question #2
A patient is diagnosed with molluscum contagiosum after a skin biopsy was performed by his dermatologist. Which of the following type of viruses is responsible for causing his lesions?
- Double stranded DNA virus replicating in the cytoplasm
- Double stranded RNA virus replicating in the nucleus
- Single stranded DNA virus replicating in the cytoplasm
- Single stranded DNA virus replicating in the nucleus
- Single stranded RNA virus replicating in the cytoplasm
Board review style answer #2
A. Double stranded DNA virus replicating in the cytoplasm. Molluscum contagiosum is part of the Poxviridae family. The poxvirus replication is unusual as it is a double stranded DNA virus replicating in the cytoplasm instead of the nucleus.
Comment Here
Reference: Molluscum contagiosum
Comment Here
Reference: Molluscum contagiosum