Table of Contents
Definition / general | Clinical features | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Hamodat M. Herpes simplex / zoster. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorherpeszoster.html. Accessed April 1st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Painful diseases caused by herpes simplex virus (HSV) or varicella zoster virus (VZV, also causes chickenpox)
Clinical features
- For both viruses, after primary infection, viral particles reside in sensory ganglia and are dormant until they erupt as recurrent herpes simplex virus or shingles (zoster)
- The two viruses are differentiated by culture (difficult to culture zoster) or immunologic methods
- Herpes simplex:
- Historically, HSV1 was associated with herpes labialis (90%), and HSV2 was associated with herpes genitalis (90%), although in some recent studies, most genital lesions are caused by HSV1
- Visceral involvement is most often seen in the lung, liver and brain
- Today, diagnosis is often confirmed by PCR or immunohistochemistry
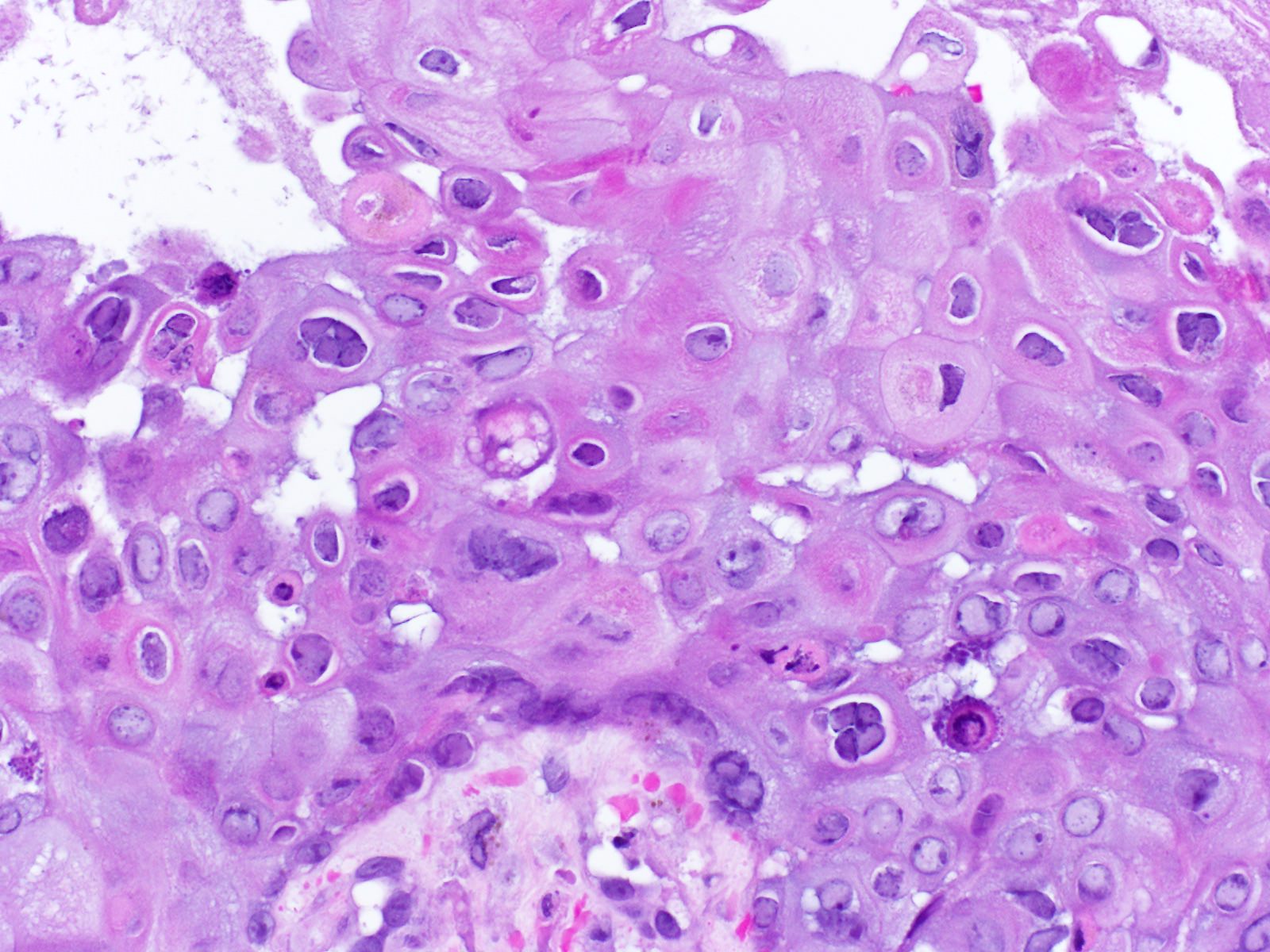
- The multinucleated cells are the diagnostic features of the historic Tzank test, a Giemsa stained smear of vesicle contents
- In the past, the laboratory diagnosis of herpes infection was confirmed by growth in tissue culture, electron microscopy, immunofluorescence of viral specific protein or viral DNA hybridization
- Varicella zoster:
- Varicella zoster is associated with leukemia and lymphoma, SLE and postradiation or postchemotherapy status
- Occurs in 40 - 50% of patients in the first year following bone marrow transplantation
- Shingles has dermatomal distribution or severe involvement of trigeminal nerve-first division (ophthalmic division) with corneal ulceration and herpetic keratitis
- Description:
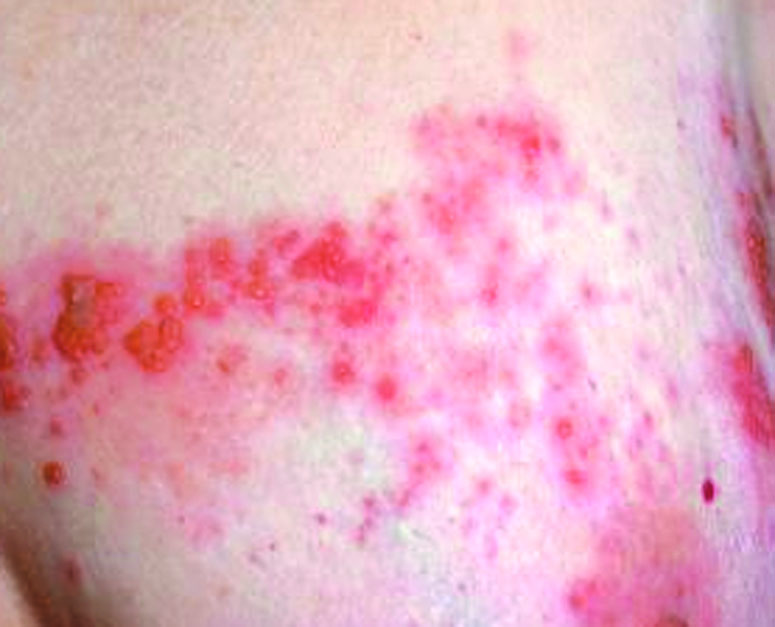
- Grouped vesicles on an erythematous base, later become pustules, then crusts
Case reports
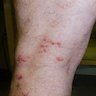
- 73 year old woman presented with a viral rash on her lower right leg (Case of the Week #423)
Treatment
- Acyclovir; also valacyclovir, penciclovir and famciclovir (eMedicine)
Clinical images
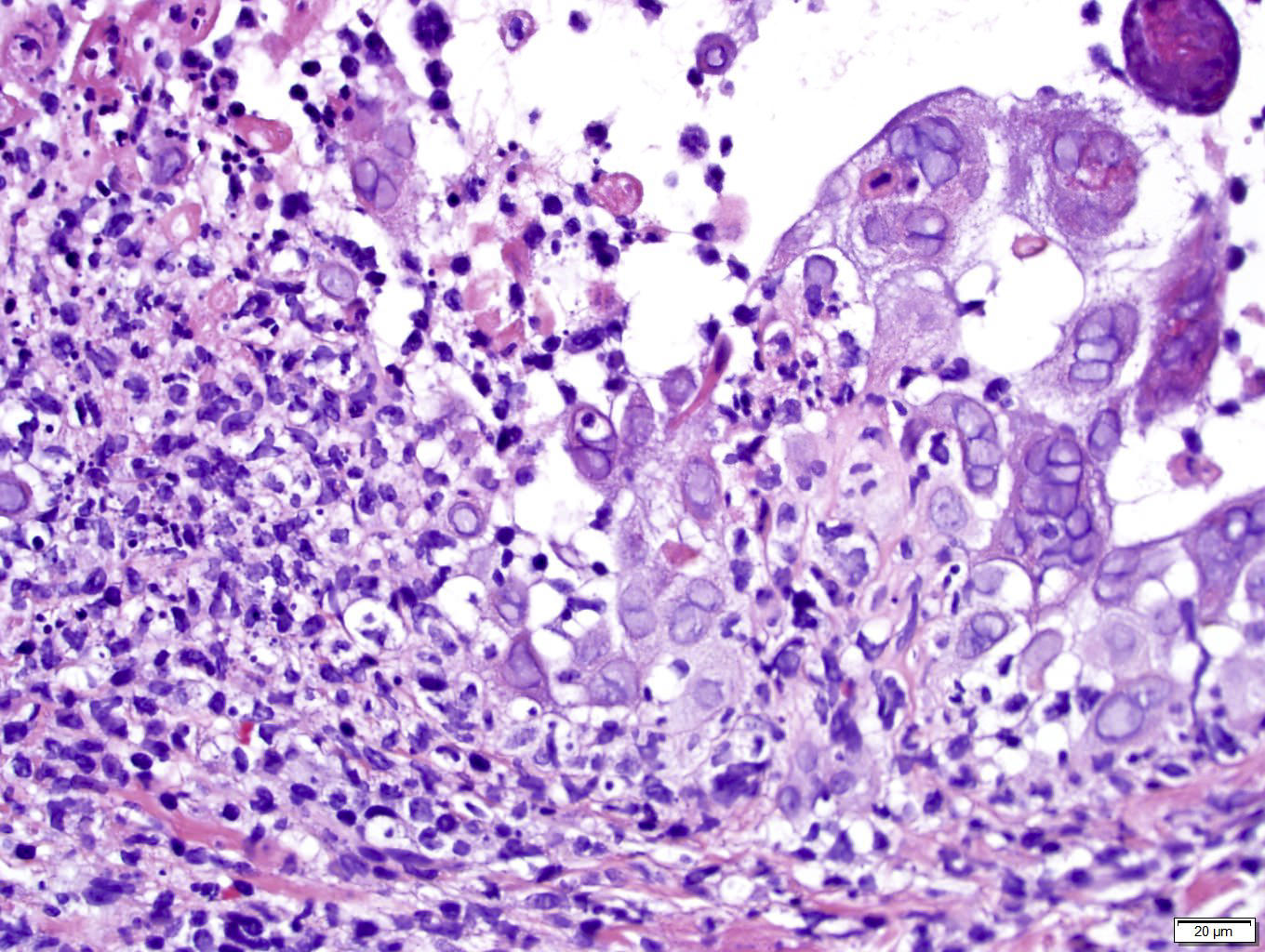
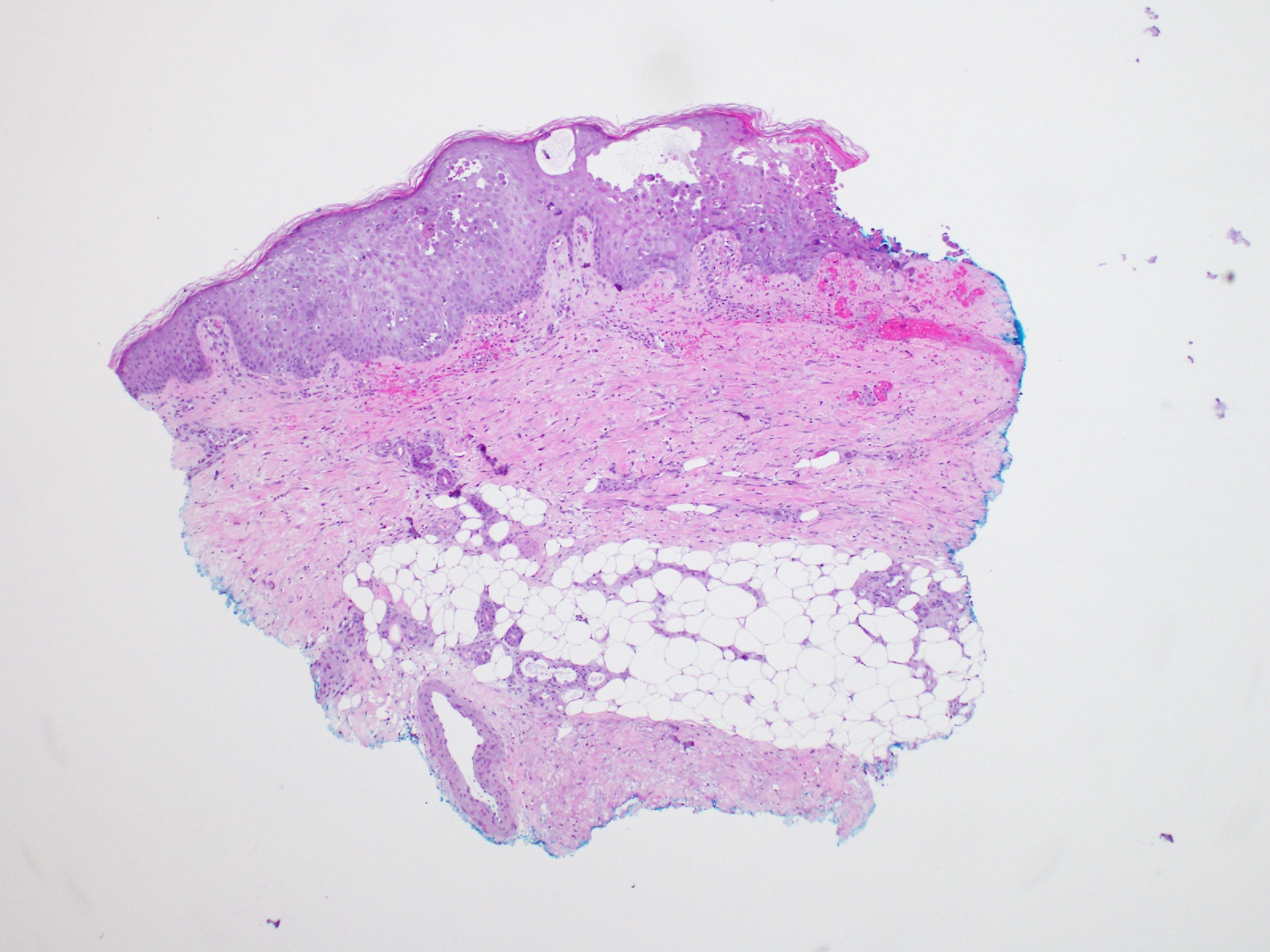
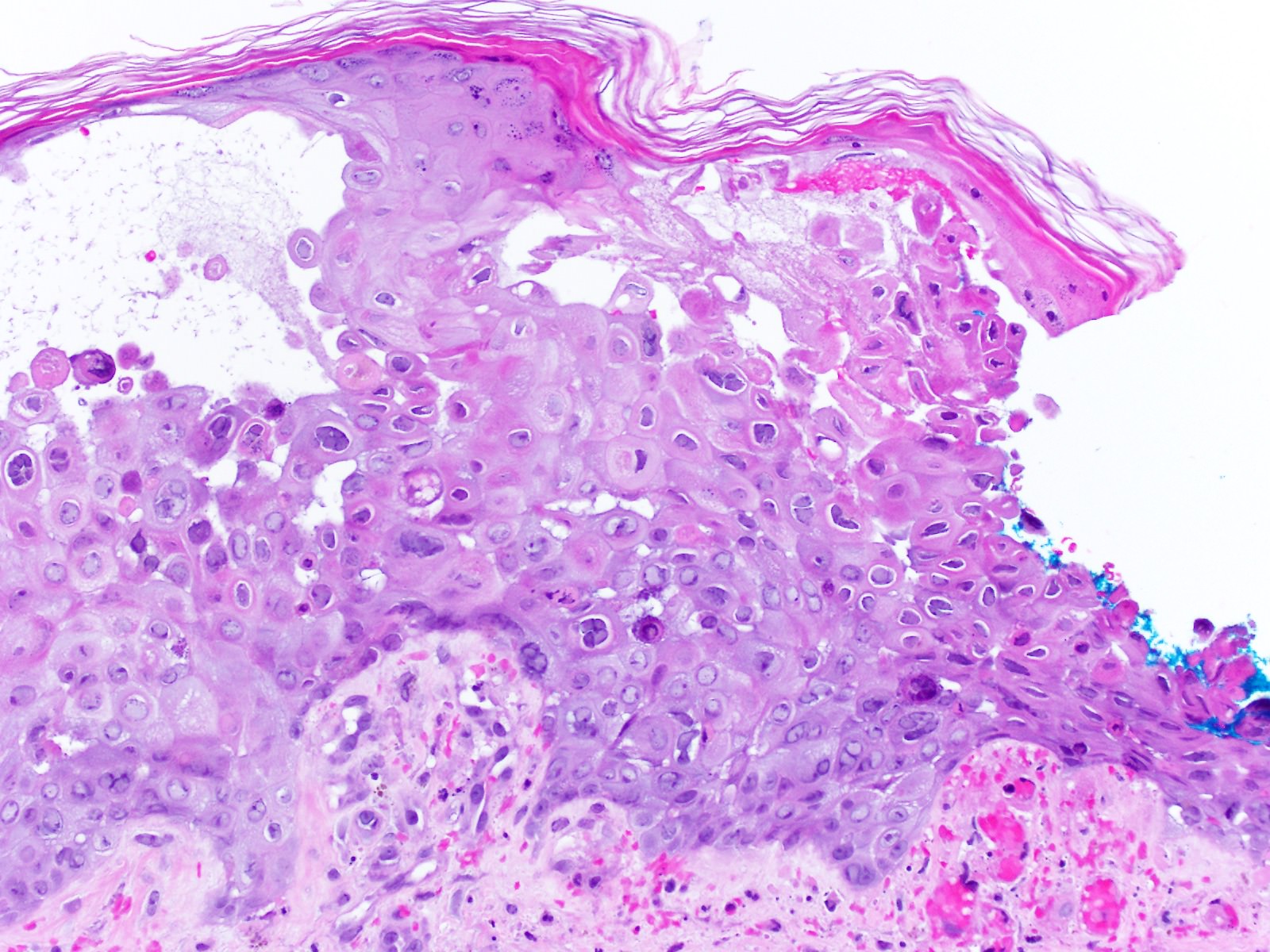
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Keratinocytes are multinucleated, acantholytic with distinct nuclear inclusions, found initially in follicular epithelium
- Late epidermal necrosis or full-thickness acantholysis
- Dermal nerve twigs may exhibit a perineural infiltrate of lymphocytes and neutrophils, sometimes associated with intraneural involvement
- Schwann cell hypertrophy and frank neural necrosis are occasionally encountered