Table of Contents
Definition / general | Case reports | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) imagesCite this page: Pernick N. Maduramycosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/skinnontumorfungimaduramycosis.html. Accessed April 20th, 2024.
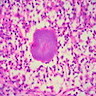
Definition / general
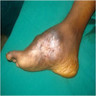
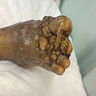
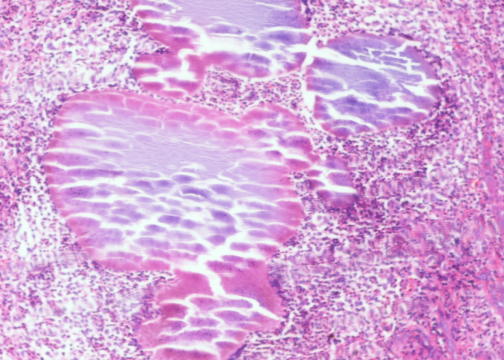
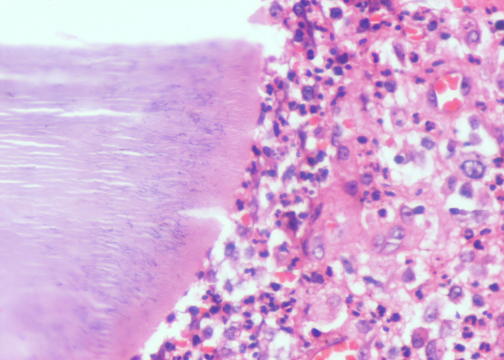
- Maduromycosis usually involves feet, and appears as a nodule or abscess, which progresses over months to years to a chronic infection with granulomatous nodules drained by skin sinuses, leading to deformities involving the bones
- May be due to bacteria (70%) or fungi (30%)
- Fungi include Madurella mycetomi; bacteria include Nocardia brasiliensis
- First described in Madurai, India
- Mycetoma caused by microaerophilic actinomycetes is termed actinomycetoma; mycetoma caused by true fungi is called eumycetoma (eMedicine)
- Note: actinomycosis affects the cervical-facial, thoracic and pelvic areas; these bacteria are smaller than in maduromycosis
Case reports
- 35 year old woman from India with steadily growing lump on foot (The Foot and Ankle Online Journal 2011;4:2)