Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Huang ML, Gupta R. Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandsepimyocarcinoma.html. Accessed April 19th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Uncommon malignant biphasic salivary gland neoplasm composed of luminal ductal cells surrounded by myoepithelial cells
Essential features
- Rare primary salivary gland neoplasm
- Biphasic neoplasm with a combination of both epithelial and myoepithelial elements
- Generally good prognosis; poorer prognosis associated with minor salivary gland location, large tumor (> 4 cm), high proliferation index, margin status, high grade transformation
Terminology
- Adenomyoepithelioma (not recommended)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8562/3 - epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma
Epidemiology
- 1 - 2% of all salivary gland tumors
- Wide age range; mean 64 years (standard deviation ± 15.4) (BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 2018;18:15)
- M:F = 1:1.6 (BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 2018;18:15)
Sites
- Major salivary glands
- Most common parotid (70%), submandibular (12%) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:44, BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 2018;18:15)
- Minor salivary glands
- Palate and upper aerodigestive tract (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:44)
Pathophysiology
- Presumed to be of intercalated duct origin
- Up to 85% of epithelial myoepithelial carcinomas carry an HRAS mutation (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:984)
Etiology
- Subset may be associated with preexisting pleomorphic adenoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:18)
- Subset may arise de novo (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:18)
Clinical features
- Slow growing, painless mass
- Usually unilateral
- Rarely presents with facial nerve palsy and lymphadenopathy, may indicate high grade transformation (Medicine (Baltimore) 2017;96:e8988)
Diagnosis
- Clinical examination and investigations such as magnetic resonance imaging and fine needle aspiration generally do not provide a definitive preoperative diagnosis
Prognostic factors
- Mean survival up to 165 months; another group found up to 81% of patients to be disease free at 15 years (BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 2018;18:15, Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 2015;153:569)
- Univariate tumor related predictors of lower disease free survival include margin status, lymphovascular invasion, tumor necrosis, myoepithelial anaplasia (> threefold variation in size, irregular nuclear membranes, coarse chromatin, macronucleoli) (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:44)
- Multivariate patient related predictors of lower disease free survival include > 80 years at time of diagnosis, worse in African American population, nonsurgical treatment (BMC Ear Nose Throat Disord 2018;18:15)
- Poorer prognosis associated with minor salivary gland location, large tumor (> 4 cm), high proliferation index, margin status, high grade transformation (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1258)
Case reports
- 52 year old man presented with dysarthria and dysphagia secondary to a base of tongue lesion (Case Rep Otolaryngol 2017;2017:4973573)
- 70 year old woman presented with a painless nodule at the angle of the left mandible (Head Neck Pathol 2020;14:554)
- 75 year old woman presented with 3 year history of nasal obstruction and epistaxis (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e19072)
Treatment
- Complete surgical resection
- Adjuvant radiotherapy provides no survival benefit but reduces locoregional recurrence (Medicine (Baltimore) 2020;99:e22671, Radiother Oncol 2019;140:125)
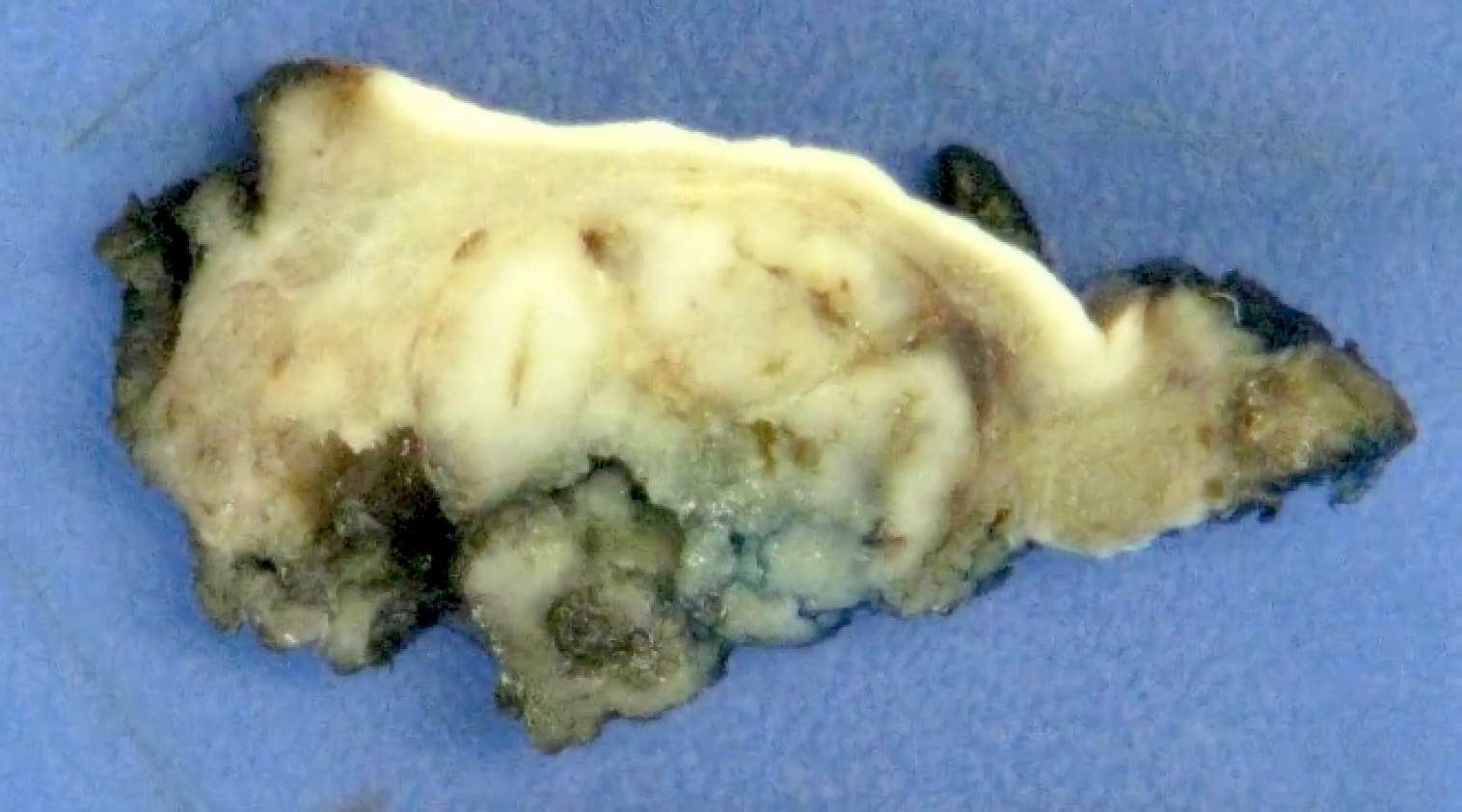
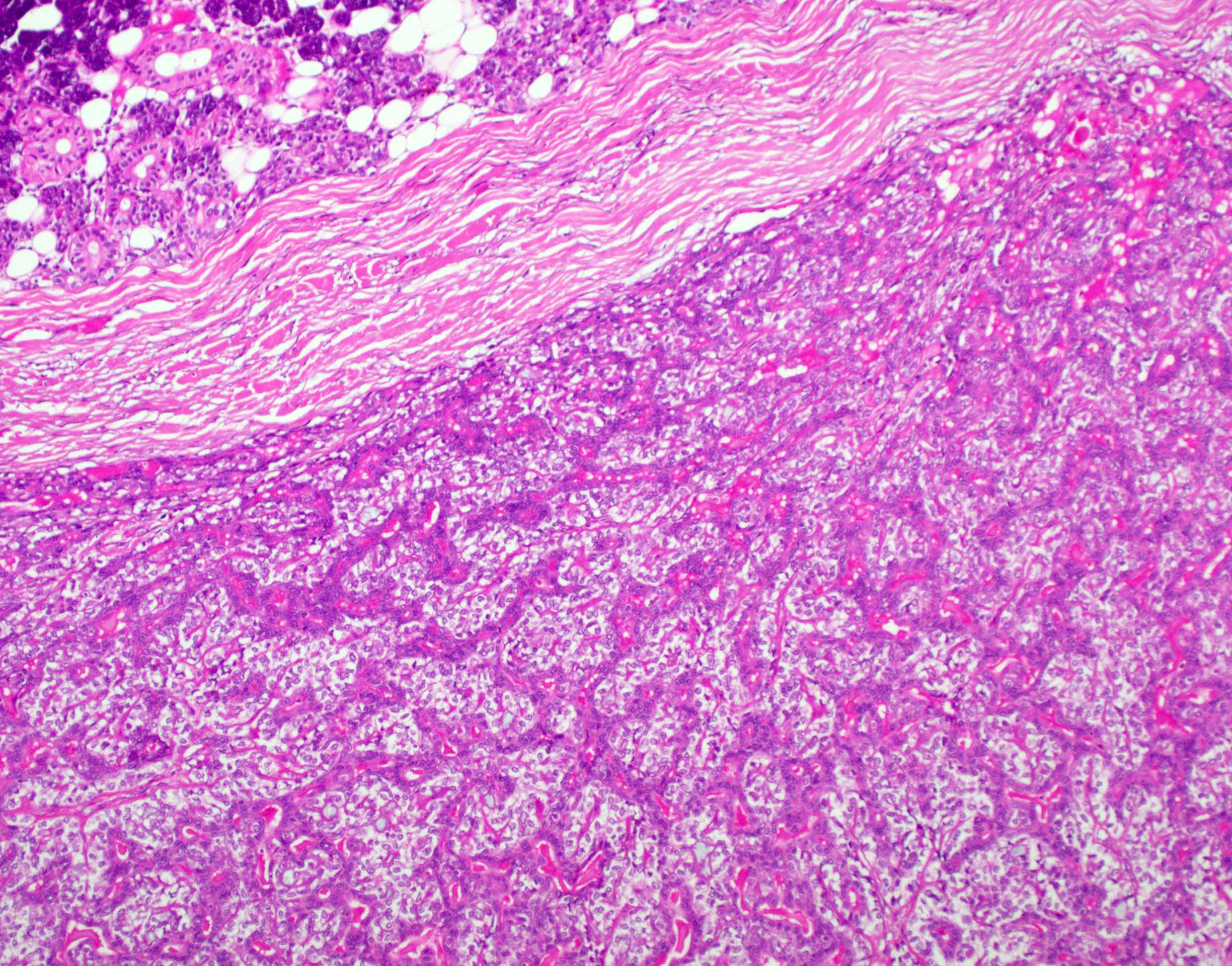
Gross description
- Lobulated, may be partially encapsulated
- Firm gray-tan rubbery mass
- Cystic change seen in up to 30% (Am J Surg Pathol 2007;31:44)
Frozen section description
- Should not be used; a reliable diagnosis of epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma may not be possible on frozen section
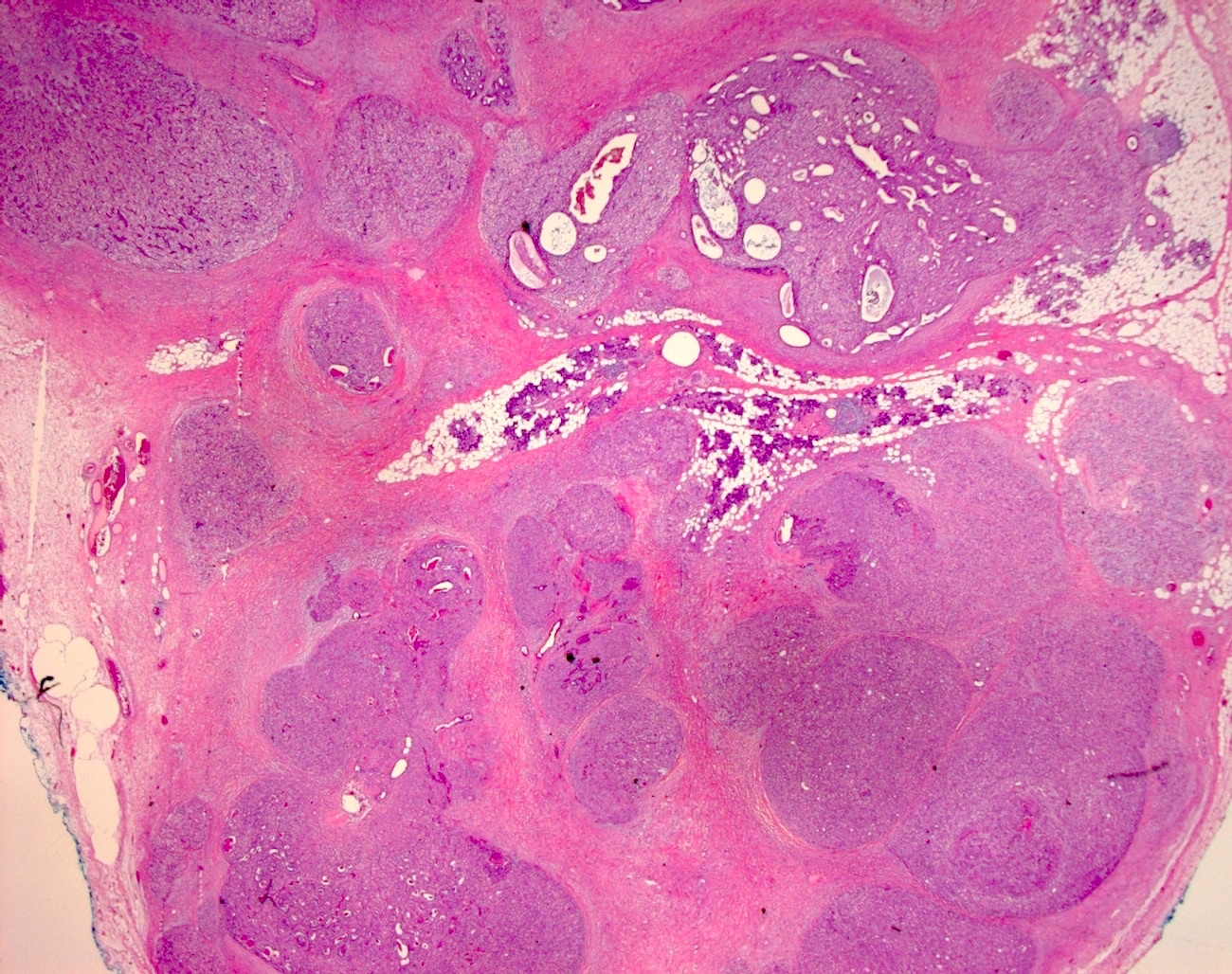
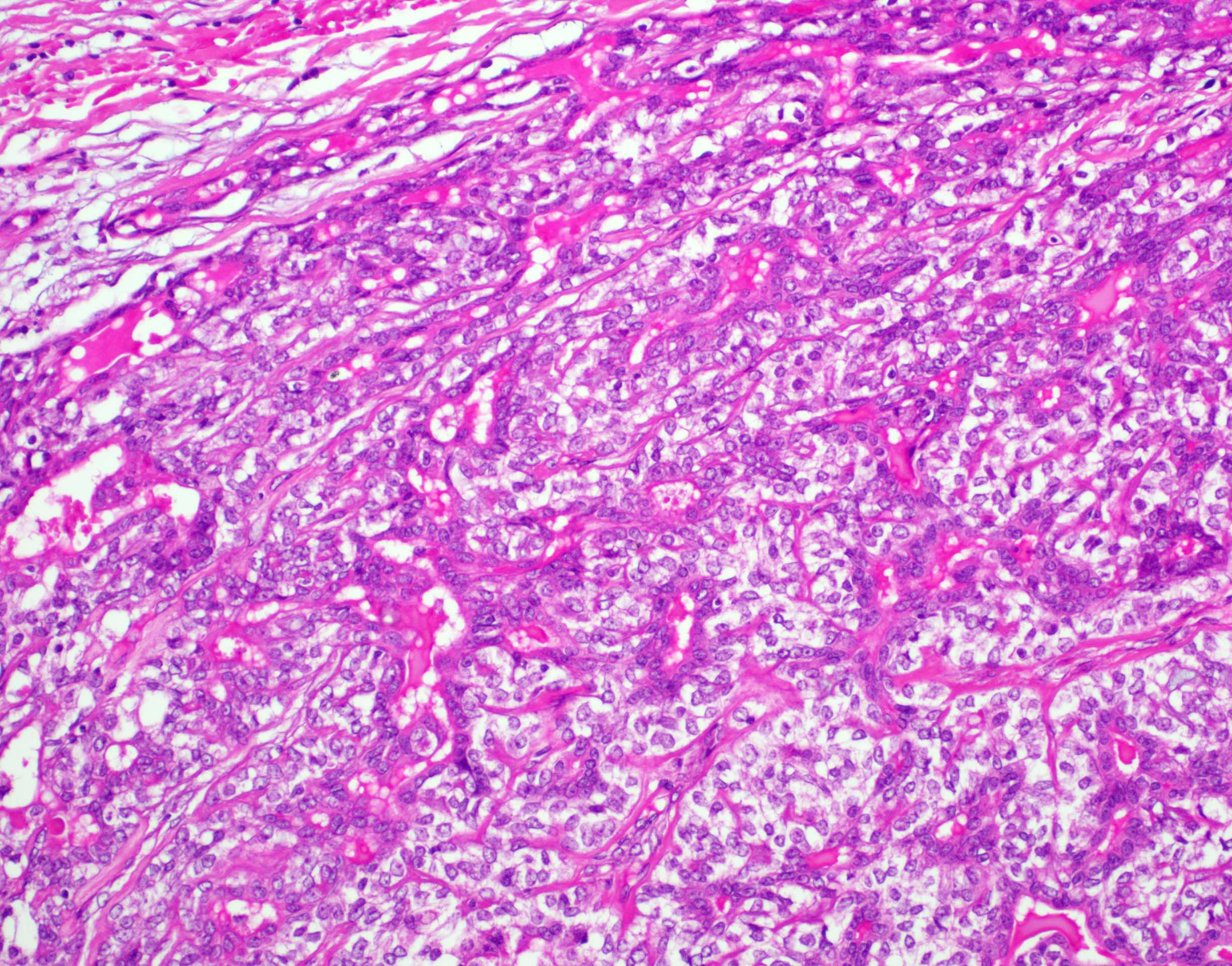
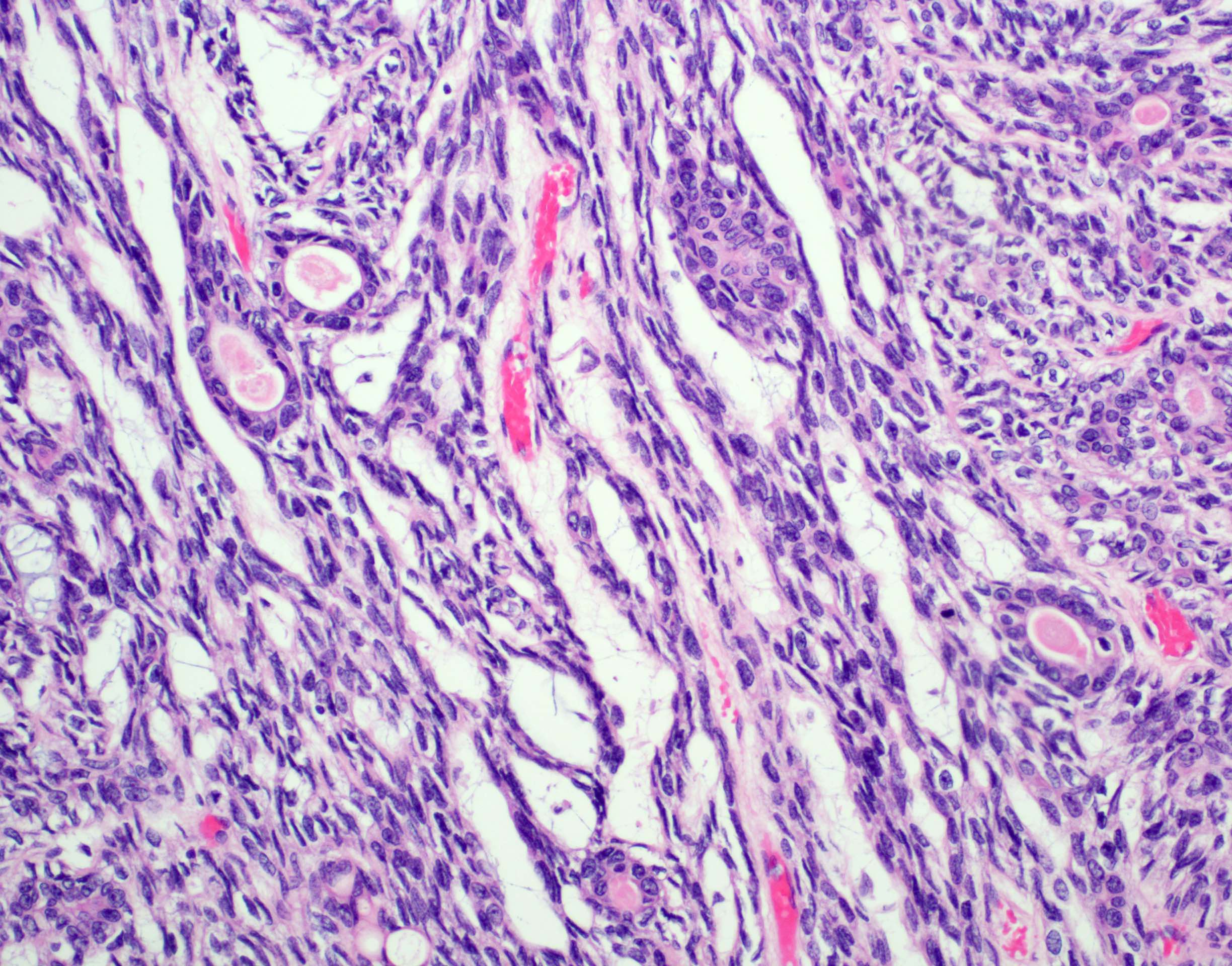
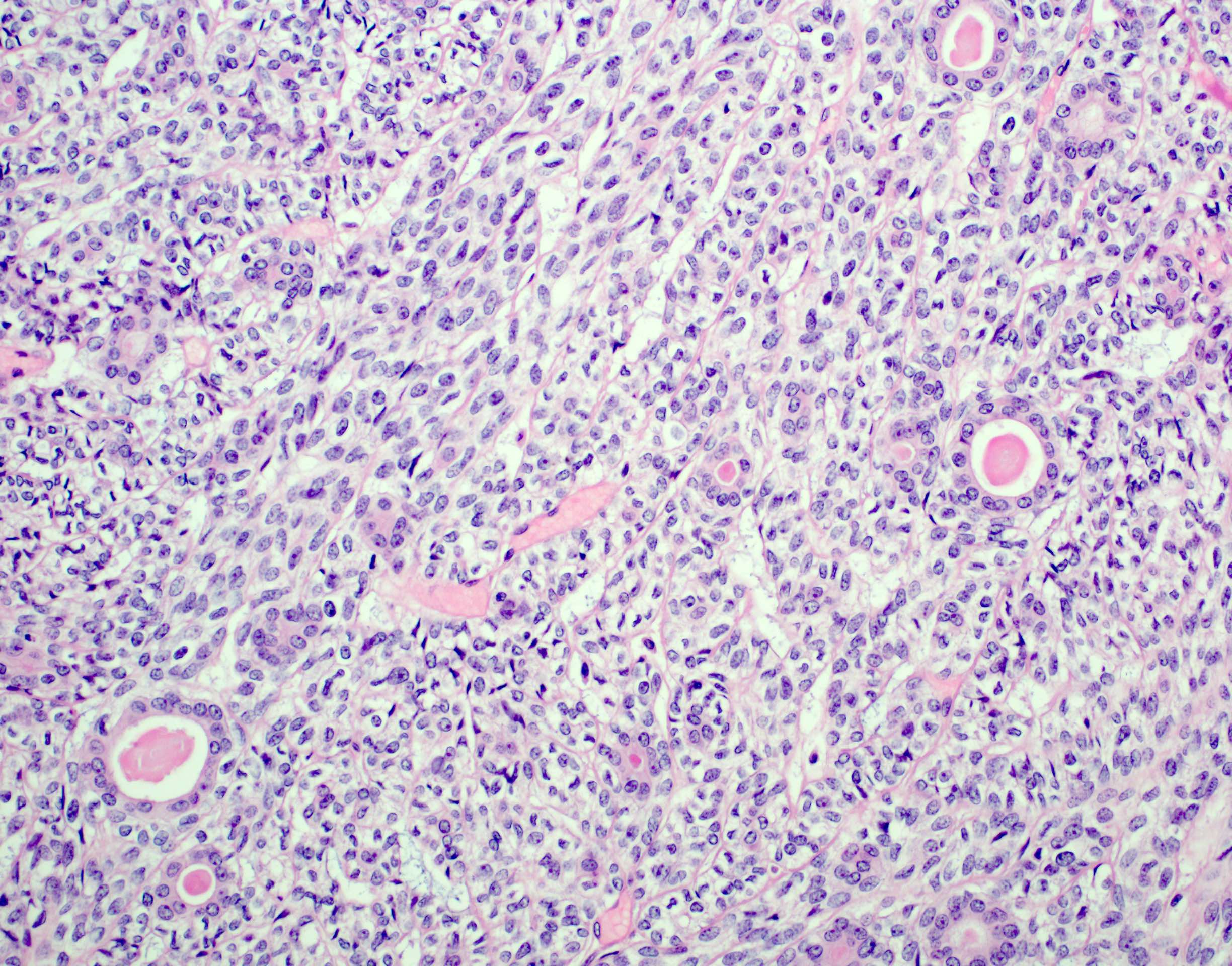
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Bilayered arrangement of small luminal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and outer myoepithelial cells with clear cytoplasm rich in glycogen (diastase sensitive PAS+)
- A few morphologic types may be seen, depending on the proportion of epithelial and myoepithelial cells present
- Classic
- Epithelial dominant
- Myoepithelial dominant
- Tubular, glandular, solid growth patterns
- Papillary and cystic areas may also be present (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:984)
- Basement membrane-like hyalinized matrix may be present
- Myoepithelial component can often be spindled or have clear cells
- High grade transformation (20%) infers poorer prognosis (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:S37)
- Usually the epithelial component
- Sheets and solid nests of markedly atypical cells with increased mitoses and necrosis
- Other morphological variants
- Oncocytic (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:S77, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:950)
- Usually presents in older patients
- Shows papillary growth pattern with calcifications
- Luminal cells contain densely granular cytoplasm
- Apocrine (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:S77, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:950)
- Brightly eosinophilic ductal cells with apical snouts and luminal secretions
- Cribriform to solid growth patterns
- Positive for androgen receptor and GCDFP-15
- Oncocytic (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:S77, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:950)
- Rare findings of squamous, sebaceous differentiation as well as ancient and Verocay-like change (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2009;133:950)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Cytology is not reliable, has a high false negative rate (Cancer Cytopathol 2020;128:392)
- Most cases may be misdiagnosed as pleomorphic adenoma due to overlapping cytological features
- Biphasic clusters of ductal cells admixed with larger clear myoepithelial cells
- Background naked myoepithelial nuclei with scant stromal fragments
- Occasional globules of hyalinized basal luminal material (Diagn Cytopathol 2003;28:163)
- Generally bland cytological features
Positive stains
- Ductal: AE1 / AE3 (100%), EMA (100%), DOG1 (53% apical) (Mod Pathol 2012;25:919)
- Myoepithelial: p63 (100%), smooth muscle actin (83%), calponin (64%), DOG1 (53% membranous), CK5/6, p40, SMMHC (Mod Pathol 2012;25:919)
- Both: S100 (49 - 95%), SOX10 (J Pathol Transl Med 2019;53:23)
Negative stains
- PAX8, HER2, GATA3, KIT and androgen receptor
Electron microscopy description
- Usually not required for diagnosis
- Ductal cells attached with junctional complexes and desmosomes and showing microvilli on luminal surface (J Med Assoc Thai 1998;81:712)
- Myoepithelial cells contain abundant glycogen (electron lucent) with cytokeratin filaments, subplasmalemmal plaques and multilayered basal lumina
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- HRAS mutations (codon 61) (Am J Surg Pathol 2019;43:984)
- PLAG1 or HMGA2 (residual pleomorphic adenoma) (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:18)
- Rarely SMARCB1 deletion and mutations in FBXW7 or TP53 (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:18)
Sample pathology report
- Left parotid, excision:
- Epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma (see comment)
- Comment: There is a lobulated and unencapsulated biphasic primary neoplasm. The tumor shows a nodular growth pattern. The tumor is composed of bilayered arrangement of small luminal cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and outer polygonal clear, rich in glycogen (diastase sensitive PAS+) myoepithelial cells. Immunohistochemically the inner epithelial cells are positive for AE1 / AE3 and EMA, while the outer myoepithelial layer shows staining for p63, smooth muscle actin and S100. There is no evidence of necrosis or high grade transformation.
Differential diagnosis
- Pleomorphic adenoma:
- Multinodular with bosselated growth
- Chondromyxoid matrix
- Can have adipose tissue as a stromal element imparting a permeative appearance
- Can show pseudopodia extending into the adjacent tissues
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Cribriform growth pattern (less common in epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma)
- MYB rearrangement
- Basal cell adenoma:
- Prominent stromal hyalinization
- Lacks invasive growth and nuclear pleomorphism
- Nuclear beta catenin
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma, clear cell variant:
- Presence of mucocytes and cyst formation
- MAML2 translocation
Board review style question #1
A 65 year old woman presented with a 3 month history of unilateral cheek lump that recently increased in size. A histologic image of the resection is provided above. What is the most common histological feature associated with this lesion?
- Anaplasia
- High proliferation index
- Lymphovascular invasion
- Necrosis
- Perineural invasion
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following immunohistochemical combinations is most helpful in diagnosing epithelial myoepithelial carcinoma?
- AE1 / AE3, CD117 and p63
- AE1 / AE3, EMA and CK7
- AE1 / AE3, S100 and p63
- Nuclear beta catenin
- p63, SMA and calponin
Board review style answer #2