Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Handra-Luca A. Canalicular adenoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/salivaryglandscanalicularadenoma.html. Accessed April 17th, 2024.
Definition / general
- 1942 (McFarland) first description; variant of monomorphic / basal cell adenoma (Am J Med Sci 1942;203:502)
- 1991 identified as separate entity in the WHO classification (Seifert: Histological Typing of Salivary Gland Tumours, 2nd Edition, 1991)
- Benign epithelial neoplasm composed of cubocolumnar cells disposed in branching and interconnecting cords and associated with a paucicellular, vascular stroma
- 1 - 3% of salivary gland tumors (Int J Oral Maxillofac Surg 2005;34:533, Oral Oncol 2008;44:407)
- 4 - 6% of minor salivary gland tumors (Oral Oncol 2007;43:463, Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1988;66:323, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol 2012;114:230)
Essential features
- Monotonous, benign epithelial neoplasm; no basal / myoepithelial layer
- Most frequently located in the minor salivary glands
- May be multifocal
- Treatment by surgical resection
Terminology
- Retired terminology: canalicular tumor; canalicular mixed tumor; monomorphic adenoma, canalicular type; cystic adenoma; adenomatosis of accessory salivary glands
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 8149/0 - canalicular adenoma
Epidemiology
- Adults; female gender predominance (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1984;57:181, Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Peak seventh decade; usually ages 50+ years
- Non-Asian population (Adv Ther 2019;36:1950)
Sites
- Upper lip (80%), followed by buccal mucosa, lower lip, hard and soft palate (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Extremely rare in major salivary glands (parotid); consider HMGA2-WIF1 fusion pleomorphic adenoma in differential diagnosis
Pathophysiology
- Derives from terminal ducts of salivary glands; intralobular ducts resemble intercalated ducts (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
Etiology
- Unknown
Clinical features
- Painful or painless, mucosal ulceration, tumor duration months to years (slow growing) (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
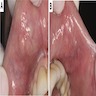
- Swelling; tumor may be multifocal, bilateral (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1982;53:375, Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 1995;33:299, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol Oral Radiol Endod 1999;87:346)
- Discomfort (with / without prothesis), pressure (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017;45:1754)
Diagnosis
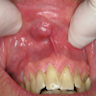
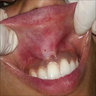
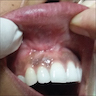
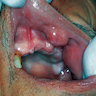
- Clinical examination: movable, well circumscribed nodule (0.5 - 2 cm); unique or multiple nodules; possibly bilateral; exophytic mass or swelling; bluish or ulcerated mucosa (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017;45:1754)
- Clinical differential diagnosis: mucocele, thrombosed vessel, lipoma, salivary gland tumor (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
Laboratory
- Lack of specific laboratory tests
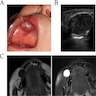
Radiology description
- Ultrasonography: relatively homogeneous, poorly echoic mass, containing a liquid region with relatively low viscosity (J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol 2020;32:525)
- Magnetic resonance imaging / MRI (J Oral Maxillofac Surg Med Pathol 2020;32:525):
- Axial T1 weighted MRI: isointense mass
- T2 weighted MRI: increased signal intensity
Prognostic factors
- Favorable prognosis: complete resection
- Persistence due to multifocality may be indistinguishable from recurrence (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Recurrence rates: 3% recurrence, 5% recurrence after surgery
Case reports
- 61 year old woman with synchronous polymorphous adenocarcinoma (Head Neck Pathol 2018;12:145)
- 78 year old woman with synchronous, multiple, bilateral tumors (Clin Exp Dermatol 2009;34:e587)
Treatment
- Surgical excision; although multifocality may suggest recurrence (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
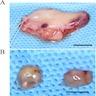
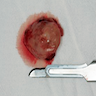
Clinical images
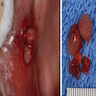
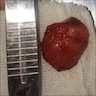
Gross description
- Often encapsulated; may be multifocal
- Tumor may be resected as 1 or fragmented specimens
- On cut surface: homogeneous or cystic spaces
- Reference: Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181
Gross images
Frozen section description
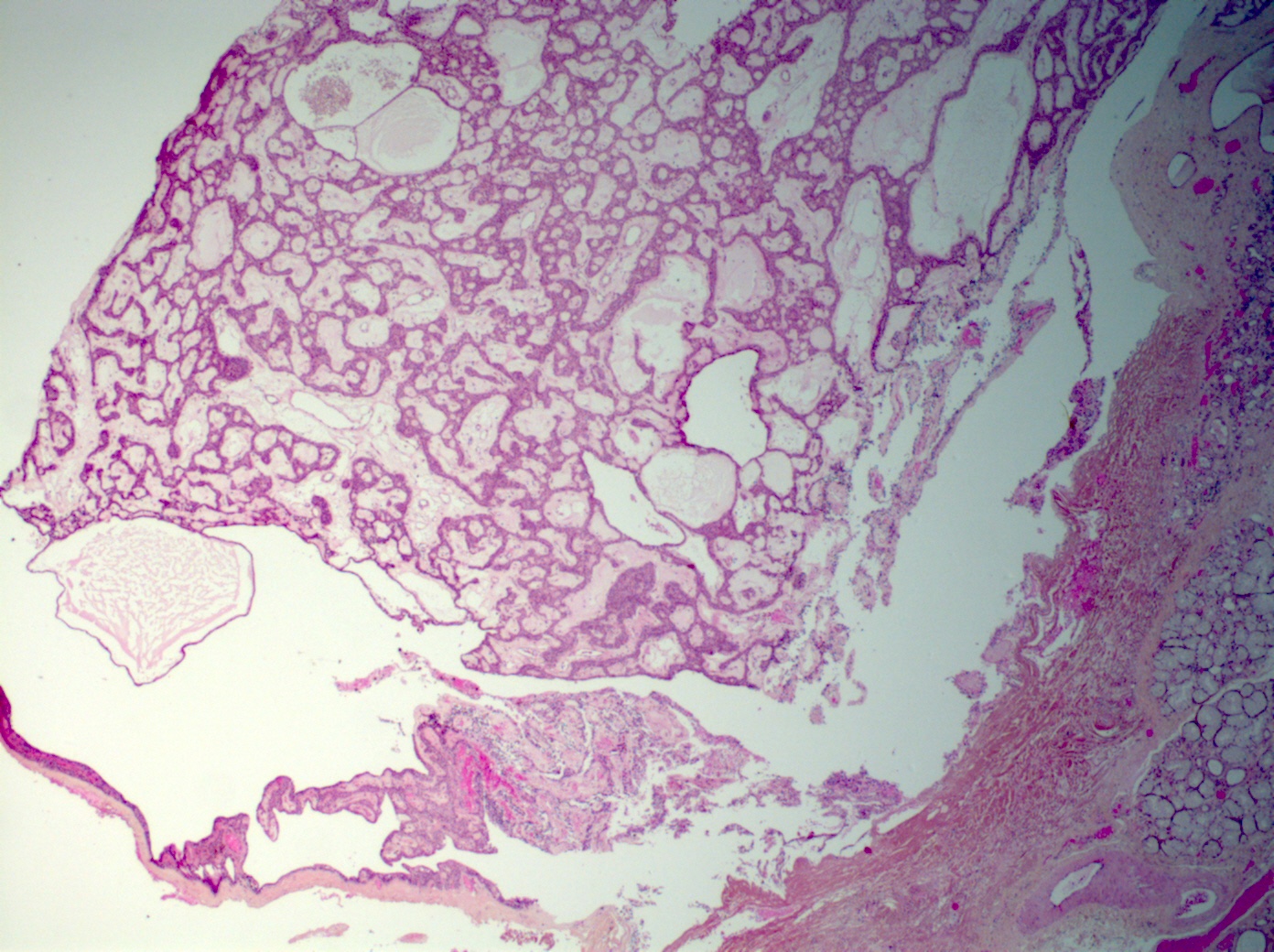
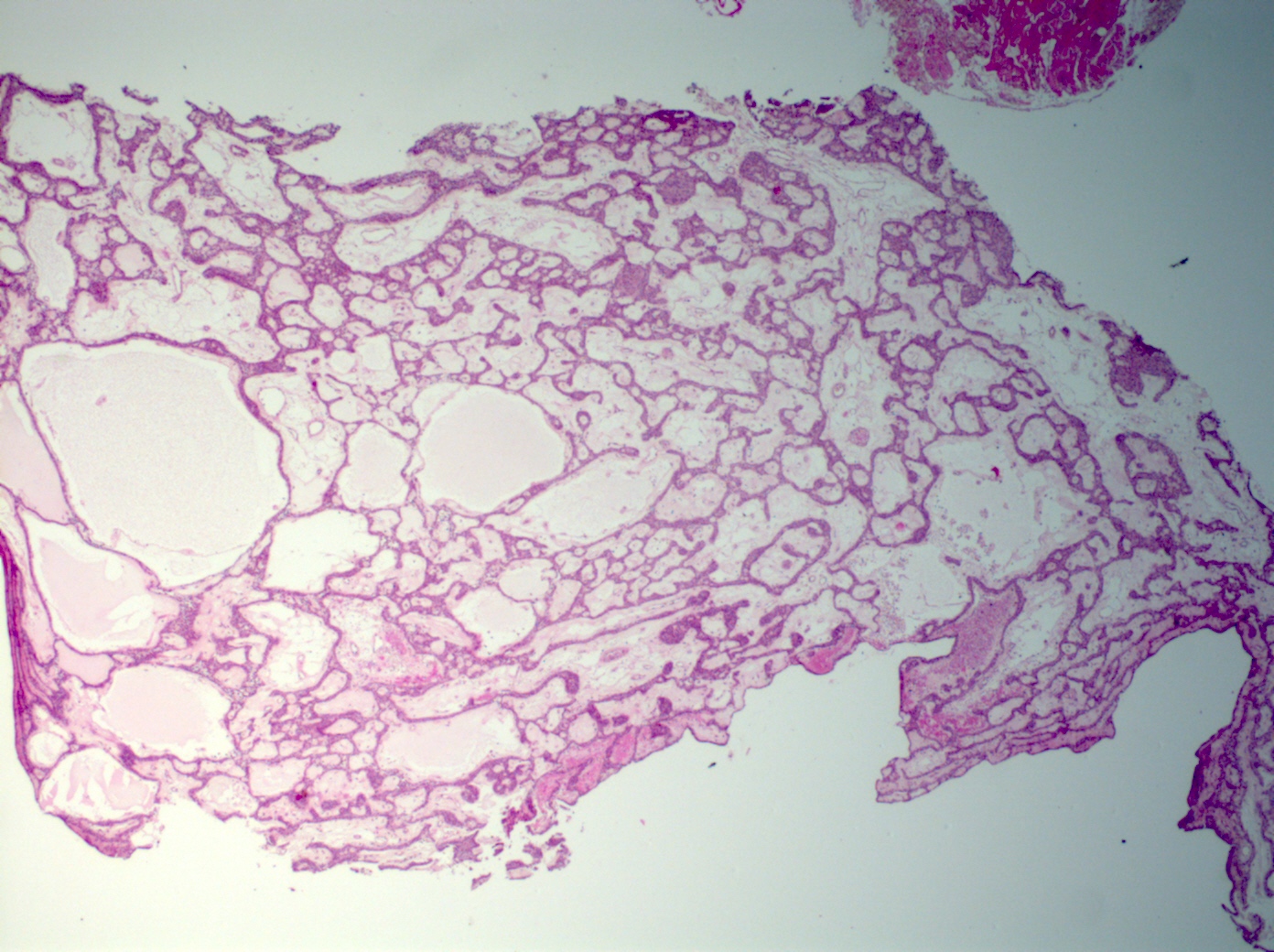
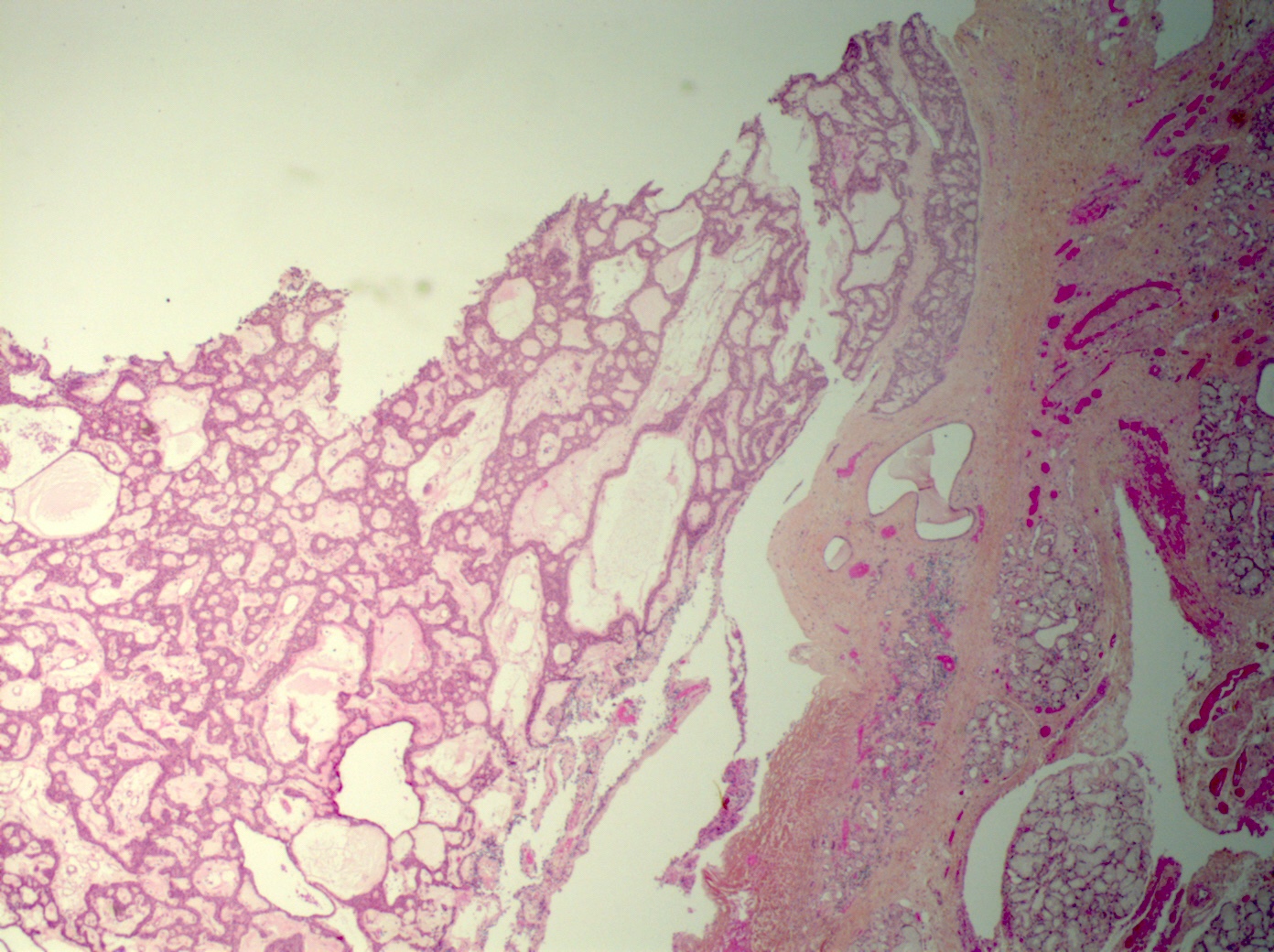
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Tumors may be single or multifocal
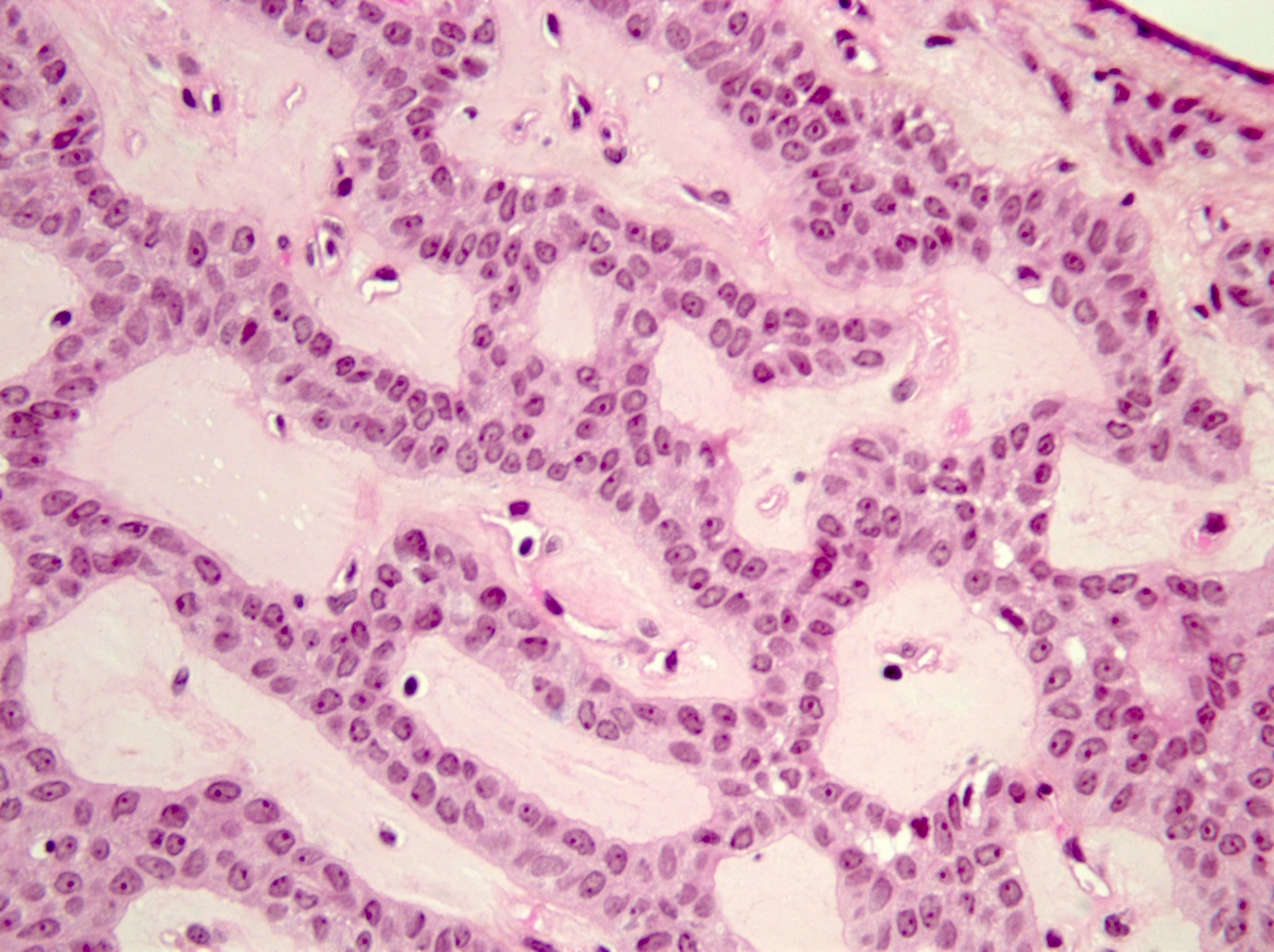
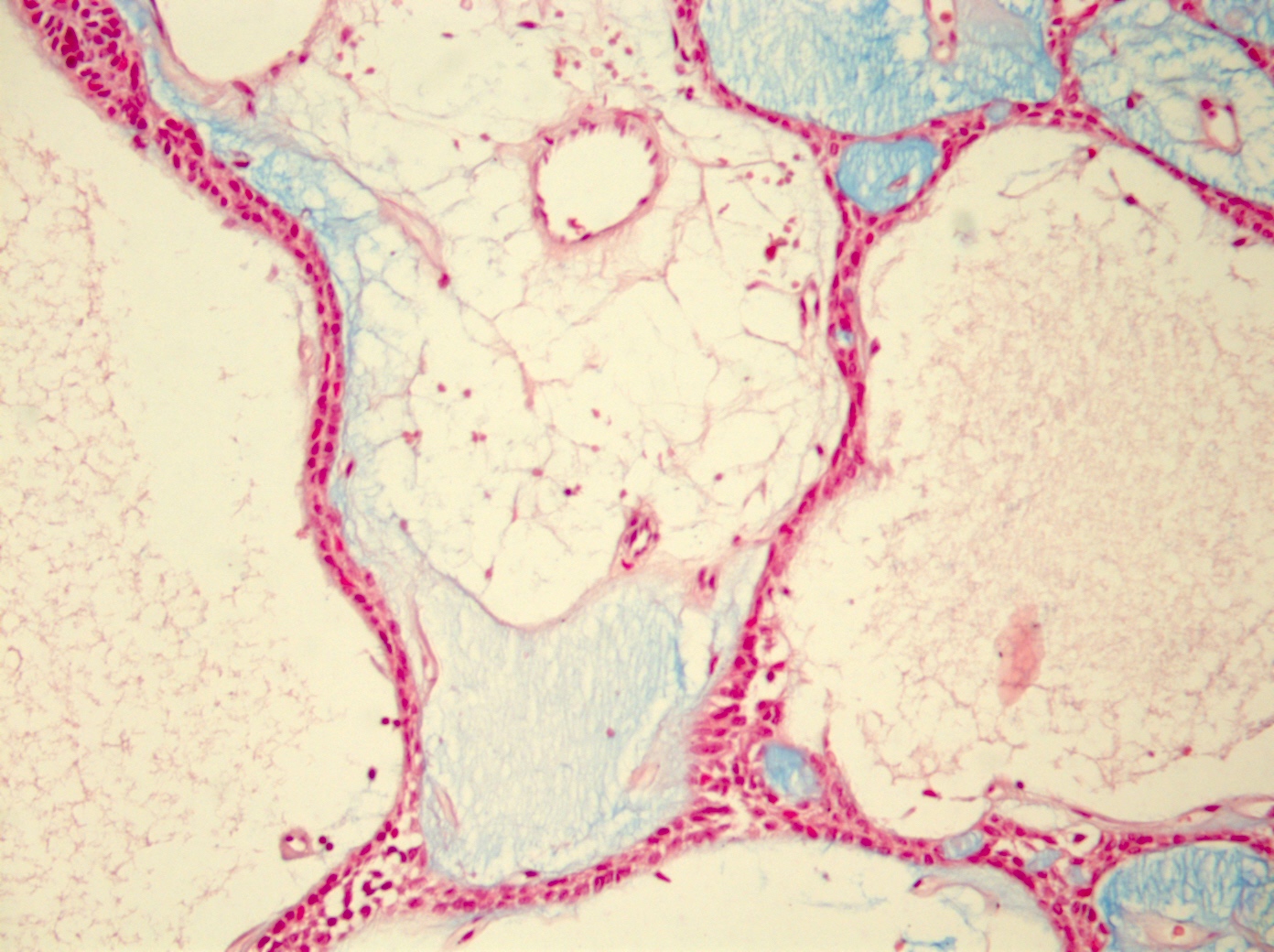
- Bilayered strands or ribbons or anastomosing cords or branching tubules
- Canalicular to cystic spaces between the cell strands; trabecular features
- Lack of an outer layer of myoepithelial cells
- Beading pattern, club ended cords
- May infiltrate capsule and show extracapsular tumor islands (including in the normal salivary gland / multiple tumors)
- Often cystic change
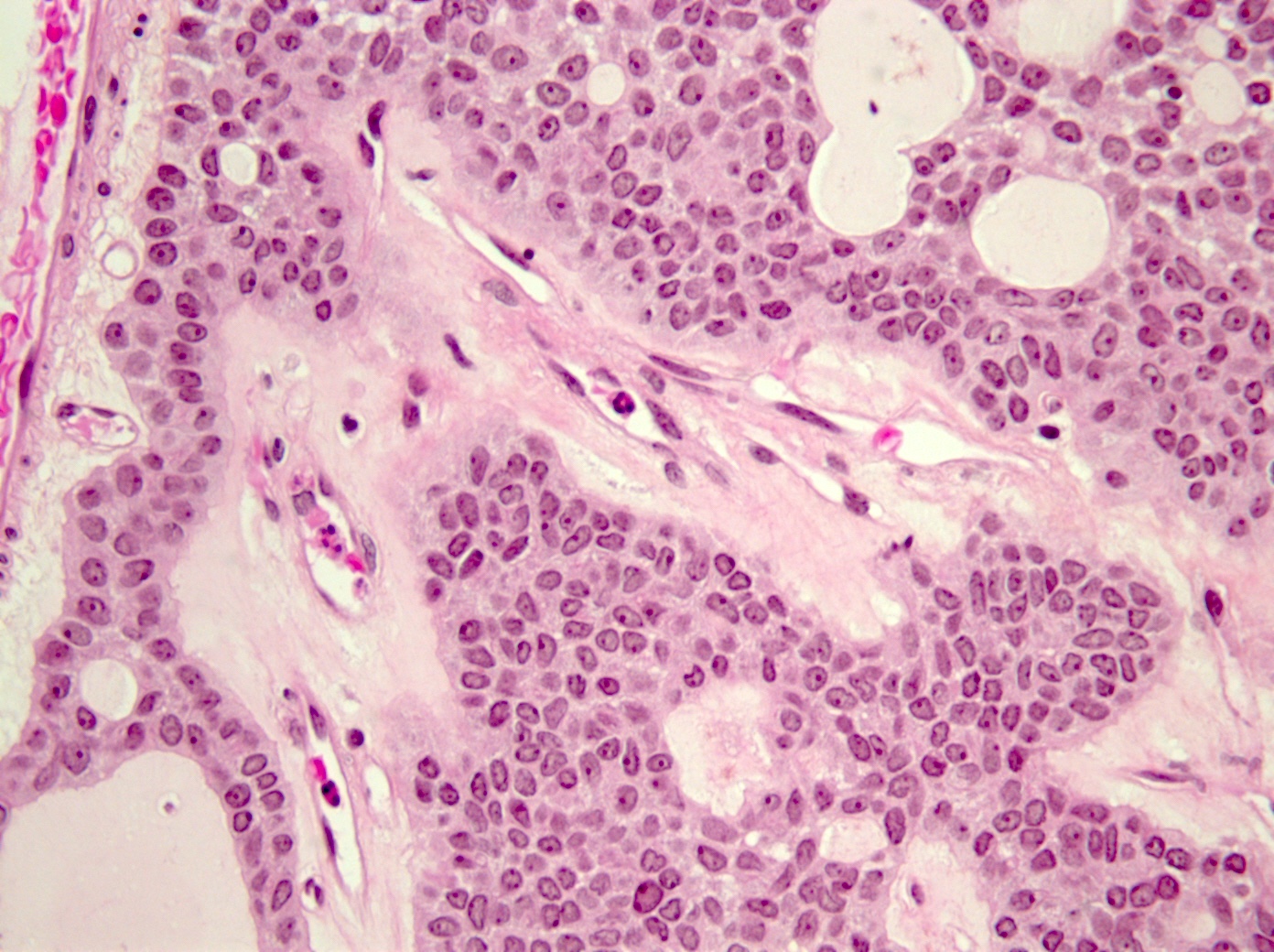
- Tumoral columnar or cuboidal cells, foci of basaloid cells
- Amphophil to eosinophilic cytoplasm, apocrine / oncocytic
- Round to elliptical, uniform nuclei, focally nucleoli, basophilic chromatin, rare to absent mitoses
- Mucous / mucinous metaplasia (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Pigmented cells
- Lacks or has exceptional necrosis (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Microliths, tyrosine crystals, morules and squamous balls (intraluminal) (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017;45:1754, Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181, Histopathology 1999;35:502)
- Well vascularized, loose stroma; possibly sclerotic; perivascular eosinophil cuffs
- Luminal or stromal histiocytes (foamy, lipofuscin, hemosiderin), luminal hemorrhage, degenerated / infarcted stroma (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Malignant transformation not reported; lack of atypical figures (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- Occasionally reported as collision tumors or hybrid tumors (Eur J Cancer B Oral Oncol 1996;32B:251)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- FNA smears (hematoxylin, eosin and May-Grünwald-Giemsa stains) pseudopapillary clusters, oval, spindle basaloid cells, scant cytoplasm or eosinophilic, isolated cells, bland nuclear chromatin, no visible nucleoli, no chondroid or myxoid substance (Head Neck Oncol 2014;6:32)
Cytology images
Positive stains
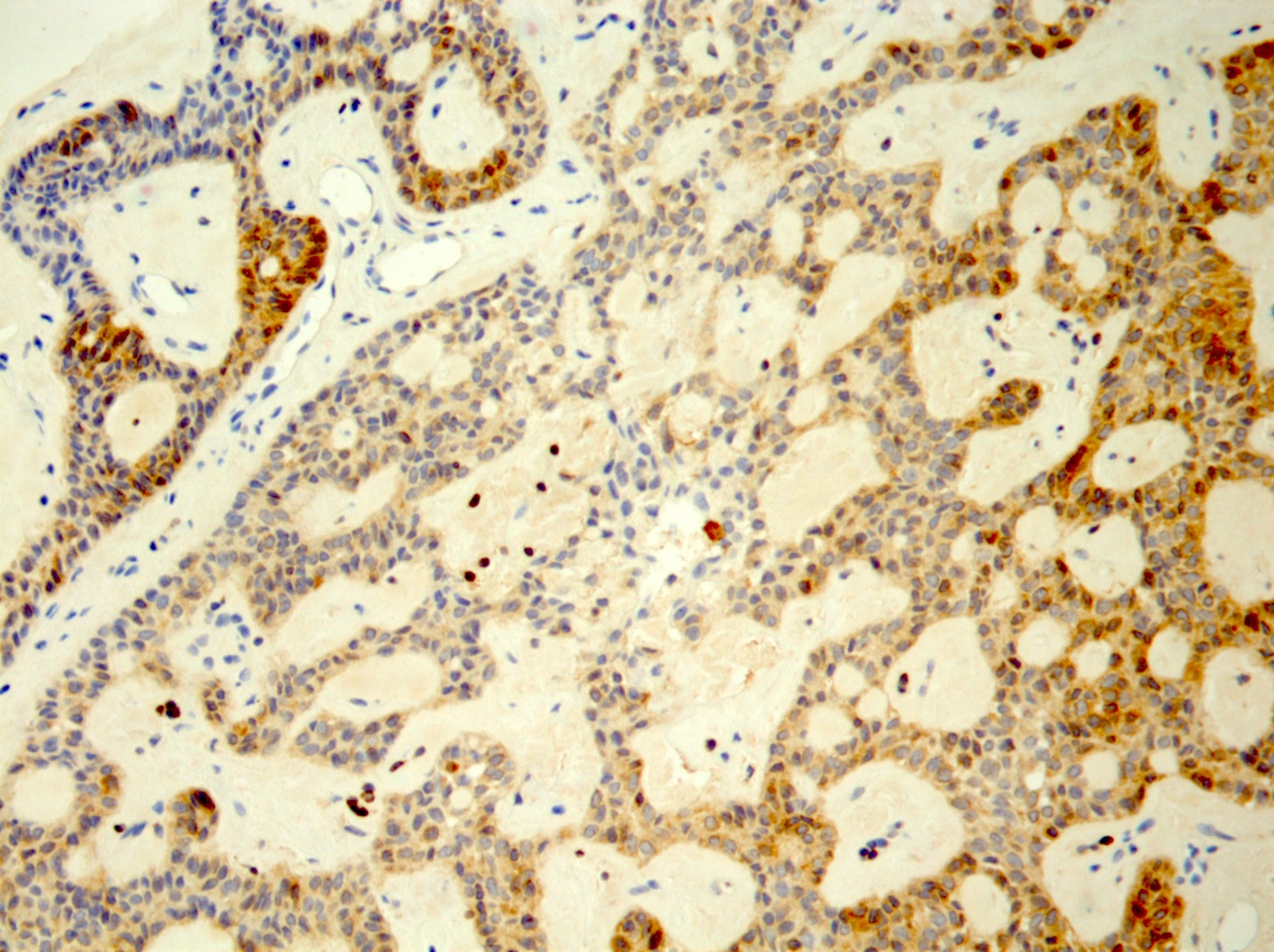
- S100, AE1 / AE3, CK19
- Pancytokeratin (heterogeneous intensity), CK7, CK8, CK13, CK14 basally (Gerodontology 2014;31:320)
- Focal GFAP; distinctive linear immunoreactive pattern of GFAP among cells in proximity to connective tissue interface (Gerodontology 2014;31:320)
- CD117 (Pol J Pathol 2013;64:71)
- BCL2
- Varied p63 expression, nuclear p63 in squamoid foci, lack of p63+ duct surrounding cells (Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol 2016;24:501, J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017;45:1754, Adv Ther 2019;36:1950, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Jul 29 [Epub ahead of print])
- Nuclear CAM 5.2, nuclear SOX10, nuclear and cytoplasmic p16, vimentin variably positive (J Craniomaxillofac Surg 2017;45:1754)
- Squamous balls: p16 and CK5/6 positive
- Heterogeneous, moderate to strong cytoplasmic WT1 (periphery of ribbon-like structures); in microadenomatous foci, associated with cuboidal cells (Pathol Res Pract 2014;210:726)
- Stroma: blue on Alcian blue / PAS stain and CD15+ (Adv Ther 2019;36:1950)
Negative stains
- E-cadherin
- Myoepithelial markers (alpha smooth muscle actin, smooth muscle myosin heavy chain, calponin)
- p40 (Head Neck Pathol 2015;9:181)
- DOG1 (Ann Diagn Pathol 2019;43:151408)
- CEA and EMA variable or negative (Adv Ther 2019;36:1950)
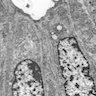
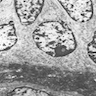
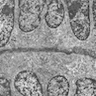
Electron microscopy description
- 2 rows of cells (tall columnar cells surrounding the canalicular lumina and conical cells situated between columnar cells, with direct contact with stromal connective tissue); interdigitating cells
- Canalicular lumen: minimum amount of cell debris; no mucoid material
- Small number of desmosomes
- Ovoid nuclei, moderately prominent nucleoli, patchy condensation of chromatin
- Reference: Cancer 1980;46:552
Electron microscopy images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- 1/21 cells: a doubled normal complement (Hereditas 1996;124:105)
- No fusions identified to date (Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Jul 29 [Epub ahead of print])
Sample pathology report
- Minor salivary gland, nodule resection:
- Canalicular adenoma (1.5 cm); excised
Differential diagnosis
- Adenocarcinoma, NOS:
- Tumoral glands and duct-like structures
- Infiltrative growth pattern
- Nuclear atypia, mitoses
- Presence of vascular emboli, perineural invasion
- Adenoid cystic carcinoma:
- Ductal and modified myoepithelial cells with hyperchromatic angular nuclei
- Hyalinized stroma
- Destructive infiltration; cribriform / tubular pattern
- Lack of capillaries in the stroma
- Pleomorphic adenoma (with canalicular-like pattern) (Adv Ther 2019;36:1950, Am J Surg Pathol 2021 Jul 29 [Epub ahead of print]):
- Presence of myxoid, chondroid mesenchymal tumor component
- HMGA2-WIF1 described
- Polymorphous low grade adenocarcinoma:
- Basal cell adenoma:
- Majority of basaloid cells
- Myoepithelial differentiation (expression of smooth muscle actin)
- Stroma: more collagenous
- Squamous differentiation
- LEF1 and beta catenin nuclear positive (Hum Pathol 2015;46:255)
- p63 positive
Additional references
- JCRI 2014;2:61, J Oral Diag 2016;1:e12, Histopathology 2006;49:538, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:140
- Rosai: Rosai and Ackerman's Surgical Pathology, 10th Edition, 2011, Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 1991;100:687, Barnes: Pathology and Genetics of Head and Neck Tumours, 3rd Edition, 2005, El-Naggar: WHO Classfication of Head and Neck Tumours, 4th Edition, 2017, Ellis: Tumors of the Salivary Glands, Atlas of Tumor Pathology, 3rd Series, 1996
- Cancer 1973;31:1511, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1983;56:608, Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1994;78:761, Ann Diagn Pathol 1998;2:224, Arch Pathol Lab Med 1999;123:801, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:401, Oral Oncol 2001;37:365, Mod Pathol 2002;15:298, Ann Diagn Pathol 2003;7:278, Head Neck Pathol 2007;1:27, J Oral Pathol Med 2007;36:207, Oral Oncol 2009;45:594
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about salivary gland canalicular adenoma?
- Cannot be multifocal
- Is a benign tumor
- Is rare in minor salivary glands
- Lacks stromal tissue
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is true about salivary gland canalicular adenoma?
- Is a type of adenocarcinoma
- Is often associated with lymph node metastases
- May contain squamous balls
- May show vascular emboli
Board review style answer #2