Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Matoso A. Mesonephric remnant hyperplasia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostatemesonephrichyper.html. Accessed November 29th, 2024.
Definition / general
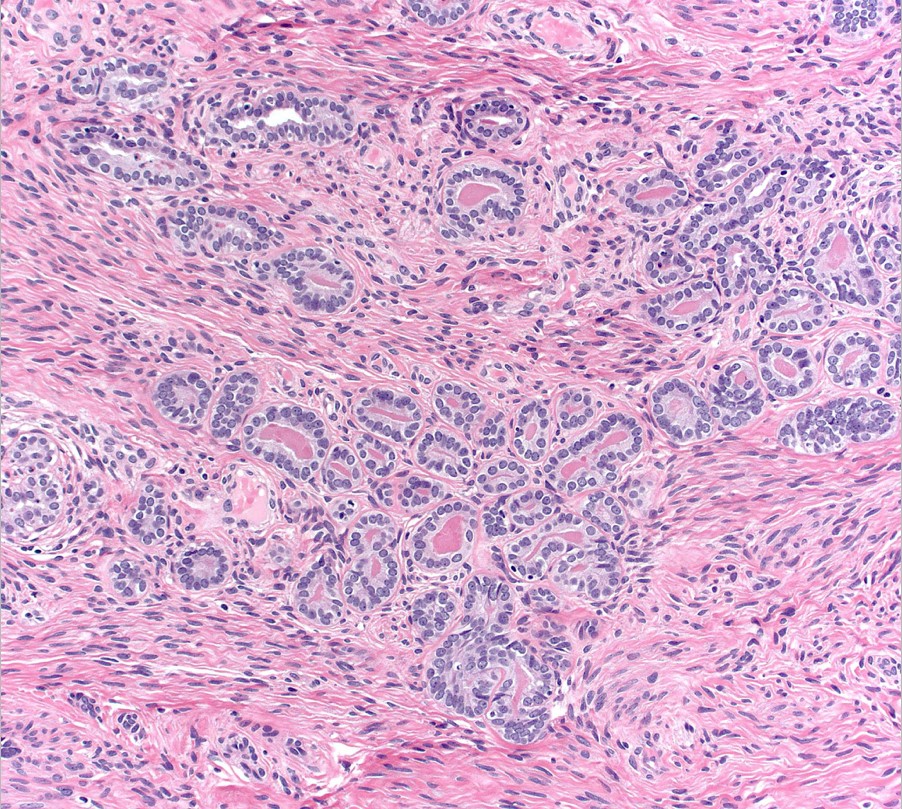
- Mesonephric remnant hyperplasia is a proliferation of small glands that mimic prostatic carcinoma
- This is more common in the female genital tract and can rarely be seen within the prostate
Essential features
- Cluster of small acini with eosinophilic secretion, cells with bland nuclei and inconspicuous nucleoli usually in a lobular distribution
- An infiltrating pattern can be seen occasionally, mimicking cancer
- Papillary infolding or small ill formed glands may mimic high grade prostate cancer
- No clinical significance
Epidemiology
- Mean age 60 years (range, 40 to 80 years)
Sites
- Prostate and periprostatic tissue
Pathophysiology
- Believed to represent an embryologic remnant
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic
Prognostic factors
- Not associated with increased risk of cancer
Treatment
- Not required
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cluster of small acini with eosinophilic secretion, with cells with bland nuclei and inconspicuous nucleoli usually in a lobular distribution
- An infiltrating pattern can be seen occasionally, mimicking cancer
- Papillary infolding or small ill-formed glands may mimic high grade prostate cancer
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- High molecular weight cytokeratin and p63 are typically positive but can be negative
- Racemase can be focally positive; when positive, along with negative p63 and high molecular weight cytokeratin, can erroneously lead to a diagnosis of adenocarcinoma of the prostate
- PAX8 is positive
Differential diagnosis
Additional references