Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Sanders M, Varma M. High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN). PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/prostateHGPIN.html. Accessed December 21st, 2024.
Definition / general
- Putative precursor of prostatic adenocarcinoma
Essential features
- Nucleoli visible at 200x magnification (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:873)
- Surrogate marker for missed cancer in negative prostate biopsies; less useful in contemporary practice as lower incidence of unsampled prostate cancer with extended biopsy protocols
- No clinical utility in radical prostatectomies and biopsies containing foci suspicious or diagnostic of prostate cancer
- Would not account for raised serum PSA or radiological abnormality
Terminology
- Formerly known as severe dysplasia, PIN 2 / PIN 3 and carcinoma in situ
- PIN = high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN); low grade PIN is not reported due to wide interobserver variability (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:873)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Needle biopsy prevalence: 0 - 25%, mean 7.7% (Korean J Urol 2012;53:297)
- Cystoprostatectomy prevalence: 11 - 34% (BJU Int 2007;99:780, Urology 2007;70:1100, Hum Pathol 2016;55:117)
- Earlier age and more diffuse in African Americans, lower incidence in Asians (Pathol Res Pract 1995;191:838)
Sites
- Prostate gland
Clinical features
- Would not account for elevated serum PSA or abnormal digital examination findings or radiological abnormality
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is made on histologic examination of biopsied prostate tissue, typically from a needle core biopsy
Radiology description
- No radiological abnormality
Prognostic factors
- Contemporary value of HGPIN as predictor of missed cancer is contentious
- Risk of finding cancer on rebiopsy following unifocal HGPIN diagnosis is similar to benign diagnosis (Pathology 2010;42:325, J Urol 2009;182:485)
- Risk of finding cancer on rebiopsy following multifocal HGPIN (2 or more cores) diagnosis is substantially higher at 30 - 40% (Pathology 2010;42:325, J Urol 2009;182:485, Urol Oncol 2020;S1078-1439:30488)
- Cancers associated with HGPIN diagnosis on initial biopsy are more likely to be low grade and organ confined as compared to cancers diagnosed in the first biopsy without preexisting HGPIN (Can J Urol 2015;22:8056, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1165)
- Prostate cancer detected at rebiopsy following diagnosis of HGPIN generally low grade and organ confined (Can J Urol 2015;22:8056, J Urol 2009;181:1069, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1165)
- Rebiopsy Gleason ≥ 7 rate following diagnosis of HGPIN in contemporary practice similar to that following an initial benign biopsy (17% versus 14%) (Hum Pathol 2018;79:116)
Case reports
- 60 year old man with foamy gland HGPIN (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:140)
- 69 year old man with foamy gland HGPIN (Human Pathology Case Reports 2017;10:32)
Treatment
- Follow up PSA
- Repeat biopsy if PSA remains elevated
- NNCCN guidelines (2021) recommendations for isolated HGPIN:
- Focal (HGPIN in 1 site): follow-up as following benign biopsy
- Multifocal (HGPIN in > 2 sites): If extended biopsies performed initially then rebiopsy only those at high risk of more aggressive prostate cancer (NNCCN.org: National Comprehensive Cancer Network Clinical Guidelines in Oncology - Prostate Cancer Early Detection, 2021 [Accessed 19 February 2021])
- No therapy is needed for HGPIN as an isolated finding in needle biopsy (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71)
Microscopic (histologic) description
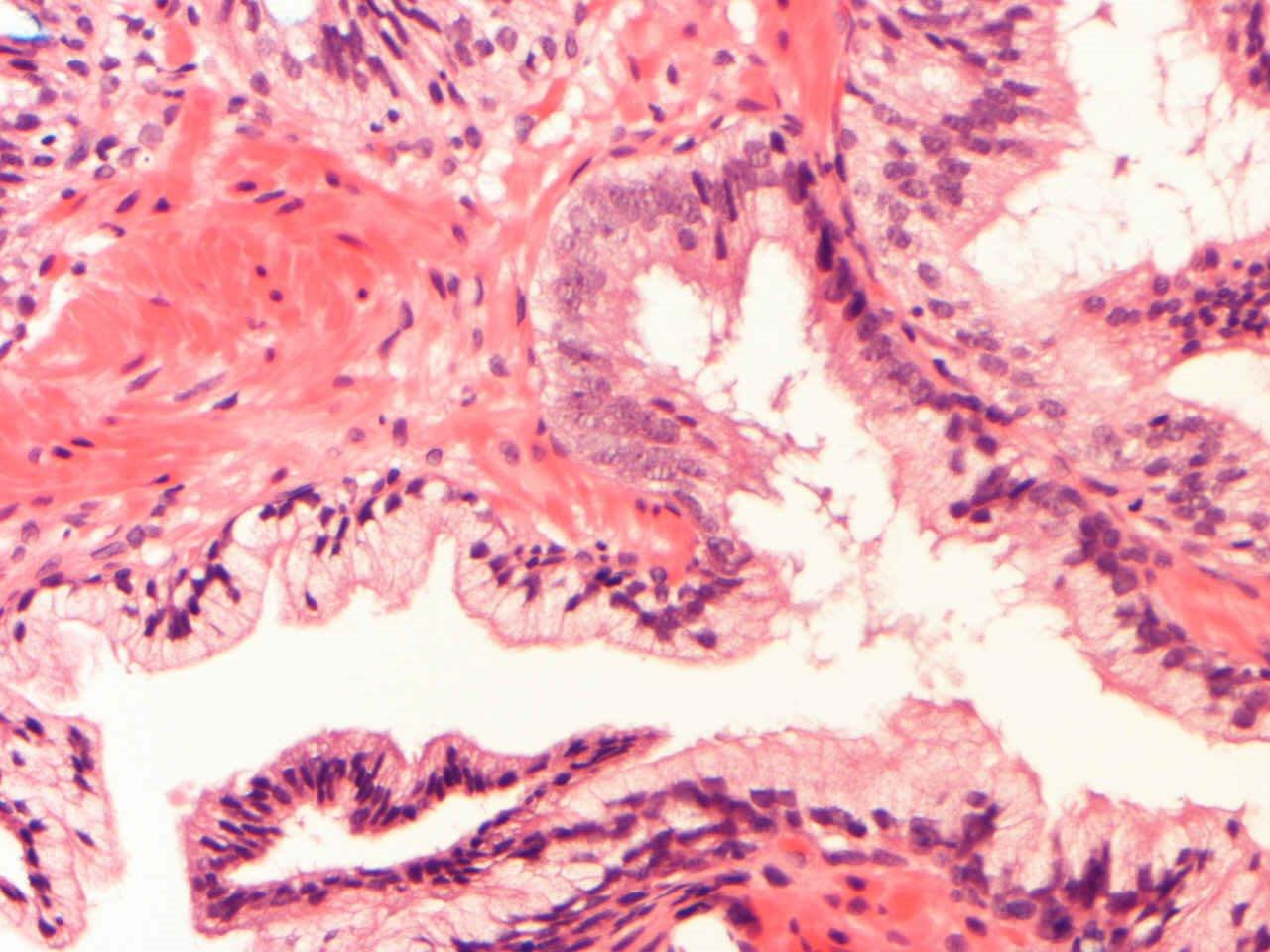
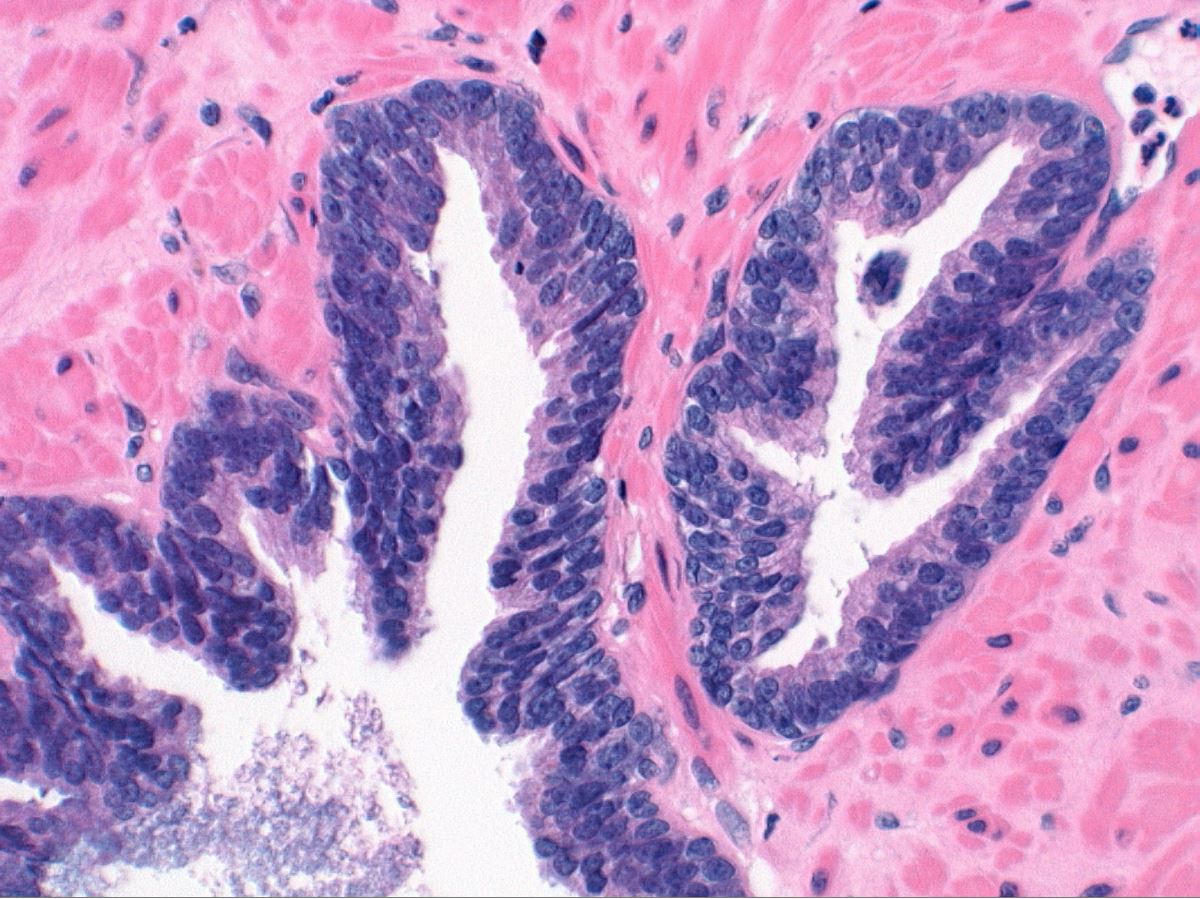
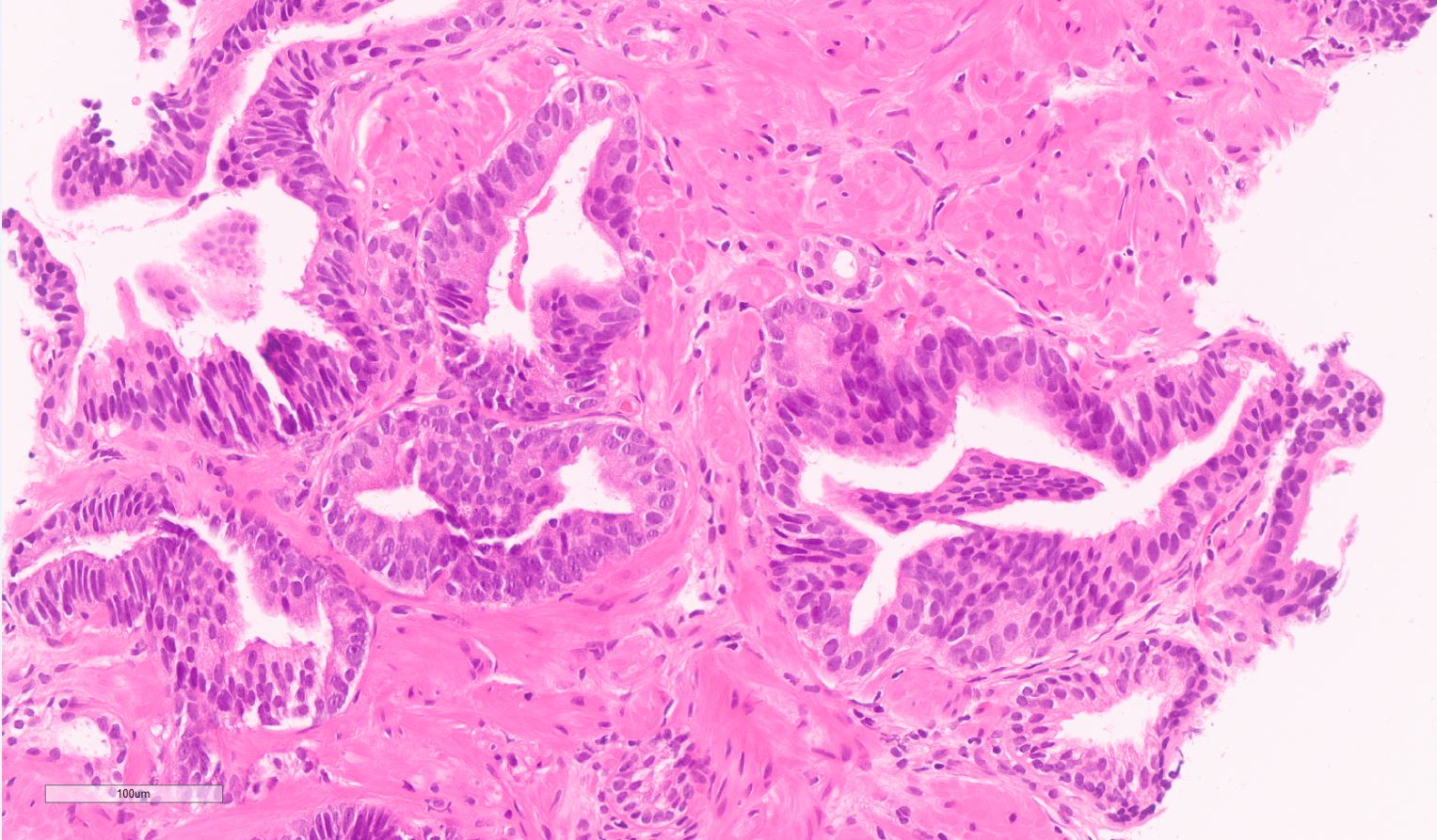
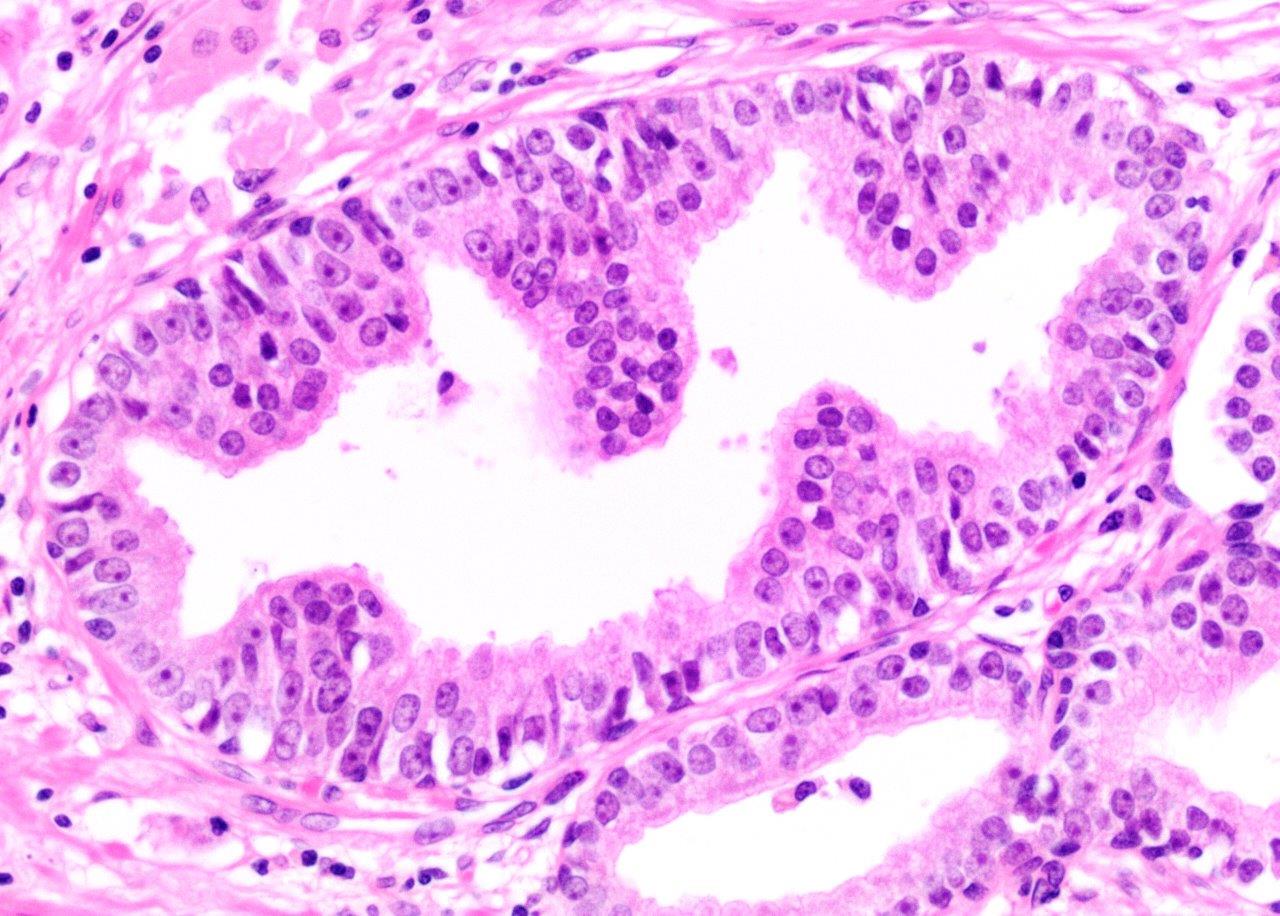
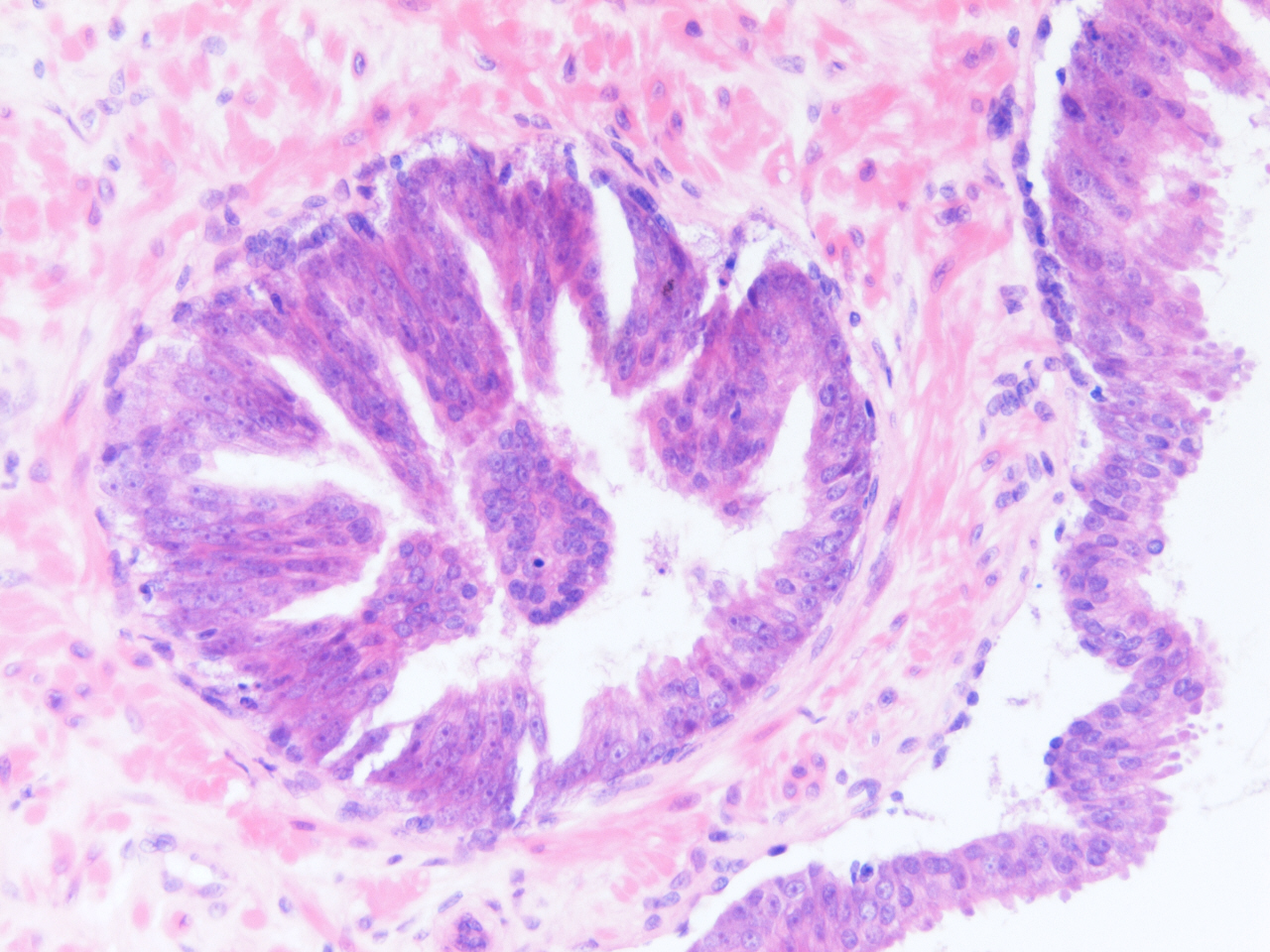
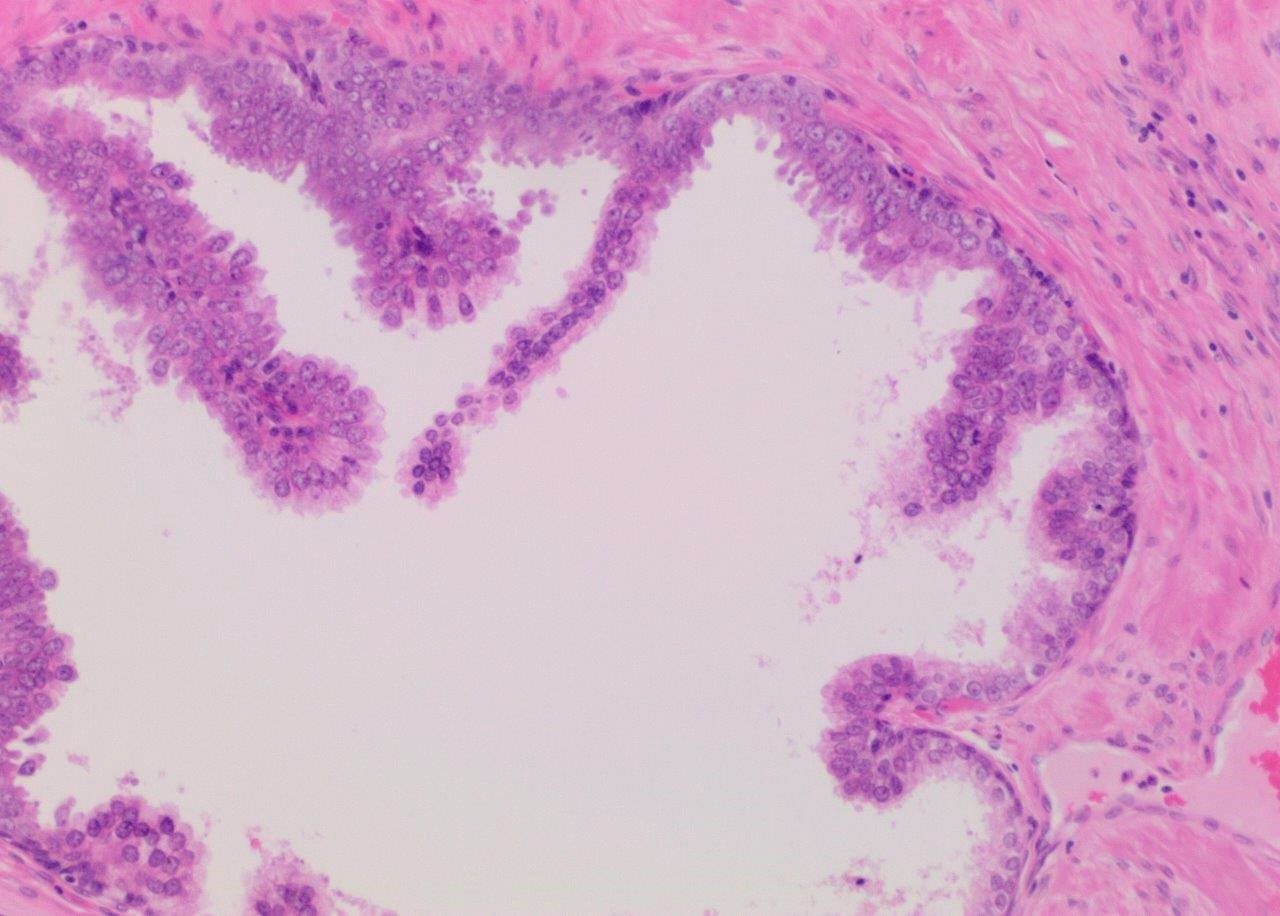
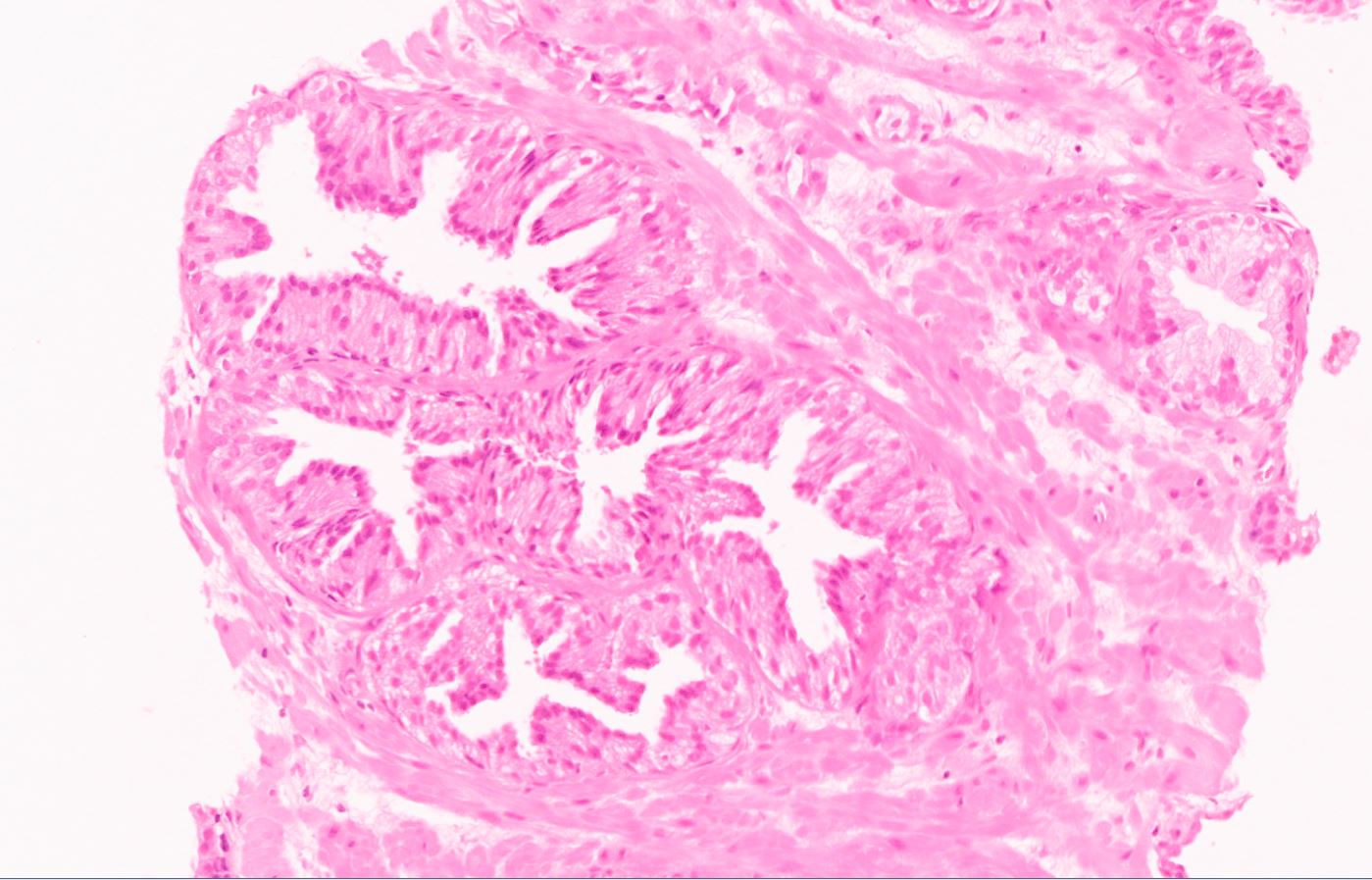
- Diagnostic feature: prominent nucleoli visible at 200x or lower magnification
- Medium to large ducts and acini with enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei and amphophilic cytoplasm
- Common architectural patterns:
- Flat: 1 - 2 layers of simple epithelium
- Tufted: stratified epithelium with small luminal protrusions
- Micropapillary: filliform structures lacking true fibrovascular core
- Cribriform: epithelial proliferation with punched out spaces
- In contemporary practice, most experts report such proliferations as atypical intraductal proliferation suspicious for intraductal carcinoma of the prostate (IDC-P), particularly on needle biopsy (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2020 Jun 26 [Epub ahead of print])
- Less common patterns: signet ring cell, foamy gland, mucinous, inverted and small cell neuroendocrine (Am J Surg Pathol 1997;21:1215, Rev Urol 2004;6:171, Oncol Lett 2015;10:2395)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
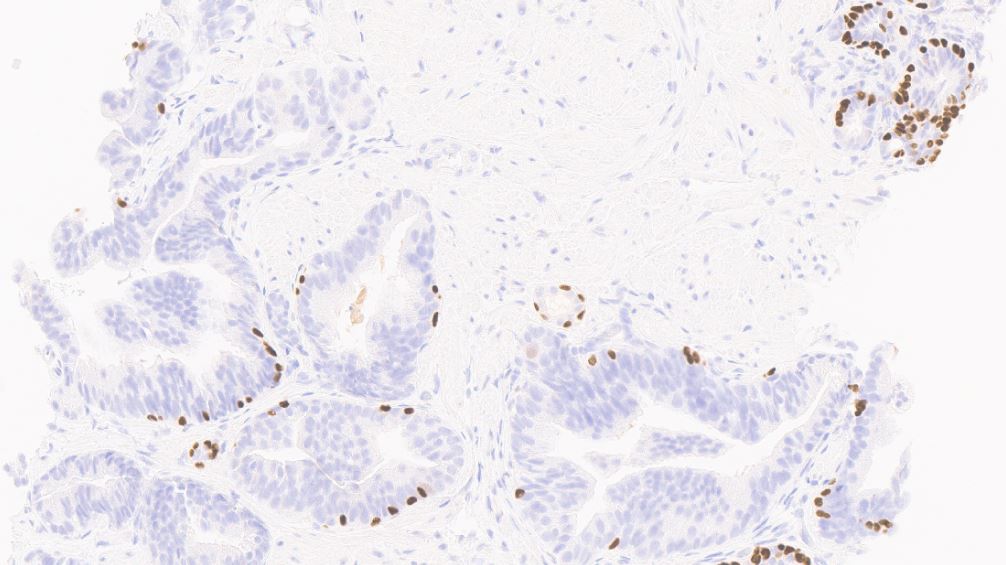
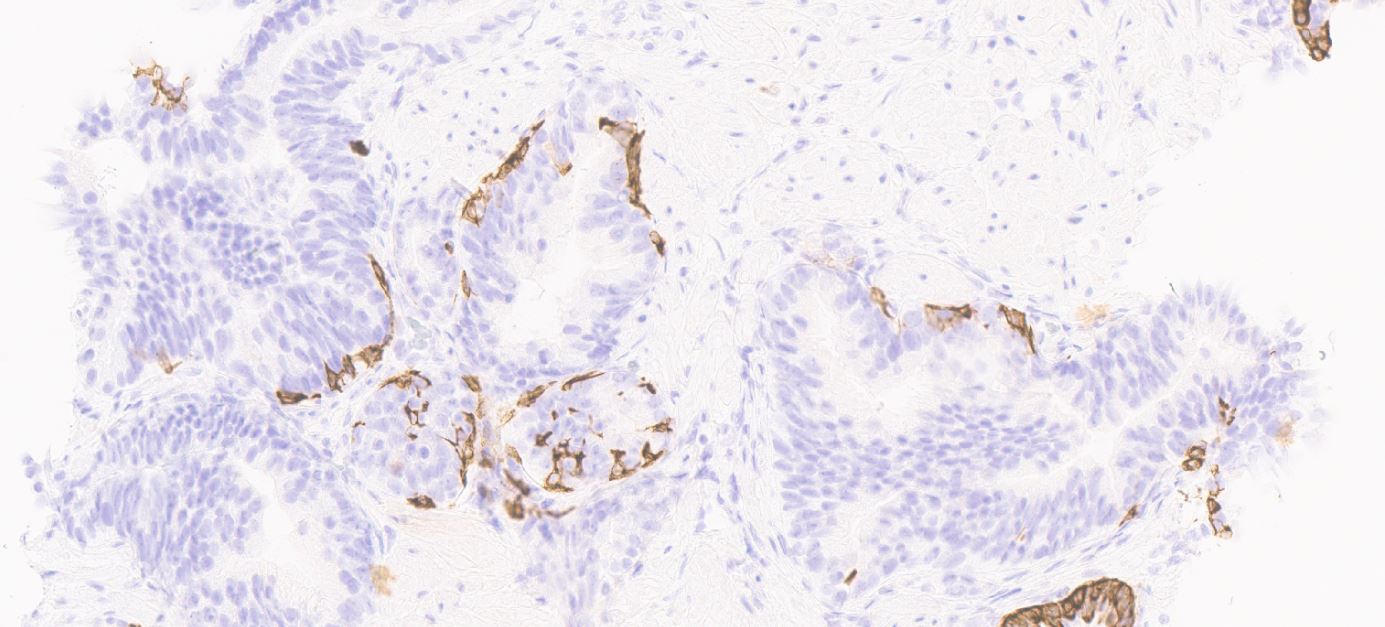
- Basal cells: high molecular weight cytokeratin (34 beta E12 / CK903), p63; may be discontinuous
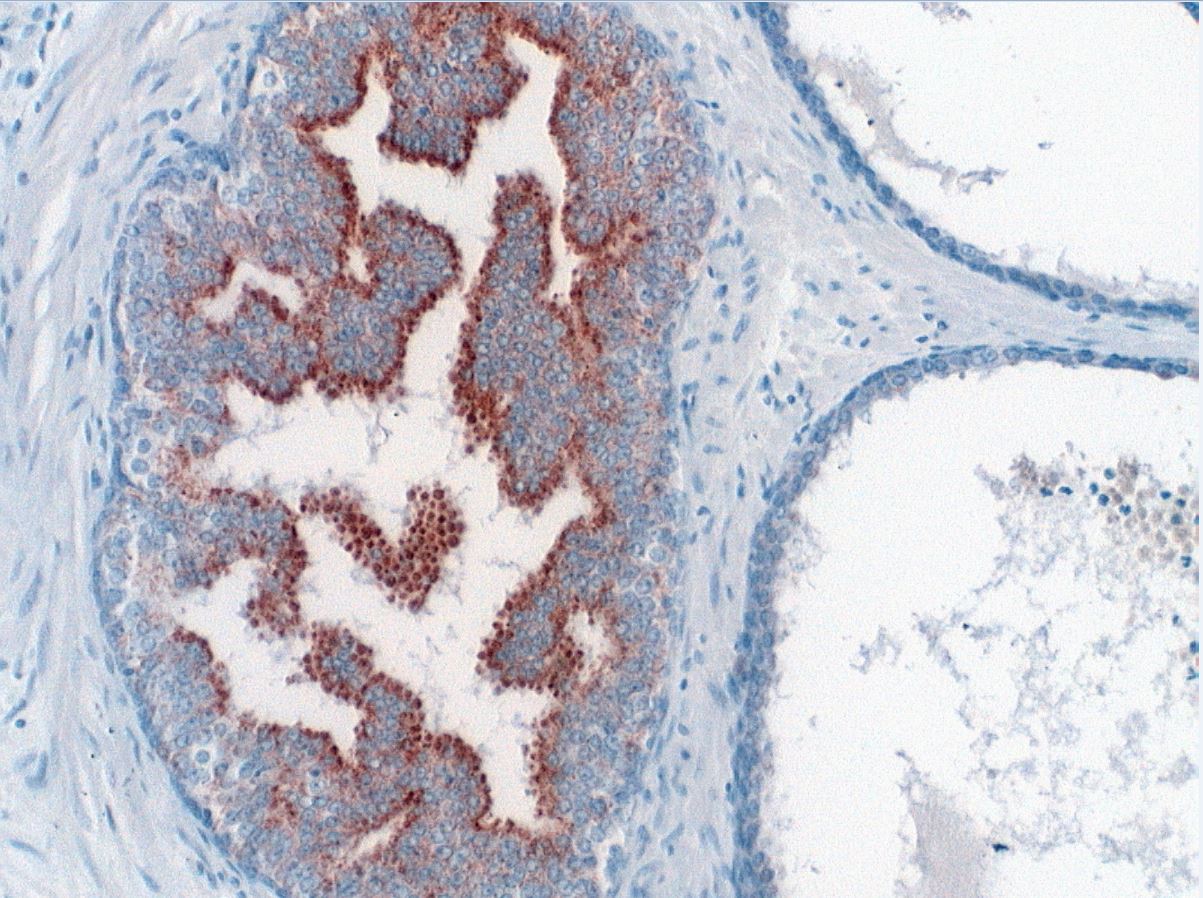
- Acinar cells: P504S / AMACR
- PTEN: normal retained pattern (Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:169)
Negative stains
- ERG could be positive in rare cases of isolated HGPIN (see ERG, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:608)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Deletions of 8p most common allelic loss; telomere shortening activity similar to prostatic adenocarcinoma
- Other chromosomal abnormalities in both HGPIN and carcinoma include gains of chromosomes 7, 8, 10 and 12 (Am J Surg Pathol 1995;19:506, Rev Urol 2004;6:171)
- TMPRSS - ERG fusion (Science 2005;310:644, Clin Cancer Res 2008;14:3380)
- Found in approximately 50% of prostate carcinoma
- Present in approximately 20% of HGPIN admixed with adenocarcinoma
- Less common in HGPIN not associated with invasive adenocarcinoma
- Hypermethylation GSPT1, the most common epigenetic change in prostate carcinoma, is also seen in HGPIN
- Other genetic features of HGPIN
- Aneuploidy (present in approximately 50%)
- Increased expression of CDKN2A, TP53, tumor suppressor genes involved in cell cycle regulation and MYC oncogene amplification (Clin Cancer Res 2001;7:544, Mod Pathol 1997;10:1113)
Sample pathology report
- Prostate, left lateral mid, needle core biopsy:
- High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia
Differential diagnosis
- Prostatic central zone glands:
- Increased architectural complexity (cribriform / micropapillary)
- Cytologically bland with inconspicuous nucleoli
- Central / basal location
- Ejaculatory duct epithelium / seminal vesicle epithelium:
- May show cribriform architecture
- Increased nuclear pleomorphism and cytoplasmic golden lipofuscin pigment (degenerative phenomena)
- Usually immunonegative for prostatic markers
- Urothelial metaplasia:
- No architectural complexity
- No prominent nucleoli
- Inflammatory reactive atypia:
- No architectural complexity
- Inflammatory cells including polymorphs
- Reactive nuclear features
- Radiation atypia:
- No architectural complexity
- Nuclear pleomorphism but no macronucleoli
- Basal cells prominent
- Clear cell cribriform hyperplasia:
- Clear cytoplasm
- Inconspicuous nucleoli and lacks nucleomegaly
- Basal cell hyperplasia:
- Proliferation of peripheral basal cells showing prominent nucleoli
- Central secretory cells lack nucleoli
- Basal cell markers demonstrate basal cell predominance
- PIN-like carcinoma:
- Architecture resembling HGPIN
- Greater crowding / dilated glands lined by columnar pseudostratified cells
- May show cystically dilated glands lined by ductal type epithelium
- Immunonegative for basal cell markers (Am J Surg Pathol 2018;42:1693)
- Pattern 4 cribriform acinar adenocarcinoma:
- Confluent, increased architectural complexity
- Immunonegative for basal cell markers
- Ductal carcinoma:
- Peri-urethral or peripheral prostatic ductal location
- Expansive, complex cribriform / papillary / solid architecture
- Tall columnar cells, oval pleomorphic nuclei
- Immunonegative for basal cell markers (Med Princ Pract 2010;19:82)
- Intraductal carcinoma:
- Solid or dense cribriform architecture
- Loose cribriform or micropapillary architecture with either marked nuclear atypia or comedonecrosis (Virchows Arch 2019;474:525, Am J Surg Pathol 2016;40:e67)
- Markedly distended glands (Mod Pathol 2018;31:S71, Mod Pathol 2006;19:1528)
- HGPIN with adjacent atypical small glands (PINATYP):
- Unresolved differential of tangential sectioning / budding of HGPIN and invasive adenocarcinoma (Hum Pathol 2001;32:389)
- AMACR immunohistochemistry unhelpful: generally positive in both scenarios (Histopathology 2005;47:1)
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
C. It is not associated with raised serum PSA. This is high grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia.
Comment Here
Reference: High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN)
Comment Here
Reference: High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN)
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is the common immunoprofile of high grade PIN?
- HMWCK-, p63-, AMACR-
- HMWCK-, p63-, AMACR+
- HMWCK-, p63+, AMACR-
- HMWCK+, p63+, AMACR-
- HMWCK+, p63+, AMACR+
Board review style answer #2
E. HMWCK+, p63+, AMACR+
Comment Here
Reference: High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN)
Comment Here
Reference: High grade prostatic intraepithelial neoplasia (HGPIN)