Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Huynh A, Roberts DJ. Chorangiosis. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentachorangiosis.html. Accessed January 10th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Capillary hyperplasia in terminal villi due to chronic placental hypoperfusion or low grade tissue hypoxia (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:588, Gynecol Obstet Invest 2012;73:141)
Essential features
- Terminal villous vascular hyperplasia resulting from longstanding low grade hypoxia in the placental tissue or fetal side hypoperfusion
ICD coding
- ICD-10: O43.89 - other placental disorders
Epidemiology
- Women living at high altitudes (Reprod Fertil Dev 1995;7:1533)
- In maternal anemia (J Pregnancy 2014;2014:193925)
- In women who smoke (Pathol Res Pract 2009;205:75)
Sites
- Terminal chorionic villi of the placenta
Pathophysiology
- Growth factor promotion of angiogenesis in response to long standing placental hypoperfusion or chronic low grade tissue hypoxia
- Chronic hypoperfusion and tissue hypoxemia may lead to an excessive villous neoangiogenesis and to a high proliferative activity of connective tissue, probably mediated by growth factors (VEGF, bFGF and PDGF) (Gynecol Obstet Invest 2012;73:141)
Etiology
- Higher incidence in maternal pathological conditions associated with hypoxemia
- Incidence is higher:
- In women living at high altitudes (Reprod Fertil Dev 1995;7:1533)
- In maternal anemia (J Pregnancy 2014;2014:193925)
- In women who smoke (Pathol Res Pract 2009;205:75)
- Also associated with placental pathology, such as single umbilical artery, placental abruption, amnion nodosum, villitis and umbilical cord anomalies (e.g. long umbilical cord)
Clinical features
- May be seen in pregnancies complicated by preeclampsia, diabetes mellitus, high altitudes, anemia, certain infections, multiple gestations, cardiovascular or respiratory disease, air pollution, obesity and tobacco smoking (BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2021;21:99, Reprod Fertil Dev 1995;7:1533, J Pregnancy 2014;2014:193925, Pathol Res Pract 2009;205:75)
- Associated with neonatal morbidity / mortality, including neurocompromise and stillbirth
- Rarely associated with placental syphilis
Diagnosis
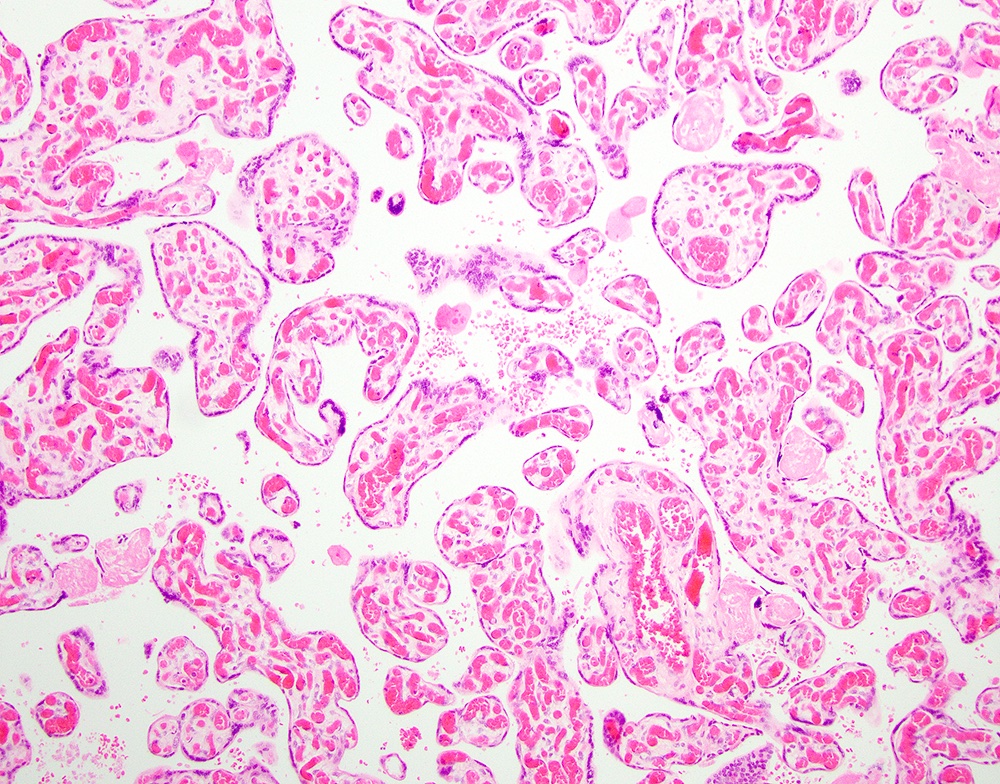
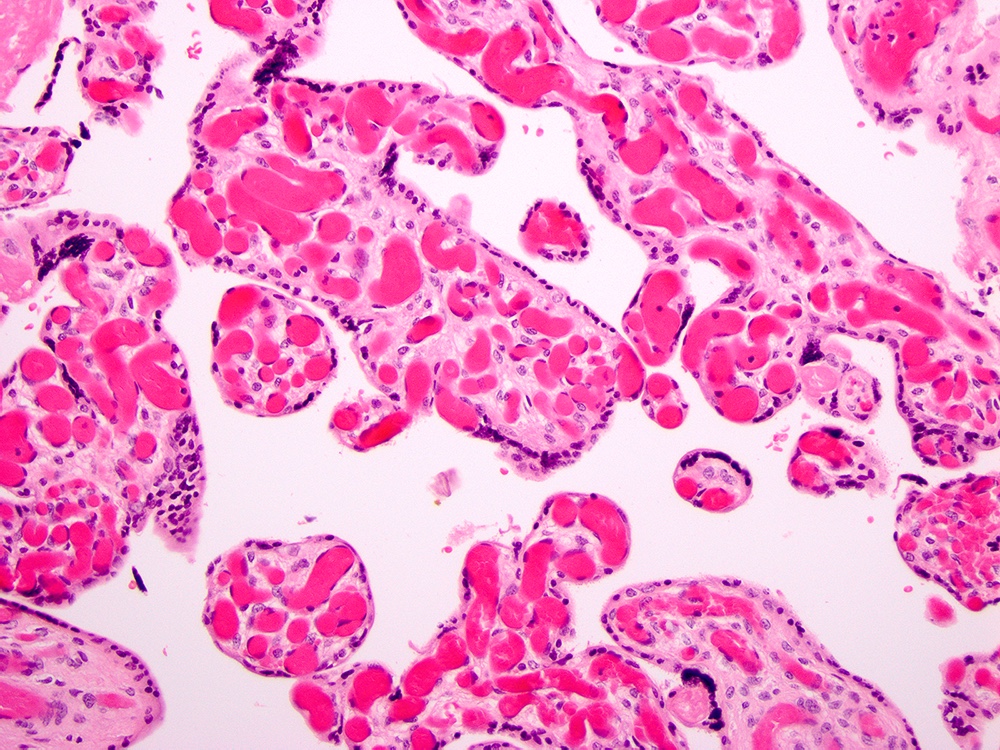
- Altshuler criteria: > 10 capillaries in at least 10 terminal villi in ≥ 10 noninfarcted areas in at least 3 low power fields of the placenta (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1984;108:71)
- Normal villi rarely have > 5 capillaries / villous
Prognostic factors
- Focal and diffuse chorangiosis have similar prognostic features (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2019;22:406)
- Increased perinatal morbidity and mortality (Gynecol Obstet Invest 2012;73:141)
- Low Apgar scores
- Neurocompromise
- Fetal growth restriction
- Neonatal death
- Congenital malformations
- No risk of recurrence
Case reports
- 23 year old woman (nullipara) with elevated hCG and singleton placenta (J Reprod Med 2003;48:827)
- 24 year old woman with a history of pregnancy induced hypertension (PJMS 2014;4:50)
- 27 year old woman with gestational hypertension and oligohydramnios (Turk J Obstet Gynecol 2018;15:270)
- 33 year old woman with stillborn fetus with giant hepatic hemangioma (Fetal Pediatr Pathol 2019;38:175)
- 38 year old woman with class C diabetes and singleton pregnancy (Case Rep Obstet Gynecol 2017;2017:5610945)
Gross description
- No distinct gross abnormalities
- Placenta may be heavy and boggy
- Other placental findings may include: single umbilical artery and other umbilical cord anomalies, retroplacental hematoma (abruptio placentae) (Gynecol Obstet Invest 2012;73:141)
Microscopic (histologic) description
- > 10 capillaries in > 10 terminal villi in at least 10 different noninfarcted areas in 3 low power fields of the placenta = diffuse chorangiosis
- Focal chorangiosis with similar morbidity associations as diffuse (Pediatr Dev Pathol 2019;22:406)
- Capillaries have distinct basement membranes but are not surrounded by a continuous layer of pericytes or associated with stromal fibrosis
- May be associated with delayed villous maturation, chorangioma(s), villitis of unknown etiology, fetal vascular malperfusion
- Must distinguish from villous vascular congestion (vessels appear prominent but are normal in number), chorangiomatosis and chorangioma(s)
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Capillary endothelial cells are highlighted by CD31, CD34 (Hum Pathol 2000;31:945)
- Reticulin stains capillaries' basement membrane
Negative stains
Sample pathology report
- Placenta:
- Heavy, slightly immature placenta (650 g fresh, trimmed; > 90th percentile for 39 weeks gestational age)
- Long umbilical cord (85 cm, expect 50 - 70 cm at term)
- Chorangiosis, diffuse (see comment)
- Comment: Chorangiosis, when diffuse, is a rare finding associated with in utero hypoxia.
Differential diagnosis
- Chorangioma:
- Nodular lesion composed entirely of capillary vascular channels with surrounding trophoblasts
- Analogous to hemangiomas occurring elsewhere
- Chorangiomatosis:
- Heterogeneous and less well defined lesion with intermediate features between chorangioma and chorangiosis
- Hyperplastic capillaries surround larger vessels in central cores of stem and intermediate villi
- Increased number of perivascular bundles of reticulin fibers and pericytes
- Smooth muscle actin positive in pericytes
- Congestion:
- Prominent capillaries in the villi but there is no numerical increase in the number of capillaries
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2