Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Kowalski PJ. Amnionic web and amniotic band syndrome. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/placentaamnioticweb.html. Accessed April 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
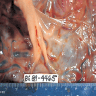
Amniotic web:
Amniotic web and rupture:
- Small portion of amniotic membrane can be present extending from the base of the umbilical cord and spanning the angle made by the fetal surface and the umbilical cord insertion
Amniotic web and rupture:
- Sporadic rupture of the amniotic sac; theories of pathogenesis vary
- Amniotic rupture is associated with amniotic band syndrome (Am J Surg Pathol 1984;8:117), in which strips of amniotic epithelium wrap around fetal surfaces and cause amputations, necrosis and deformations
- Craniofacial defects and limb abnormalities are the most common results
- Early rupture is associated with more severe fetal defects
Terminology
- Amnion is the single layer of cuboidal to columnar cells that lines the entire amniotic cavity, including the fetal surface of the placenta and the umbilical cord
- Amniotic web should be distinguished from an amniotic band, which is a congenital amniotic malformation that can result in serious constriction or entrapment of fetal parts (amniotic band syndrome or amniotic rupture sequence)
Epidemiology
- Uncommon finding, present in < 1% of uncomplicated live births
Pathophysiology
- Amnion (and its underlying thin layer of amniotic mesoderm) is only loosely adherent to the adjacent chorion
- This incompletely anchored nature of the amnion allows for incomplete investment of the acute angle made by the umbilical cord insertion and fetal surface
Clinical features
- Generally an incidental finding with no clinical significance
- Potential restriction of umbilical cord movement or constriction of vascular flow may be seen due to traction
Gross description
Amniotic web:
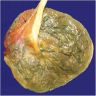
Amniotic band and rupture:
- Translucent, delicate, sail-like portion of amnion spans the distance between a short segment of umbilical cord and the adjacent fetal surface
- Retraction of the amnion can cause the umbilical cord to become tethered or anchored closely to the fetal surface
Amniotic band and rupture:
- Fetal surface may appear rough
- Residual strips of amnion may be seen but are usually overlooked
Microscopic (histologic) description
Amniotic band and rupture:
- Vernix granulomas in separated amniotic mesenchyme and in denuded mesenchyme of chorionic plates confirm antepartum amniotic rupture
- Biopsies of maternal placental bed may show desquamated stratified squamous epithelial cells in edema fluid between muscle fibers surrounded by marked neutrophilic infiltrate, uterine venules with fibrin clots containing squamous epithelial cells; veins with plugs of amniotic thrombi (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1997;121:167)
- In prolonged amniotic leakage, may see subchorionic squames or subchorionic foreign body reaction (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1986;110:47)
Differential diagnosis
- Amniotic bands vs. webs: amniotic bands consist of sheets or thicker strands / bands of amnion that can be found tethering any portion of the umbilical cord (not just its insertion site) or spanning between any portion of placenta and developing fetus