Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Tintle SJ, Jia L. Verruciform xanthoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/penscrotumcutaneousverruciform.html. Accessed April 18th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare, nonneoplastic lesion of verrucous epidermal acanthosis, foamy histiocytes aggregates in papillary dermis and neutrophilic inflammation
Essential features
- Nonneoplastic verrucous lesion characterized by aggregates of lipid laden macrophages in papillary dermis
- Closely resembles other verrucous lesions clinically and microscopically
ICD coding
- ICD-10: E75.5 - other lipid storage disorders
Epidemiology
- Mean age: 54.5 - 62 years; range: 8 - 85 years (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65, Histopathology 2020;77:841)
- M > F (Histopathology 2020;77:841)
- Majority reported in Caucasians (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65)
- May be present several years before diagnosis (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65)
Sites
- Usually in oral cavity; majority of nonoral cases involve anogenital skin (penis, scrotum and vulva) (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65, Australas J Dermatol 2015;56:e99)
Etiology
- Uncertain etiology; likely local irritation, inflammation or trauma inciting an immune reaction with consequent keratinocyte degradation (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:479, J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:392, J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:895)
- Keratinocyte degradation resulting in release of chemotactic cytokines, attracting neutrophils as well as plasma cells and lymphocytes
- Macrophages (CD68+ dermal dendritic cells) phagocytose neutrophilic and keratinocyte debris with eventual formation of foamy cells (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:479, Oral Oncol 2001;37:326)
- HPV association variable (Australas J Dermatol 2015;56:e99, J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:895)
- In several reports coexisting with inflammatory cutaneous disorders (graft versus host disease, pemphigus vulgaris, discoid lupus erythematosus, lichen planus) or associated with immunocompromise
- Not associated with underlying disorders of lipid metabolism (J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:895)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic, slow growing, persistent and usually solitary papule(s) or plaque resembling viral warts, particularly on the scrotum in males (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65, Histopathology 2020;77:841)
- Difficult to distinguish clinically; may resemble fibroepithelial polyp, seborrheic keratosis, condyloma acuminatum, squamous cell carcinoma or verrucous carcinoma (Histopathology 2020;77:841)
Diagnosis
- Punch biopsy with subsequent histological examination
Case reports
- 38 year old man with multiple, coexisting verruciform xanthomas of anogenital region associated with cutaneous trauma (J Cutan Pathol 2010;37:895)
- 50 year old man with scrotal verruciform xanthoma (Dermatol Online J 2014;20:21253)
- 64 year old man with penile verruciform xanthoma (Arch Ital Urol Androl 2016;88:284)
- 75 year old man with scrotal verruciform xanthoma (J Med Case Rep 2012;6:260)
- 78 year old man with penile verruciform xanthoma (Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol 2018;84:600)
Treatment
- Majority cured by complete excision; typically do not recur (Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65)
Gross description
- Yellow, pink, brown or flesh colored pedunculated papules or plaques, 0.5 - 2.5 cm, with a verrucous or pebbly surface (Australas J Dermatol 2015;56:e99, Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65, Histopathology 2020;77:841)
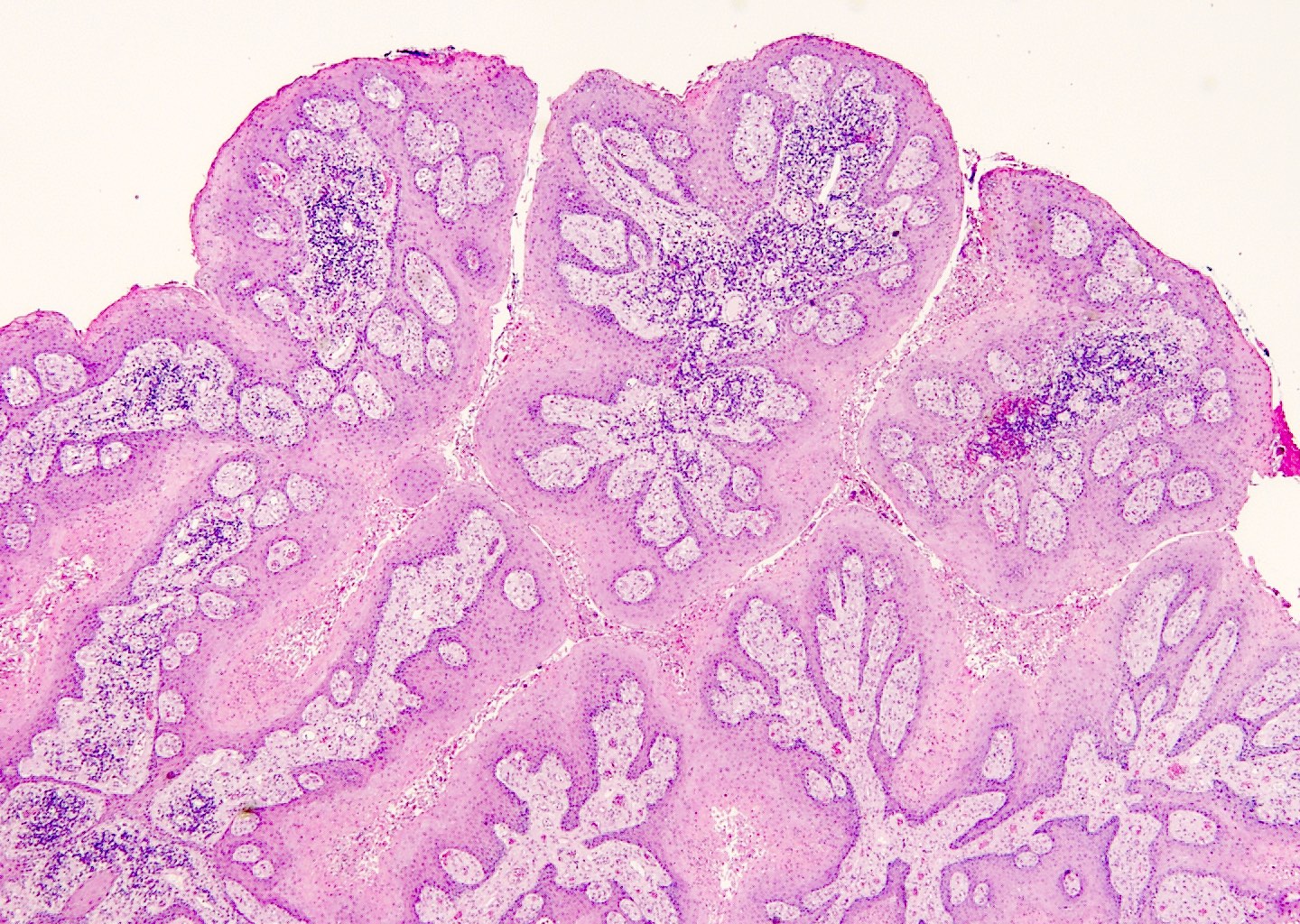
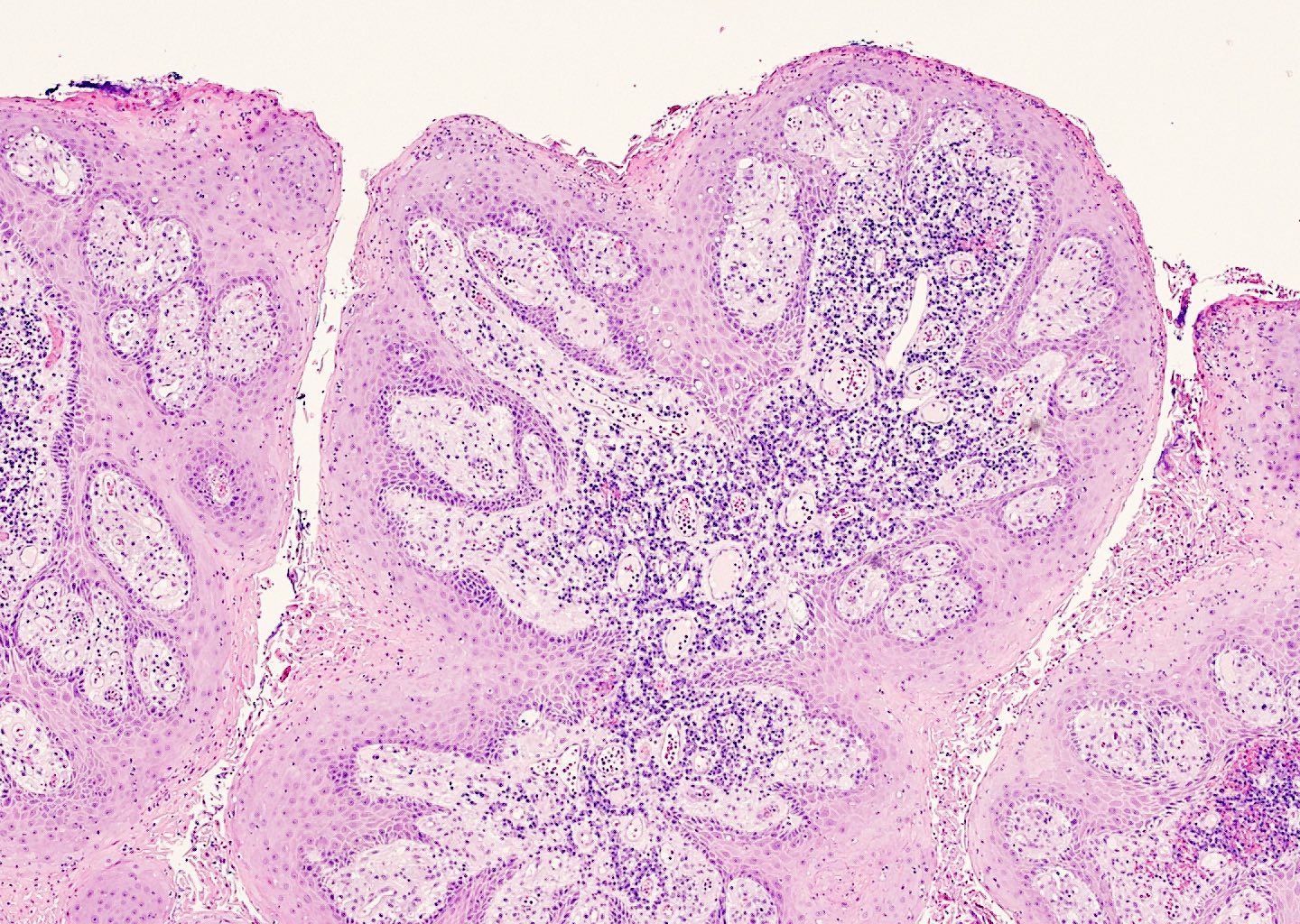
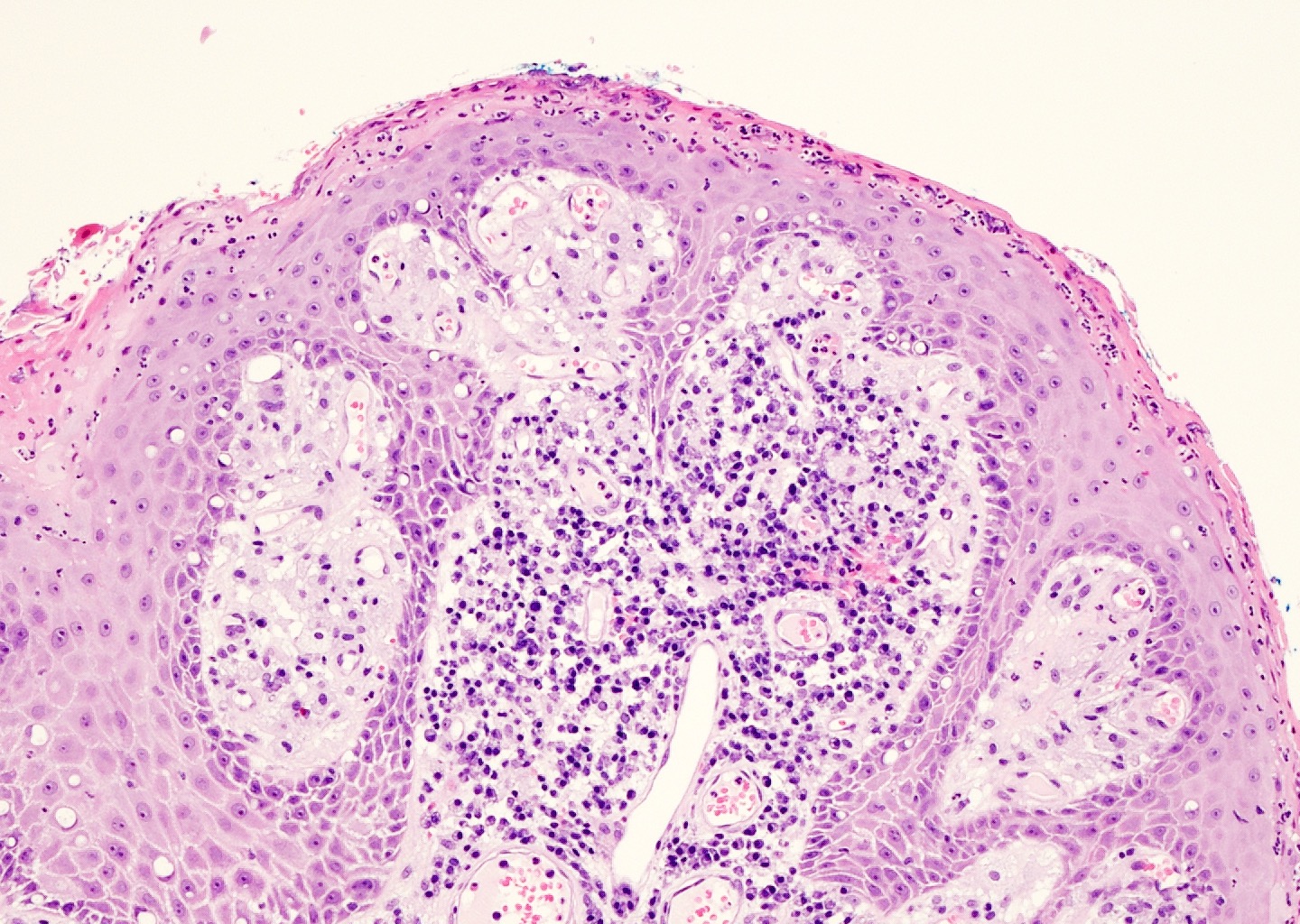
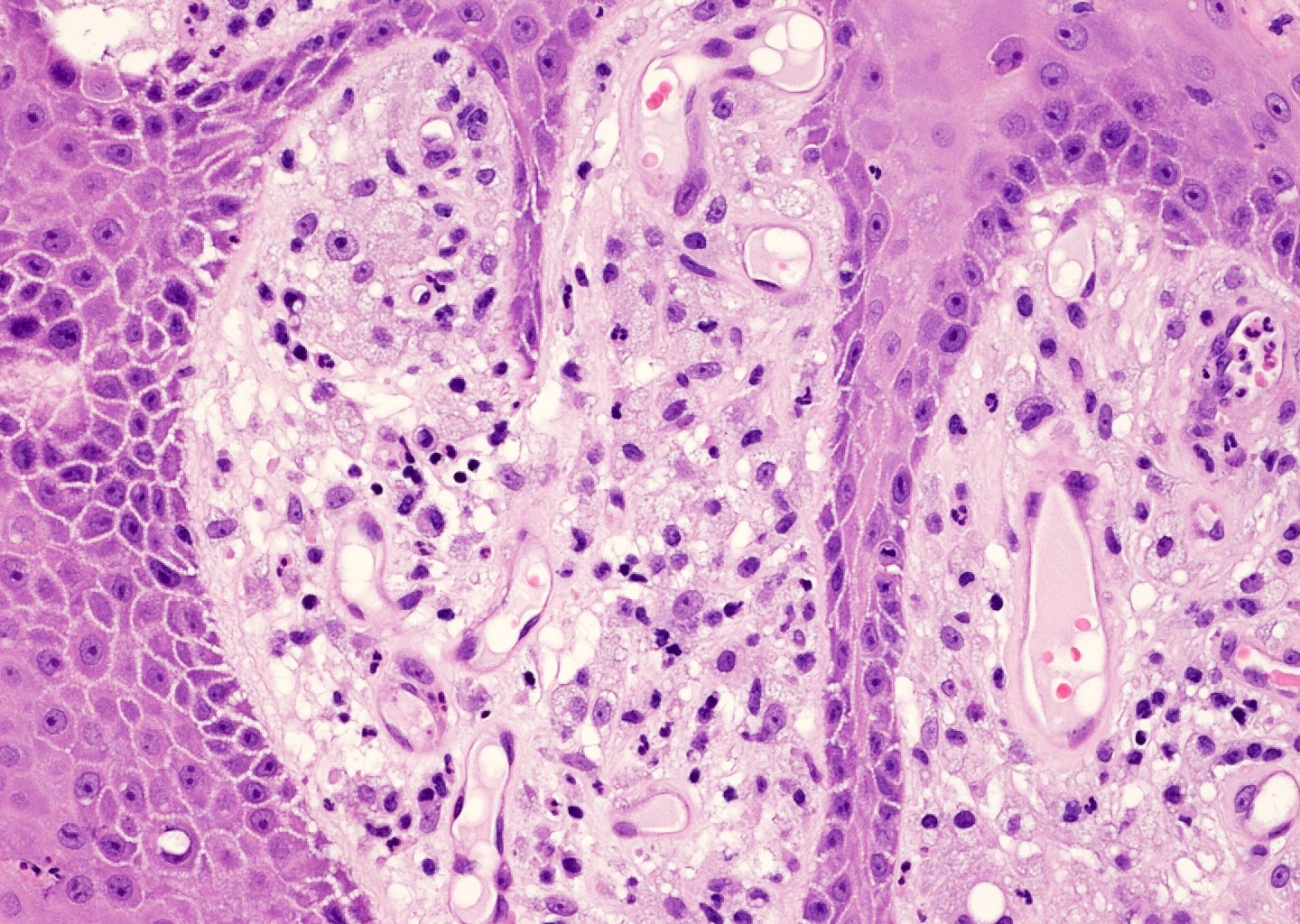
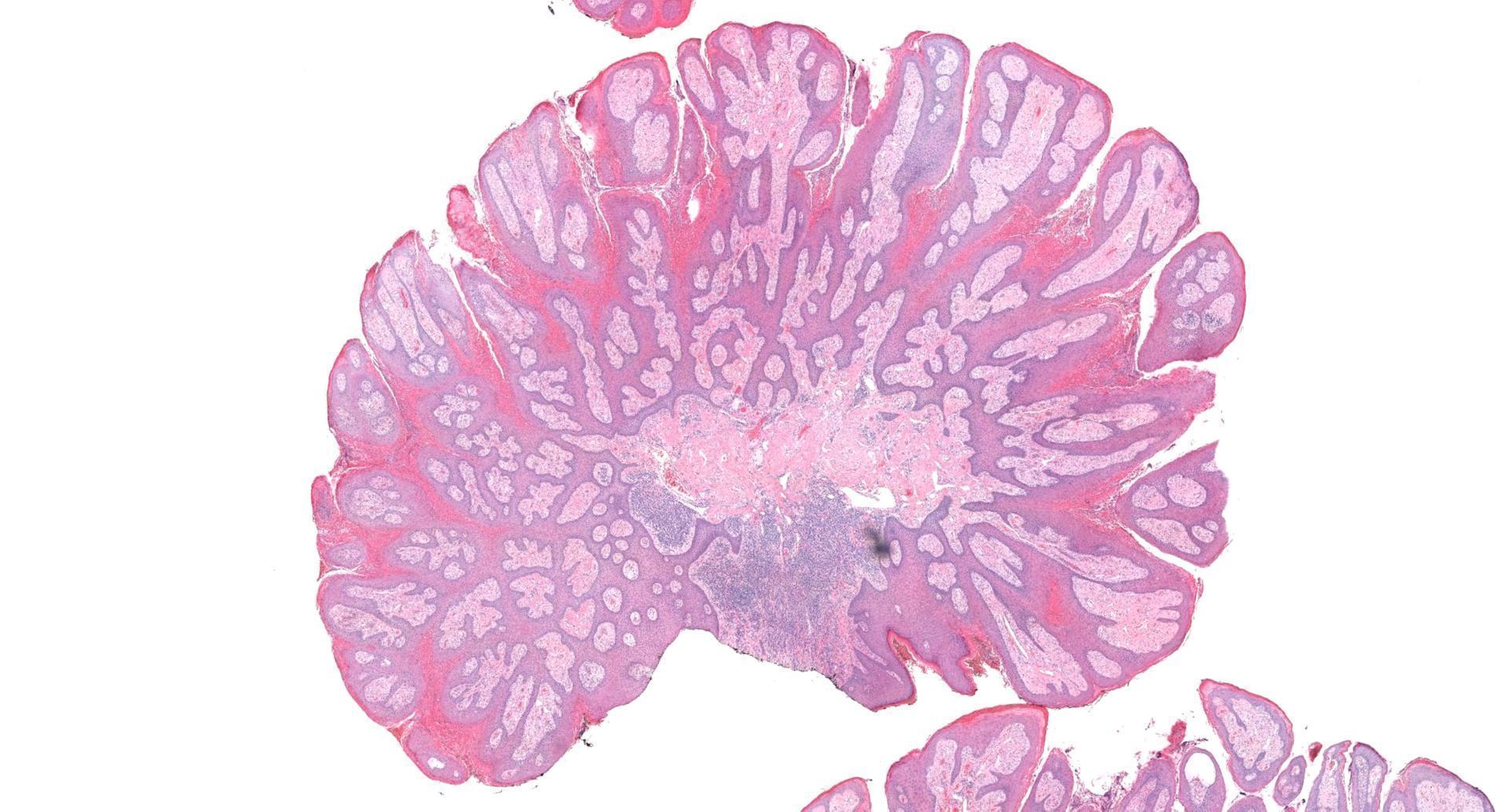
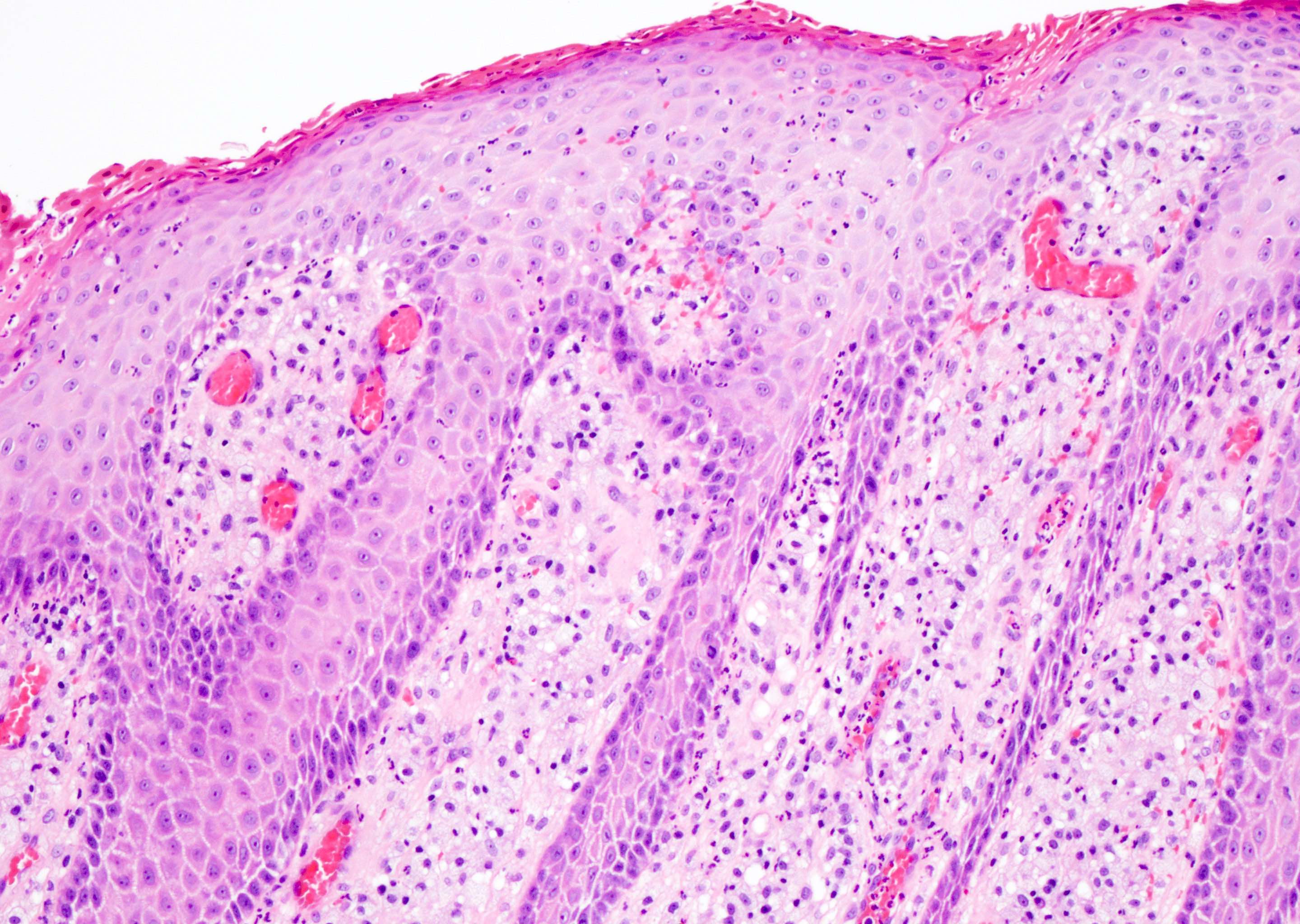
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Verrucous epidermal acanthosis, papillomatosis and hyperkeratosis
- Uniform depth of rete ridges
- Parakeratosis, often wedge shaped, filling clefts between epidermal projections (Histopathology 2020;77:841)
- Large foamy histiocytes (lipid laden macrophages) in aggregates in elongated dermal papillae, may be scattered or scarce (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:392, Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65, Histopathology 2020;77:841)
- Neutrophils, particularly in the stratum corneum, as well as dermis and occasionally prominent neutrophilic exocytosis (Australas J Dermatol 2015;56:e99, Dermatol Ther (Heidelb) 2017;7:65, Histopathology 2020;77:841)
- Mixed inflammatory infiltrate in the submucosa (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:392)
- Vascularized papillary dermis (J Am Acad Dermatol 2015; 72:e147)
- Absence of keratinocyte atypia
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Foamy cells: CD68+, PAS+ and diastase resistant (Virchows Arch A Pathol Anat Histopathol 1993;423:243, J Periodontol 2001;78:504)
- Adipophilin (Clin Exp Dermatol 2015;40:156)
- Factor VIIIa
- Vimentin
Negative stains
Electron microscopy description
- Xanthoma cells contain membrane bound lysosomes, myelin figures and fragmented desmosomes (Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol 1975;40:246)
Sample pathology report
- Penis, dorsal, biopsy:
- Verruciform xanthoma
Differential diagnosis
- Verruca vulgaris:
- Koilocytes, coarse hypergranulosis, prominent papillomatosis, rete ridges curve inward
- Condyloma acuminatum:
- Prominent koilocytotic atypia in upper epidermis
- No prominent foamy macrophages
- Xanthoma:
- Foamy cells are located in the mid dermis
- Clinical hyperlipidemia
- Squamous cell carcinoma:
- Marked atypia, no prominent foamy histiocytes
- Verrucous carcinoma:
- Ulcerating or fungating lobules of mature squamous epithelium
- Minimal atypia but no prominent foamy histiocytes
- Bowenoid papulosis:
- Resembling basaloid PeIN
- Spotty cytological atypia
Board review style question #1
A 58 year old Caucasian man presents with a 1.0 cm pink, warty lesion on the glans penis. The biopsy shows verruciform hyperplasia of the epidermis with hyperkeratosis, parakeratosis and acanthosis (figure 1). No keratinocyte atypia or dyskeratotic cells are seen. There is a dense infiltrate of lipid laden macrophages (foamy cells) in the papillary dermis (figure 2) which are positive for CD68 and negative for S100. Which statement is true of cutaneous verruciform xanthoma?
- It is frequently caused by HPV genotypes 6 and 11
- Approximately 2 - 5% will either harbor or progress to a squamous cell carcinoma
- It is usually associated with underlying immunosuppression
- It is a nonneoplastic lesion that typically does not recur after excision
Board review style answer #1
D. It is a nonneoplastic lesion that typically does not recur after excision. The diagnosis of the lesion is cutaneous verruciform xanthoma.
Comment Here
Reference: Cutaneous verruciform xanthoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cutaneous verruciform xanthoma
Board review style question #2
Which best summarizes the immunohistochemical profile of the characteristic cells infiltrating the dermal papillae in cutaneous verruciform xanthoma?
- CD68 positive; PAS positive diastase resistant; positive granular cytoplasmic staining of adipophilin; S100 negative
- CD68 positive; S100 positive; CD1a positive; Langerin positive
- CK5/6 positive; p16 positive; p63 positive
- CD10 positive; CK5/6 negative; S100 negative
Board review style answer #2
A. CD68 positive; PAS positive diastase resistant; positive granular cytoplasmic staining of adipophilin; S100 negative
Comment Here
Reference: Cutaneous verruciform xanthoma
Comment Here
Reference: Cutaneous verruciform xanthoma