Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Electron microscopy images | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Gastrinoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreasgastrinoma.html. Accessed April 24th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Pancreatic well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor that causes clinical symptoms secondary to secretion of gastrin
Essential features
- Functionally active and usually aggressive neuroendocrine tumor
- Gastrin secretion causes Zollinger-Ellison syndrome
- May occur sporadically or in the setting of MEN1
Terminology
- Pathology diagnosis should be well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor, as gastrinoma is a clinical determination
- Sometimes called G cell neoplasm
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Roughly 20% of functional pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are gastrinomas, though only about 5% of overall pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are gastrinomas (Surg Pathol Clin 2014;7:559, World J Gastroenterol 2006;12:5440)
Sites
- Gastrinomas are more common in duodenum than in pancreas
- Rare examples of so called primary lymph node gastrinoma can occur:
- Gastrin producing tumors in lymph nodes with no GI or pancreatic primary, generally in patients with MEN1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1101)
- Occur in gastrinoma triangle: from cystic and common bile ducts to the second and third portion of the duodenum to neck and body of the pancreas
- May be due to gastrin secreting neuroendocrine cells within these nodes or due to occult duodenal microgastrinomas with lymph node metastasis (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2000;124:832, Am J Surg Pathol 2008;32:1101)
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Hypersecretion of gastrin stimulates secretion of gastric acid by parietal cells, leading to ulcer formation
Etiology
- 80% of cases are sporadic; 20% are familial due to MEN1 (Hepatogastroenterology 2005;52:1668)
Clinical features
- Associated with hypersecretion of gastric acid and severe peptic ulceration
- 90% have ulcers (85% in duodenum / jejunum, 15% in stomach)
- 33% of patients have diarrhea
- May be metastatic at time of diagnosis
Diagnosis
- Glucagon provocative test is useful (Surg Today 2013;43:1281)
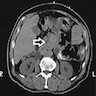
Radiology description
- Highly vascular and well circumscribed, as with other neuroendocrine tumors of pancreas
- Imaging may detect positive lymph nodes within the gastrinoma triangle (Diagn Interv Imaging 2016;97:1241)
- Octreotide scans have high sensitivity
Prognostic factors
- Sporadic tumors are usually solitary, aggressive and located in pancreas
- MEN1 cases are often multicentric, less aggressive and arise in duodenal wall (Gut 2007;56:606)
Case reports
- 25 year old woman with mass blocking the pancreatic duct (Surgery 2005;138:111)
- 37 year old woman with von Hippel-Lindau syndrome and 2 pancreas lesions (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017;109:154)
- 68 year old woman with abdominal pain and diarrhea (Oncol Lett 2016;11:3433)
- 73 year old man with pancreatic gastrinoma and endobronchial metastasis (Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2012;185:590)
Treatment
- H2 blockers for symptom management
- Surgical resection of tumor
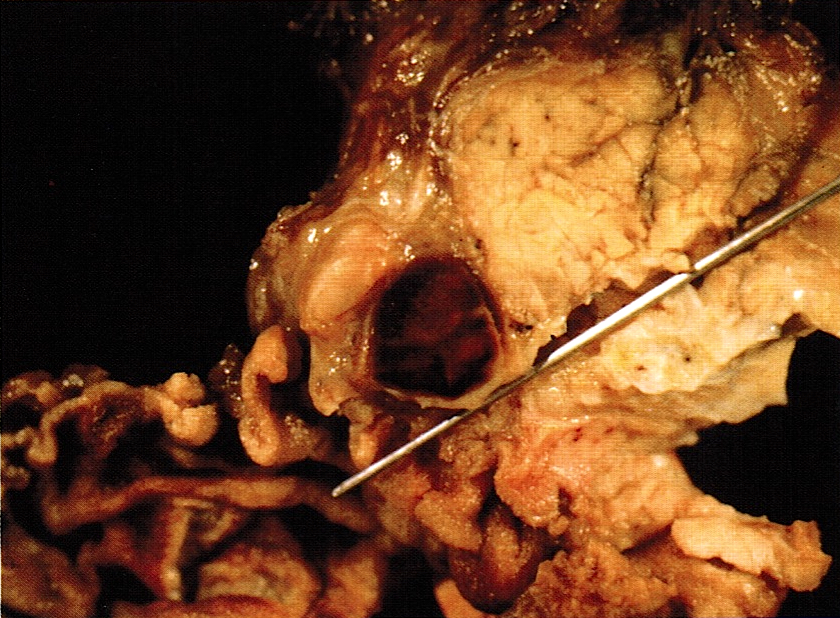
Gross description
- Single or multiple lesions, most commonly in head of pancreas
- Firm, homogeneous, well circumscribed
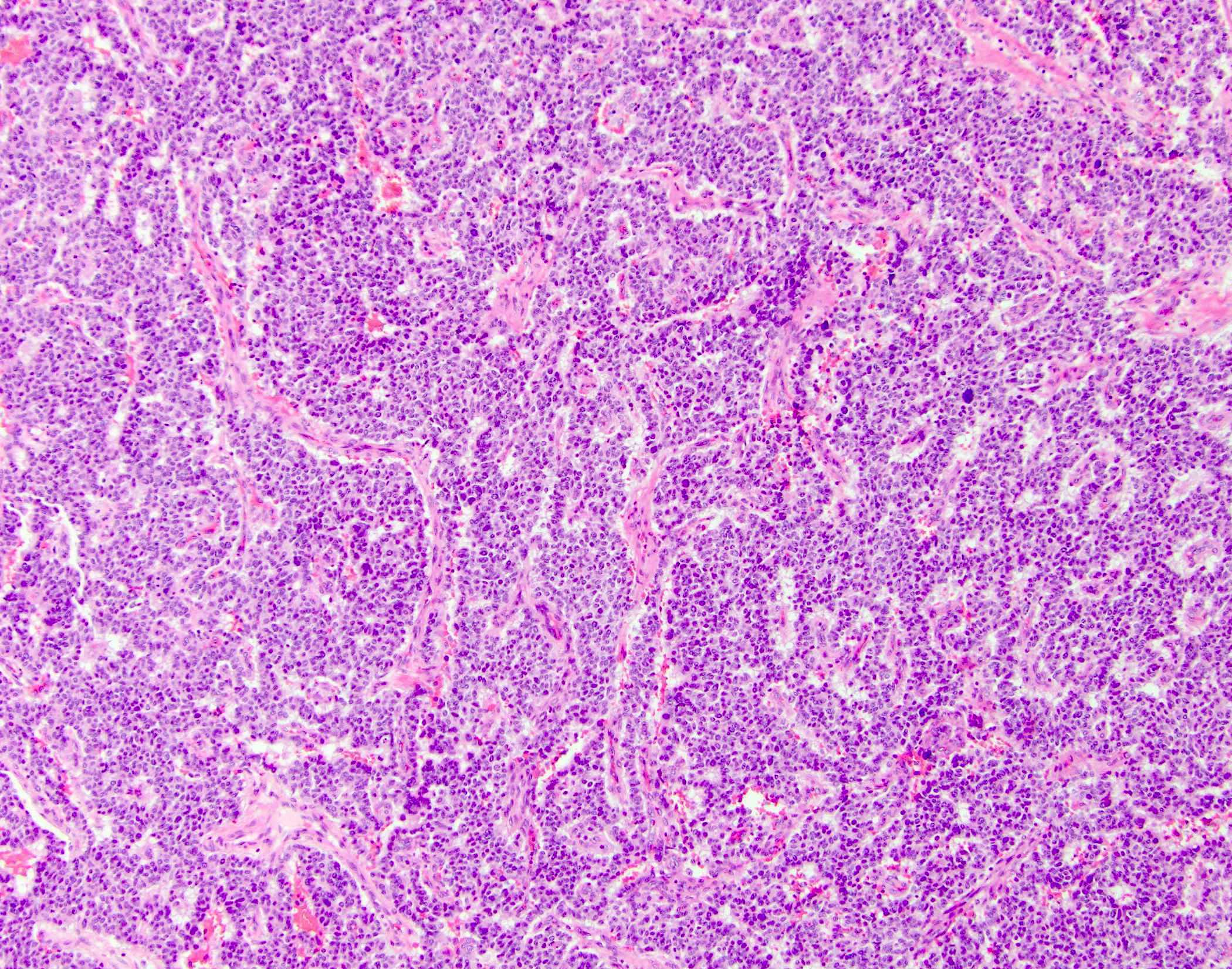
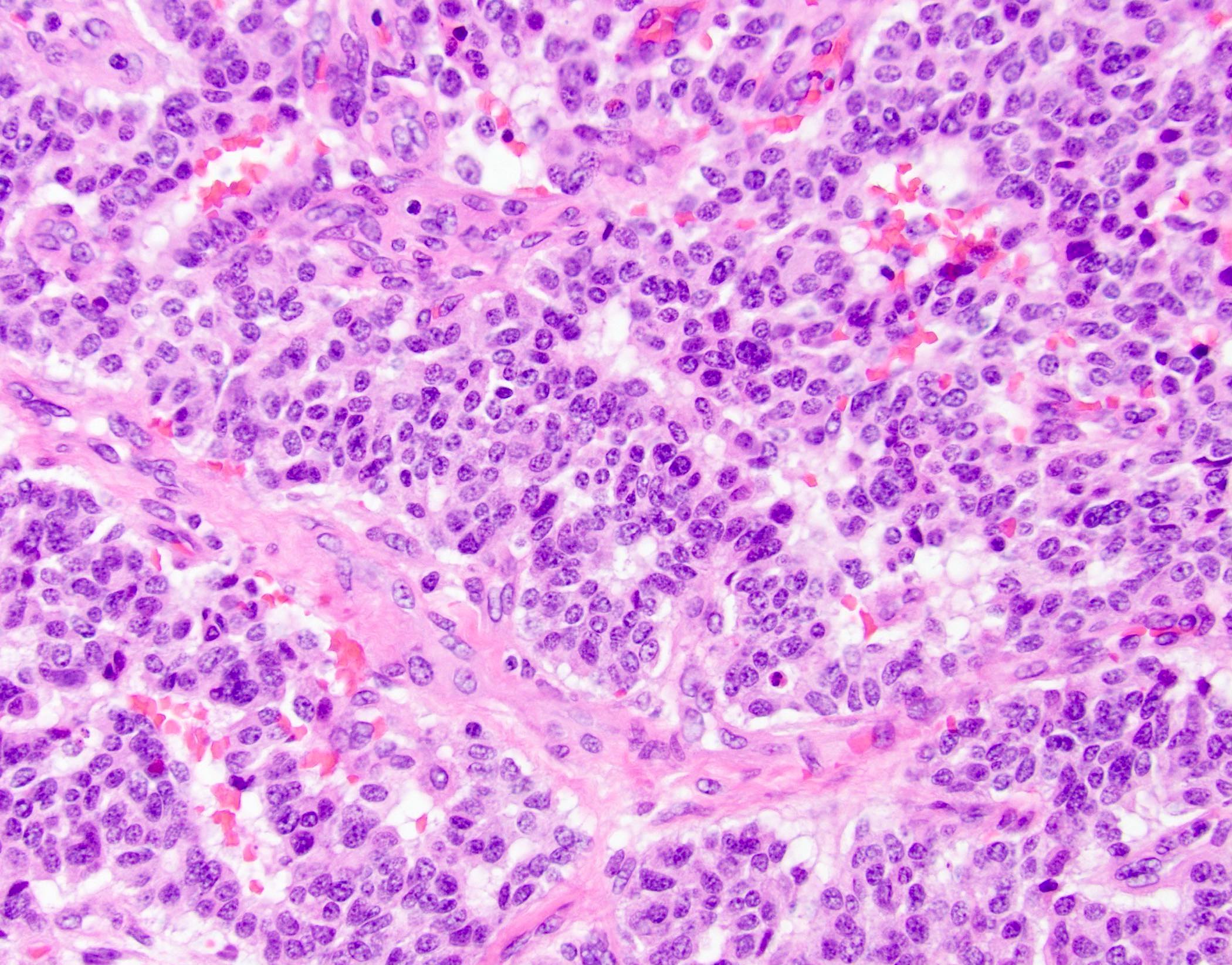
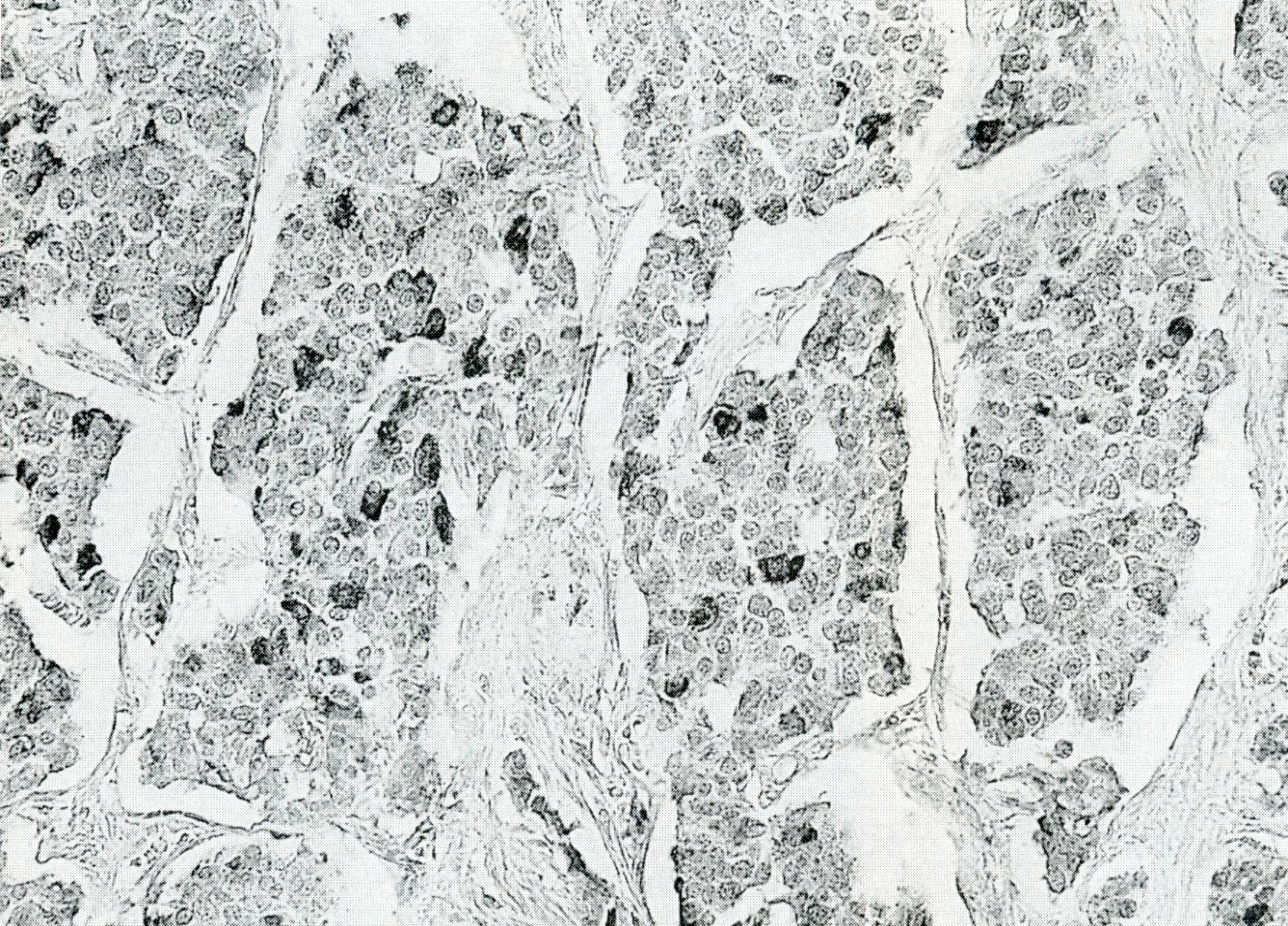
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nests of monotonous low grade neuroendocrine cells with salt and pepper nuclei and ample amphophilic cytoplasm, as with any other well differentiated neuroendocrine tumor
- Associated with pancreatic polypeptide cell hyperplasia (Hum Pathol 1997;28:149)
- Nonneoplastic pancreas may show large islets and nesidioblastosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Gastrin (though this does not establish the diagnosis)
- Synaptophysin, chromogranin
- PDX1, INSM1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:737)
Negative stains
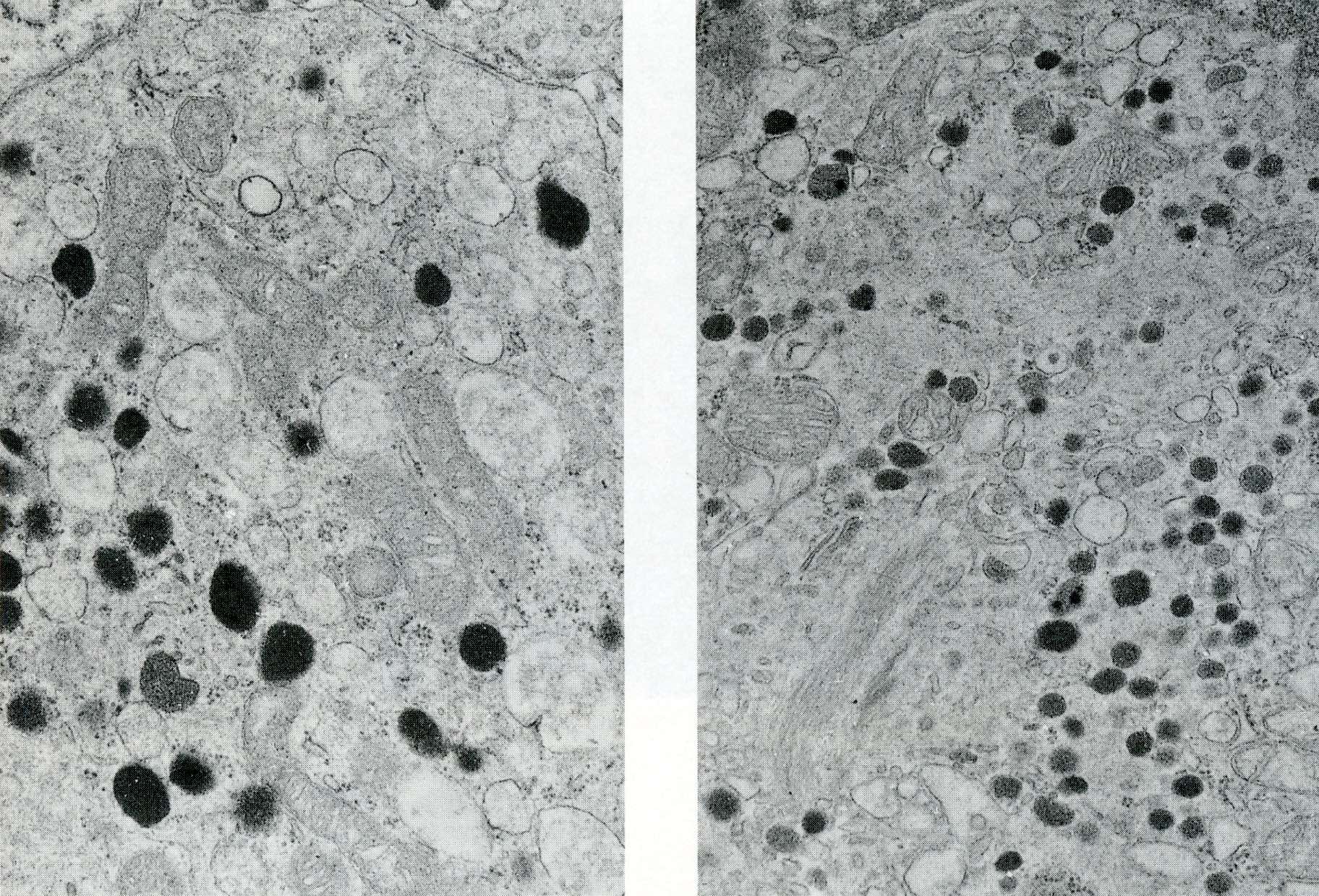
Electron microscopy description
- Tumor cells may contain small, electron dense granules
Sample pathology report
- Pancreas and duodenum, Whipple procedure:
- Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor, WHO grade 2 (see synoptic report and comment)
- Comment: The patient’s clinical history of Zollinger-Ellison syndrome is noted. This may be due to gastrin secretion by this tumor, which would make it a gastrinoma. Immunohistochemical stains for synaptophysin and chromogranin are positive and the Ki67 index is approximately 4.5%.
Differential diagnosis
- Nongastrin secreting pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor:
- No histopathologic differences
- Must be determined on clinical grounds
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following types of neuroendocrine tumor may arise primarily within a lymph node near the duodenum and pancreas?
- Gastrinoma
- Glucagonoma
- Insulinoma
- Somatostatinoma
- VIPoma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
- Gastrinomas arising sporadically, compared to those arising in the setting of MEN1, are more likely to be
- Benign clinically
- Cystic
- Located in the pancreas
- Multifocal
- WHO grade 1
Board review style answer #2