Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains (IHC and special stains) | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Gonzalez RS. Cystic endocrine tumors. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/pancreascysticendocrine.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Distinctive subgroup of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors that are well differentiated with a low mitotic rate and low Ki67 proliferative index as well as have a cystic component (Am J Surg Pathol 2012;36:1666)
Essential features
- Histologically resembles typical pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor but with cystic component
- Improved prognosis
- Occurs more frequently in patients with MEN1
ICD coding
- ICD-10: C25.4 - malignant neoplasm of endocrine pancreas
Epidemiology
- Up to 17% of pancreatic neuroendocrine tumors are purely or partially cystic, due to cystic degeneration of originally solid tumor (J Am Coll Surg 2008;206:1154, Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2018;110:130)
Sites
- More common in tail of pancreas
Pathophysiology
- 10 - 25% are associated with MEN1, occur in younger patients and are more often multiple and functional (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017;109:778)
Clinical features
- Usually (85%) nonfunctional (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017;109:778)
- If functional, usually insulinoma
- Often (45%) diagnosed incidentally (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017;109:778)
Diagnosis
- Can be confirmed by octreoscan scintigraphy
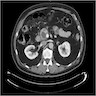
Radiology description
- Cystic, making diagnosis difficult; may be confused with other pancreatic cystic lesions (including intraductal papillary mucinous neoplasm and mucinous cystic neoplasm)
- Usually shows peripheral enhancement (AJR Am J Roentgenol 2013;200:W283)
Prognostic factors
- Better prognosis than noncystic neuroendocrine tumors of pancreas
- 60% disease free survival at 10 years (Rev Esp Enferm Dig 2017;109:778)
Case reports
- 20 year old woman with incidental tumor (J Cancer Res Ther 2012;8:289)
- 42 year old woman with cystic mass and tumorlets (World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:6911)
- 51 year old woman with multicystic pancreas mass (Clin J Gastroenterol 2018;11:87)
- 66 year old woman with lesion mimicking mucinous cystic neoplasm (Clin J Gastroenterol 2018;11:333)
- 78 year old man with epigastric pain (BMC Res Notes 2014;7:510)
Treatment
- Surgical excision
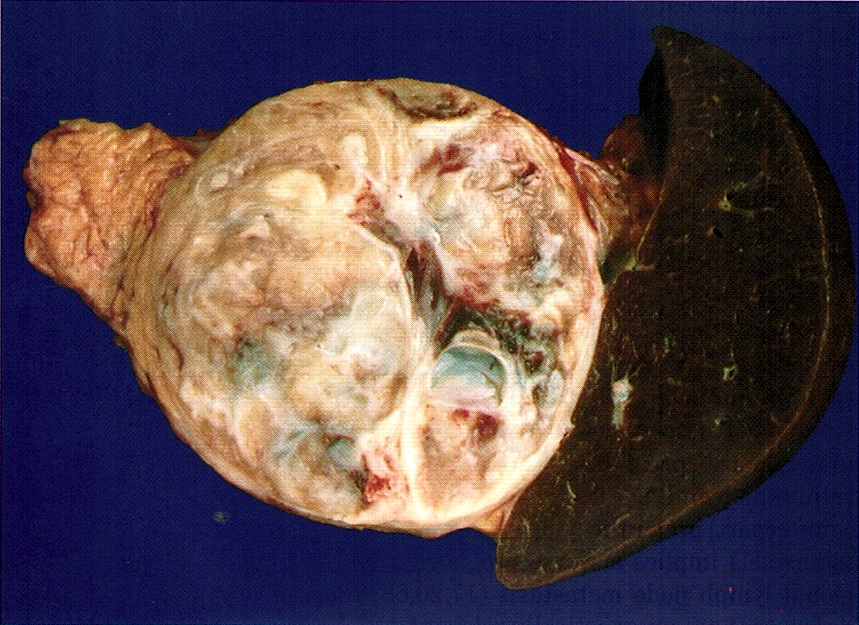
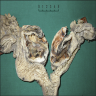
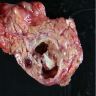
Gross description
- Mean 5 cm
- Generally unilocular cystic lesion filled with straw colored fluid
Gross images
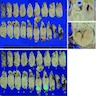
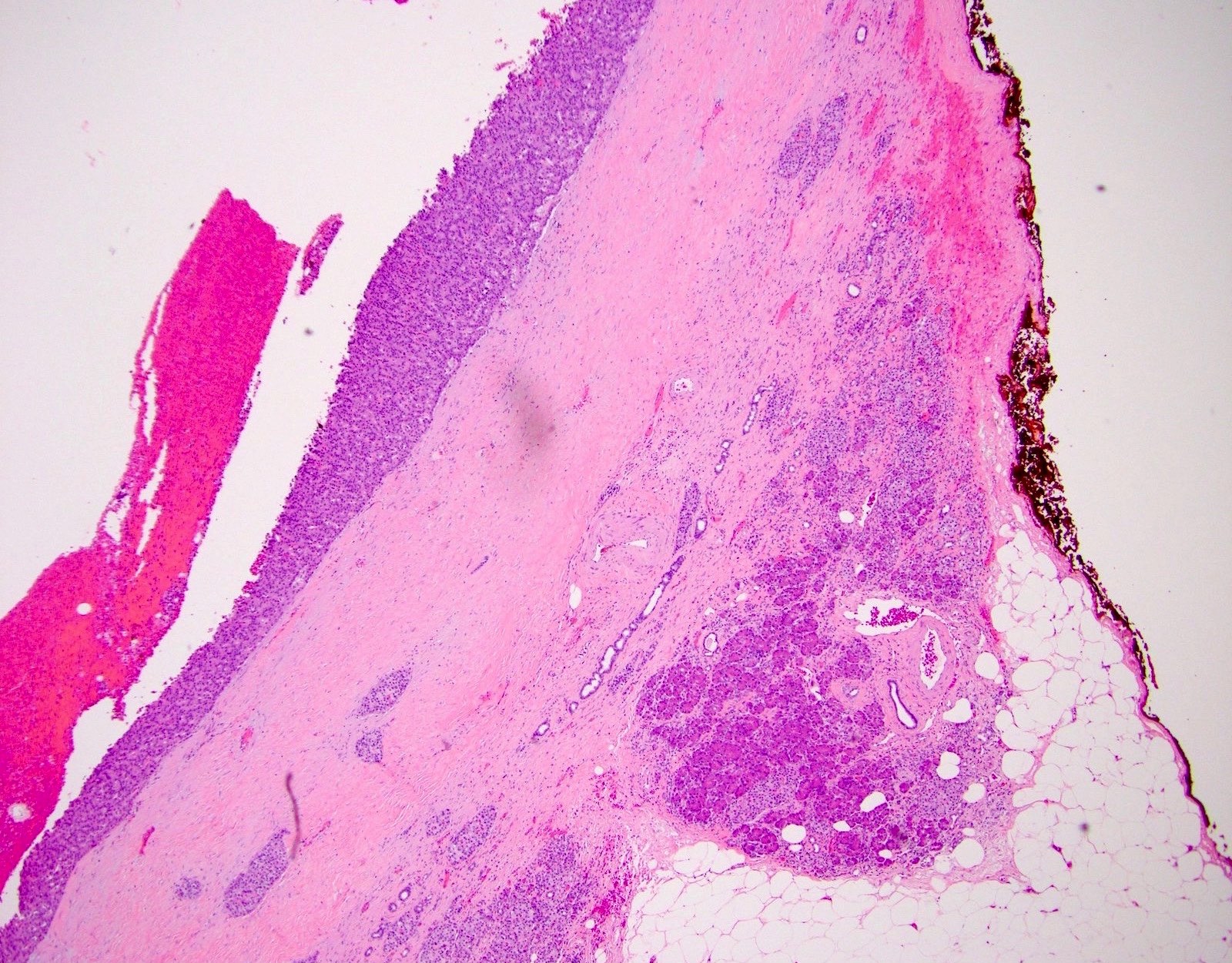
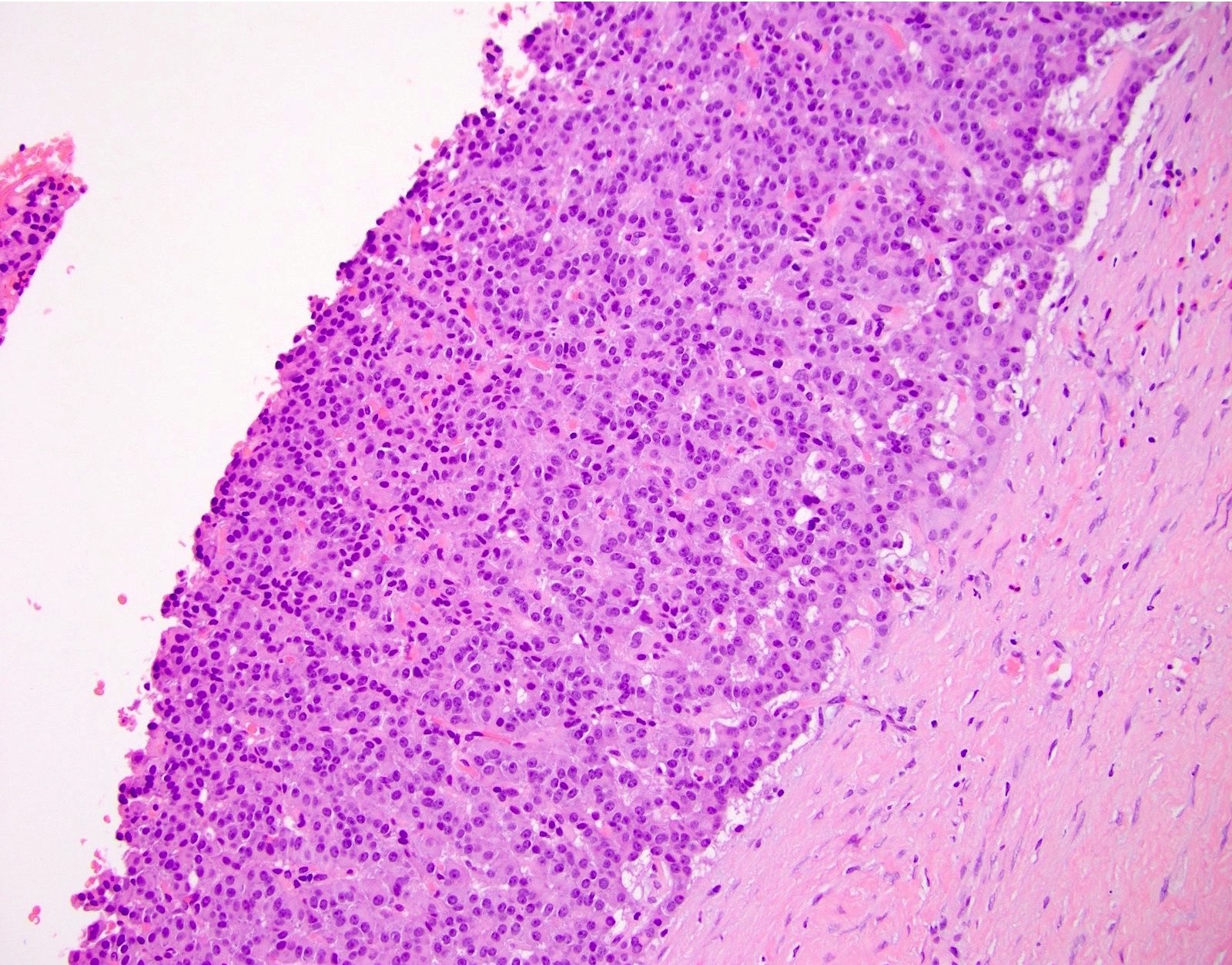
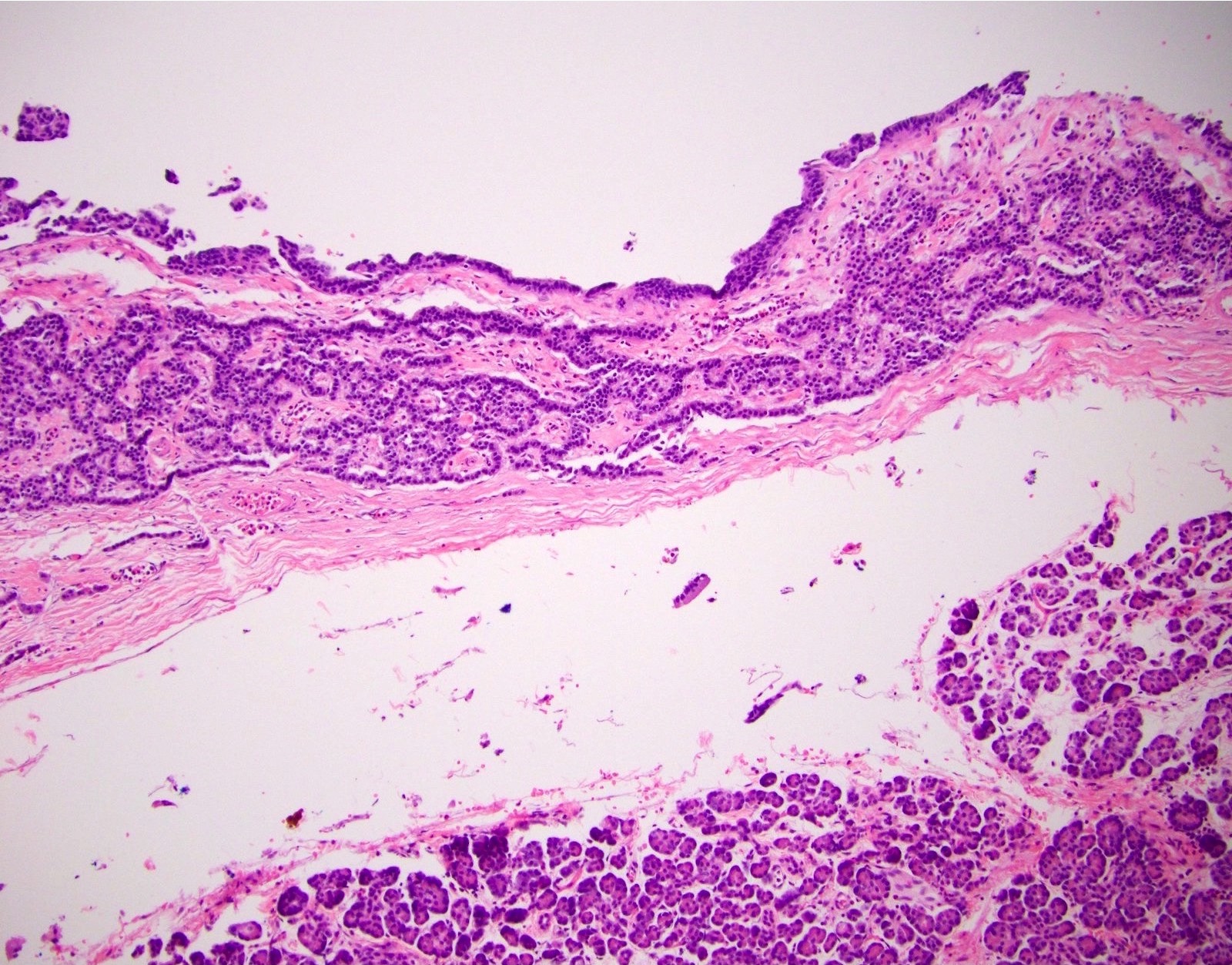
Microscopic (histologic) description
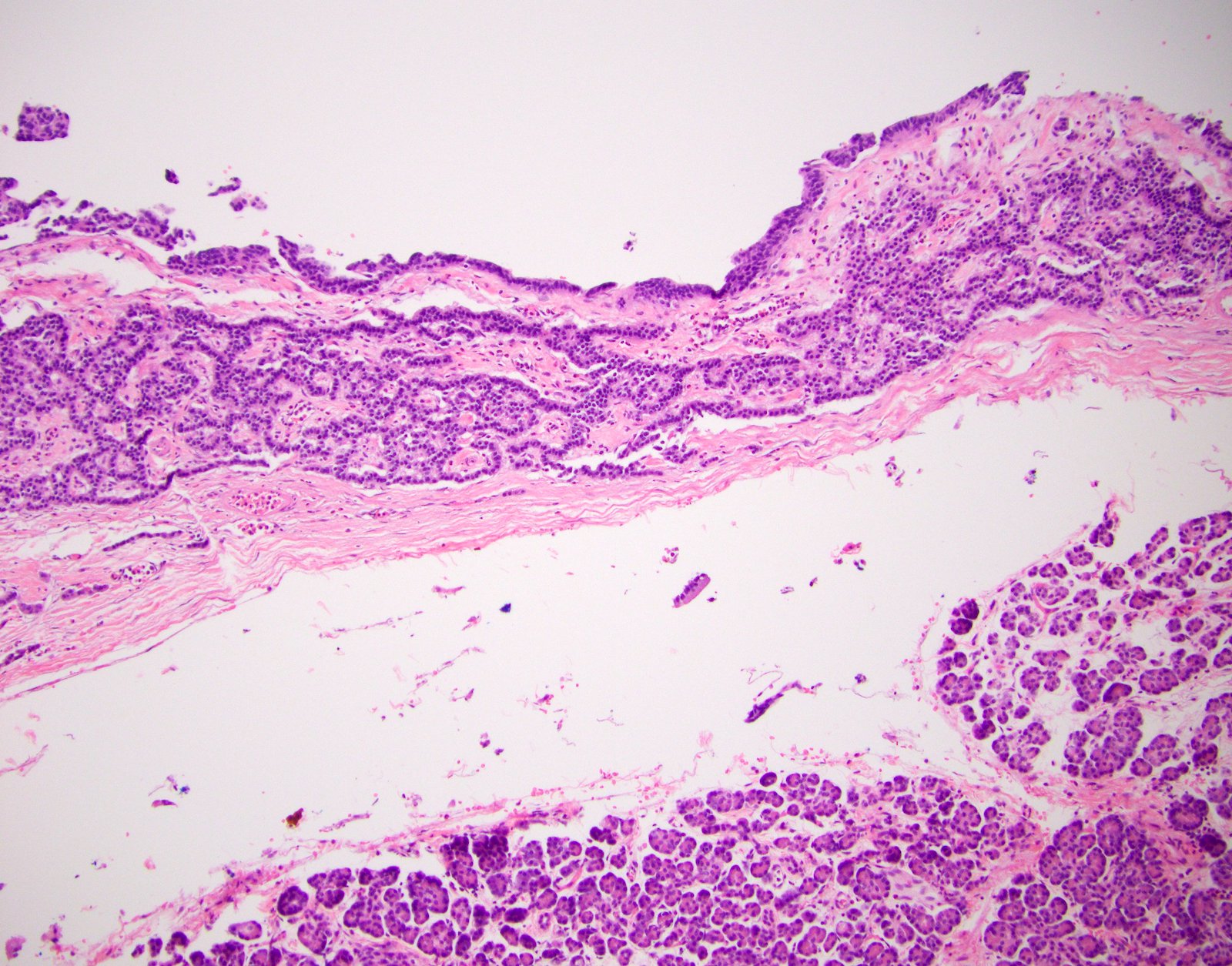
- Typically appears as a thick fibrous wall with neuroendocrine cells lining the central cystic space and sometimes forming nests or vesicular structures within the fibrosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2001;25:752)
- Necrosis and lymphovascular invasion are uncommon
Microscopic (histologic) images
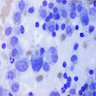
Cytology description
- Loosely cohesive aggregates and single cells
- Cells are small and plasmacytoid with occasional cytoplasmic vacuoles; nuclei are round / oval and uniform with finely and evenly distributed chromatin (Cancer 2009;117:203)
Positive stains (IHC and special stains)
- Neuroendocrine markers (synaptophysin / chromogranin)
- Often express glucagon but do not behave clinically as glucagonomas
Sample pathology report
- Pancreas, tail, resection:
- Pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor with cystic degeneration, WHO grade 1 (see synoptic report and comment)
- Comment: Immunohistochemical stains for synaptophysin and chromogranin are positive and the Ki67 index is approximately 1.1%.
Differential diagnosis
- Acinar cell cystadenoma / cystadenocarcinoma:
- Cysts are lined by acinar cells without associated acinar cell nests
- Negative for synaptophysin and chromogranin
Board review style question #1
- A patient is found to have an incidental cystic pancreatic mass on CT. Fine needle aspiration is performed and shows loosely cohesive tumor cells with a plasmacytoid appearance. Immunostains performed on the cell block show the cells are positive for synaptophysin and chromogranin. What is true about this lesion?
- Almost never incidental, despite this case
- More common in patients with MEN1 syndrome
- Probably arose in the head of the pancreas
- Very poor prognosis
Board review style answer #1
B. More common in patients with MEN1 syndrome. This is a cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Cystic endocrine tumors
Comment Here
Reference: Cystic endocrine tumors
Board review style question #2
Board review style answer #2
C. Chromogranin and synaptophysin. This is a cystic pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor.
Comment Here
Reference: Cystic endocrine tumors
Comment Here
Reference: Cystic endocrine tumors