Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Frozen section description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Busca A, Parra-Herran C. Corpus luteum cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/ovarynontumorcorpuslutcyst.html. Accessed January 21st, 2025.
Definition / general
- Ovarian cyst > 3 cm in diameter, lined by luteinized granulosa and theca cells
Essential features
- Cyst over 3 cm in size
- Cyst lining composed of inner layer of luteinized granulosa cells and outer layer of theca cells
ICD coding
- ICD-11: GA18.1 - Corpus luteum cyst
Epidemiology
- Functional cysts in women of reproductive age, including pregnancy
- Rare in postmenopausal women
Sites
- Ovary
Pathophysiology
- Corpus luteum is a physiological postovulatory structure formed after the dominant follicle releases the ovum
- Its main purpose is to secrete estrogen and progesterone and it normally regresses at the end of the cycle
- Cystic dilation happens when corpus luteum fails to regress and becomes enlarged with fluid / blood
- Reference: StatPearls: Anatomy, Abdomen and Pelvis, Ovary Corpus Luteum [Accessed 20 May 2021]
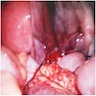
Clinical features
- Patients can be asymptomatic or present with menstrual irregularities, amenorrhea, abdominal pain, palpable abdominal mass if large size
- If cyst ruptures, patient may present with acute abdomen and hemoperitoneum
- Reference: Turk J Obstet Gynecol 2020;17:300
Diagnosis
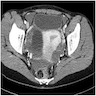
- On pelvic ultrasound, appears as simple ovarian cyst, often hemorrhagic; incidental finding or diagnosed during symptomatic workup
Laboratory
- No specific laboratory findings
Radiology description
- On ultrasound: unilocular cyst with prominent peripheral blood flow and thick crenulated vascular walls
- On CT: unilocular structure with crenulated walls and brisk enhancement (Abdom Radiol (NY) 2016;41:2270)
Prognostic factors
- Most cysts resolve spontaneously
- Hemorrhagic cysts over 5 cm or simple cysts between 5 and 7 cm in women of reproductive age require follow up to ensure resolution (Ultrasound Q 2010;26:121)
- In postmenopausal women, consider surgical evaluation of hemorrhagic cysts, as the etiology is more likely neoplastic than functional (Radiology 2010;256:943)
- Vast majority of pregnancy associated simple cysts < 5 cm resolve by weeks 16 - 20 and require no intervention (Clin Obstet Gynecol 2006;49:492)
Case reports
- 15 year old girl with ruptured hemorrhagic corpus luteum cyst of undescended ovary, a rare cause of acute abdomen in an adolescent (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2016;29:e21)
- 15 year old girl with ruptured corpus luteum cyst of pregnancy with massive hemoperitoneum (J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2007;20:97)
- 16 year old girl with hemoperitoneum from corpus luteum cyst rupture (Case Rep Emerg Med 2014;2014:252657)
- 18 year old woman with congenital hypofibrinogenemia with hemoperitoneum caused by ovulation (Obstet Gynecol Sci 2015;58:427)
Treatment
- Resection if symptomatic, rupture or suspicion for neoplastic process (Radiology 2010;256:943)
- For asymptomatic unilocular cysts with normal CA125, optimal management includes surveillance with ultrasound (Clin Obstet Gynecol 2006;49:506, Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2014;41:609)
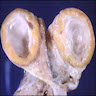
Gross description
- Single unilocular cyst with smooth surface
- Cyst wall and lining appears yellow and convoluted
- Serous or hemorrhagic contents
- Reference: Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract, 7th Edition, 2019
Frozen section description
- Convoluted cyst wall lined by cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and bland nuclear features
- Cytoplasm may appear vacuolated on frozen tissue
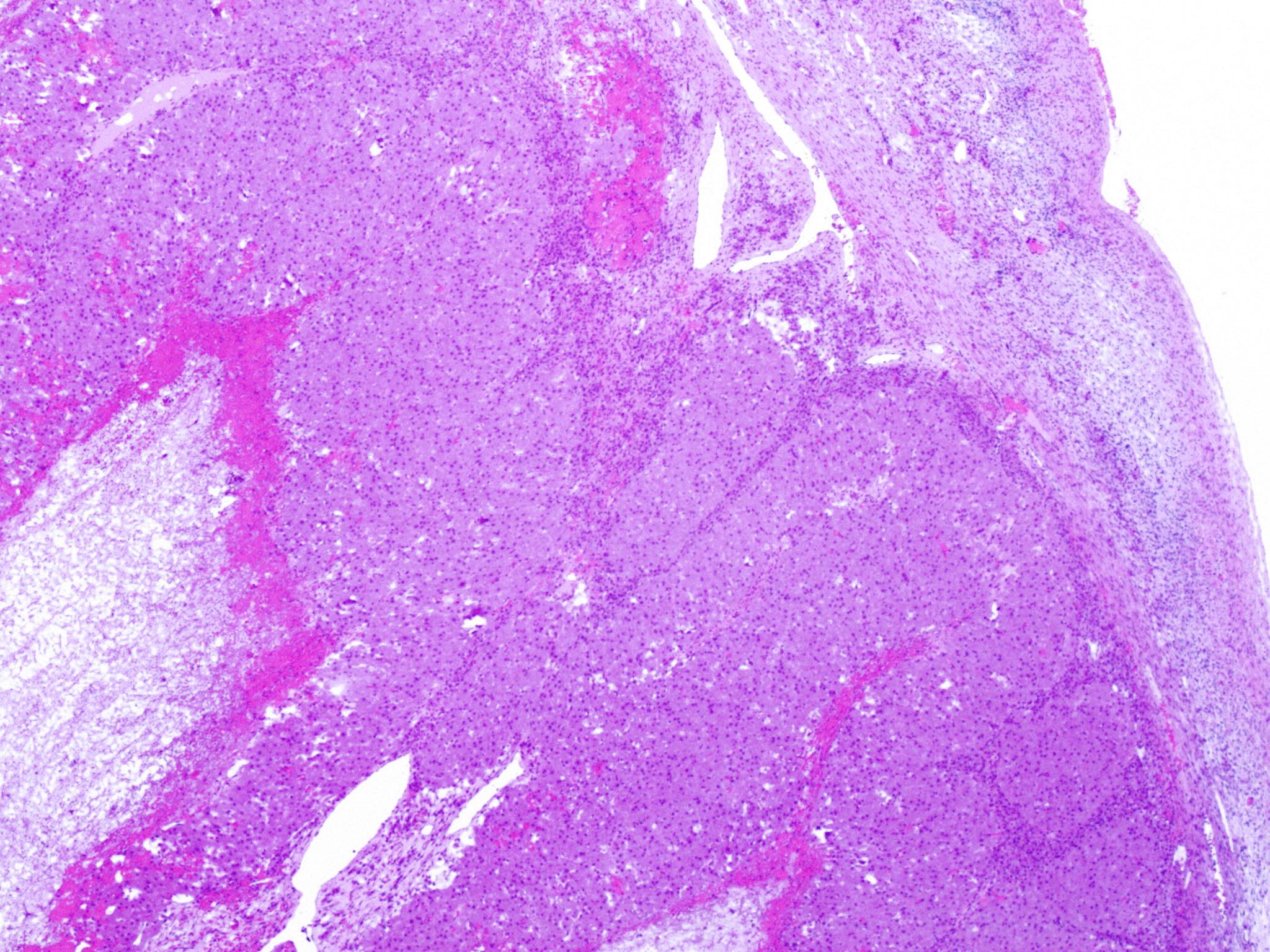
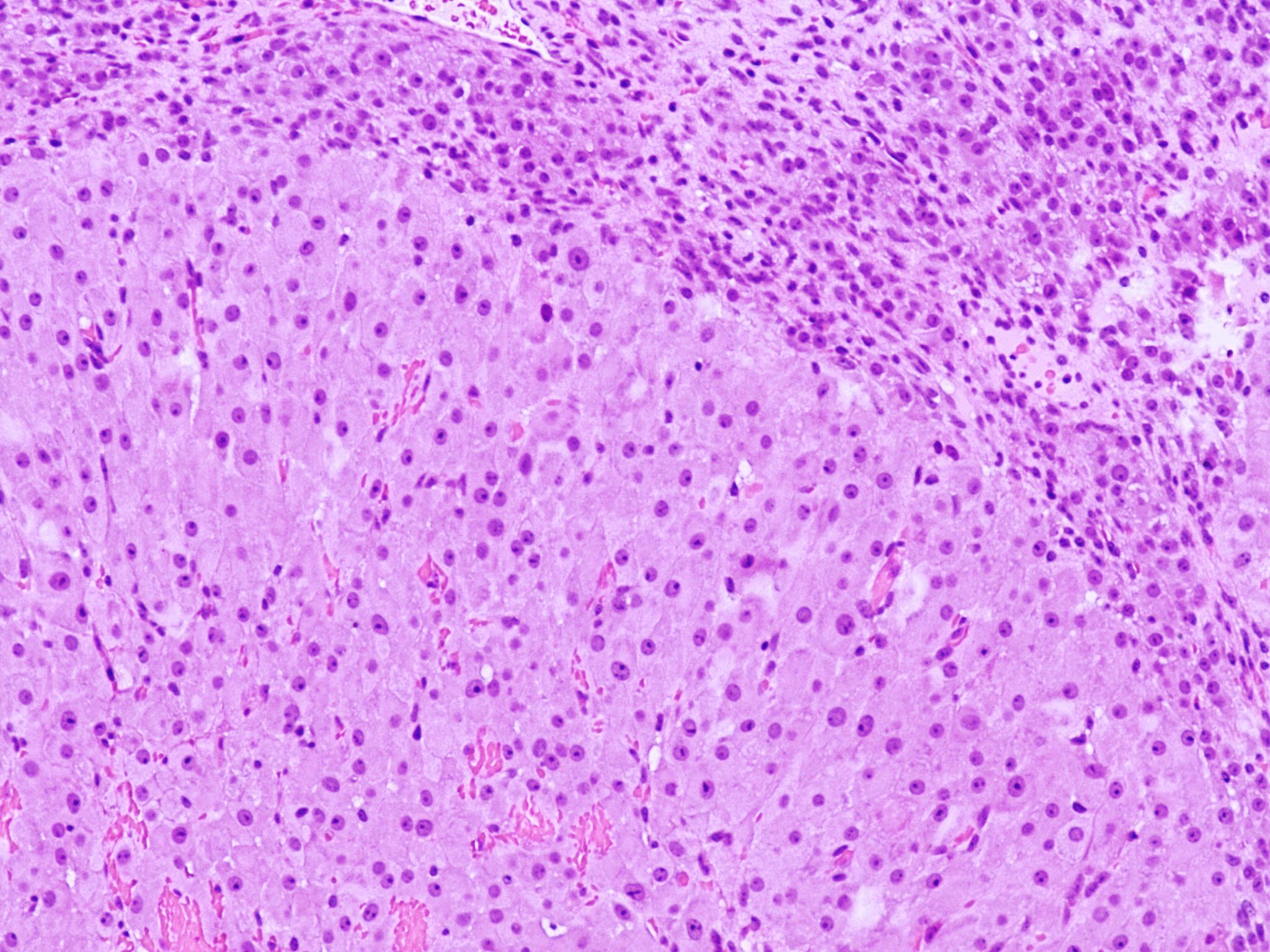
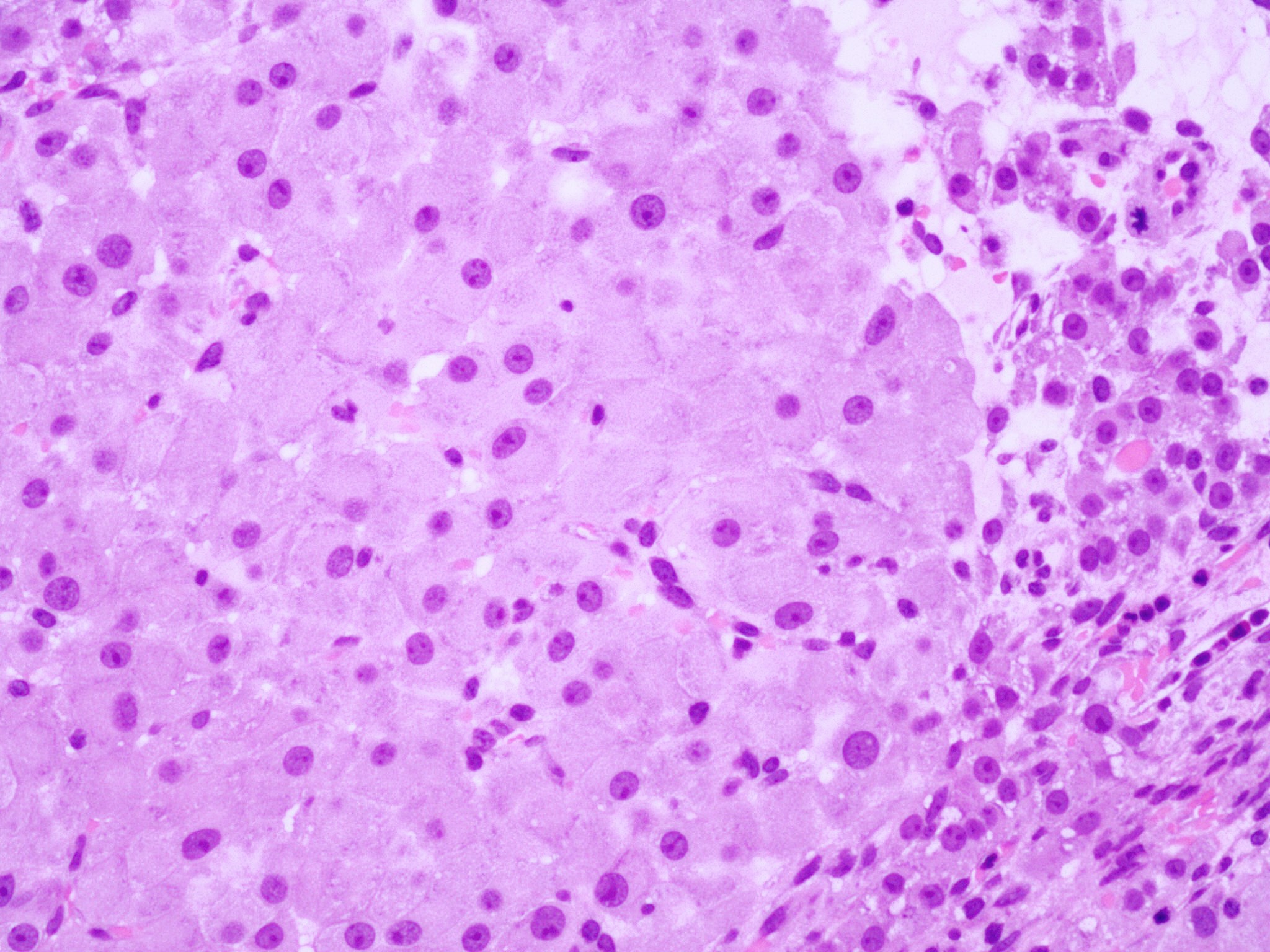
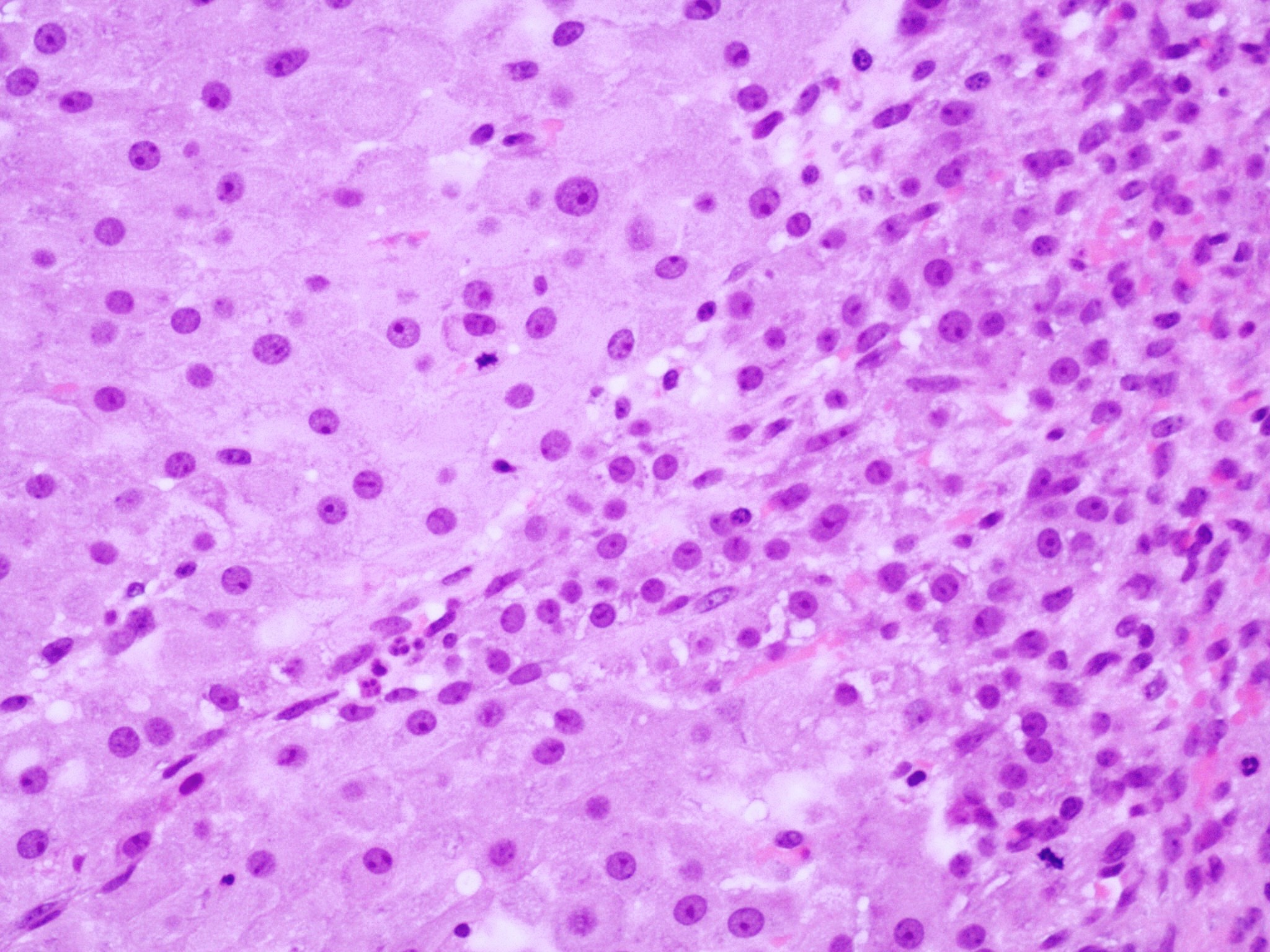
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Cyst lining is convoluted, composed of an inner layer of luteinized granulosa cells and outer layer of theca cells
- Granulosa cells are polygonal in shape, with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and central round nuclei
- Mitotic figures may be seen in the granulosa cells
- Outer theca cells are smaller in size
- Prominent inner layer of fibrous tissue
- Reference: Kurman: Blaustein's Pathology of the Female Genital Tract, 7th Edition, 2019
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Rarely performed
- Luteinized granulosa cells and hemosiderin laden macrophages in the background of blood and fibrin (Diagn Cytopathol 1990;6:77)
Positive stains
- Usually not necessary for diagnosis
- Calretinin (Histopathology 2001;38:403)
- Inhibin (J Clin Endocrinol Metab 1991;73:470)
- Progesterone receptor (Reproduction 2004;128:423)
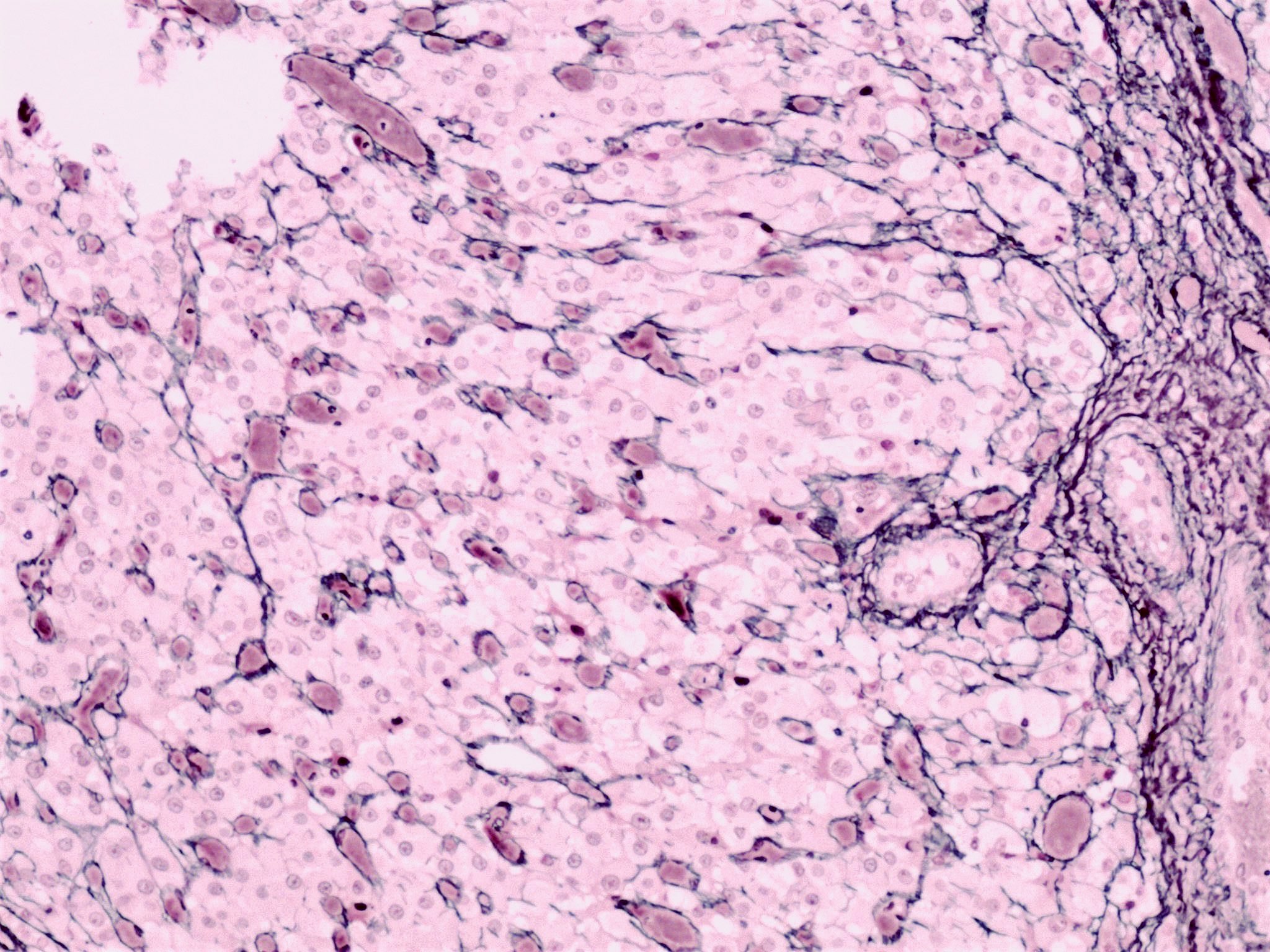
- Reticulin preserved within the theca interna layer
Negative stains
- Cytokeratin
- Reticulin diminished / absent in the granulosa layer
Sample pathology report
- Ovary, right, cystectomy:
- Corpus luteum cyst
- Background ovary with cystic follicles and epithelial inclusion cysts
- Negative for malignancy
Differential diagnosis
- Cystic granulosa cell tumor:
- Usually larger
- The 2 cell types in the cyst wall have a more disorderly pattern
- Neoplastic cells can infiltrate the cyst wall
- With or without Call-Exner bodies
- Endometriotic cyst:
- Endometrial glands and stroma, hemosiderin laden macrophages
- Epithelial inclusion cyst:
- Lined by either ciliated (tubal type) or flat (ovarian surface / peritoneal type) epithelium
- Follicular cyst:
- > 3 cm: lined by an inner layer of granulosa cells and an outer layer of theca cells
- Luteinization is either absent or only focal
- Lacks the convoluted appearance on low power magnification
- Cystic corpus luteum:
- Size < 3 cm
Board review style question #1
Board review style answer #1
B. It is a benign finding, expected to undergo regression
Comment Here
Reference: Corpus luteum cyst
Comment Here
Reference: Corpus luteum cyst
Board review style question #2
Which of the following is characteristic of a corpus luteum cyst of the ovary?
- Bilayered lining of granulosa and theca cells
- Presence of endometrial type stroma
- Single layer of ciliated cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm
- Single layer of granulosa cells
Board review style answer #2