Table of Contents
Definition / general | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Pernick N. Peripheral giant cell granuloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillaperipheralgiantcellgranuloma.html. Accessed December 21st, 2024.
Definition / general
- Also called giant cell epulis
- Resembles pyogenic granuloma but may erode alveolar bone or involve periodontal membrane
- Usually women, mean age 30 years, although may involve children or elderly patients without teeth
- May be due to trauma, local irritation or chronic infection
- Recurs if not completely excised
Treatment
- Excision with curettage of base of lesion extending into adjacent periodontal membrane
Gross description
- Inflammatory lesion up to 1.5 cm that protrudes from gingiva at site of chronic inflammation
- Covered by gingival mucosa or ulcerated
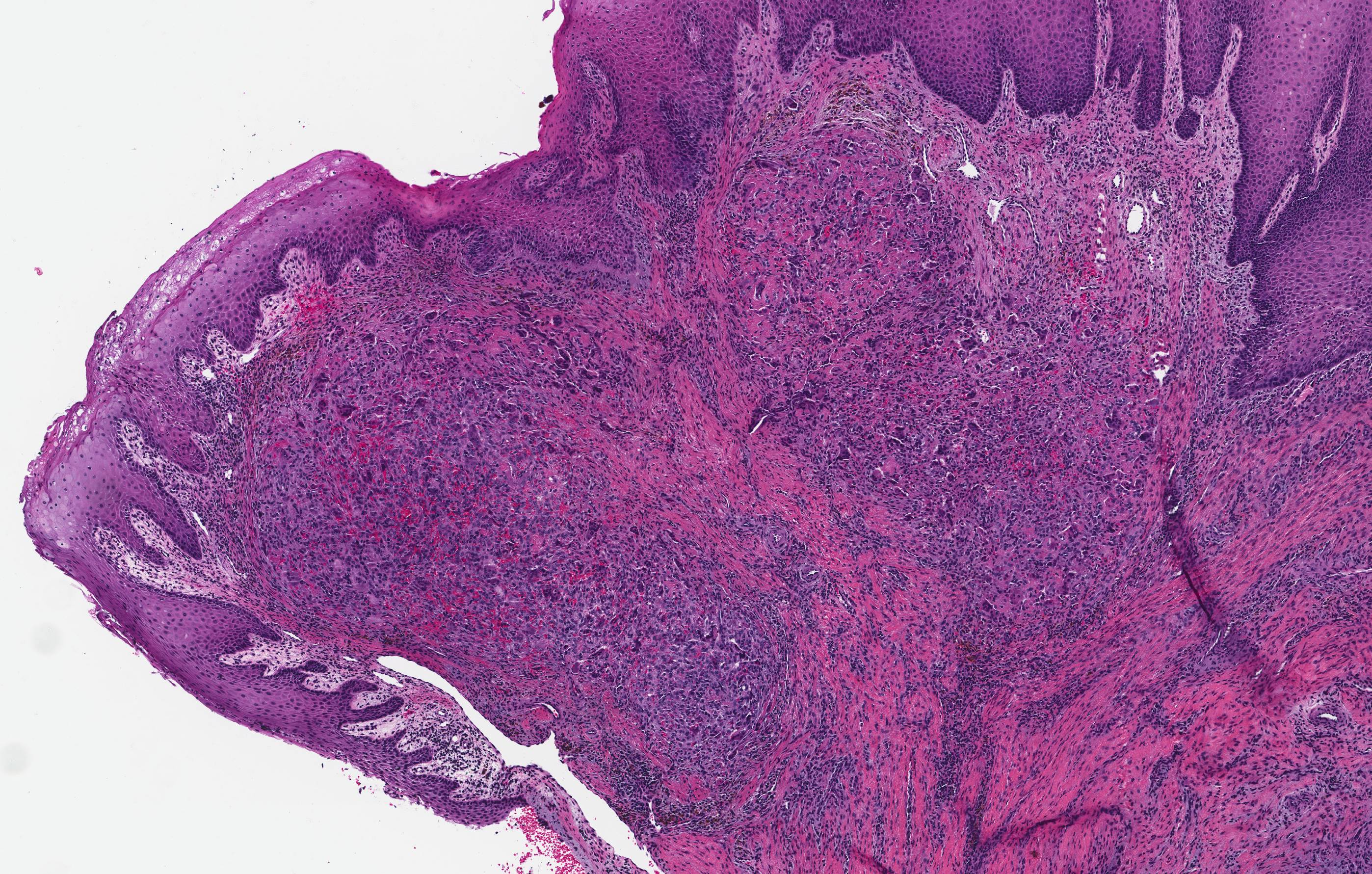
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Nonencapsulated aggregates of foreign body giant cells and fibroangiomatous stroma with hemorrhage, hemosiderin, acute and chronic inflammatory cells
- Alveolar bone often expanded in edentulous patients leading to superficial bone loss with peripheral cuffing
Microscopic (histologic) images
Differential diagnosis
- Giant cell granulomas of maxilla / mandible
- Giant cell "brown tumors" of hyperparathyroidism