Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Epidemiology | Sites | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognosis and treatment | Radiology description | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Immunohistochemistry & special stains | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosisCite this page: Martinez A. Nasolabial cyst. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/mandiblemaxillanasolabial.html. Accessed December 25th, 2024.
Definition / general
- A rare, developmental non-odontogenic cyst that occurs in the soft tissues of the upper lip lateral to midline
Terminology
- Klestadt cyst
- Nasal alveolar cyst
- Nasoalveolar cyst
- Nasal wing cyst
- Nasal vestibule cyst
- Mucoid cyst of the nose
Epidemiology
- Rare, represents:
- < 1% of jaw cysts
- 2.5% of non-odontogenic cysts
- Adults, peak prevalence in fourth and fifth decades
- 3:1 predilection for women
Sites
- Nasolabial region of the facial soft tissues
- Does not involve the underlying bone, therefore nasoalveolar cyst is a misnomer
Etiology
- Unsettled, but two main theories:
- First suggests remnants of the embryonic nasolacrimal ridge, duct or rod as origin
- Support for this theory is the immunohistochemical protein expression pattern which is very similar to the physiologic pattern of normal nasolacrimal duct epithelium
- Second theory, now less favored:
- Suggests entrapped epithelial remnants along fusion line of medial nasal, lateral nasal and maxillary processes as an origin
Clinical features
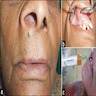
- Benign, slow growing cystic mass usually less than 3 cm in size
- Usually asymptomatic, rarely nasal obstruction or reports of pain if infected
- Most common patient concern is swelling
- Mass effect results in distention of nasolabial fold and elevation of the ala of the nose, extraorally
- Presentation could result in clinical differential diagnosis of odontogenic infection
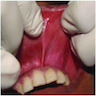
- Intraorally, obliterates the mucolabial fold
- 10% of cysts are bilateral
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis dependent of clinical, radiologic and pathologic correlation
Prognosis and treatment
- Malignant transformation has never been reported
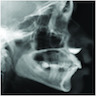
Radiology description
- On CT, will appear as ovoid, well circumscribed lesion, distortion of the affected nasolabial area / base of the nose
- Aside from subtle surface saucerization of bone, bone changes are not identified with this soft tissue cyst
Case reports
- 45 year old woman with Klestadt cyst visualized with radiographic contrast medium (J Clin Diagn Res 2014;8:ZD33)
- 54 year old woman with nasolabial cyst (Head Neck Pathol 2013;7:155)
- 69 year old woman with bilateral nasolabial cysts (J Oral Maxillofac Pathol 2013;17:443)
Treatment
- Surgical excision, performed intraorally, is most common
- Transnasal marsupialization has also been performed
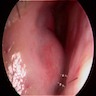
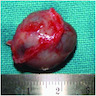
Clinical images
Gross description
- Rubbery, smooth surfaced mass, ballotable soft tissue cyst
- Sectioning reveals cystic and fibrous areas, without internal surface papillary projections
Microscopic (histologic) description
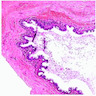
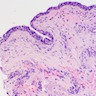
- Histologic examination often reveals lining of multilayered or pseudostratified, cuboidal to columnar epithelium
- Presence of true 'ciliated' epithelium has been described but there is a question whether true cilia remains
- Other combinations possible:
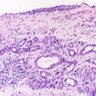
- Bilayered epithelium with a cuboidal basal layer and a columnar luminal layer that contains interspersed scattered mucinous goblet cells
- Both stratified squamous and cuboidal epithelium
- Cuboidal epithelial lining only
- A minority exhibit pseudostratified columnar, stratified squamous and cuboidal epithelium together
- Scattered interspersed luminal goblet cells are common
- Focal squamous metaplasia or apocrine changes may be present
- Cyst wall is composed of hypocellular fibrous connective tissue and may include skeletal muscle
- Inflammation may be present if a history of secondary infection
Microscopic (histologic) images
Immunohistochemistry & special stains
Electron microscopy description
- Bilayered structure of the lining epithelium with cuboidal basal layer and columnar luminal cells and mucous (goblet) cells
- Nonmucous luminal cells frequently feature prominent rough endoplasmic reticulum and numerous submembranous secretory granules, some with electron dense cores
- Microvilli decorated with glycocalix, but no true cilia present, which is in keeping with the newer literature
Differential diagnosis
- Cyst of the incisive papilla:
- Soft tissue cyst with similar histologic features to nasolabial cyst, but distinguished by anatomic site
- Cyst of the incisive papillae occurs within the soft tissue of the anterior hard palate only and shows no communication with the upper lip or nasal area
- Cystic salivary gland neoplasms (benign or malignant) could show overlapping features with nasolabial cyst, particularly on small biopsies:
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma
- Mammary analogue secretory carcinoma
- Pleomorphic adenoma
- Cystadenoma
- Dilated salivary duct due to obstruction:
- Soft tissue cystic proliferation, typically associated with inflammation in fibrous connective tissue wall
- Epidermal inclusion cyst:
- Soft tissue cyst distinguished from nasolabial cyst by keratinizing epithelium
- Glandular odontogenic cyst:
- Is an intraosseous cyst
- If bony cortical perforation has occurred, then a sampling of the 'soft tissue' component of the cyst lining will create a diagnostic dilemma
- Hidrocystoma:
- Soft tissue cyst of the skin, usually occurring in the periorbital region. Thin, uniform lining, usually 2 cell layers
- Nasopalatine duct cyst:
- Is an intraosseous cyst with histologic features similar to nasolabial cyst
- If bony cortical perforation has occurred, then a sampling of the 'soft tissue' component of the cyst lining will create a diagnostic dilemma
- Contents of incisive foramen typically identified in the surgically resected specimen (peripheral nerve, cartilaginous rests, vascular channels)