Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Peripheral smear description | Peripheral smear images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Flow cytometry description | Flow cytometry images | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Wood RK, Shawwa A, Werner D. Prolymphocytic leukemia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomaprolymphocyticleukemia.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Rare aggressive mature B cell neoplasm that represents less than ~1% of all leukemias
- Characterized by the presence of large lymphoid cells (prolymphocytes) accounting for at least 55% of total circulating cells in the peripheral blood
- Prolymphocytes are defined as large cells (> 2 erythrocytes) with clumped chromatin (but more open than in chronic lymphocytic leukemia [CLL]), a large single prominent vesicular nucleolus and abundant cytoplasm (Br J Haematol 2016;174:767)
Essential features
- Aggressive B cell neoplasm defined by large prolymphocytes accounting for 55% of total circulating cells in the peripheral blood
- Main sites of involvement are peripheral blood, spleen and bone marrow
- Marked absolute lymphocytosis (usually > 100 x 109/L)
- Poor prognosis in general; the degree of treatment response is dictated by anemia, degree of lymphocytosis and molecular prognostic markers
Terminology
- Prolymphocytic leukemia, B cell type (B-PLL)
ICD coding
- ICD-O: 9833/3 - Prolymphocytic leukemia, B cell type
Epidemiology
- Rare, accounting for less than 1% of all leukemias
- Patients are typically > 60 years old (median age of 65 - 69 years)
- M = F (Br J Haematol 1986;63:377)
- Additional reference: Cancer Causes Control 2008;19:379
Sites
- Sites of involvement are peripheral blood, bone marrow and typically the spleen
Pathophysiology
- Limited data on this apart from molecular characteristics
Etiology
- Very rare malignancy; no specific etiology or causal lesion associated with it
Clinical features
- Peripheral blood lymphocytosis usually > 100 x 109/L
- Patients often present with constitutional symptoms and massive splenomegaly
- Lymphadenopathy is typically absent or mild (Semin Oncol 2006;33:257)
Diagnosis
- Peripheral blood: CBC count, morphology review and flow cytometry
- Bone marrow biopsy: morphology, flow cytometry and immunohistochemistry studies
- Molecular and cytogenetic analysis have prognostic significance but are not necessary for a diagnosis
Laboratory
- Additional laboratory findings to the presence of marked absolute lymphocytosis in the CBC include anemia and thrombocytopenia; these are present ~50% of the time
Radiology description
- No specific radiology findings
Prognostic factors
- Aberrations in MYC and TP53 portend worst prognosis (Blood 2019;134:1821)
- Lymphocytosis > 100 x 109/L and anemia associated with shorter survival (Leuk Lymphoma 1999;33:169)
Case reports
- 48 year old man with 17p deletion shows response to sequential kinase inhibition (Case Rep Hematol 2017;2017:8563218)
- 53 year old man with transformation from CLL and unexpected response to R-CHOP (Perm J 2016;20:74)
- 84 year old man with 17p and 13q14 deletions with ibrutinib resistance (Cureus 2019;11:e5629)
- 84 year old man with B-PLL and concurrent warm and cold autoimmune hemolytic anemia (Acta Haematol 2019;141:222)
Treatment
- Rare cases that present as indolent disease and are asymptomatic can be followed with a watch and wait approach without immediate treatment; however, cases often progress rapidly and will require close monitoring
- Chemotherapy is the treatment indicated; in the absence of 17p deletion or TP53 mutation, rituximab in association to FC (fludarabine, cyclophosphamide) or bendamustine is the recommended first line therapy (Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2015;2015:361)
- Chemotherapy for poor prognosis cases is different; in del(17p) or TP53 mutated tumors, treatment with alemtuzumab or more recently ibrutinib are used (Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2015;2015:361, Br J Haematol 2017;179:501)
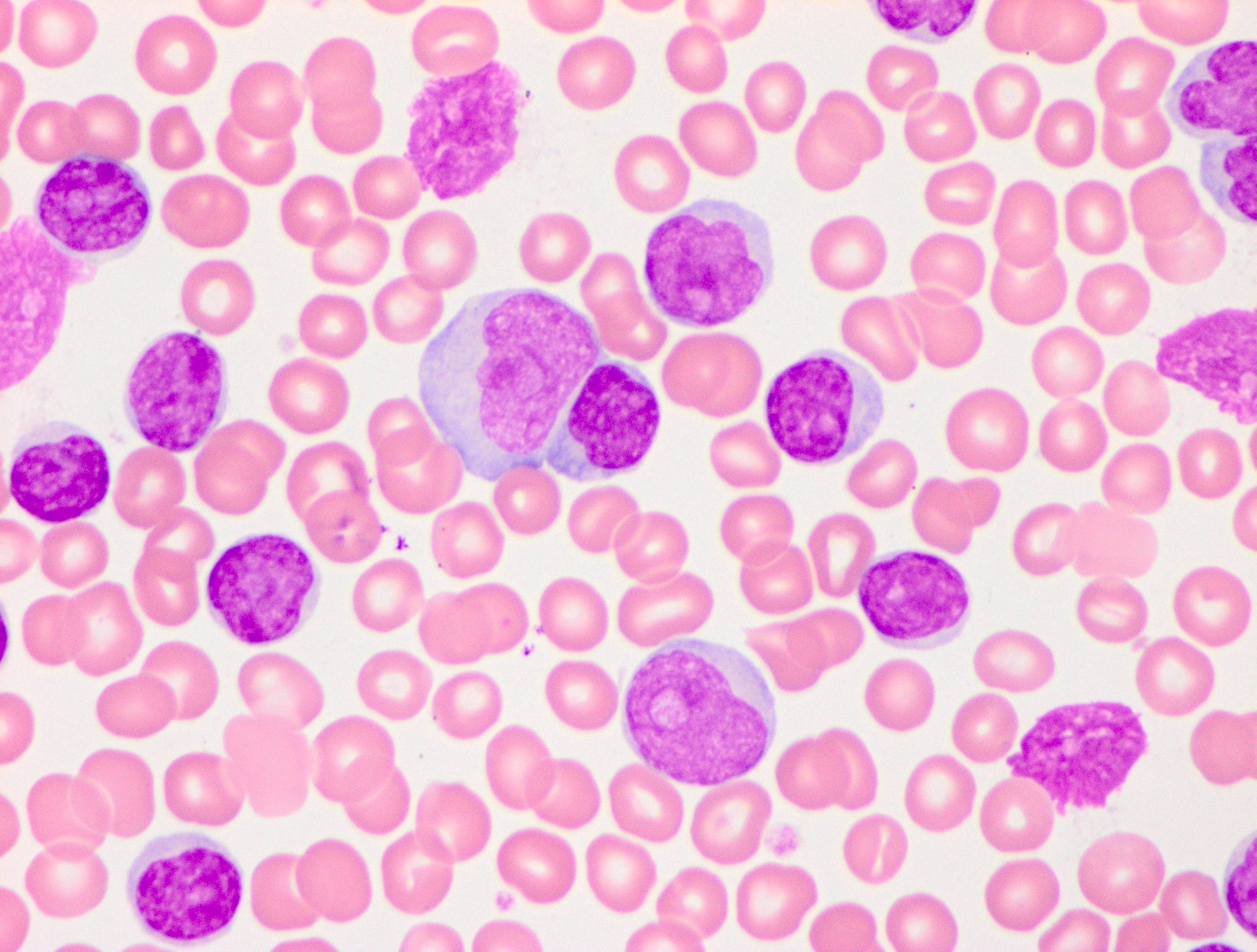
Microscopic (histologic) description
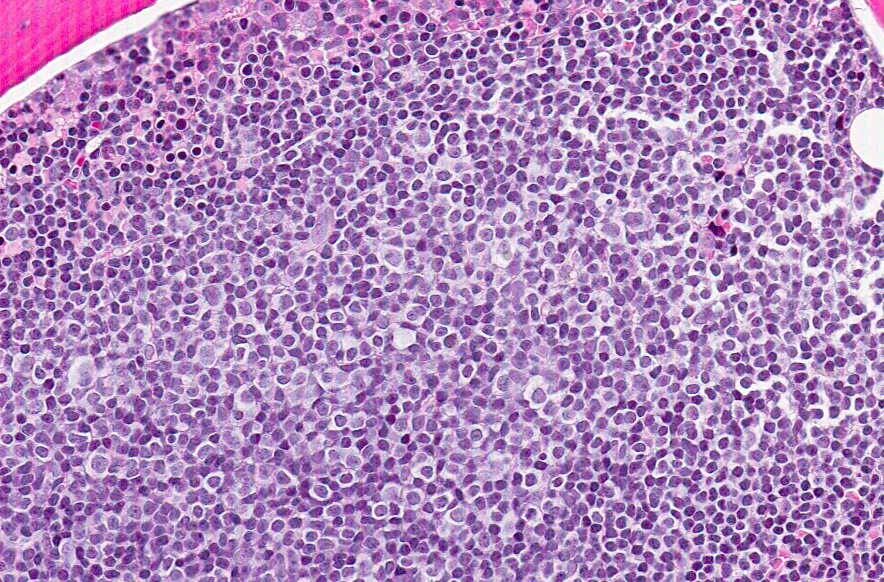
- Bone marrow involvement shows neoplastic infiltrates with a mixed nodular, interstitial or diffuse patterns composed of medium to large lymphoid cells
- Spleen shows expanded white pulp with red pulp infiltration by medium to large neoplastic cells with ample cytoplasm, round or irregular nuclei and a central large, eosinophilic nucleolus
- Lymph node involvement when present shows diffuse or nodular infiltration by neoplastic lymphoid cells without proliferation centers
Microscopic (histologic) images
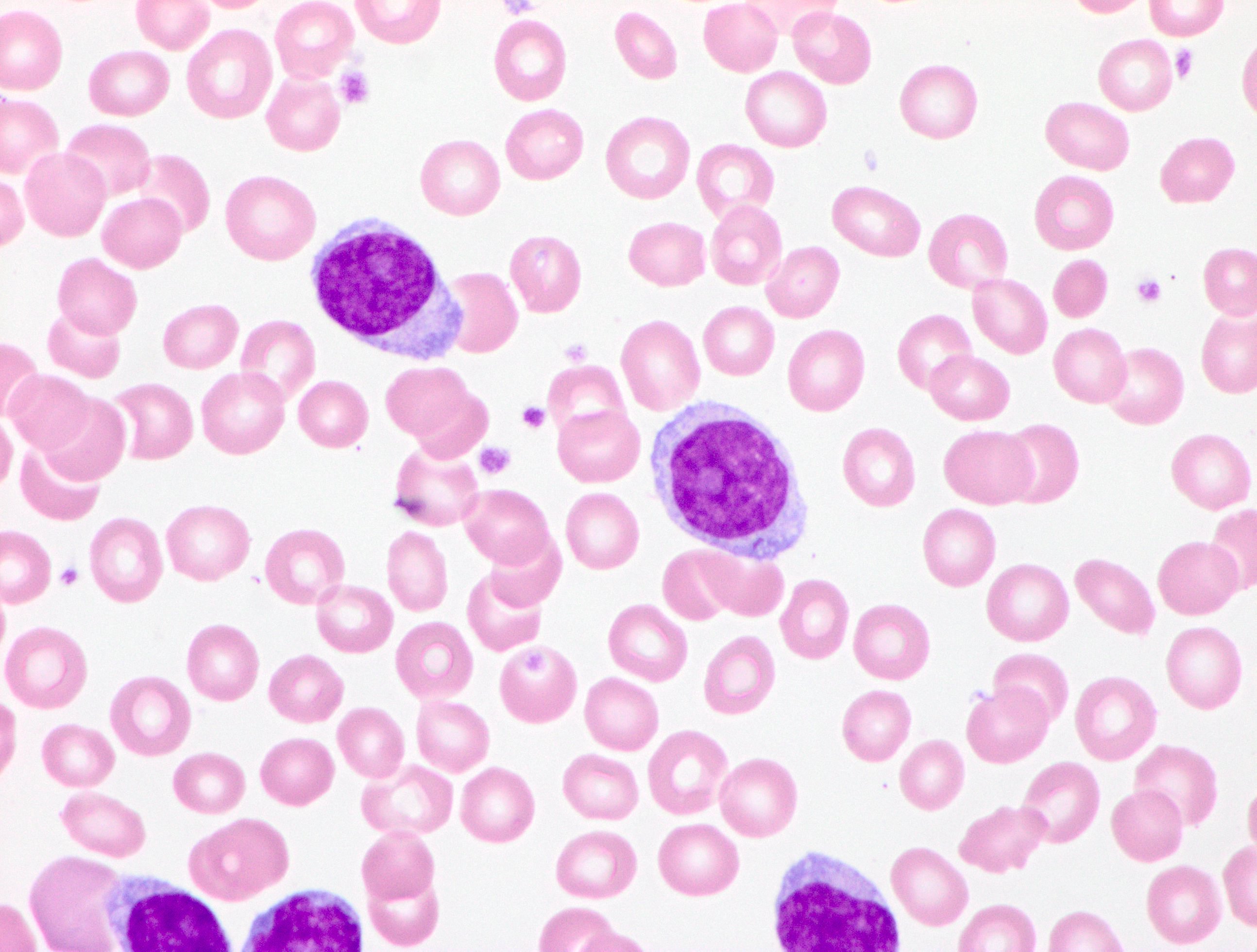
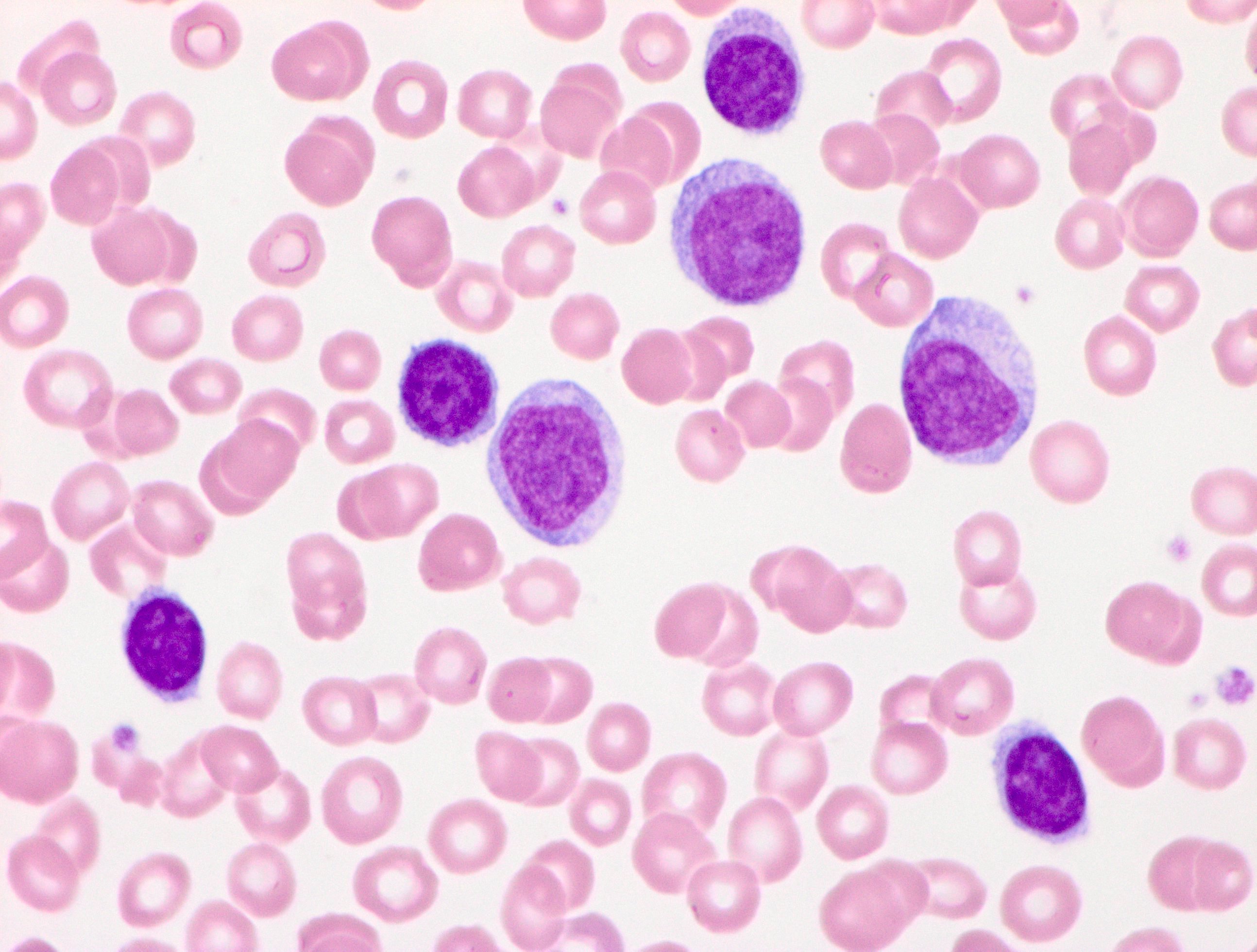
Peripheral smear description
- Marked absolute lymphocytosis with at least a 55% prolymphocyte count out of total circulating cells
- Prolymphocytes:
- Medium to large sized lymphoid cells with round or occasionally indented nuclei
- Moderately condensed to open chromatin
- Single large prominent central nucleolus
- Moderate amount of basophilic cytoplasm
- Reference: Br J Haematol 1974;27:7
Peripheral smear images
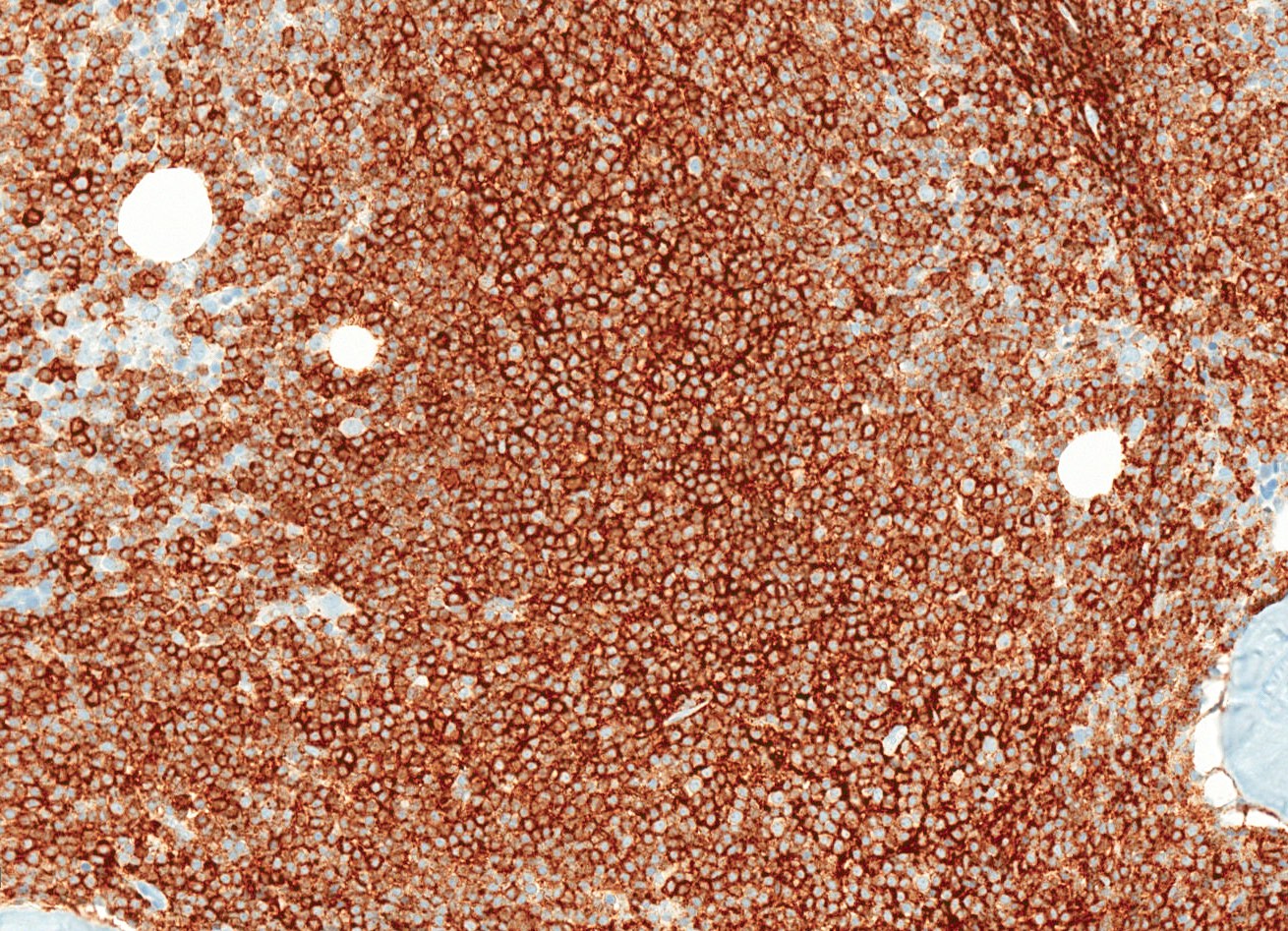
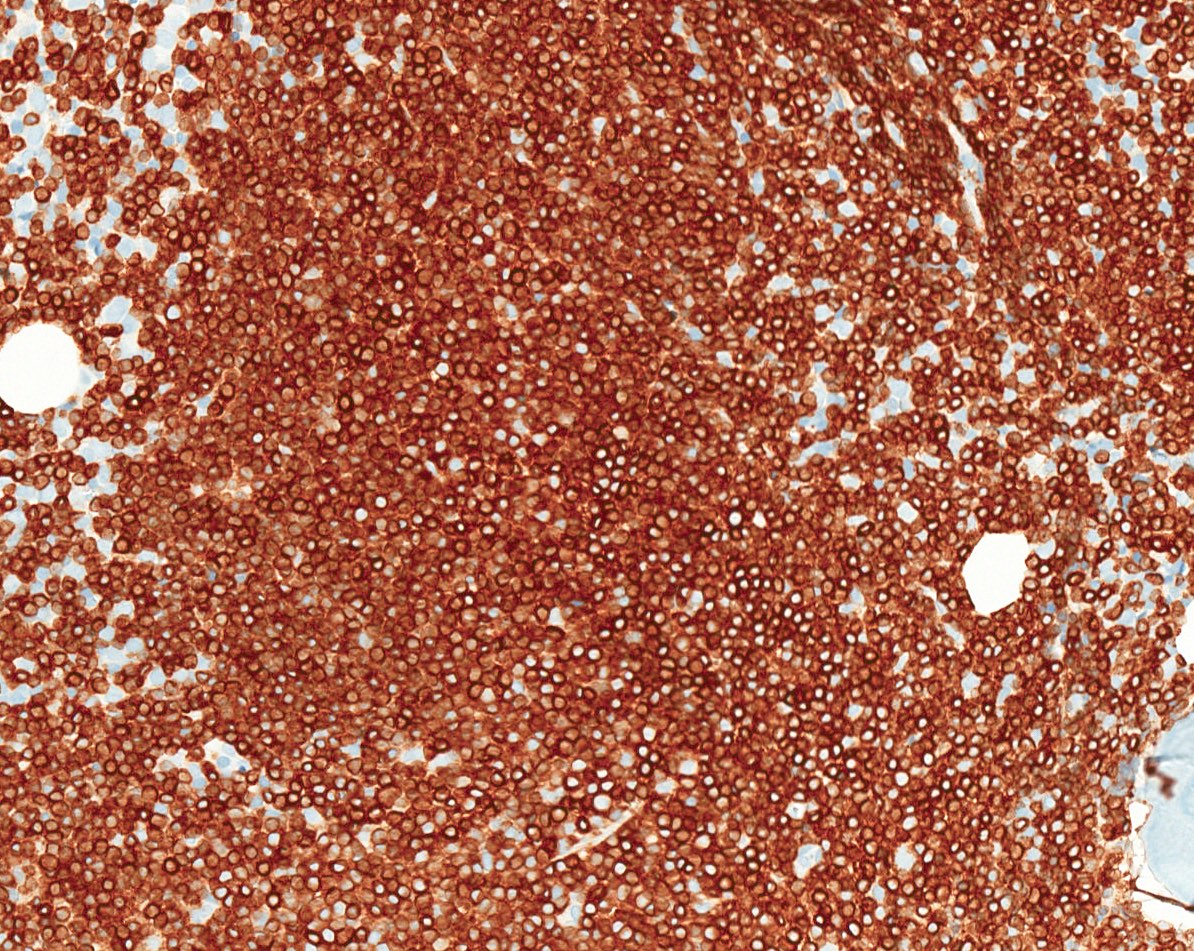
Positive stains
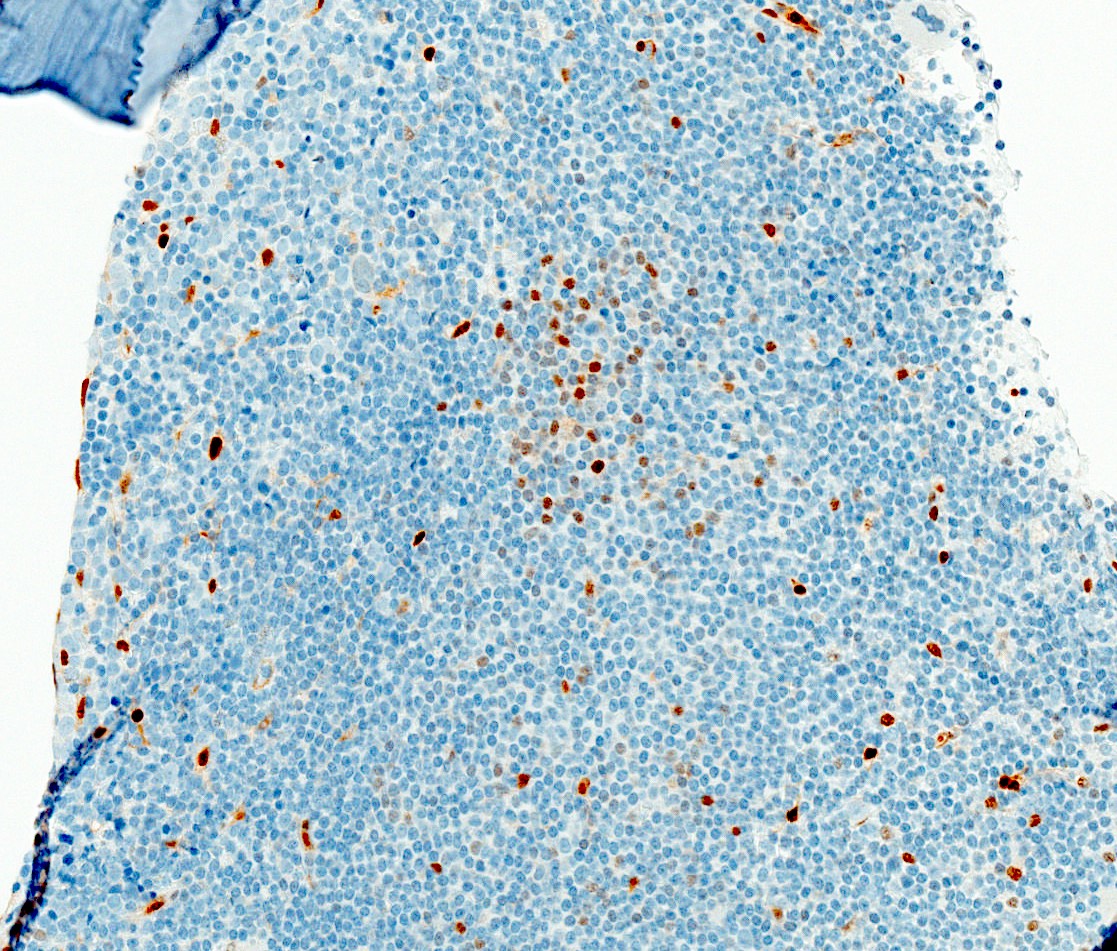
Negative stains
- In contrast to chronic lymphocytic leukemia, CD5 and CD23 are usually negative (expressed in 20 - 30% and 10 - 20%, respectively) (Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2019;32:217)
- Negative for cyclin D1, CD10 and BCL6 (Semin Oncol 2006;33:257)
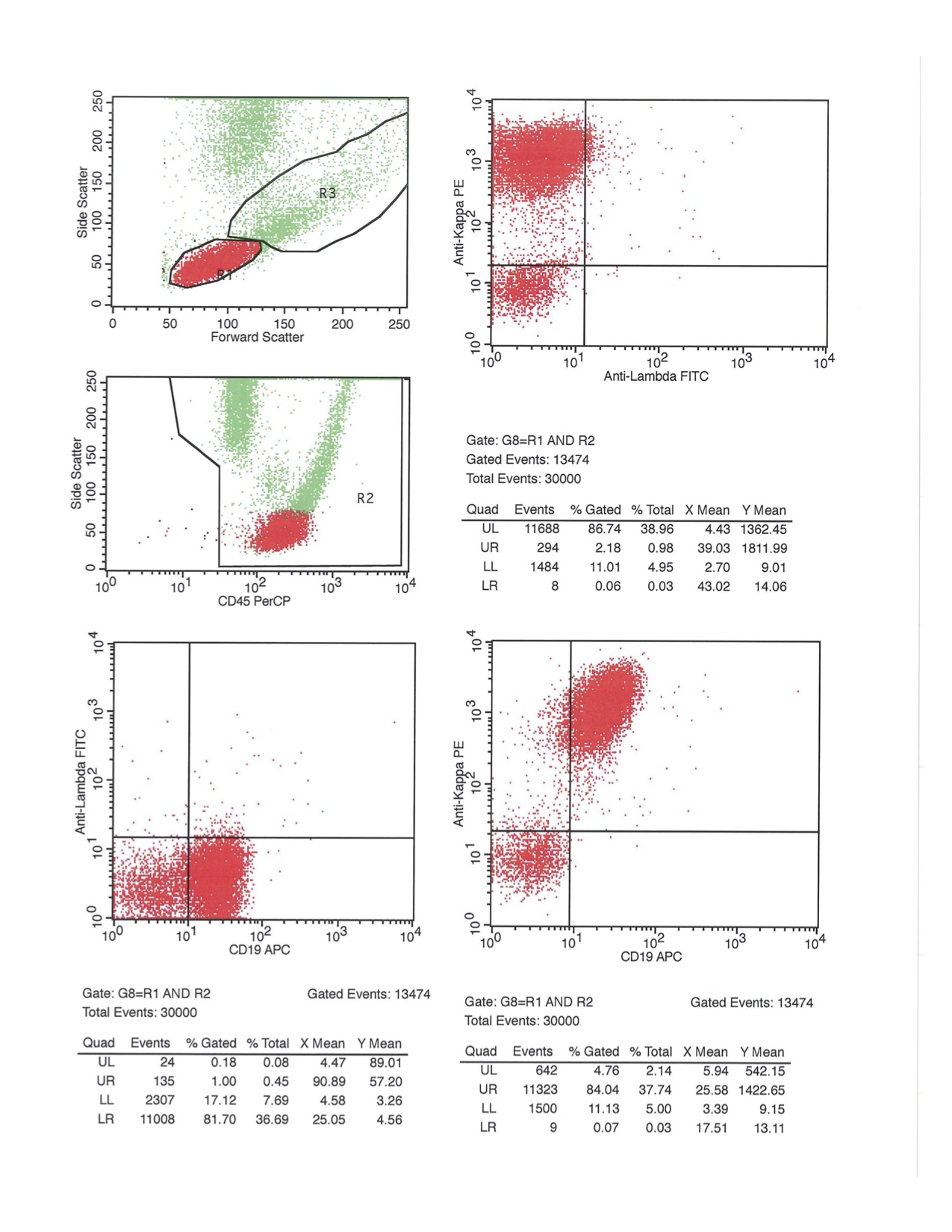
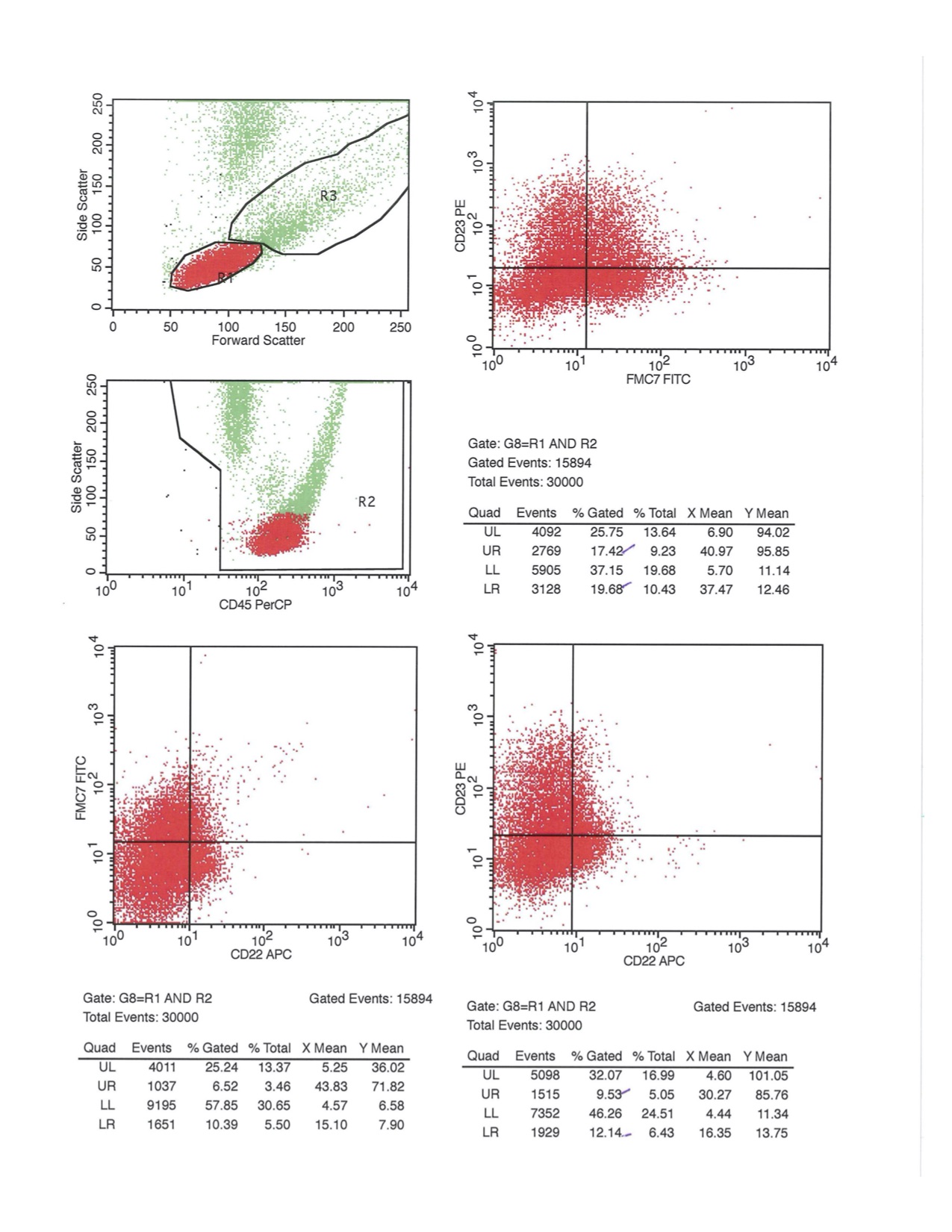
Flow cytometry description
- Positive
- Negative
- Reference: Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2019;32:217
Flow cytometry images
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- No molecular or cytogenetic specific signature exists for B-PLL and data is limited given its rarity
- Clonal rearrangement of IGHV is commonly found, with preferential use of IGHV3 and IGHV4 (Leukemia 2006;20:1231)
- Deletion of 17p13 was found in 53% of B-PLL and is associated with TP53 mutations (Leukemia 2006;20:1231)
- Deletions of 11q23 and 13q14 are frequently found (Leukemia 2006;20:1231, Leukemia 2000;14:427)
- Mutations in MYC have been reported, including translocations involving IGH, IGK or IGL (Am J Clin Pathol 2014;142:347)
Sample pathology report
- Bone marrow, right posterior iliac crest, biopsy, aspirate and clot section:
- B cell prolymphocytic leukemia (B-PLL) (see comment)
- Comment: This is a 79 year old man presenting with an elevated CBC count of 153 x 109/L and an absolute lymphocyte count of 124 x 109/L. A manual peripheral blood smear count shows a prolymphocyte count of 74%.
- Bone marrow aspirate:
- Quality of specimen: particulate
- Cellularity: hypercellular
- Approx. M:E ratio: 4:1
- Erythropoiesis: normoblastic and decreased
- Granulopoiesis: all stages of maturation present and decreased
- Megakaryocytopoiesis: normal
- Lymphocytes: increased with two monomorphic populations noted. The first is characterized by medium sized cells with prominent central nucleoli and abundant cytoplasm. The second consists of small lymphocytes with densely packed chromatin and minimal cytoplasm.
- Plasma cells: normal; not increased
- Bone marrow aspirate differential:
- Metamyelocytes: 3%
- Bands: 7%
- Seg. neutrophils: 10%
- Eosinophils: 1%
- Lymphocytes: 72%
- Monocytes: 2%
- Erythroblasts: 8%
- Total cells counted: 500
- Bone marrow biopsy:
- A trephine biopsy with a length of 1.5 cm is submitted. The sample is adequate for examination. The specimen is hypercellular at approximately 70% cellularity. Trilineage hematopoiesis is decreased. Megakaryopoiesis is nondysplastic. Granulopoiesis is decreased but still shows a normal range of maturation and geographic distribution. There is a diffuse, interstitial and nodular infiltrate of lymphocytes consisting of two discrete populations. The first shows medium to large sized cells with prominent nucleoli and vesicular chromatin while the second consists of small, monomorphic lymphocytes with densely packed chromatin.
- Ancillary testing:
- Immunohistochemical evaluation of the larger cell population shows expression of CD20, CD19 and CD79a while CD5 and CD23 are not expressed. The population of smaller cells expresses CD20, CD19, CD5 and CD23. Both populations are negative for expression of CD3, SOX11 and cyclin D1.
- The flow cytometry report shows two neoplastic cell populations surface light chain kappa restricted. The first larger population represents 69% of the sample and is positive for CD19, CD20 bright and kappa bright and is negative for CD5, CD10 and CD23. A second smaller population in 18% of the sample is positive for CD19, CD20 dim, CD5, CD23 and kappa dim.
- Molecular and cytogenetic studies demonstrated deletion of 17p13. Translocation (11;14)(q13;q32) was not detected.
Differential diagnosis
- Mantle cell lymphoma:
- T cell prolymphocytic leukemia:
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia with increased prolymphocytes:
- Hairy cell leukemia variant:
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma:
- Neoplastic cells show characteristic short polar villi and do not have prominent nucleoli
- Splenic involvement by MZL shows prominent marginal zone
- Marrow involvement may show follicular arrangement with surrounding marginal zone B cells
- Molecular analysis shows in some cases NOTCH2 and NFκB mutations (not reported in B-PLL)
- Follicular lymphoma:
- Typically follicular pattern and often involving lymph nodes
- Expresses CD10
- Lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma:
- Plasmacytoid appearance of neoplastic cells often accompanied by rouleaux
- MYD88 mutation in > 90% of cases
Additional references
Board review style question #1
You review the peripheral blood smear of a 74 year old man with a high WBC count of 117 x 109/L, anemia and thrombocytopenia. The majority of the cells (75%) have the appearance shown in the above image. Flow cytometry shows that these cells have the following immunophenotype: CD20+, CD19+, FMC7+, CD200+ and CD10-, CD5-, CD23-. What is your diagnosis?
- Acute myeloid leukemia
- B cell prolymphocytic leukemia
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia
- Mantle zone lymphoma
- Splenic marginal zone lymphoma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
Which of the following findings is the required criteria for a diagnosis of B cell prolymphocytic leukemia?
- Anemia
- Bone marrow involvement
- Deletion of 17p13
- Lymphocytosis over 100 x 109/L
- Medium to large sized lymphocytes with central, large nucleoli that are greater than 55% of the total WBC
Board review style answer #2
E. Medium to large sized lymphocytes with central, large nucleoli that are greater than 55% of the total WBC
Comment Here
Reference: Prolymphocytic leukemia
Comment Here
Reference: Prolymphocytic leukemia