Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Clinical images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Marques-Piubelli ML, Torres-Cabala CA, Miranda RN. Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomanonBnasal.html. Accessed April 16th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Aggressive and predominantly extranodal lymphoma of NK / T cell origin characterized by angiotropism and angiodestruction, necrosis and association with Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
Essential features
- Aggressive and predominantly extranodal lymphoma of NK / T cell origin characterized by angiotropism and angiodestruction, necrosis and association with EBV (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- More frequent in East Asia and Latin America, while rare in U.S. and Europe (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Leukemia 2014;28:338, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
- Nasal presentation (65 - 85%) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses and orbit, regardless of the dissemination to other sites
- Nasal presentation (65 - 85%) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Ulceration of mucosa with diffuse infiltration of lymphoid cells with broad cytological spectrum, ranging from small to large cells (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
Terminology
- Synonyms
- Polymorphic reticulosis
- Malignant midline reticulosis
- Lethal midline granuloma
- Angiocentric T cell lymphoma (Blood 1994;84:1361)
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Rare: 0.2% of all non-Hodgkin lymphomas and 1 - 2% of all NK / T cell lymphomas (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Oncol 2018;8:139, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71)
- More frequent in East Asia and Latin America and rare in U.S. and Europe (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Leukemia 2014;28:338, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
- Incidence is rising in U.S.
- 5 - 10% of all lymphomas in China
- Western countries: more common in Hispanic population (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514)
- M > F (~ 2:1) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Blood 2015;126:1424, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
- More common in fifth to seventh decade (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Blood 2015;126:1424, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
Sites
- Extranodal presentation
- Nasal presentation (65 - 85%) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71,Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Nasopharynx, paranasal sinuses and orbit, regardless of the dissemination to other sites
- Extranasal presentation (15 - 35%) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:211, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Ulcer, bleeding and perforation
- Skin
- Usually in fifth decade
- M < F (1:2)
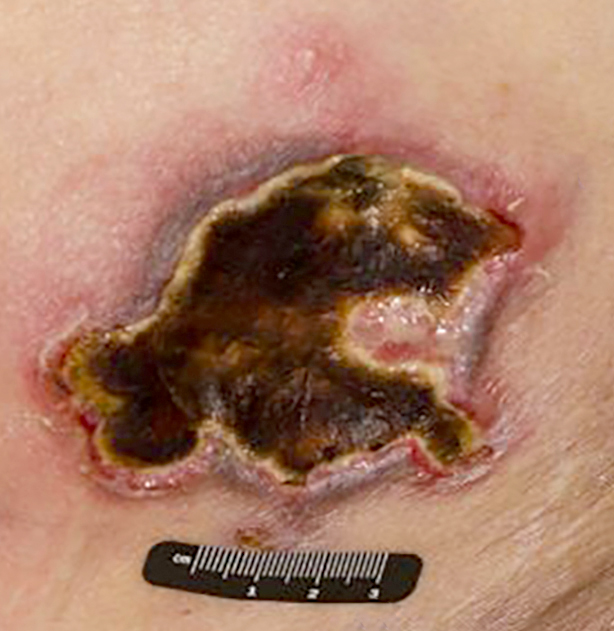
- Nodular and ulcerative violaceous nodules
- Usually multiple lesions
- Upper and lower extremities
- More frequent lymph node involvement
- Testis
- Lung
- Spleen
- Liver
- Gastrointestinal tract
- Nasal presentation (65 - 85%) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71,Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Uncommon nodal presentation or bone marrow involvement (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- Occurs in advanced stage and older patients
Pathophysiology
- EBV implicated in the lymphomagenesis: clonal episomal form present prior to clonal expansion (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
- NK cells infected by EBV secrete IL9 and IL10, which promote cell activation and proliferation
- Frequent 30 base pair deletion in LMP1 gene leads to a decrease in immune recognition and plays role in the lymphomagenesis
Etiology
- EBV is present in all cases (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Leukemia 2014;28:338, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- Diagnosis is questionable if EBV is not detected
- Latency type I (EBER positive) or II (LMP1 positive)
Clinical features
- Nasal / upper airways obstruction, purulent discharge, epistaxis and facial mass with surrounding edema (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624, Ann Oncol 2008;19:1477, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Duration: median of 5 months (1 - 36 months)
- Variable presentation of B symptoms (Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Blood 2015;126:1424)
- Pleural effusion and ascites (Hum Pathol 2015;46:981)
- Elevated serum lactate dehydrogenase (Hum Pathol 2015;46:981)
- Hemophagocytosis: 3% of cases (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
Diagnosis
- Diagnosis is commonly difficult, particularly when atypia is not readily apparent or when only limited viable cells are identified (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- Variable staging at clinical presentation (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Blood 2015;126:1424, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Ann Oncol 2008;19:1477, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- Primary cutaneous form: usually stage I / II
- After initial evaluation (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861)
- Standard hematological and serum biochemistry
- Positron emission tomography / computed tomography (PET / CT)
- Plasma EBV DNA quantification
- Bone marrow trephine biopsy
Radiology description
- Both CT and MRI are useful for evaluation of extension in nasal lesions (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861)
- No pathognomonic findings
- PET / CT is used to identify extranasal lesions (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861)
- F-18 fluorodeoxyglucose avid
- Standard uptake value is typically less than aggressive B cell lymphomas
Prognostic factors
- Poor (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Blood 2015;126:1424, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
- Estimated 5 year overall survival (OS): 40 - 60%
- Better prognosis if disease is treated early when confined to nasal region
- High risk of relapse up to 10 years from the diagnosis
- Involvement of extranasal sites is related to poor prognosis
- Risk stratification (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Cancer Sci 2009;100:2242, Blood 2009;113:3931)
- IPI (international prognostic index)
- KIPI (Korean IPI)
- FOXP3+ regulatory T cells expression of tumor infiltrating lymphocytes is related to early stage and predicts better prognosis (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Mod Pathol 2020;33:603)
- Immunosilenced microenvironment (low expression of FOXP3 / PDL1 and high expression of CD68) is related to aggressive behavior and advanced clinical stage (Mod Pathol 2020;33:603)
- Negative prognostic markers (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1)
- Age > 60
- Extranasal disease
- B symptoms
- Elevated beta 2 microglobulin
- Soluble IL2 > 600 U/ml
- C reactive protein > 1 mg/dl
- High levels of serum or plasma cell free EBV DNA by quantitative PCR
- Stage III / IV
Case reports
- 28 year old man with primary adrenal extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type (BMC Cancer 2017;17:15)
- 40 year old man with primary esophageal extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type of biphasic morphology (Medicine (Baltimore) 2015;94:e1151)
- 50 year old man with extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type, presenting with gastrosplenic fistula after chemotherapy (World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:6491)
- 53 year old man with primary pulmonary extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma (Thorac Cancer 2016;7:140)
- 55 year old man with extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type presenting with hemophagocytic syndrome (Am J Case Rep 2017;18:160)
Treatment
- Chemotherapy
- SMILE chemotherapy regimen (World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:6491, BMC Cancer 2017;17:15, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1)
- S (steroid), M (methotrexate), I (ifosfamide), L (L-asparaginase) and E (etoposide)
- Frontline therapy in fit patients
- Improved response rates in relapsed or advanced stage disease
- CHOP (BMC Cancer 2017;17:15)
- C (cyclophosphamide), H (hydrxydaunorubicin), O (vincristin), P (prednisone)
- ESHAP (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514)
- Etoposide, methylprednisolone, cytarabine and cisplatin
- DeVIC (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861)
- D (dexamethasone), E (etoposide), VI (ifosfamide) and C (carboplatin)
- Overall response rate (ORR) of 81% and complete remission (CR) in 77% of the stage I / II patients when associated with concurrent radiation therapy
- SMILE chemotherapy regimen (World J Gastroenterol 2017;23:6491, BMC Cancer 2017;17:15, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1)
- Radiation therapy (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Blood 2015;126:1424)
- 45 to 60 Gy
- L-asparaginase based chemotherapy followed by involved field radiation therapy (IFRT)
- ORR of 92 - 93% and complete remission (CR) in 42 - 69% of stage I / II patients, according the chemotherapy regimen
- Autologous and allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HSCT) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861)
- Associated with better complete response rates
- No consensus about the indication
- Novel agents: clinical trials level (Front Oncol 2018;8:139)
- Anti-CD30 (brentuximab vedotin) associated with L-asparaginase
- CD3 chimeric antigen receptor T cells (CAR-T)
- Anti-CD38 (daratumumab)
- Anti-PD-1 therapy (pembrolizumab)
- Anti-LMP1 / LMP2 therapy
- Surgery (BMC Cancer 2017;17:15)
- Localized cases
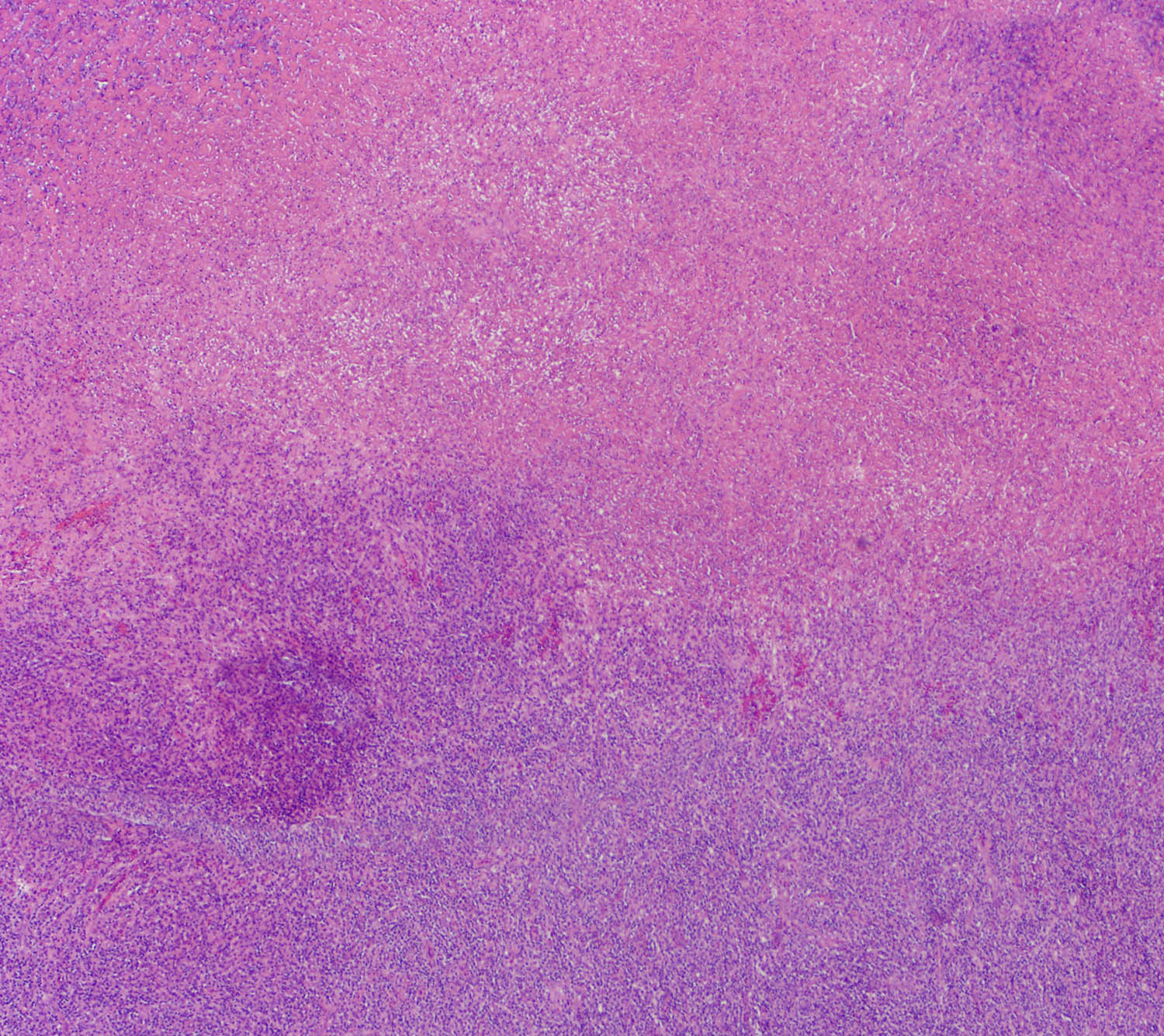
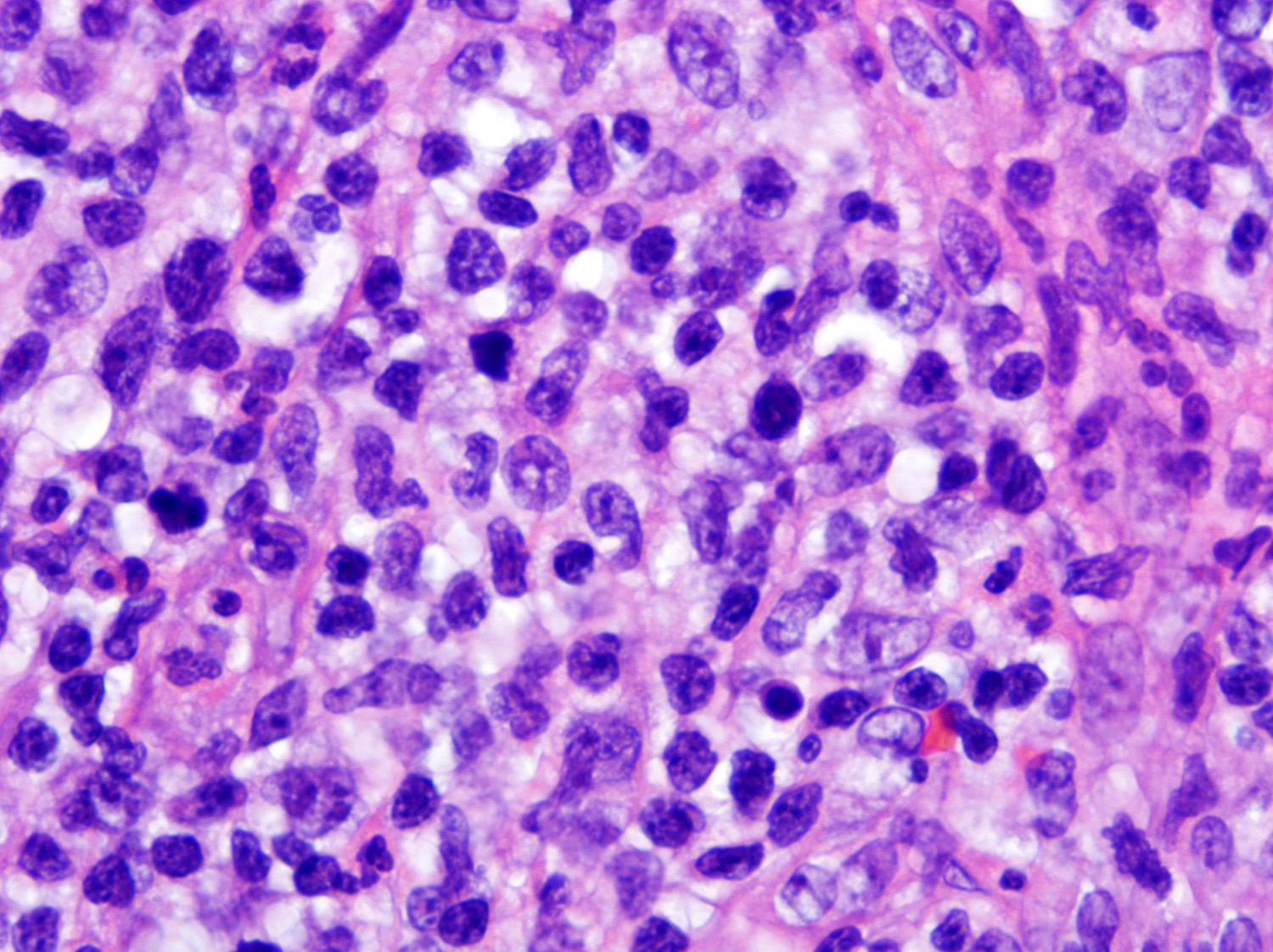
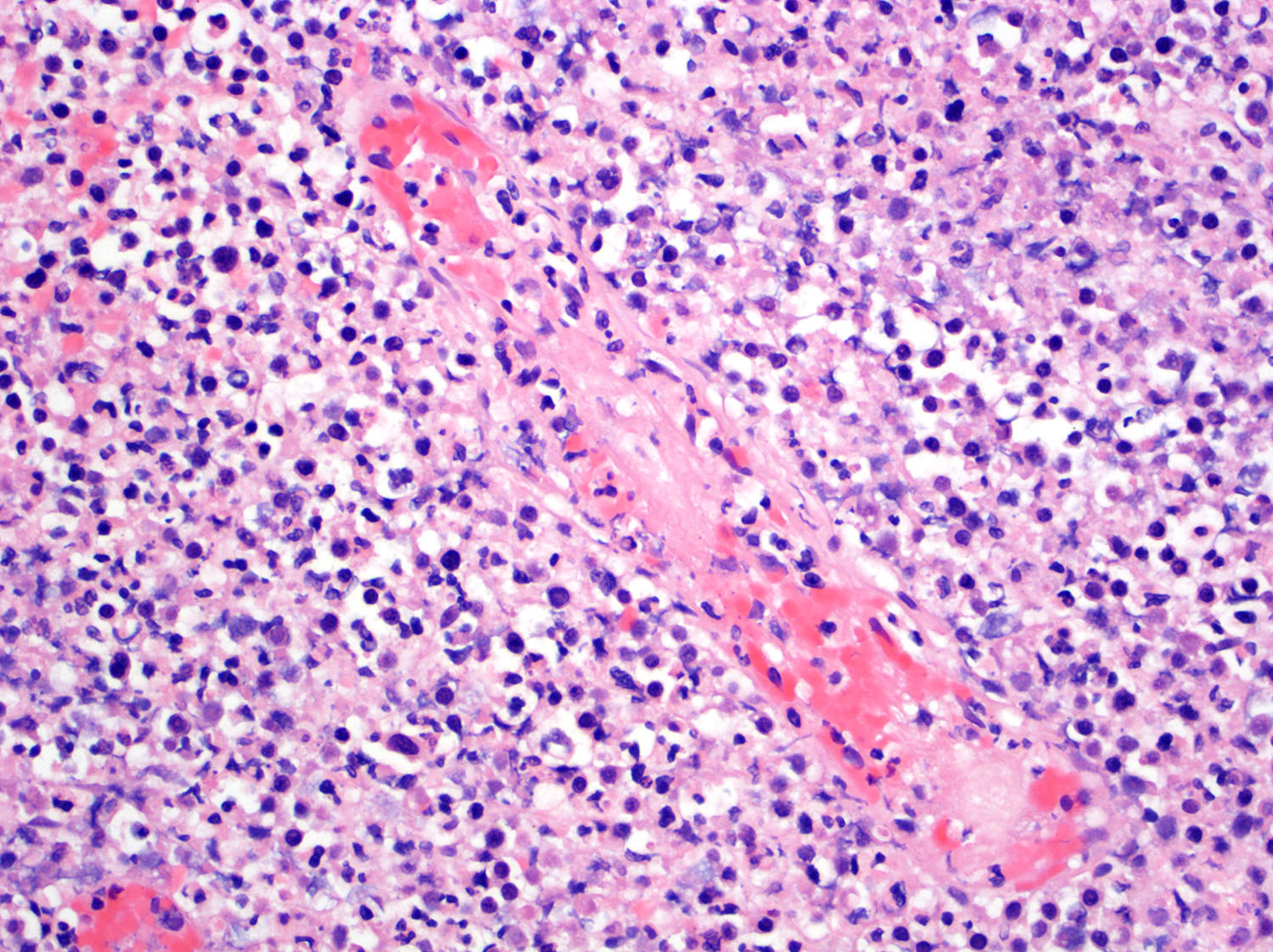
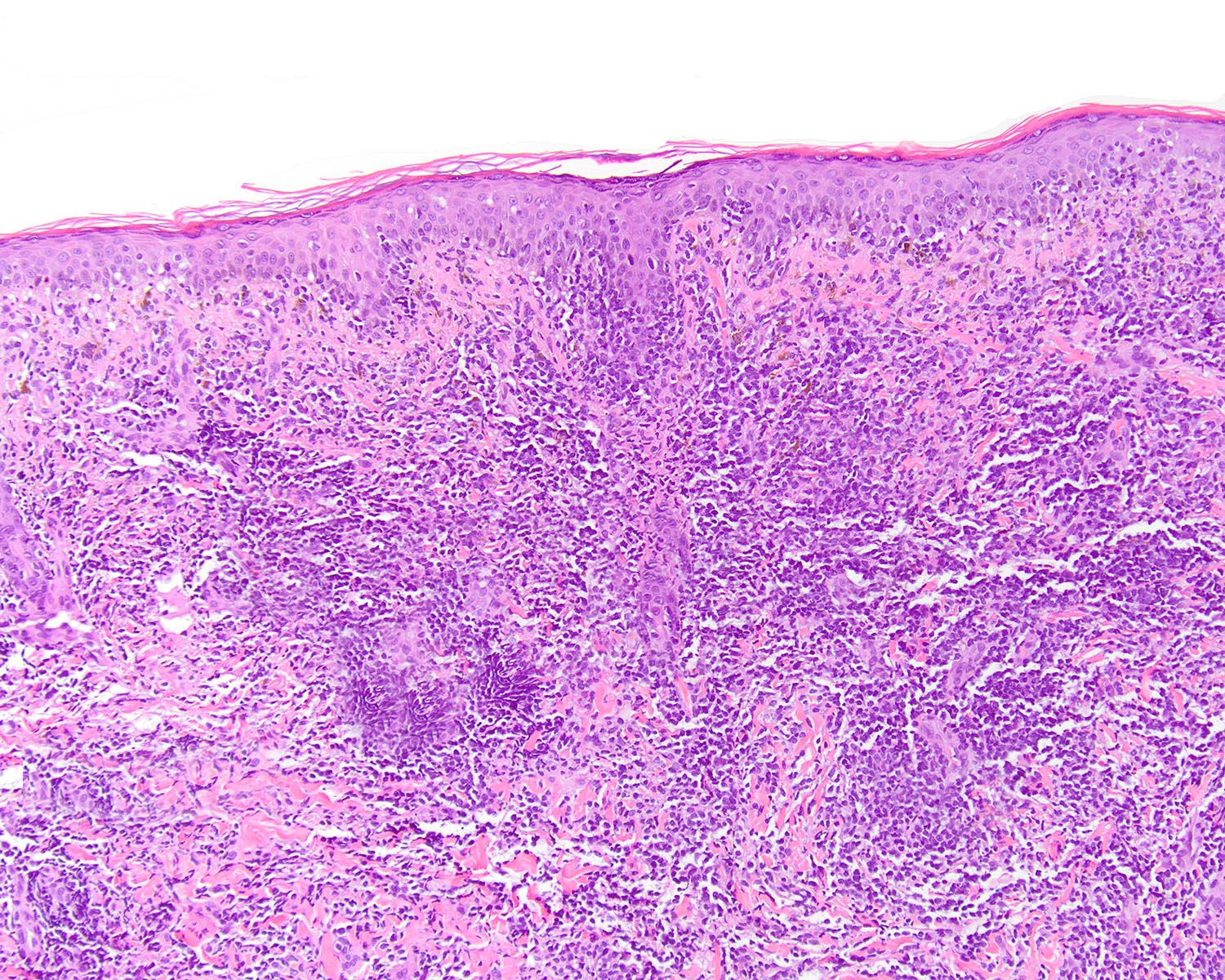
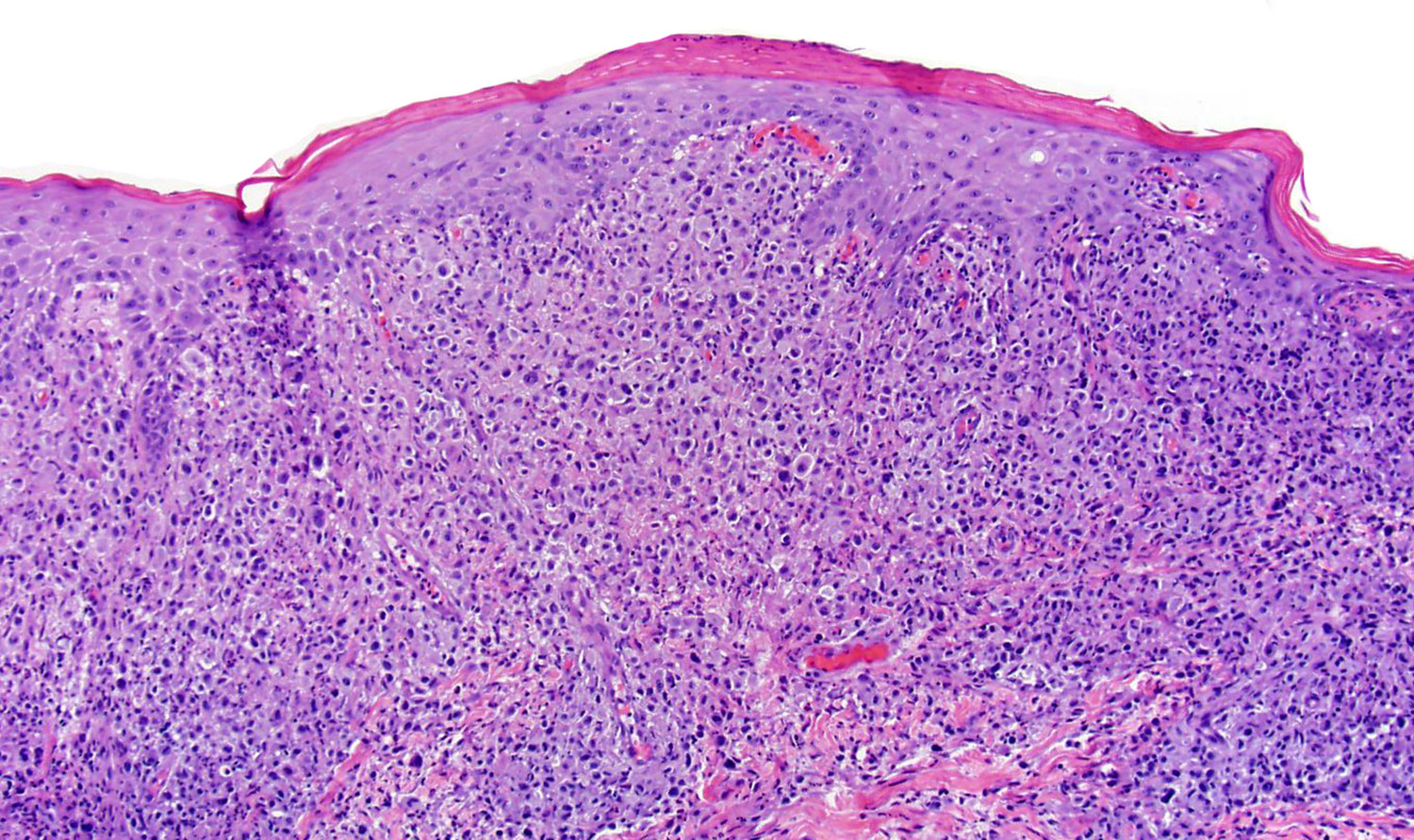
Microscopic (histologic) description
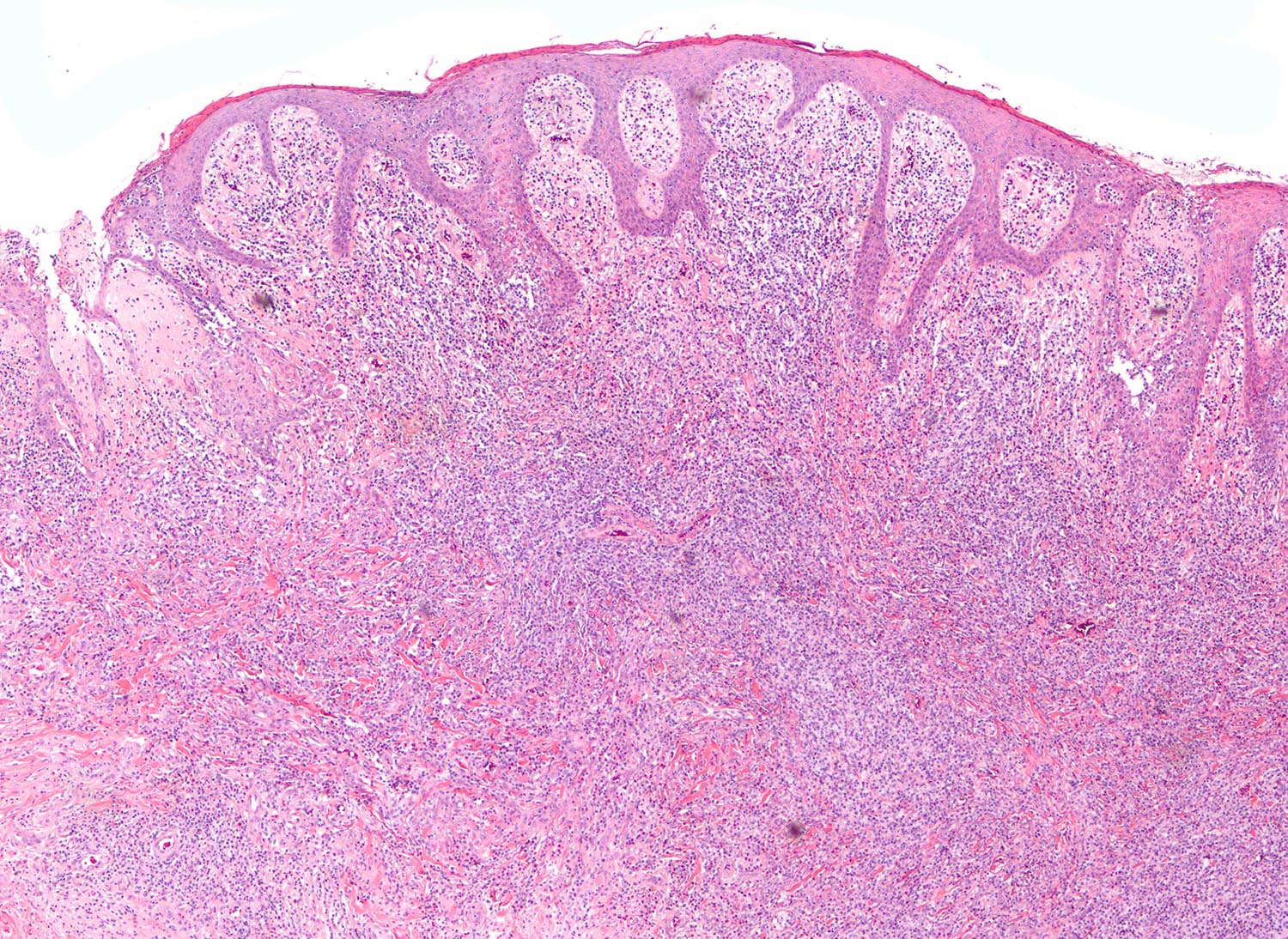
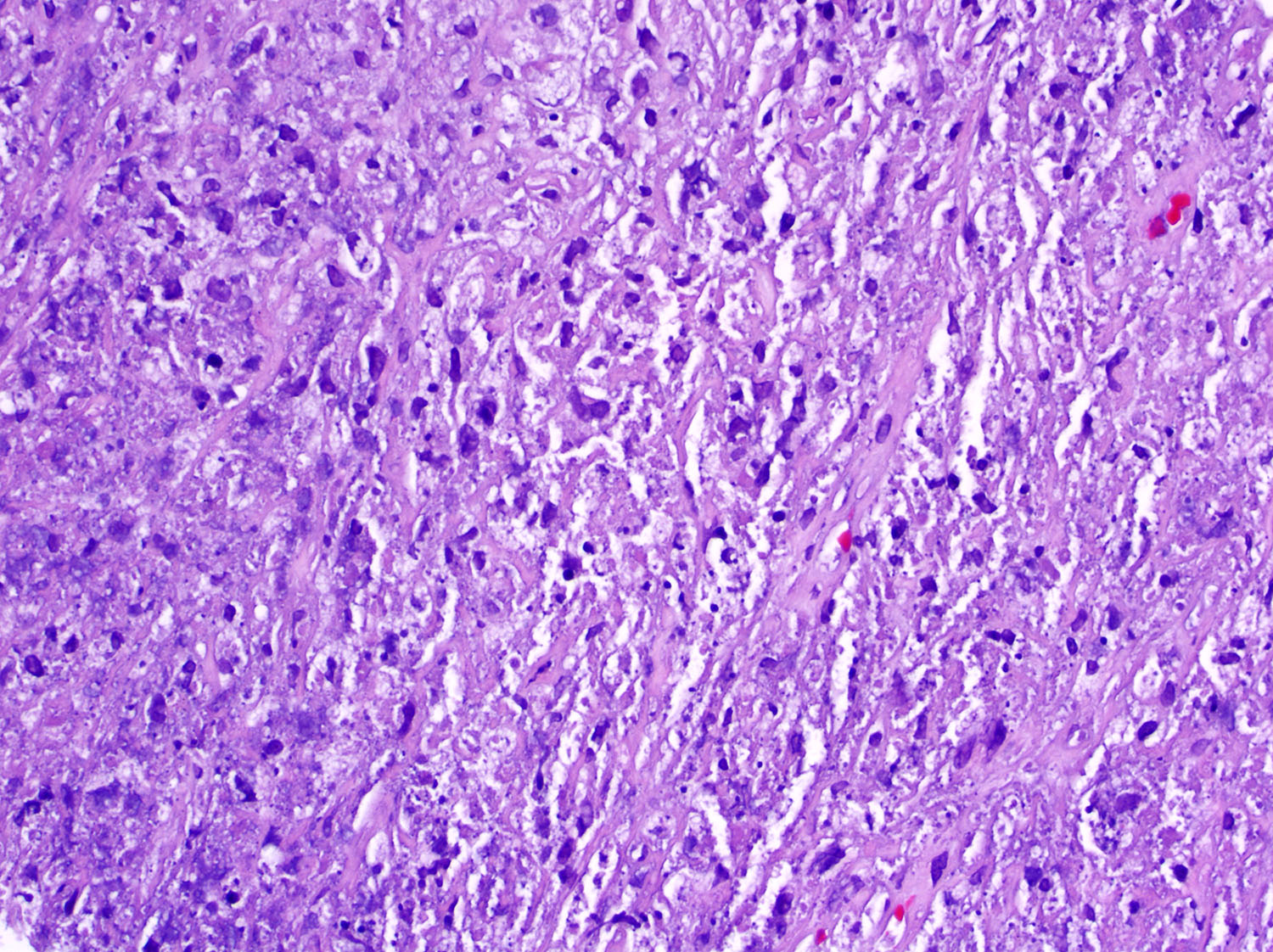
- Ulceration of mucosa with diffuse infiltration of lymphoid cells with broad cytological spectrum, ranging from small to large cells (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
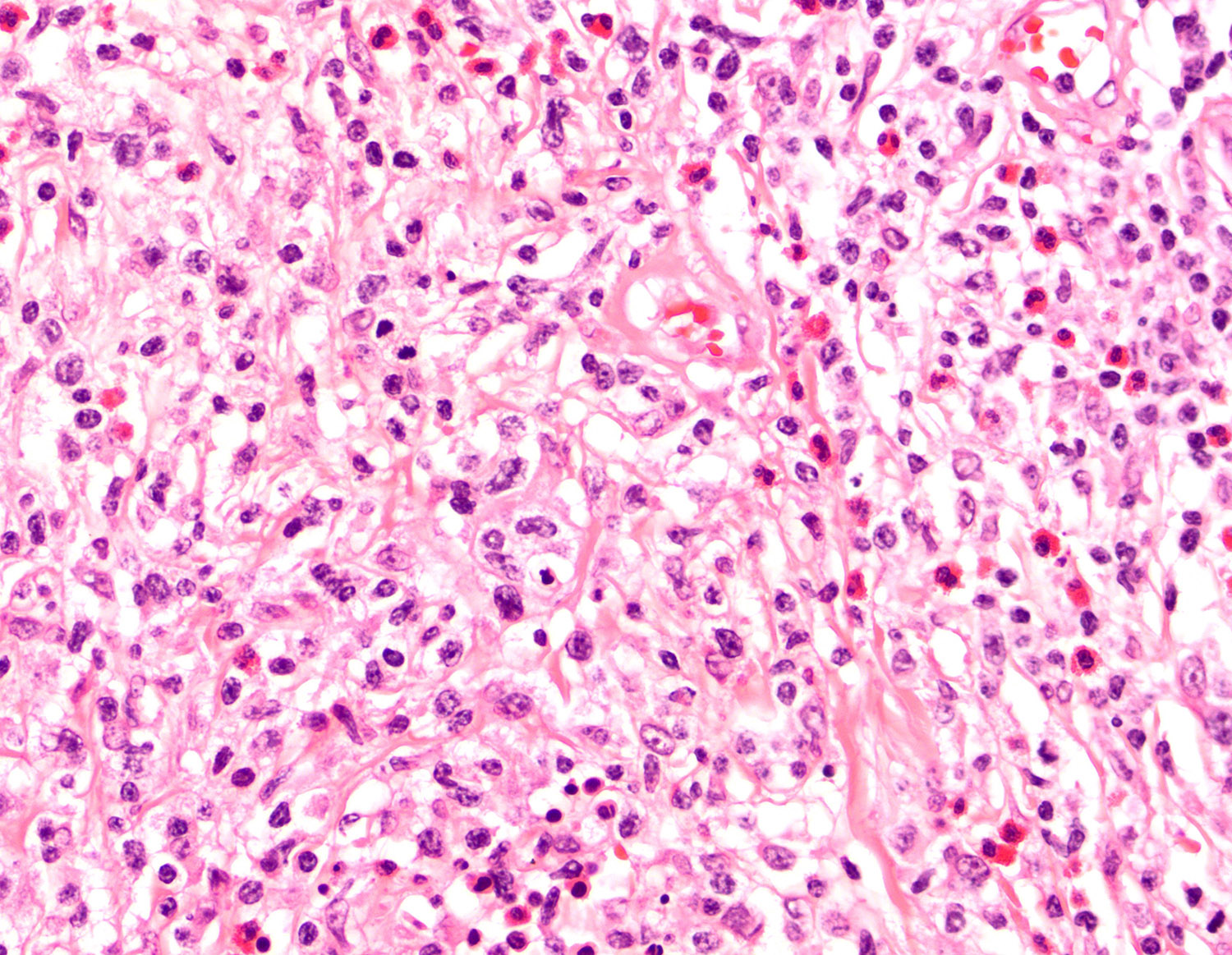
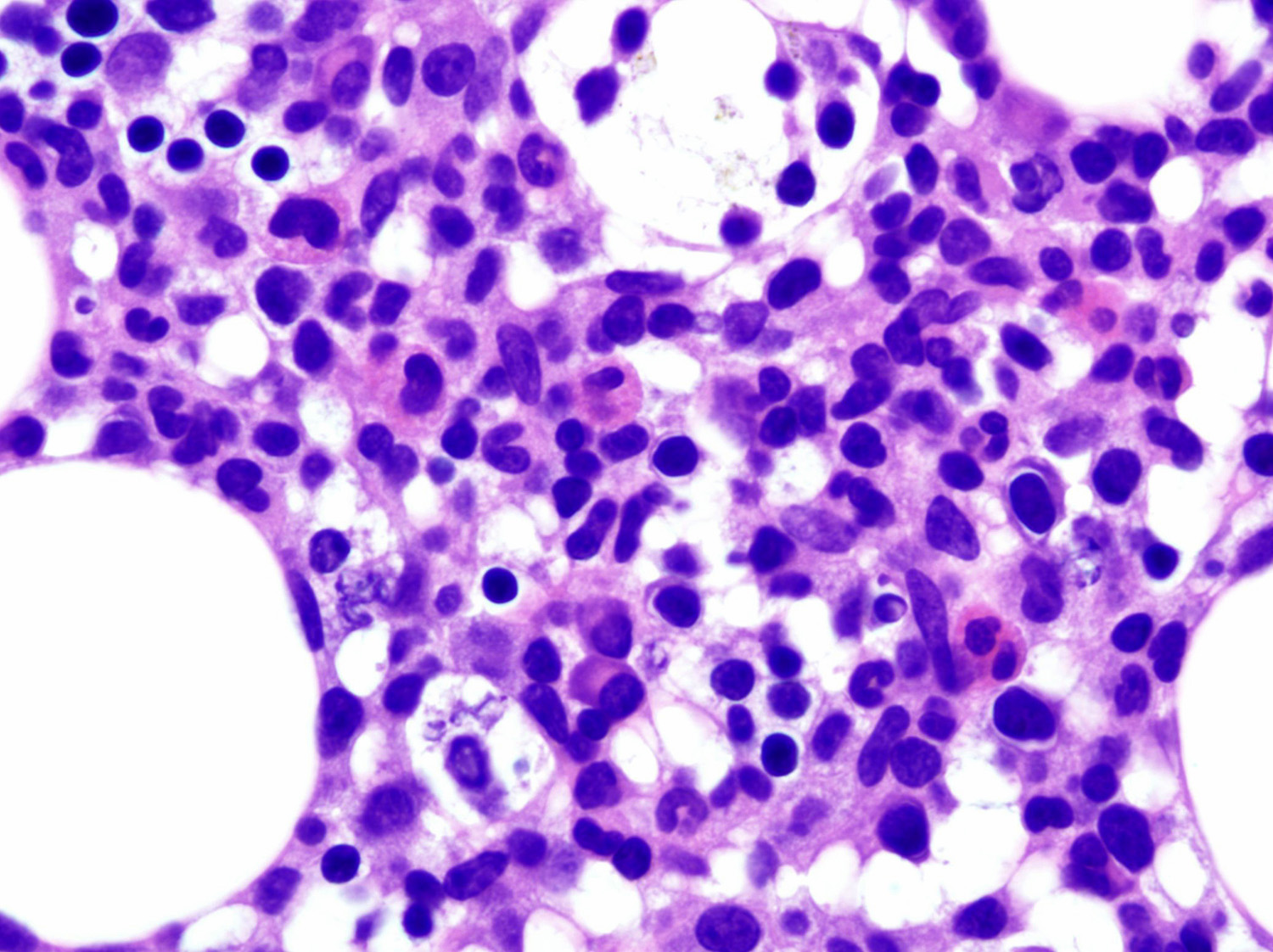
- Most cases: monotonous population
- Folded nuclei and indistinct nucleoli
- Moderate amount of cytoplasm
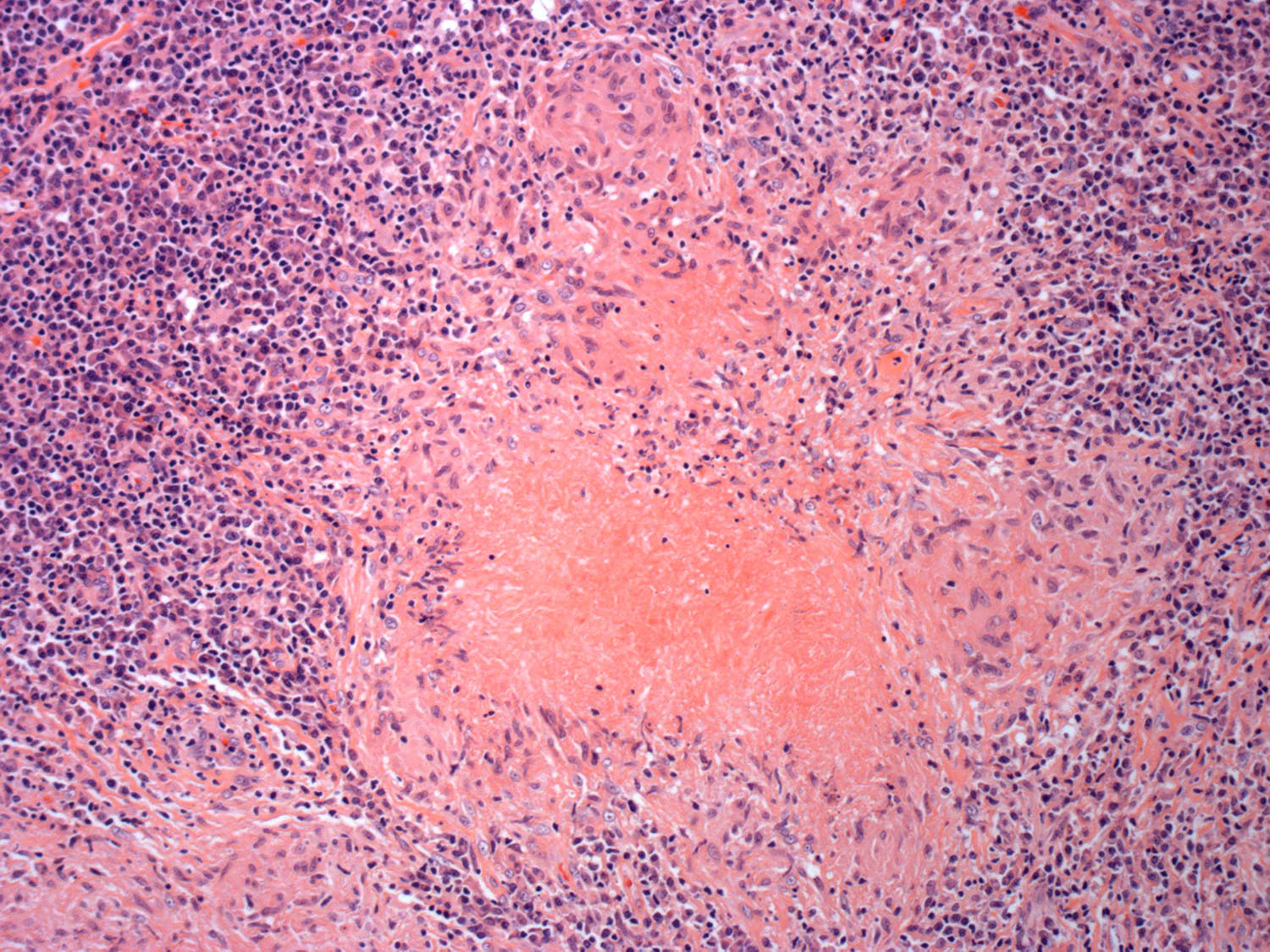
- Angiocentric and angiodestructive (Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- May not be apparent in small biopsies
- Coagulative necrosis (Oncol Lett 2016;12:825, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- Frequent mitoses (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
- Pseudoepitheliomatous hyperplasia in adjacent epithelium (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
- Nodal infiltration: paracortex or medulla (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
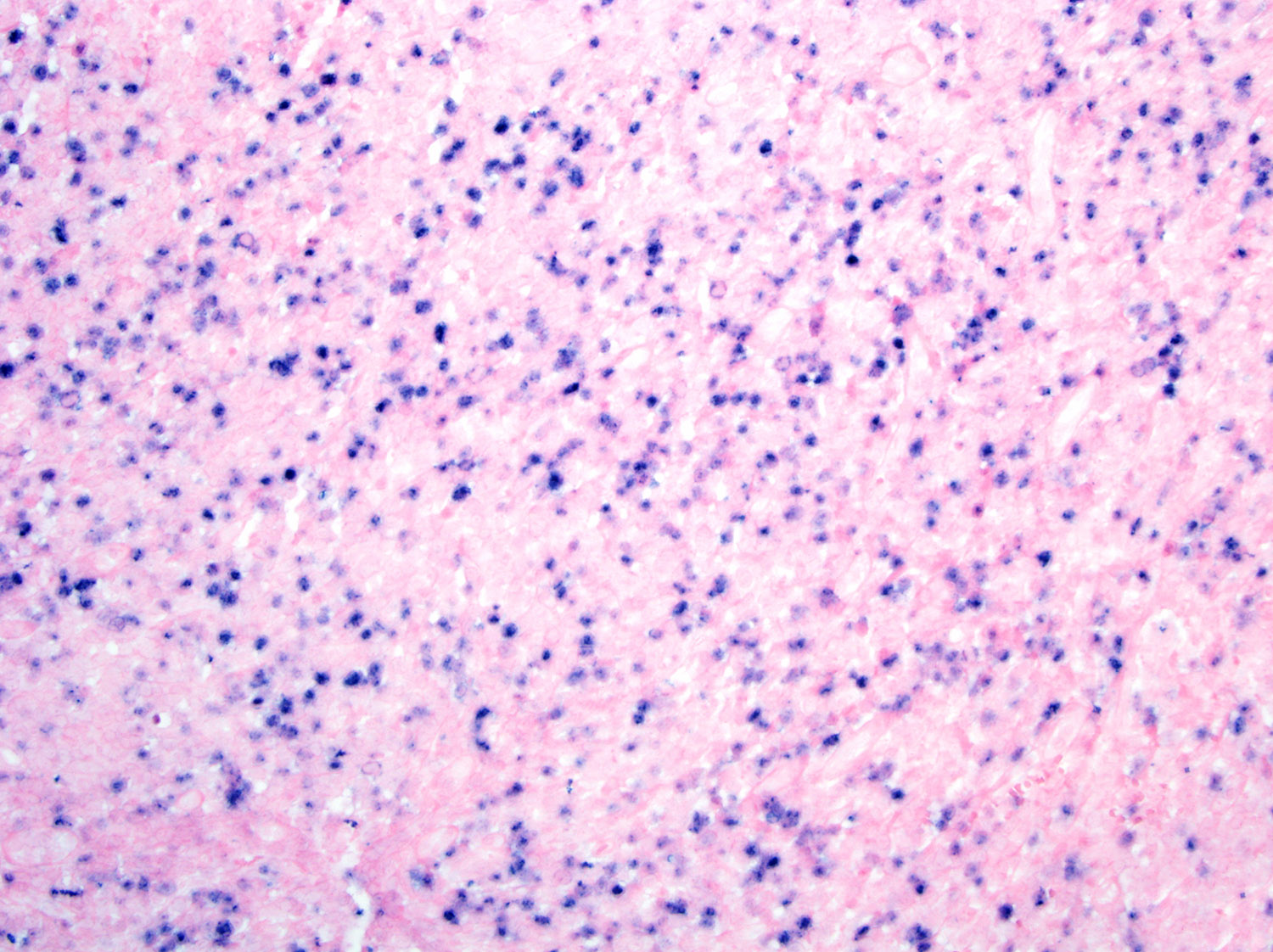
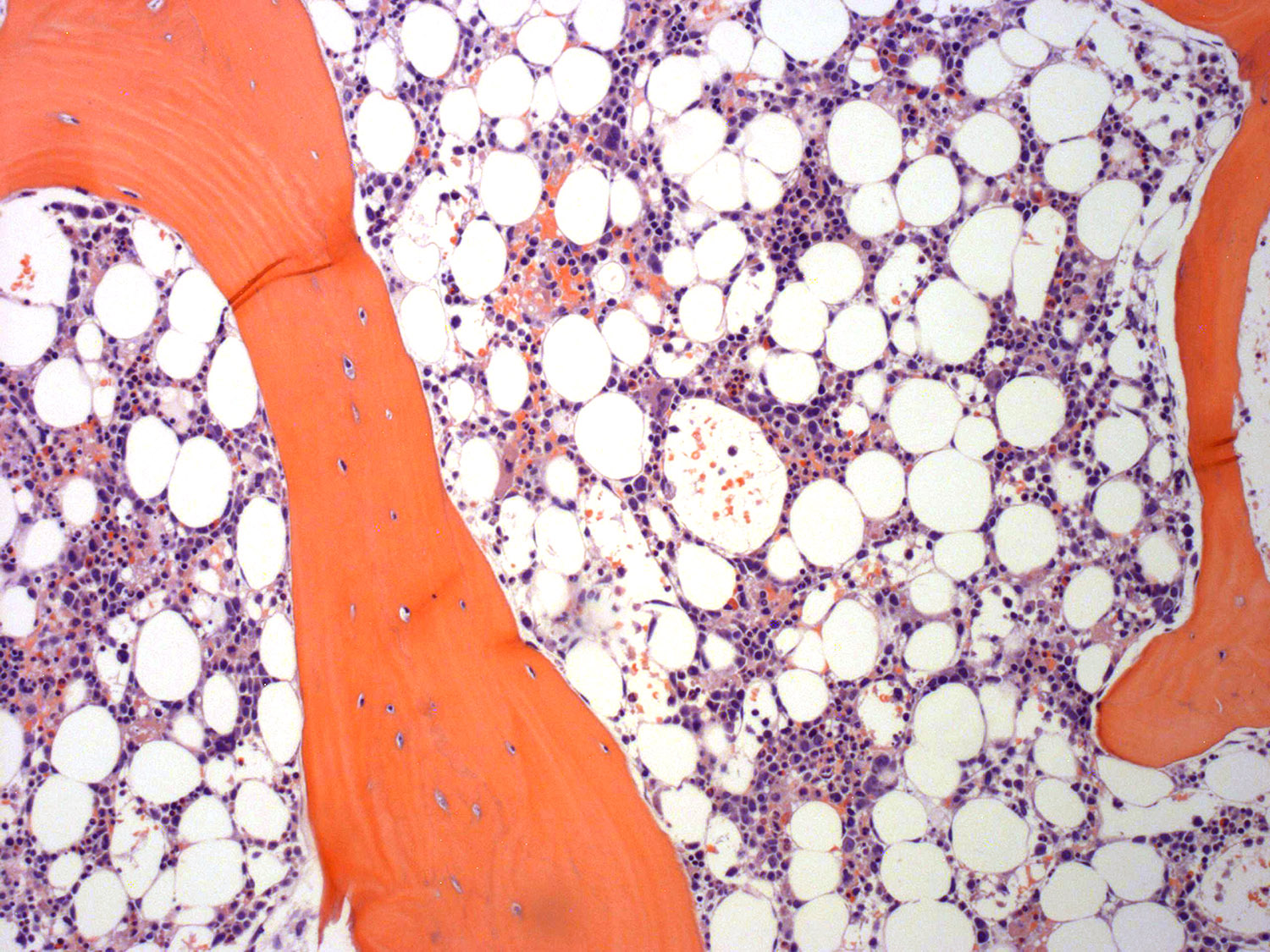
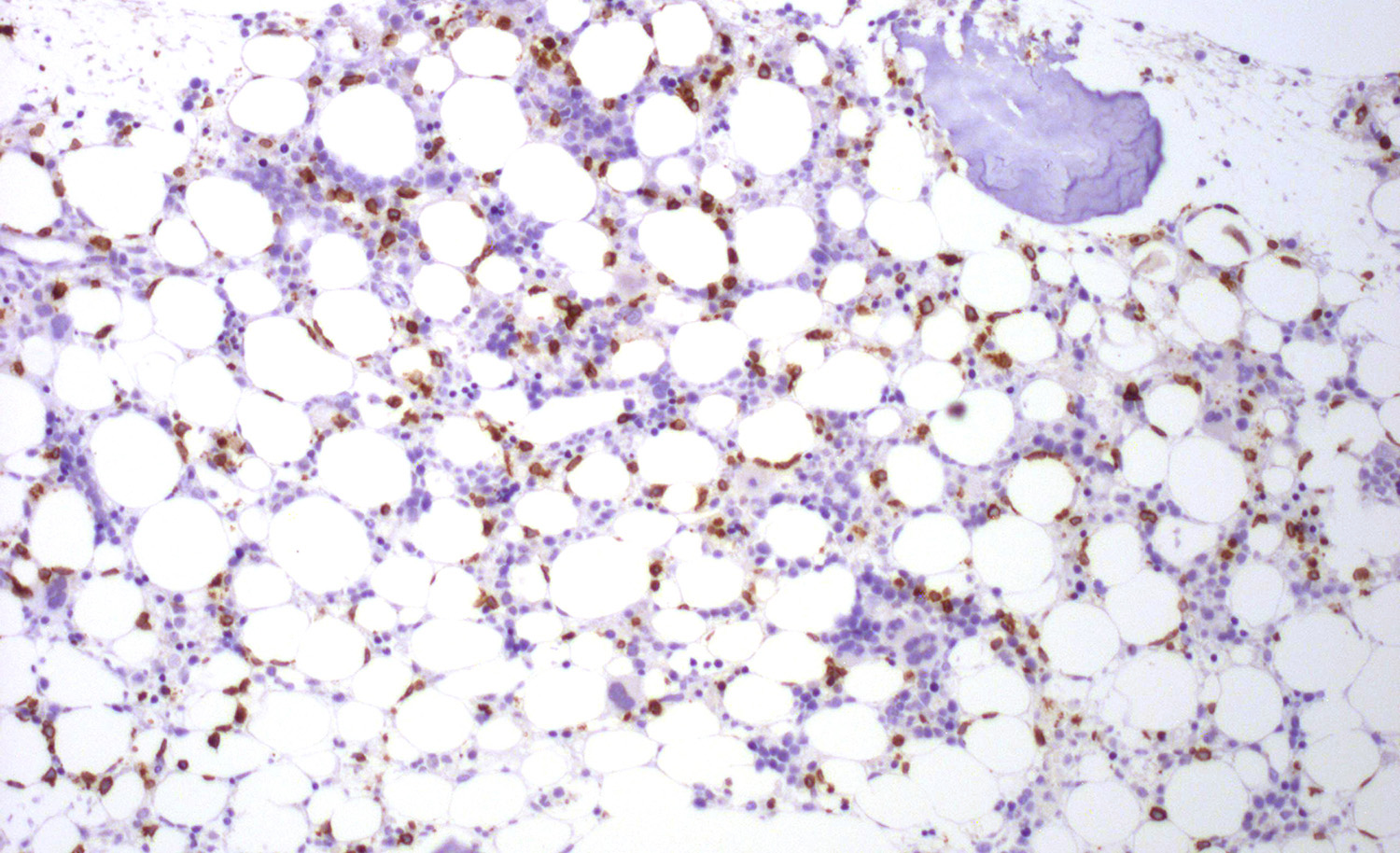
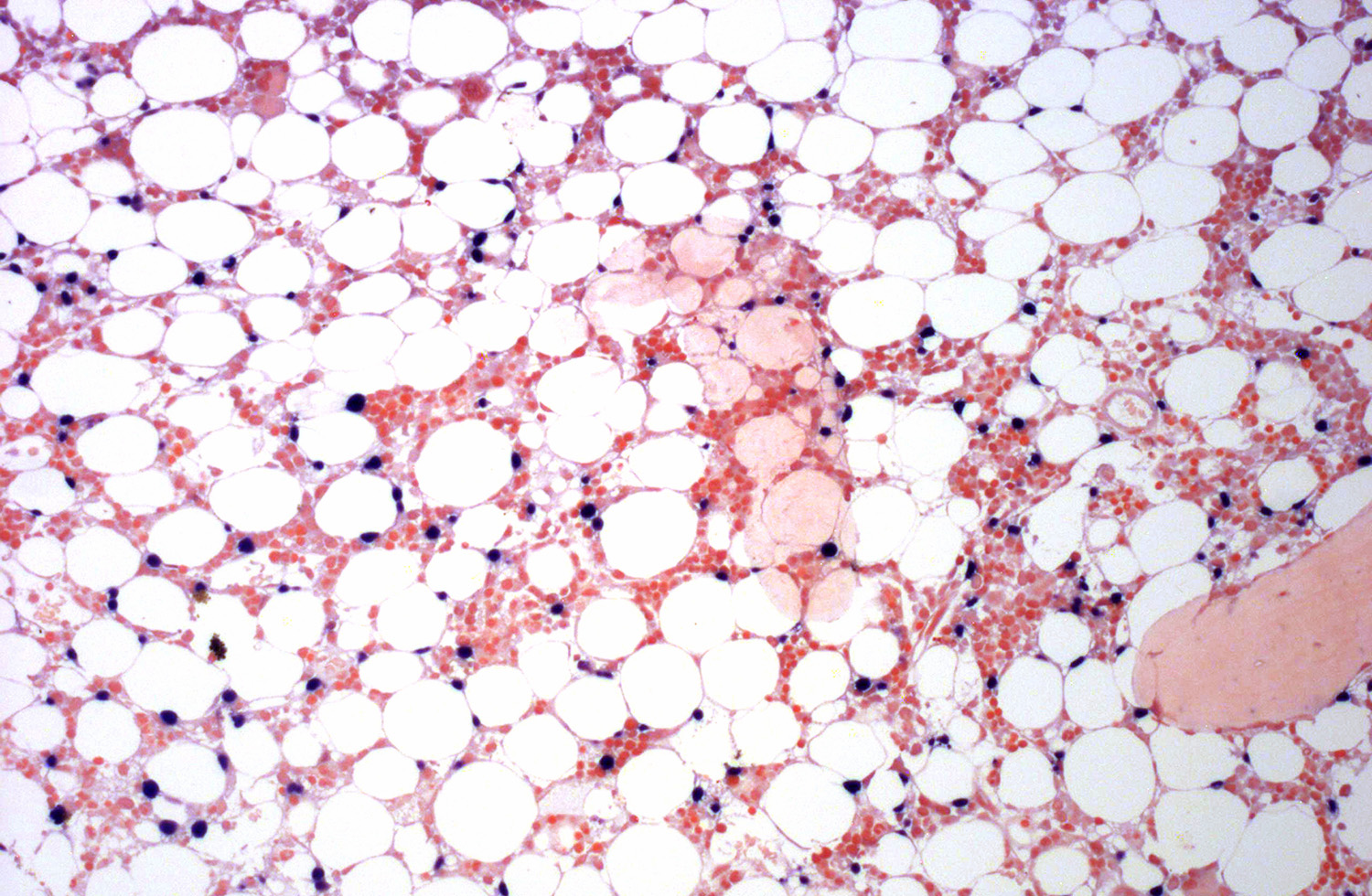
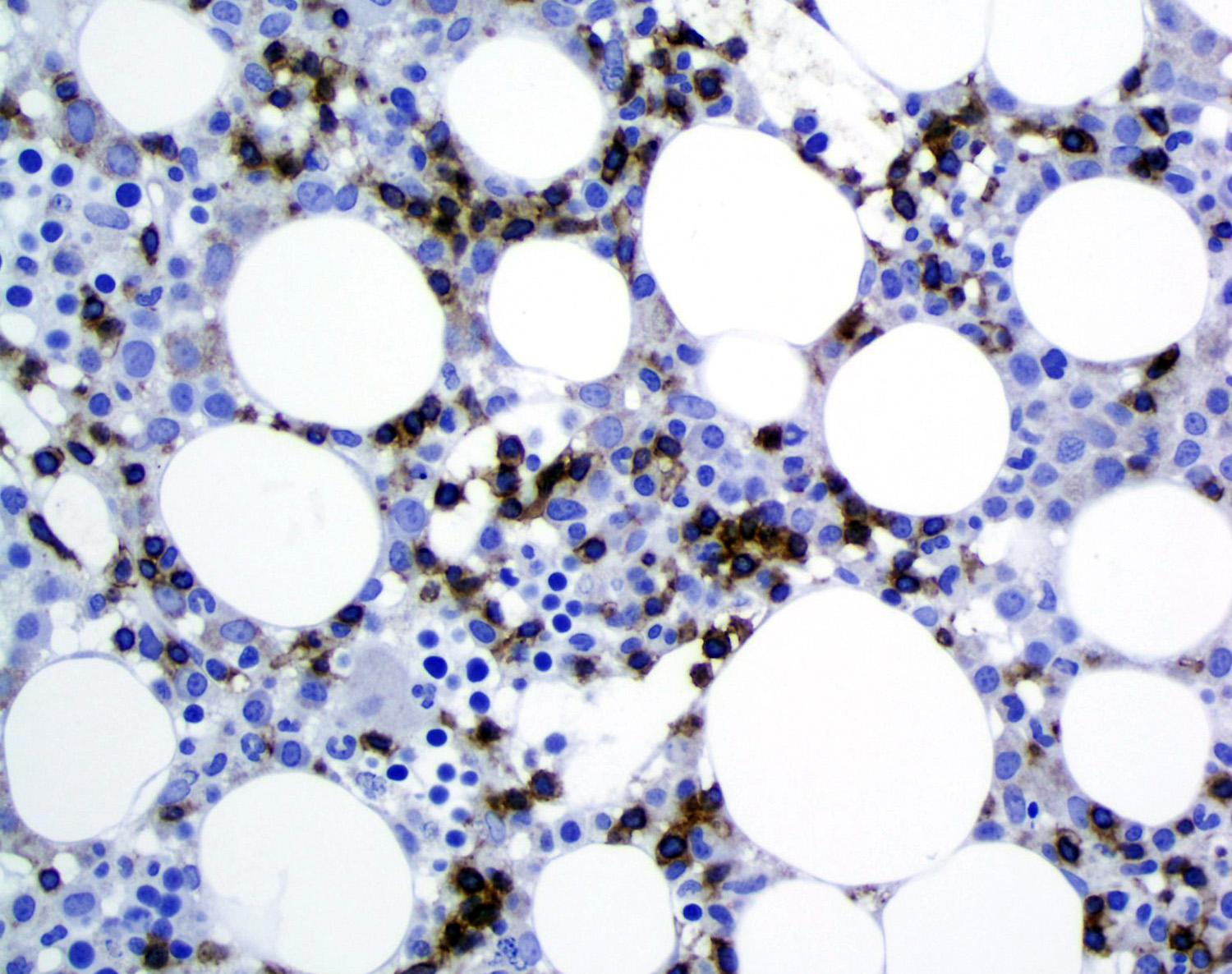
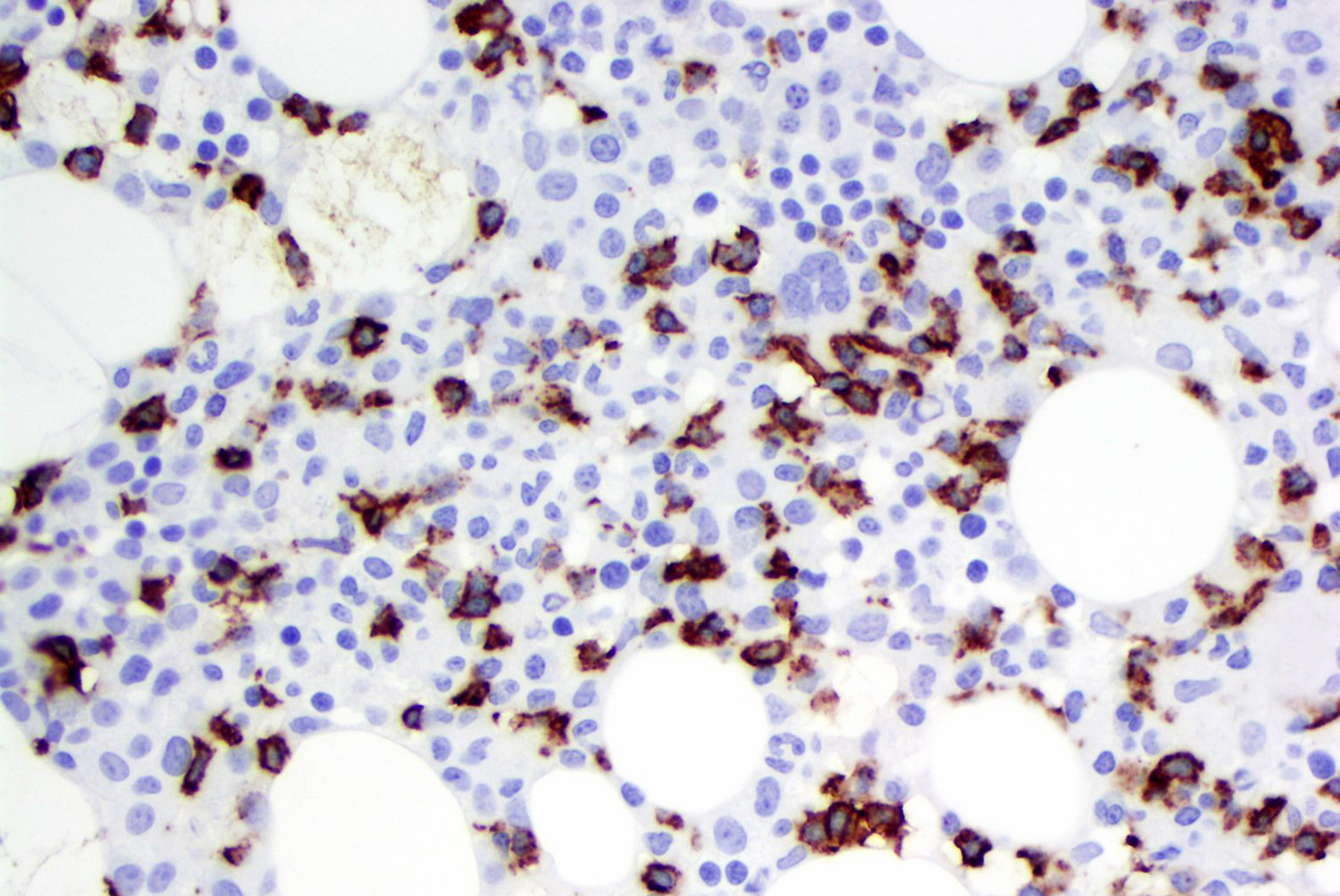
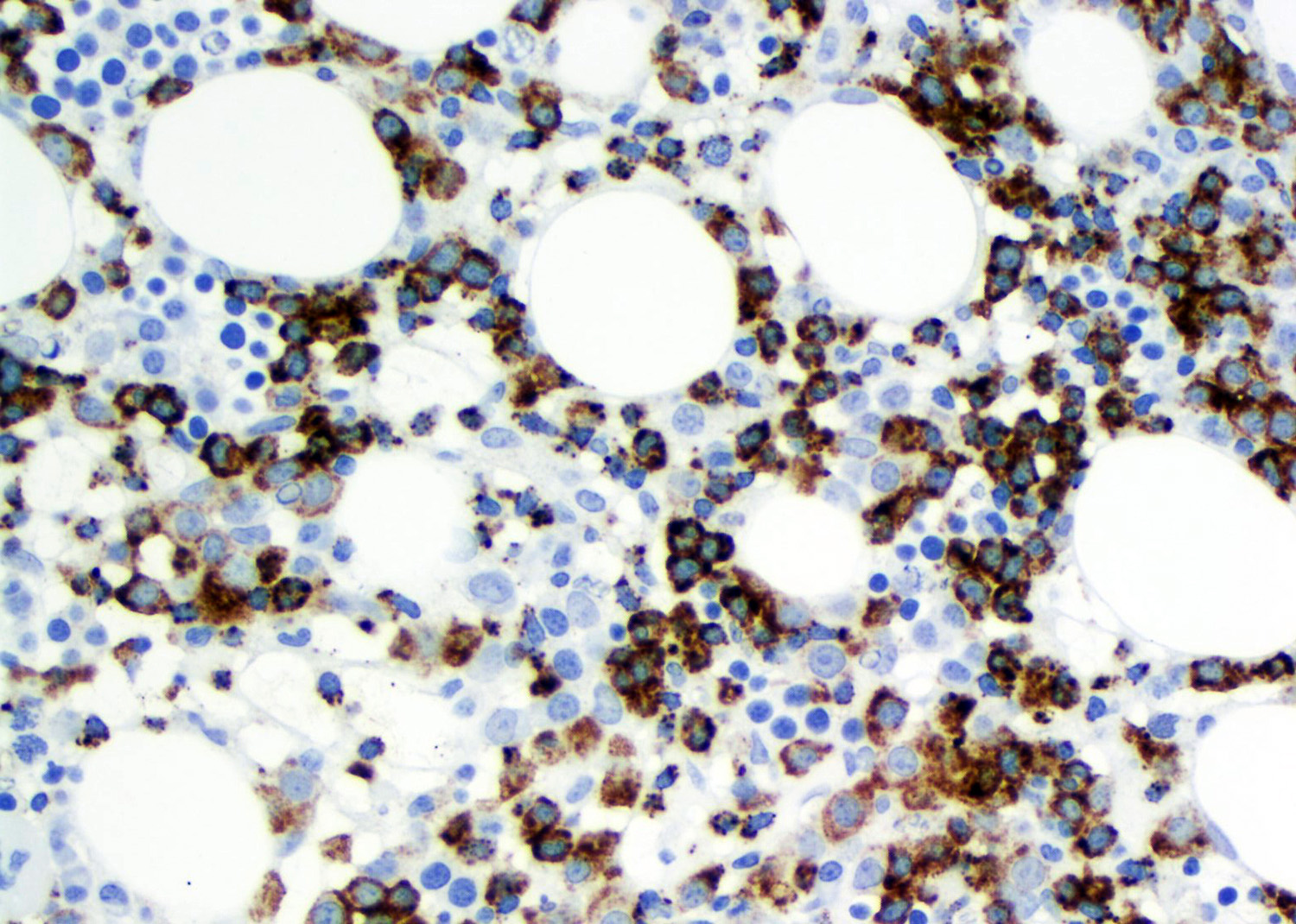
- Bone marrow: subtle interstitial infiltration; EBER can be very helpful for identifying lymphoma cells (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
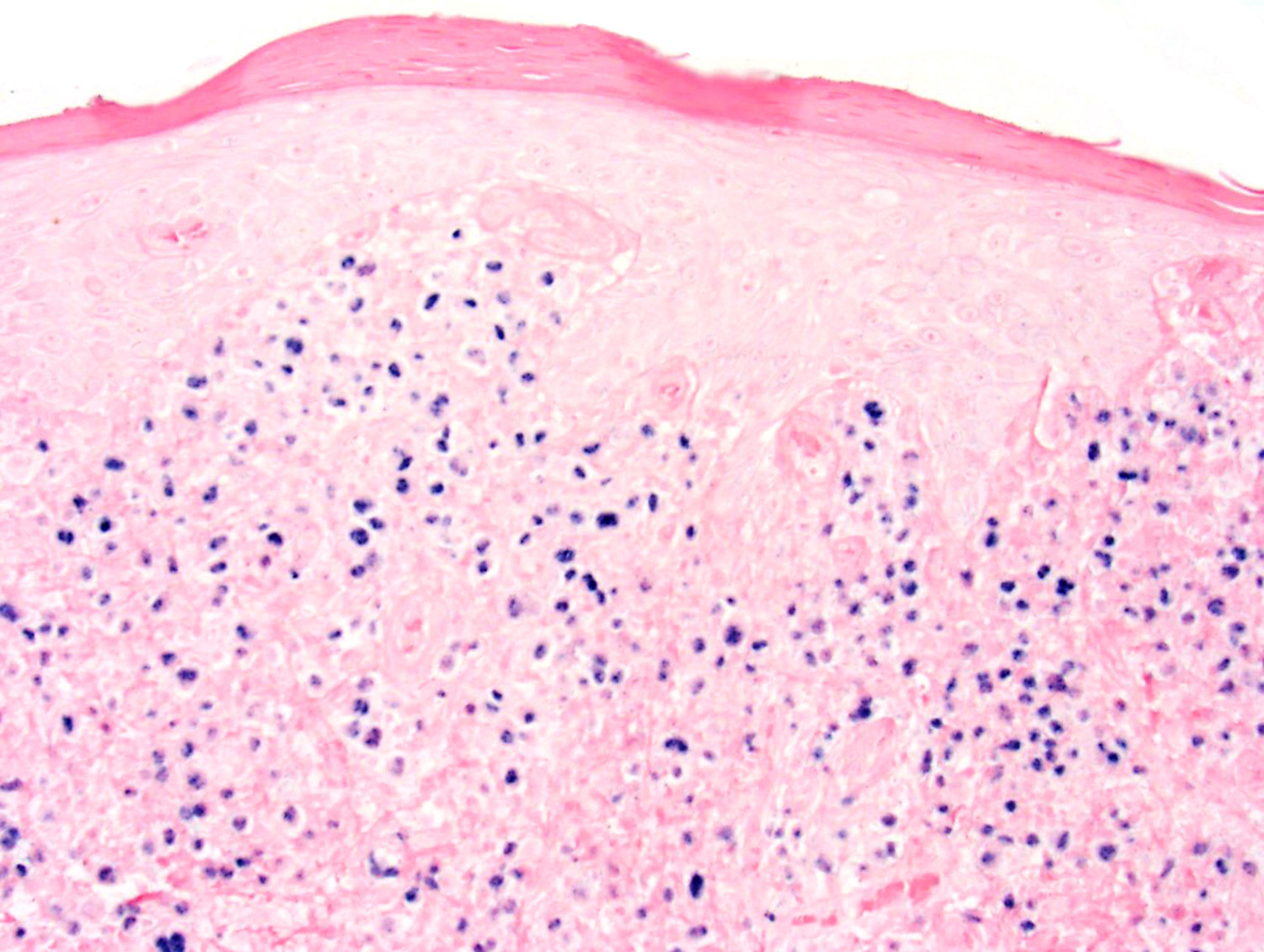
- Skin (Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:211, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1)
- Can be epidermotropic
- Dense and atypical lymphoid infiltrate in dermis and subcutis
- Frequent mitoses, necrosis and angioinvasion
- Association with microthrombi
- Involvement of hair follicles and sweat glands
- Variable amount of reactive inflammatory cells: eosinophils and histiocytes (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
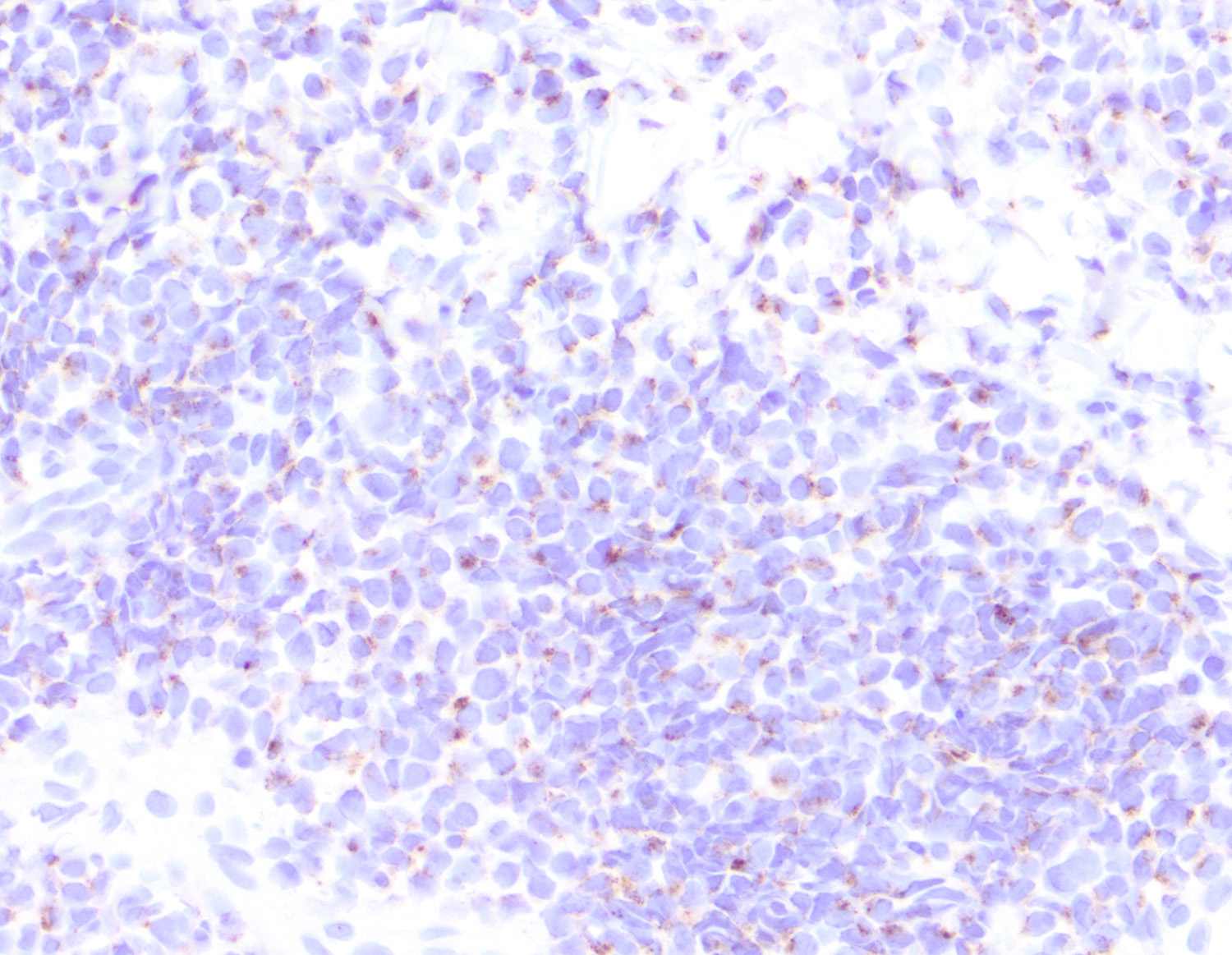
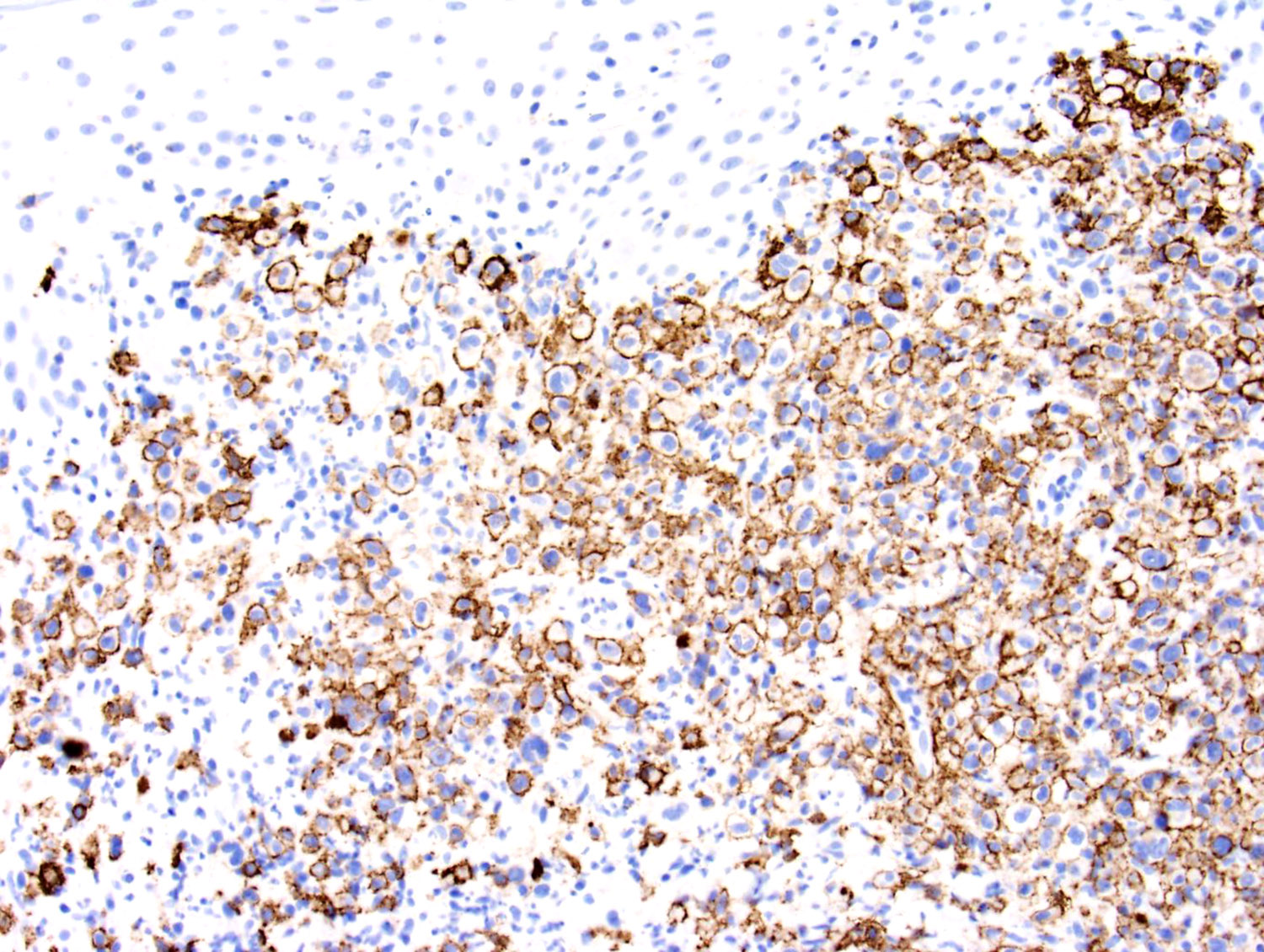
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roberto N. Miranda, M.D. and Carlos A. Torres-Cabala, M.D.
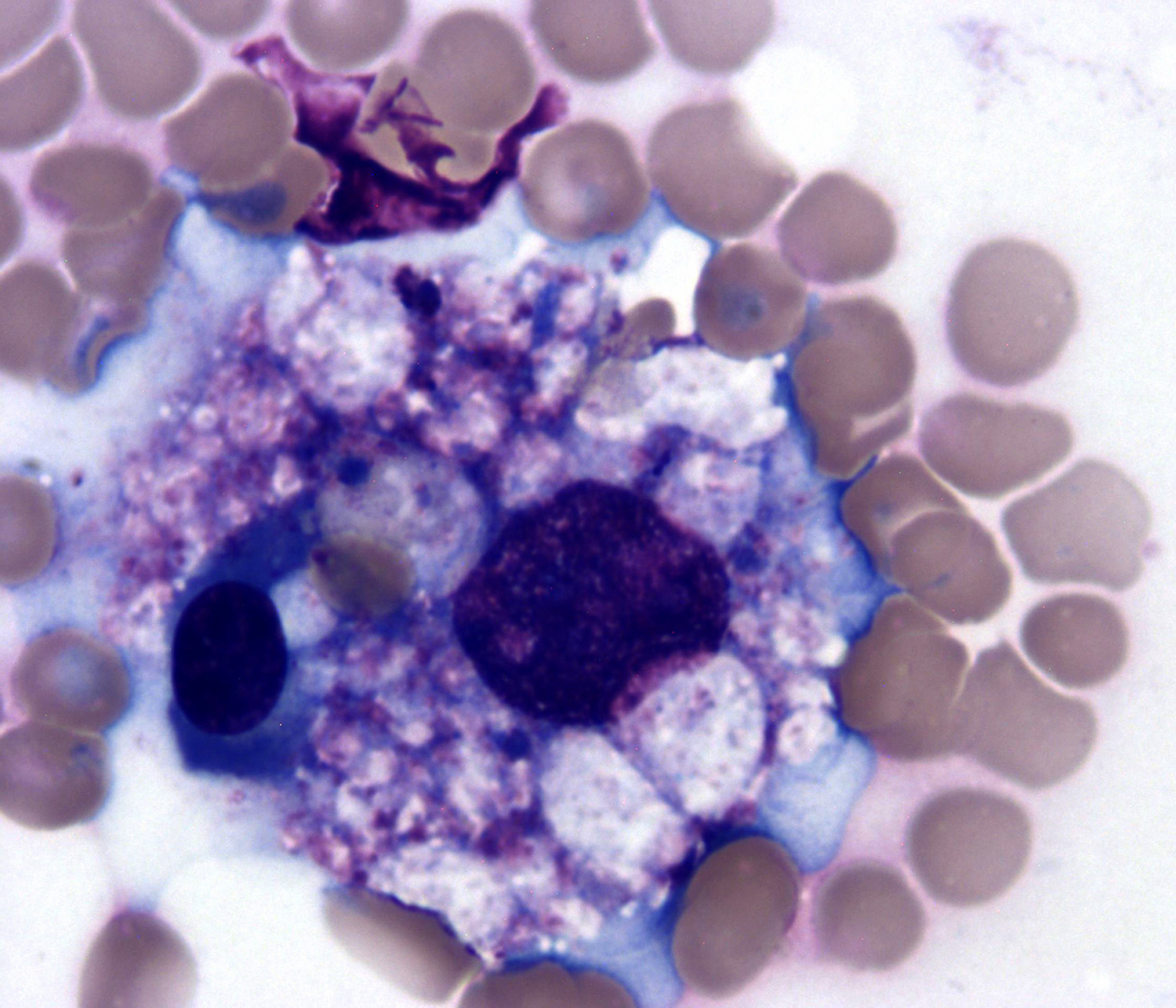
Cytology description
- Uncommonly assessed by fine needle aspiration
- Cells range from small to large with irregular nuclear contours and variable chromatin (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
- Cytoplasm is scant to moderately abundant (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- Cytoplasmic granules may be demonstrated with Wright-Giemsa stain (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
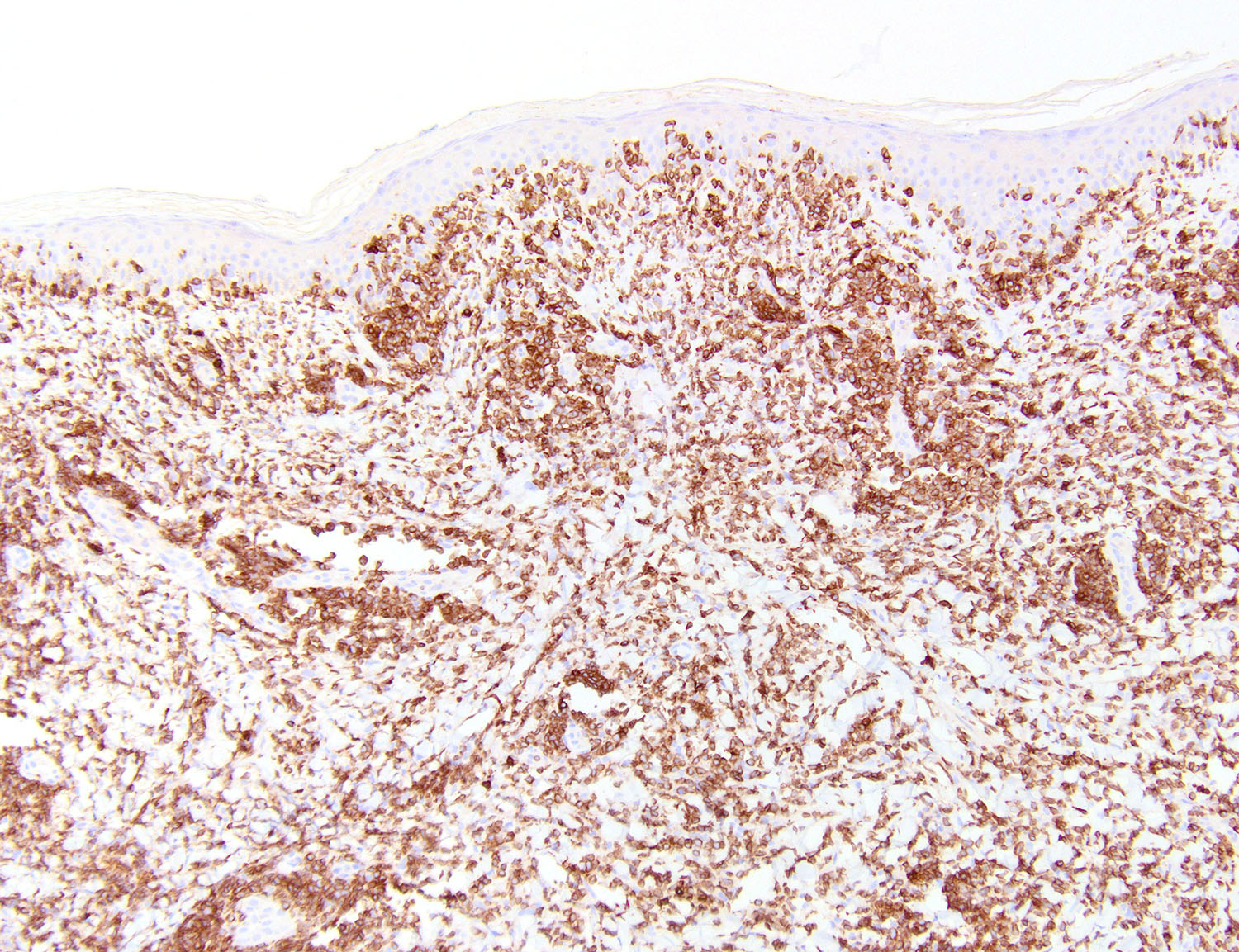
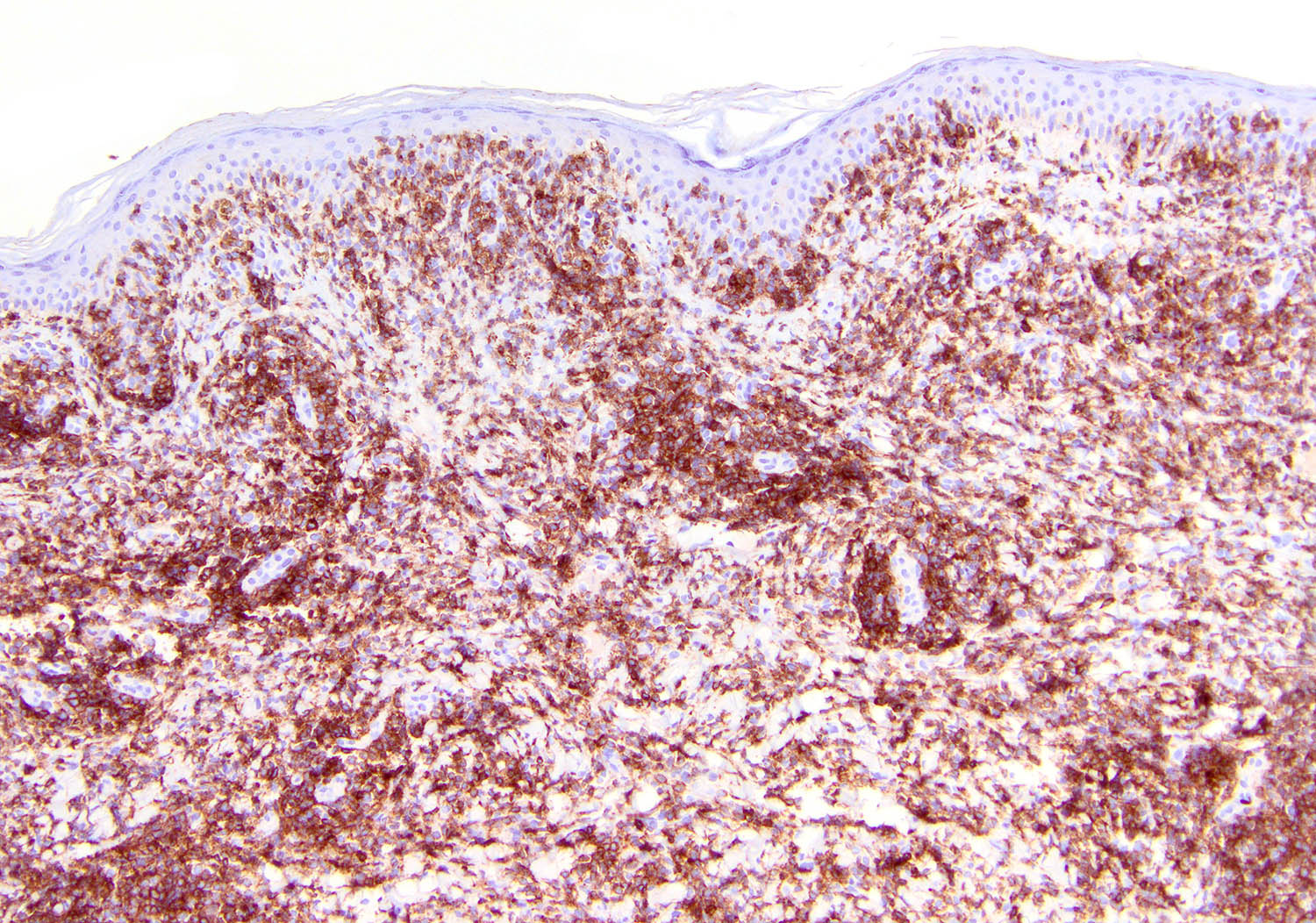
Positive stains
- NK cell lineage in ~ 70% of cases (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- T cell lineage in ~ 30% of cases (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- EBER (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- Present in 100% of cases
- CD25, CD95 (Fas), CD178 (FasL) and HLA-DR (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71)
- CD30: 20 - 70% of cases (Front Oncol 2018;8:139, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- CD38 (Front Oncol 2018;8:139)
- CD43 (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- CD29 (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- CD54 (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- CXCR3 (CD183) (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- Variable PD-1: 40 - 100% (Front Oncol 2018;8:139, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
- T-bet (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
- ETAS-1 (Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14)
- CD45RO (Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
- High Ki67: ≥ 60% (Hum Pathol 2015;46:981, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
Negative stains
- sCD3 negative in NK cells (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- CD4, CD5 (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1, Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- Negative in cases of NK cell lineage
- May be expressed in cases of T cell lineage
- Cases of T cell lineage: CD56 (variable) (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861)
- BCL2 (Am J Clin Pathol 2008;130:343)
- CXCL13 (Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- TCRαβ and TCRγδ (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Hum Pathol 2015;46:981)
- Can be positive in cases of T cell lineage
- Consistently negative in cases of NK cell lineage
- B cell antigens (CD19, CD20, PAX5) (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195, Head Neck Pathol 2019;13:624)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- JAK / STAT activation (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Nat Commun 2015;6:6025, Leukemia 2014;28:338, Oncol Rep 2019;41:3219, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, J Hematol Oncol 2019;12:33)
- JAK3 mutation in 33% of cases
- JAK3 inhibition leads to decrease the invasiveness in cell lines
- Therapeutic potential
- Plays important role in lymphomagenesis
- STAT3 and STAT5B mutations
- STAT3 mutations in exon 20 and 21 in 33% of patients
- JAK3 / STAT3 may stratify clinicopathologic features
- JAK3 mutation in 33% of cases
- Mutations of DDX3X in 20% of cases (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71)
- Loss of cell cycle suppression and activation of NFκB and MAPK pathways
- TP53 mutation in ~ 10% of cases (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, J Hematol Oncol 2019;12:33)
- Other commonly mutated genes: KMT2A, FOXO3, PTPRK, ASXL1, ARID1A and EP300 (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Leukemia 2014;28:338, Oncol Rep 2019;41:3219, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, J Hematol Oncol 2019;12:33)
- Upregulation of miR-155 and miR-21 (Nat Commun 2015;6:6025, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57)
- Germline configuration of T cell receptor in NK cell lineage (Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Am J Surg Pathol 2013;37:14, Am J Surg Pathol 2011;35:1195)
- Monoclonal rearrangement of T cell receptor in T cell lineage cases
- Genomic hybridization (Expert Rev Hematol 2016;9:861, Front Pediatr 2019;7:71, Oncol Rep 2019;41:3219, Best Pract Res Clin Haematol 2013;26:57, J Hematol Oncol 2019;12:33)
- Common gains: 1q21-q44, 2q13-q14, 2q31-q32, 6p25-p11, 7q11-q34, 7q35-36, 17q21, 20q11
- Common losses: 6q16-q25, 11q23, 11q24-q25, 13q14, 17p13
Sample pathology report
- Left maxillary sinus, biopsy:
- Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type (see comment)
- Comment: According to clinical records, patient is a 56 year old Hispanic male with recent clinical history of nasal obstruction, purulent discharge, epistaxis and B type symptoms. In the last 5 months, the patient has received several antibiotic regimens with no improvement of the clinical course. A recent CT of the head and neck showed a 6 cm mass in the left maxillary sinus with invasion of the adjacent bone.
- The biopsy is adequate and shows respiratory type mucosa with underlying dense and monotonous lymphoid infiltrate with focal vascular invasion. The lymphocytes are of medium size, folded nuclei, indistinct nucleoli and moderate amount of cytoplasm. Frequent mitoses are observed. There is focal ulceration and extensive coagulative necrosis.
- Immunohistochemical studies are performed and the atypical cells are positive for CD30, CD56, granzyme B and TIA1. Ki67 proliferation index is 60%. In situ hybridization for EBV encoded RNA (EBER) shows reactivity in most tumor cells. The abnormal cells are negative for sCD3, CD5, CD8, CD20, PAX5 as well as for TCRδ and TCRαβ. Acid fast bacilli stain and Gomori methenamine silver stain for fungal organisms are negative.
- Next generation sequencing demonstrated mutation of STAT3.
- Polymerase chain reaction for Ig heavy chain (IGH) and T cell receptors gamma (TRG) and beta (TRB) chains revealed a germline pattern.
Differential diagnosis
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis (Wegener granulomatosis) (Hum Pathol 1997;28:450):
- Usually present with lung and kidney disease
- Mixed inflammatory infiltrate: granulocytes, lymphocytes, histiocytes and plasma cells
- Stains and cultures for microorganisms are negative
- Invasive fungal infection (Front Immunol 2019;10:1524):
- Aggressive NK cell leukemia (ANKL) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Am J Surg Pathol 2020;44:1235):
- Angioimmunoblastic T cell lymphoma (AITL) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514):
- Peripheral T cell lymphoma, NOS (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514):
- Intestinal T cell lymphomas - enteropathy associated T cell lymphoma (EATL) and monomorphic epitheliotropic intestinal T cell lymphoma (MEITL) (Curr Hematol Malig Rep 2016;11:514, Nat Commun 2015;6:6025):
- Lymphomatoid granulomatosis (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:e35):
- EBV positive diffuse large B cell lymphoma (Pathology 2020;52:40):
- T cell large granular lymphocytic leukemia (Am J Clin Pathol 2015;144:607, Am J Surg Pathol 2017;41:82, Histopathology 2014;64:171):
- Primary cutaneous gamma delta T cell lymphoma (Ann Diagn Pathol 2015;19:211, Am J Surg Pathol 2015;39:1):
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following is true about extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type (ENKTCL)?
- Frequently presents as an indolent disease with favorable prognosis
- JAK / STAT pathway is usually activated
- More common in young (second and third decades) patients
- Necrosis and angiotropism are usually absent
Board review style answer #1
B. JAK / STAT pathway is usually activated
Comment Here
Reference: Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type
Comment Here
Reference: Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type
Board review style question #2
What is the most common immunophenotype of extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type?
- εCD3+ / sCD3- / CD5- / CD16+ / CD56+ / EBER+
- εCD3+ / sCD3+ / CD5- / CD16+ / CD56+ / EBER+
- εCD3- / sCD3+ / CD5- / CD16- / CD56- / EBER+
- εCD3- / sCD3- / CD5- / CD16- / CD56+ / EBER+
Board review style answer #2
A. εCD3+ / sCD3- / CD5- / CD16+ / CD56+ / EBER+
Comment Here
Reference: Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type
Comment Here
Reference: Extranodal NK / T cell lymphoma, nasal type