Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology / etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Khanlari M, Chapman J. Follicular lymphoma-duodenal type. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphomafolliculargi.html. Accessed January 20th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Duodenal type follicular lymphoma is a variant follicular lymphoma (FL) characterized by:
- Morphologic features and immunophenotype similar to nodal follicular lymphoma
- Distinct entity in 2016 WHO
- Unlike nodal follicular lymphoma, is almost always diagnosed at a low stage and stays localized to the small intestine
- Treatment is local, not systemic
Essential features
- Low grade cytology
- Indolent clinical course
- Usually carries the t(14;18) (q32;q21) translocation
Terminology
- Primary intestinal follicular lymphoma
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- 4% of gastrointestinal (GI) lymphomas (Am J Surg Pathol 2000;24:688, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2018;142:542)
- Middle aged patients
- M = F (female predominance in some series)
Sites
- A high proportion (38 - 81%) arise in the duodenum (D2)
- Other segments of the small intestine and colorectum (28% in some series)
Pathophysiology / etiology
- Origin from memory B cell with germinal center marker expression
- t(14;18)(q32;q21) translocation: duodenal type follicular lymphoma is part of follicular lymphoma family
- Immune microenvironment of duodenal type follicular lymphoma is distinct from nodal follicular lymphoma (Blood 2018;132:1695)
- Some shared features with MALT lymphoma
- Chronic inflammation signature
- Restricted immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region genes (IGHV): suggests development related to chronic antigen stimulation (Cancer Sci 2014;105:608)
Diagrams / tables
| Nodal Follicular Lymphoma | Duodenal Follicular Lymphoma |
| Grade 1 - 2 or 3 | Grade 1 - 2 |
| Stage III or IV | Stage I or II |
| BCL2, CD10, BCL6: Positive | BCL2, CD10, BCL6: Positive |
| AID: Positive | AID: Negative |
| CD21 stain: Dense stain in the center of germinal center of follicles |
CD21 stain: Accentuated staining at the periphery of germinal center of follicles |
| BCL2 and BCL6 rearrangements: + | BCL2 and BCL6 rearrangements: + |
| CREBBP mutations present | CREBBP mutations present |
| KMT2D mutations present | Lower KMT2D mutations present |
Clinical features
- Second portion of the duodenum is the most common site
- Asymptomatic or abdominal symptoms
- Low grade histology (grade 1 - 2)
- Low stage presentation
- Incidental polyp in patients undergoing upper endoscopy
- Multifocal involvement of the gut by polypoid and nodular lesions
- Multiple lesions more in the jejunum and ileum rather than duodenum (J Clin Oncol 2011;29:1445)
- Rarely ulcerated mucosal lesion
Diagnosis
- Solitary or multiple nodules in endoscopy (1 - 5 mm)
- Biopsy
Prognostic factors
- A small subset of patients (< 10%) progress to nodal disease
- 5 year progression free survival 98% in duodenal type follicular lymphoma with restricted duodenal involvement (Cancer Sci 2011;102:1532)
Case reports
- 34 year old man with primary multifocal small bowel follicular lymphoma discovered incidentally on diagnostic endoscopy (Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 2017;15:A27)
- 52 year old man with duodenal type follicular lymphoma in which histological transformation into diffuse large B cell lymphoma developed 7 years after diagnosis (Oncotarget 2019;10:3424)
- 52 year old woman who was eventually diagnosed with primary follicular lymphoma of the duodenum showed atypical endoscopic features, namely, erosions with peripheral whitish edematous mucosa (Case Rep Med 2012;2012:582607)
- 58 year old man who was diagnosed with duodenal type follicular lymphoma and was treated with clarithromycin monotherapy (Case Rep Oncol 2018;11:239)
Treatment
- Two approaches:
- Watch and wait approach
- Localized radiation with or without chemotherapy (+/-Rituximab)
Gross description
- Almost all diagnoses are made on endoscopic biopsy
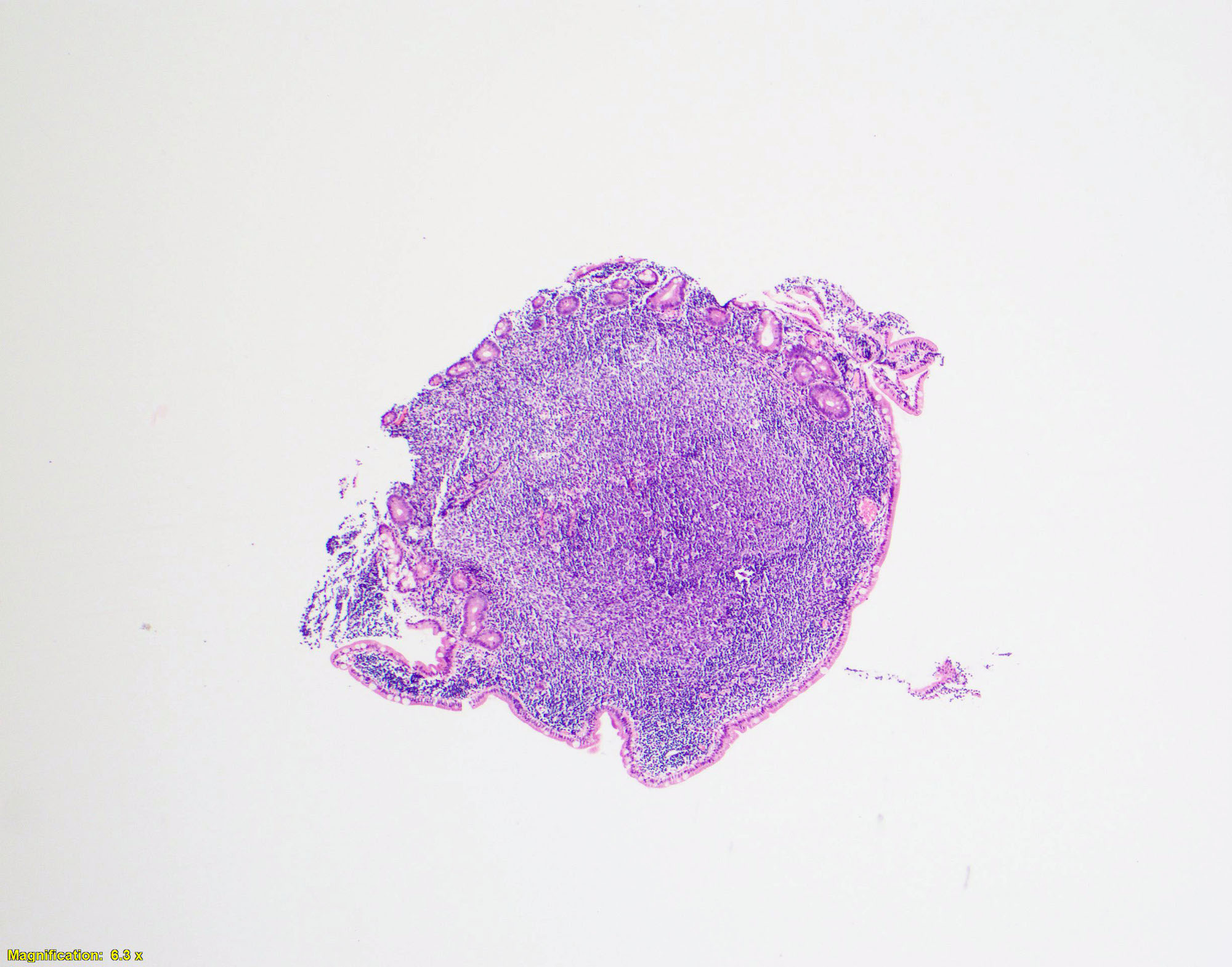
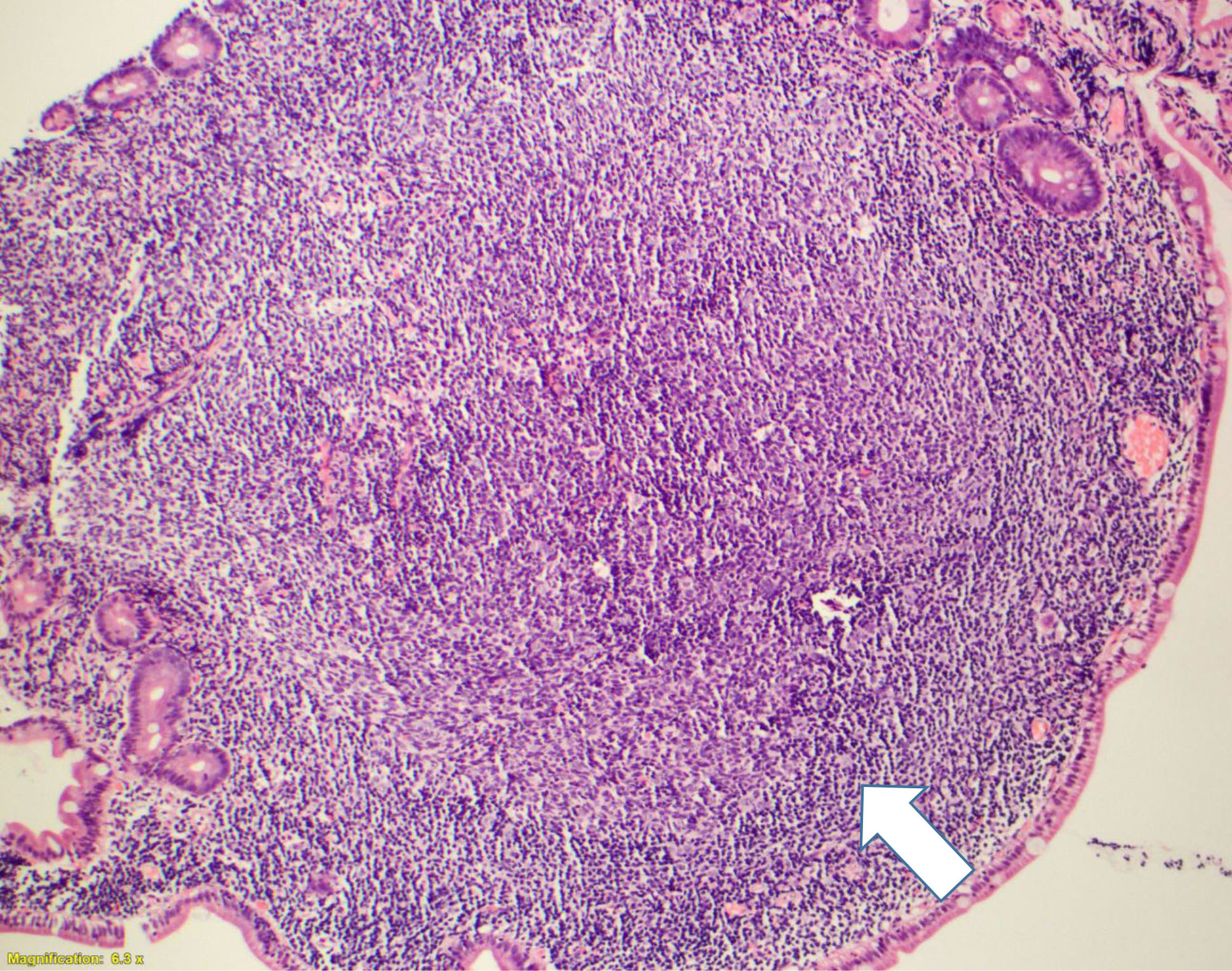
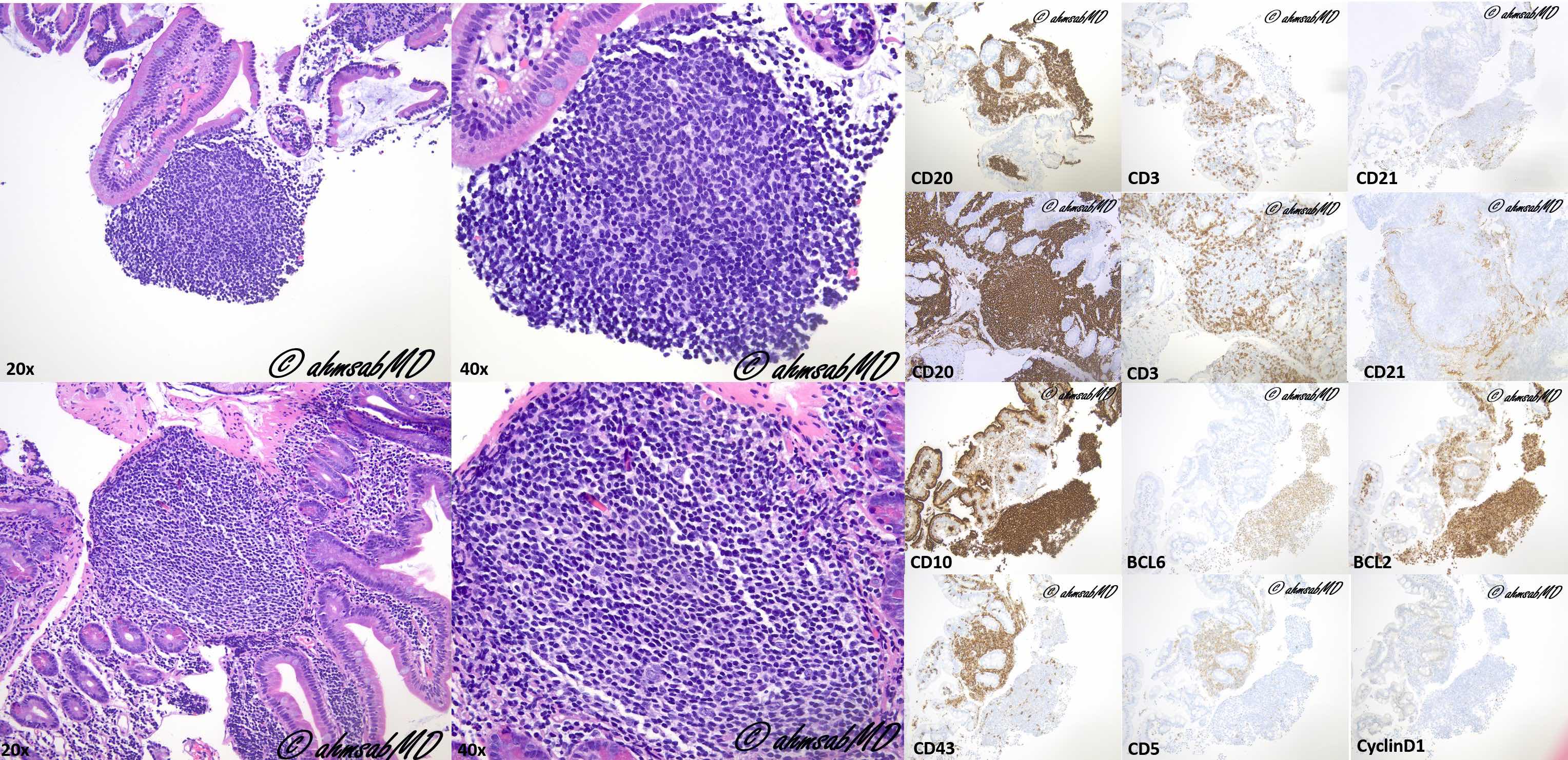
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Several well circumscribed lymphoid aggregates
- Composed of centrocytes (with infrequent centroblasts)
- Lymphoma usually involves the mucosa and submucosa
- Spares the muscularis propria
- Neoplastic cells commonly involve duodenal villi
- Hollowed out follicular dendritic cell meshworks (Mod Pathol 2009;22:940)
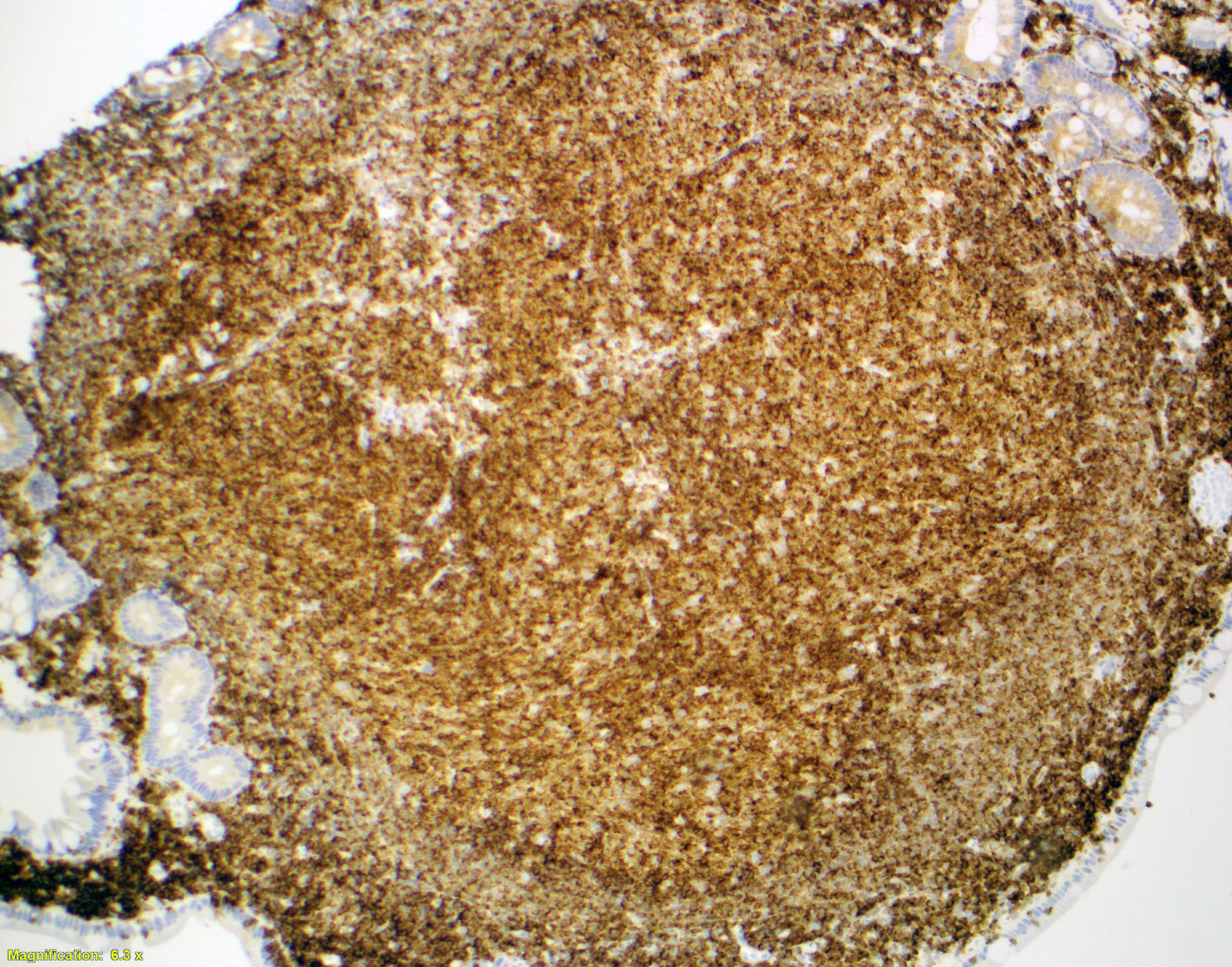
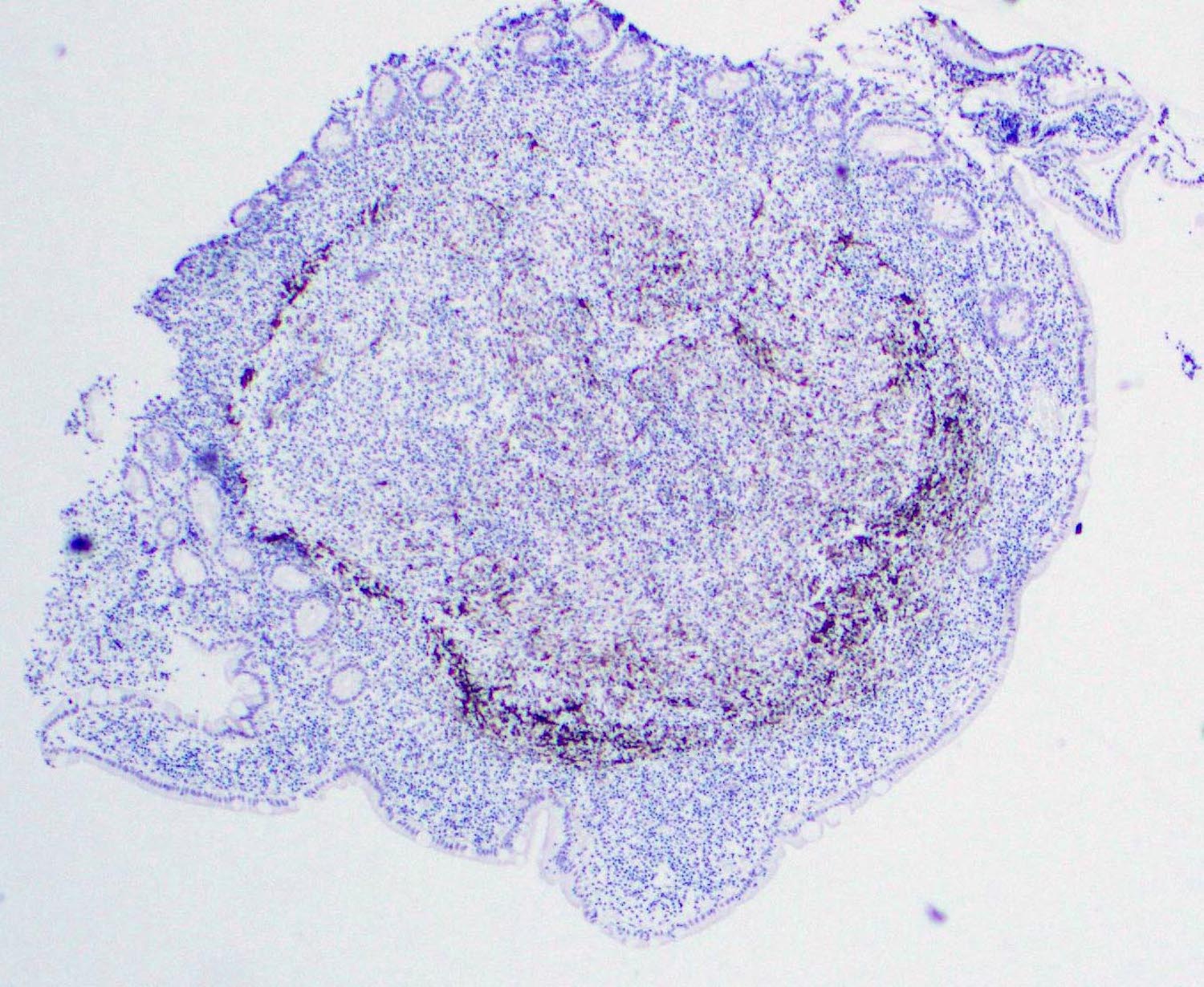
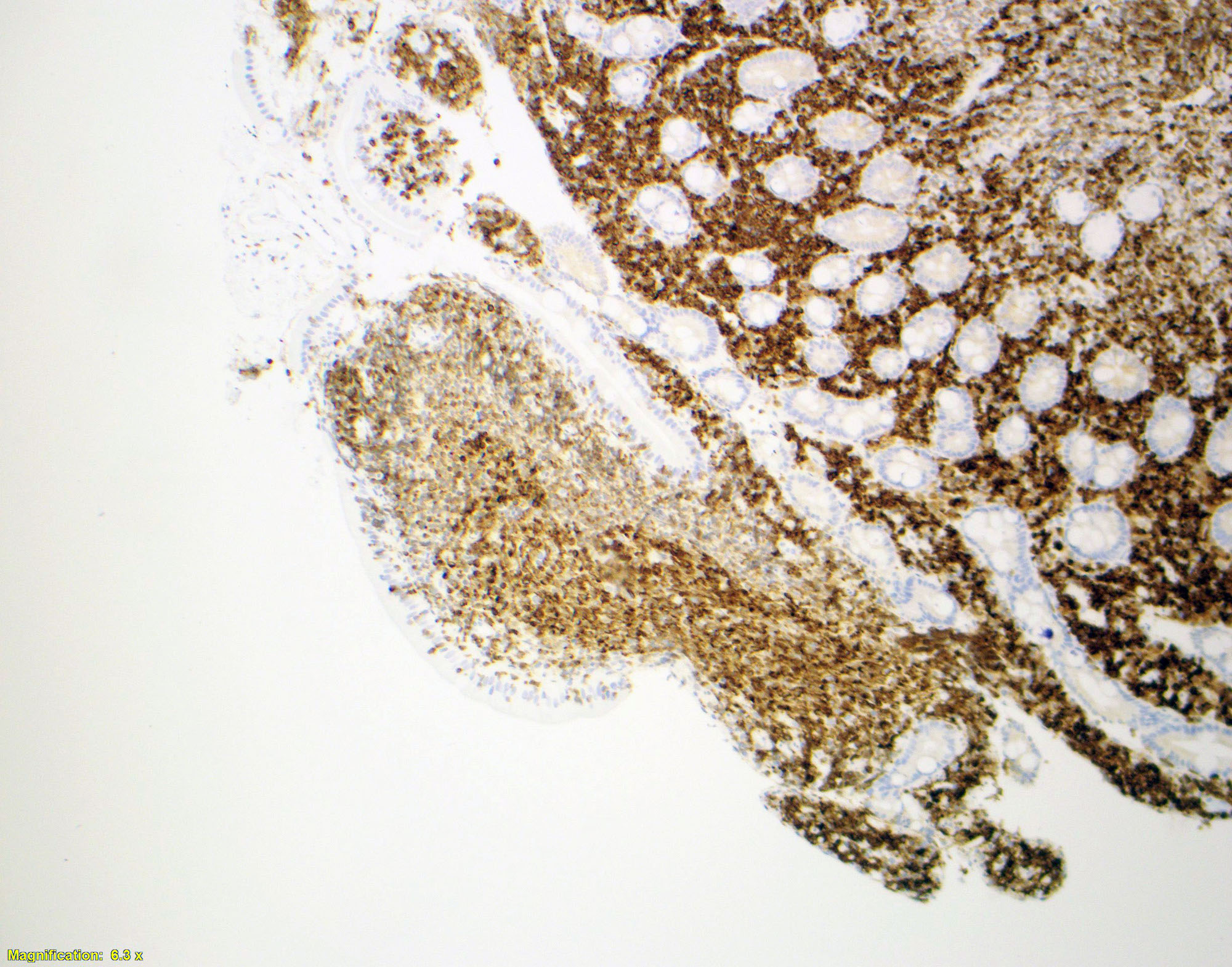
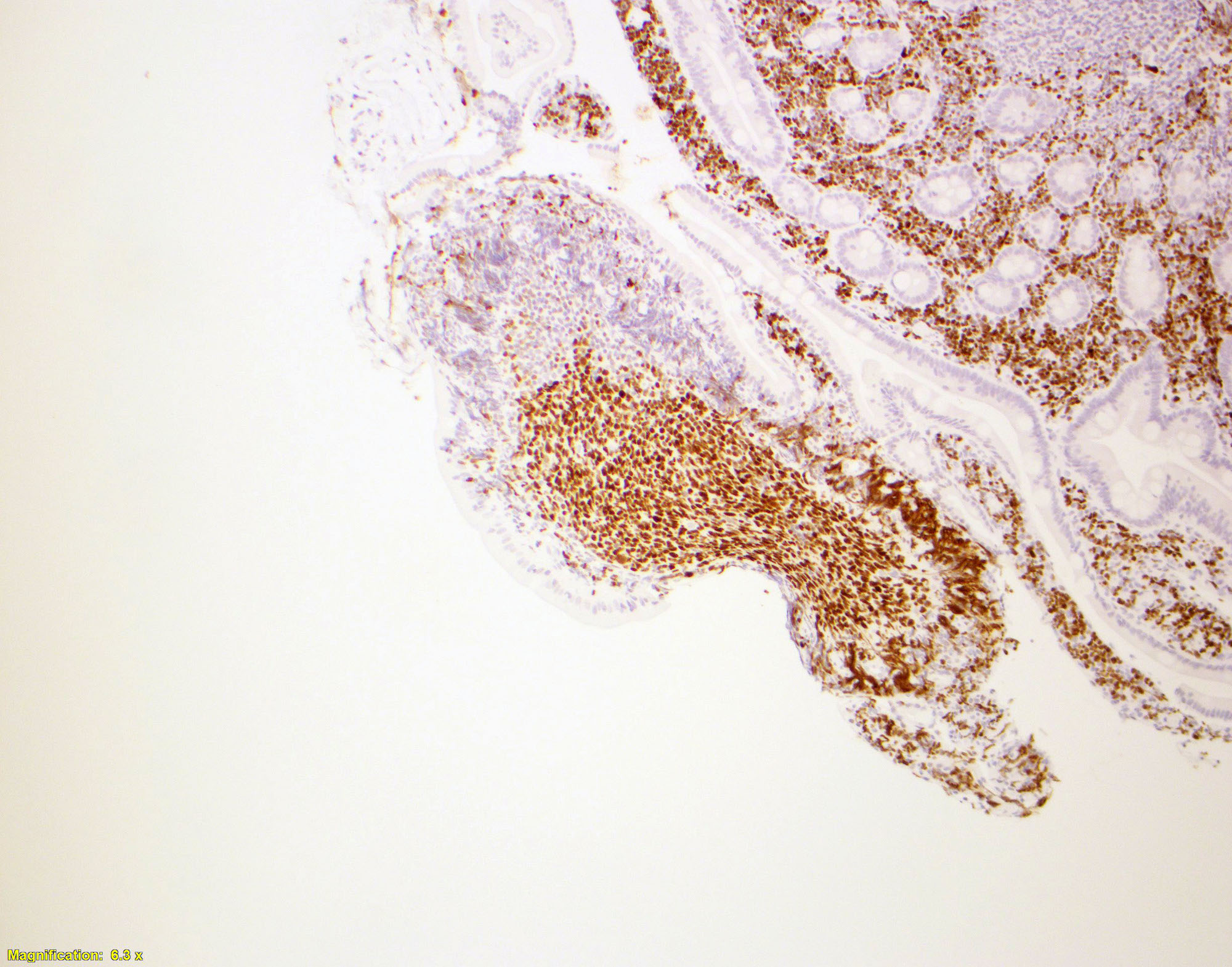
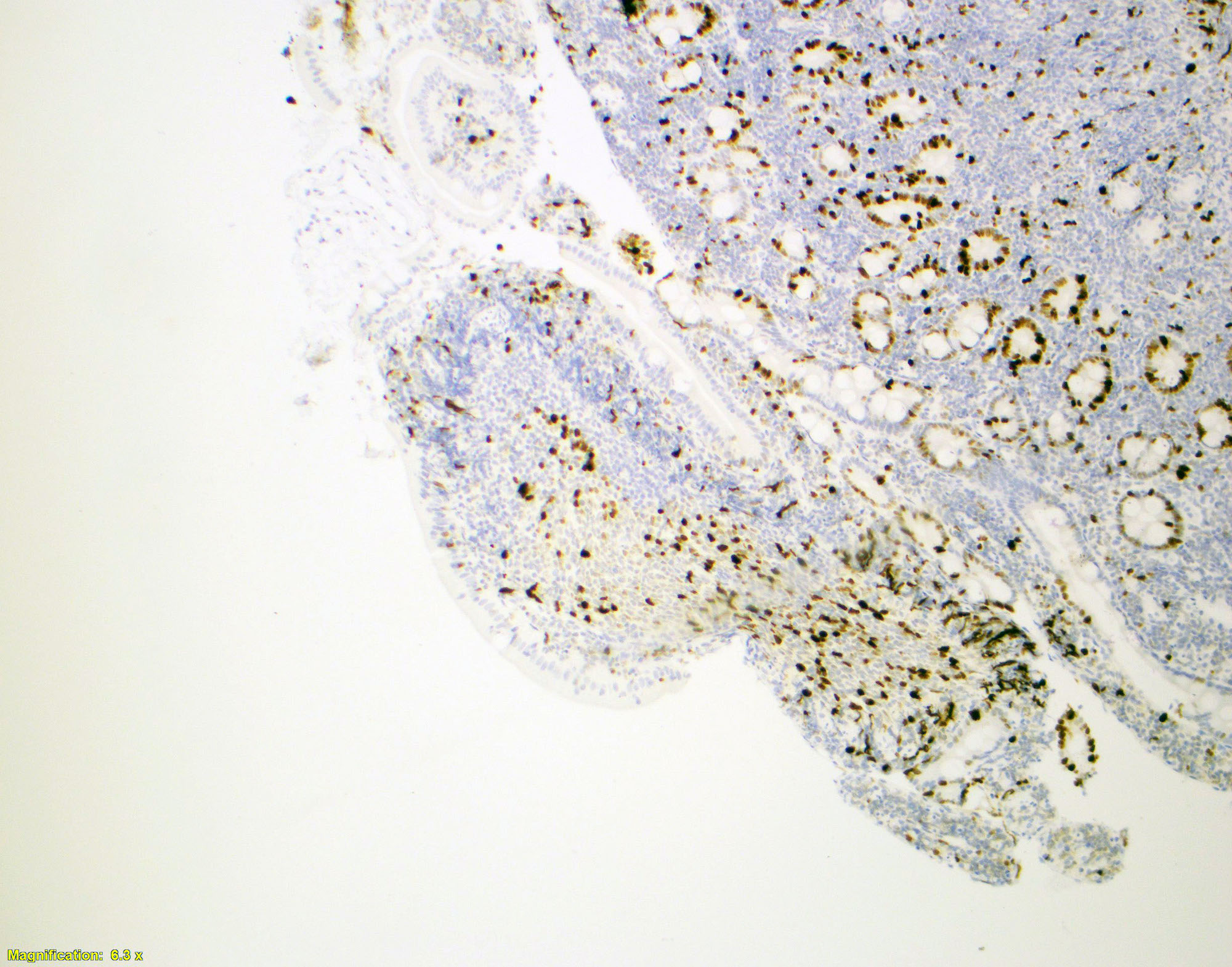
Microscopic (histologic) images
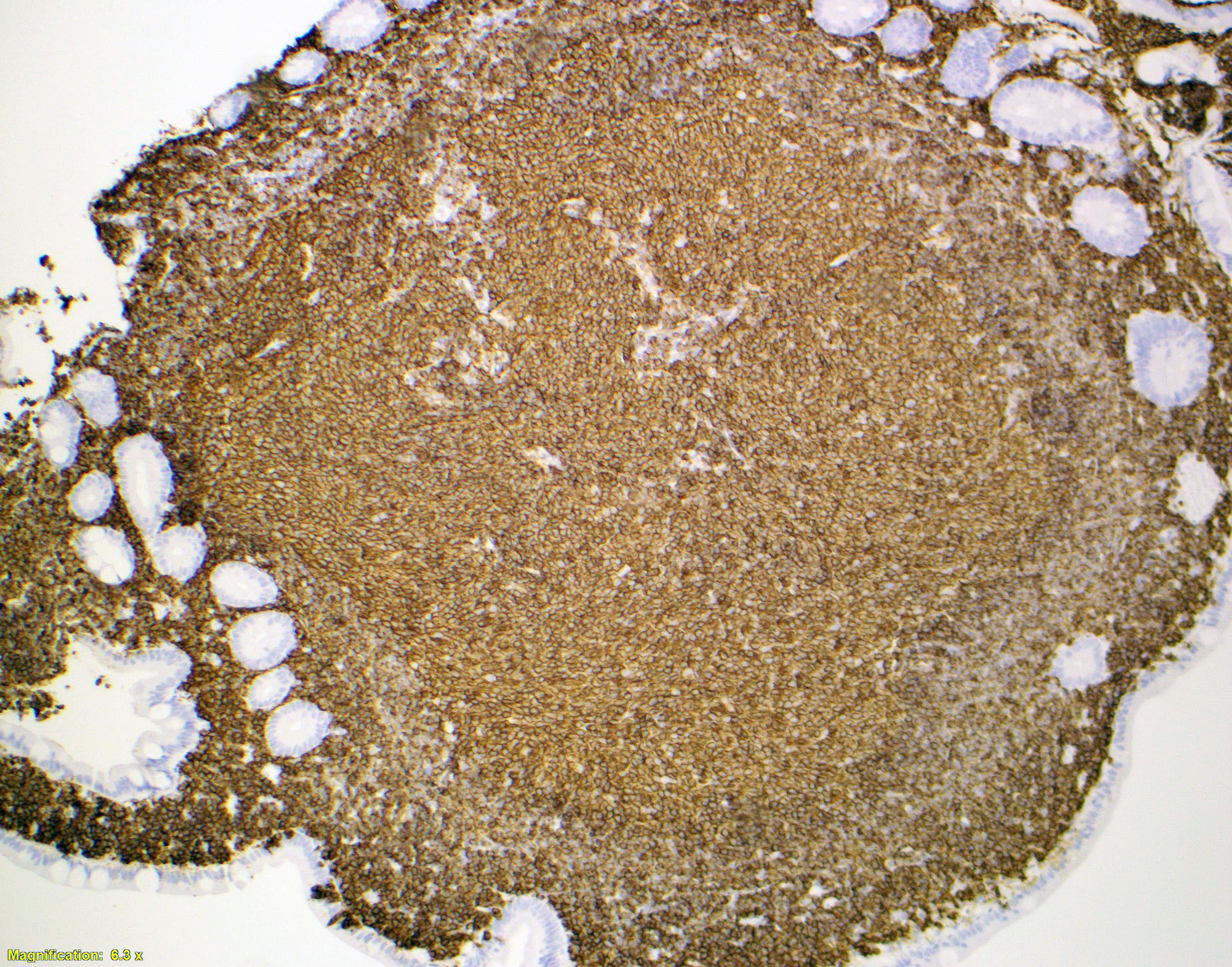
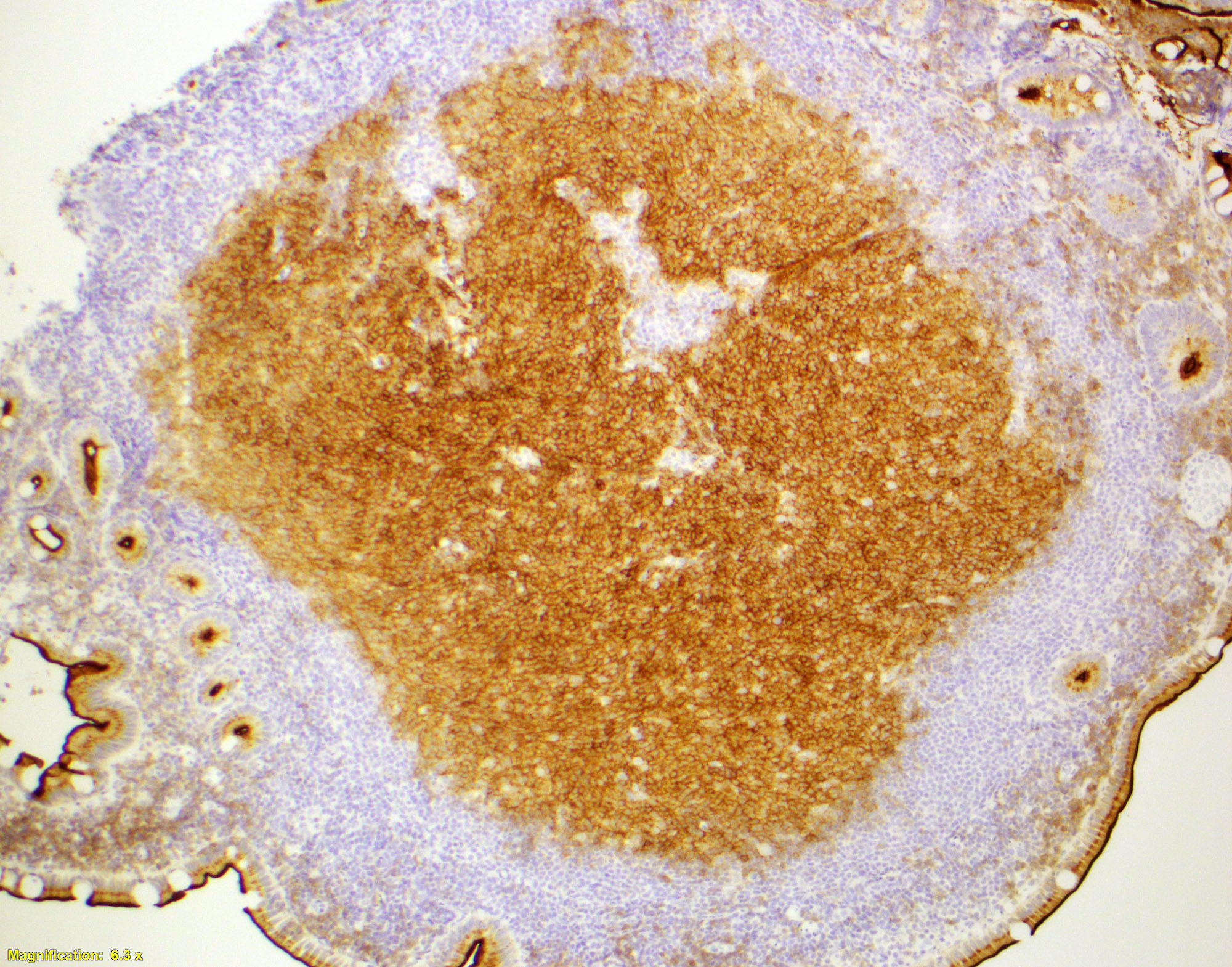
Positive stains
Negative stains
- CD5, CD23, CD43, BCL1 (cyclin D1), MUM1
- T cell markers
- Activation induced cytidine deaminase (AID) (Mod Pathol 2013;26:22)
- AID: Class switching and somatic hypermutation in B cells (Cell 2000;102:553)
- AID expression is related to poor prognosis in some B cell lymphomas
- Expressed in germinal centers and nodal follicular lymphoma (Pathol Int 2018;68:665)
- Lack of AID expression: limit the tumor stage / better prognosis in duodenal follicular lymphoma (Mod Pathol 2013;26:22)
- In duodenal type follicular lymphoma, the follicular dendritic cells (FDCs) are located at the periphery of the neoplastic follicle
- Stained with CD21 and CD23 (Mod Pathol 2013;26:22)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- t(14;18)(q32;q21)(IGH/BCL2) translocation (Br J Haematol 2019 Dec 27 [Epub ahead of print])
- BCL6 rearrangement (Pathol Int 2018;68:665)
- Lower rate of KMT2D inactivation in comparison to nodal follicular lymphoma (Blood 2018;132:1695)
- Lower frequency of genetic aberrations than nodal follicular lymphoma (low mutation burden) (Blood 2018;132:1695)
- Mutations common between nodal follicular lymphoma and duodenal type follicular lymphoma:
- CREBBP, KMT2D, TNFRSF14 and EZH2 somatic mutations (Blood 2018;132:1695)
- Gene expression profile common between MALT and duodenal type follicular lymphoma:
- Overexpression of CCL20 and MADCAM1 (J Clin Pathol 2008;61:377, Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:22)
Sample pathology report
- Biopsy, endoscopic, duodenum:
- Follicular lymphoma involving duodenum (see comment)
- Comment: The patient is a 45 year old female with history of vague abdominal pain. Histologic sections consist of endoscopic biopsies of duodenum showing involvement by an atypical lymphoid infiltrate. Lymphoid cells are arranged in a follicular distribution and consist of small lymphoid cells with mature nuclear chromatin and frequent centrocytic features. Centroblasts are rare and scattered.
- By immunohistochemistry the atypical lymphoid cells are positive for CD20 and CD79a with coexpression of CD10, BCL6, LMO2 and BCL2. CD3 and CD5 highlight reactive T cells surrounding the neoplastic B cell aggregates. Ki67 proliferative rate is low within neoplastic follicles, ~5%. These findings support the above interpretation.
- Correlation with clinical features and staging procedures is required to determine whether the patient’s follicular lymphoma is a primary duodenal type follicular lymphoma, or a systemic follicular lymphoma secondarily involving duodenum. In the sampled material the lymphoma is of low histologic grade (grade 1).
Differential diagnosis
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia
- Follicles vary in size and shape
- Tingible body macrophages
- Polarized germinal centers
- Preserved dendritic cell meshwork
- Interfollicular lymphocytes will differ from the follicular lymphocytes
- Germinal center B cells will stain for BCL6 and CD10 but not for BCL2
- MALT lymphoma
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia / small lymphocytic lymphoma
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- GI involvement by systemic follicular lymphoma (nodal follicular lymphoma)
- Perform clinical staging (e.g., imaging, bone marrow biopsy) to rule out systemic disease
Additional references
- Jaffe: Hematopathology, 2nd Edition, 2016, Hsi: Hematopathology - Foundations in Diagnostic Pathology, 3rd Edition, 2017, Swerdlow: WHO Classification of Tumours of Hematopoietic and Lymphoid Tissues, 4th Edition, 2017, Aster: Hematopathology - A Volume in the High Yield Pathology Series, 1st Edition, 2013, Medeiros: Diagnostic Pathology - Lymph Nodes and Extranodal Lymphomas, 2nd Edition, 2017
Board review style question #1
- Which of the following follicular lymphoma variants usually has the t(14; 18) (q32;q21) IGH/BCL2 translocation?
- Diffuse follicular lymphoma variant
- Duodenal type follicular lymphoma
- Pediatric type follicular lymphoma (PTFL)
- Primary testicular follicular lymphoma
Board review style answer #1
Board review style question #2
- 54 year old man presents with a dyspepsia. In his upper endoscopy a small polypoid lesion is detected in duodenum. Part of the immunohistochemical stains are provided in this case (left to right: BCL2, BCL6 and Ki67 immunostains). What is the most probable diagnosis?”
- Chronic lymphocytic leukemia / small lymphocytic lymphoma
- Follicular lymphoma
- Mantle cell lymphoma
- Reactive lymphoid follicle in a small intestine polyp
Board review style answer #2