Table of Contents
Definition / general | Laboratory | Case reports | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Electron microscopy description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: DePond W. Chronic granulomatous disease. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodeschronicgranulomatousdisease.html. Accessed March 30th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Due to congenital enzymatic defect of NADPH oxidase in granulocytes and monocytes
- White blood cells cannot generate superoxide ion which kills microorganisms in lysosomes
- Either Y linked or autosomal recessive
- Diagnose with nitro blue tetrazolium test (almost always positive)
- Clinically, patients have recurrent lymphadenitis, hepatosplenomegaly, skin rash, pulmonary edema
Laboratory
- Anemia, leukocytosis, hypergammaglobulinemia
Case reports
- Child with Hansenula polymorpha infection (Arch Pathol Lab Med 1980;104:290)
Microscopic (histologic) description
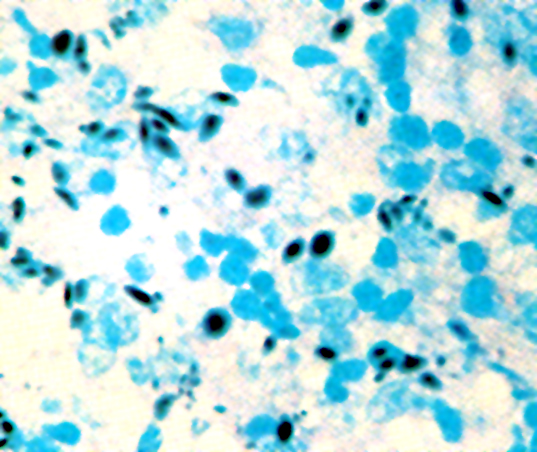
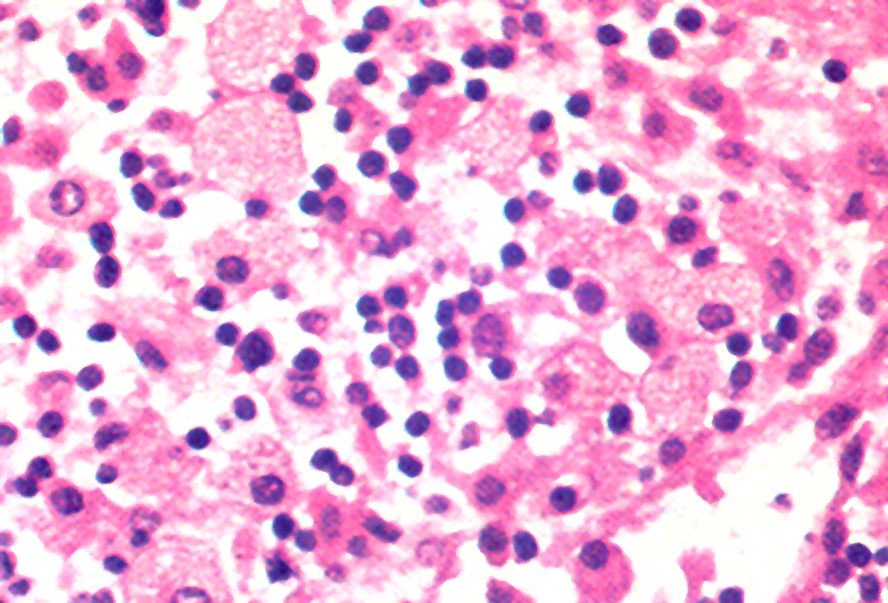
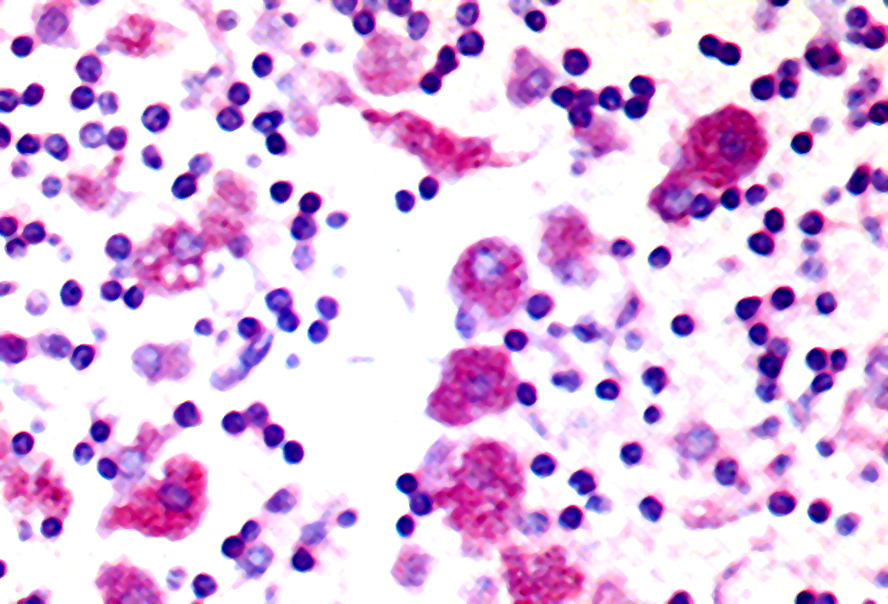
- Granulomas with central necrosis in lymph nodes and other organs
- Pigment laden histiocytes
Microscopic (histologic) images
Cytology description
- Necrotizing granuloma, pigmented histiocytes (Diagn Cytopathol 1991;7:57)
Electron microscopy description
- Pigment is lipofuscin, apparently from lysosomes (Pediatr Pathol 1992;12:839)
Differential diagnosis
Additional references