Table of Contents
Definition / general | Terminology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Clinical features | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Positive stains | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Balakrishna J, Sharabi A. Epithelial inclusions. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lymphnodesbreastepithelium.html. Accessed January 5th, 2025.
Definition / general
- Rare presence of benign, well differentiated epithelial cell clusters in lymph nodes
- May coexist with breast micrometastases (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:513)
- In axilla, may be due to pre-sentinel lymph node biopsy breast massage (Am J Surg Pathol 2004;28:1641, Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e25)
Terminology
- Also called benign metastasis or heterotopia
Sites
- Axillary, cervical, mediastinal, mesenteric, para-aortic, pelvic, renal lymph nodes
Pathophysiology
- Different theories regarding the pathogenesis:
- Benign metastasis
- Developmental heterotopia
- Metaplasia of multipotent cells
- Iatrogenic displacement and transport (J Clin Oncol 2006;24:2013)
Clinical features
- Asymptomatic, incidental finding
Prognostic factors
- Benign with no significant clinical implications
- Rarely may undergo disease processes and become cystic, a benign tumor or malignant
Case reports
- 44 year old woman with right breast carcinoma and benign Müllerian inclusions coexisting with breast metastatic carcinoma in an axillary lymph node (Virchows Arch 2005;446:467)
- 48 year old woman with axillary intranodal cysts associated with breast malignancy (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2004;128:361)
- 50 year old woman with unusual cystic epithelial choristoma in a celiac lymph node (Hum Pathol 1987;18:866)
- 52 year old woman with squamous inclusion cyst in a sentinel axillary lymph node associated with breast malignancy (J Coll Physicians Surg Pak 2012;22:50)
- 65, 66 and 75 year old women with endosalpingiosis in axillary sentinel lymph nodes obtained for staging of breast carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2010;34:1211)
- 70 year old woman with invasive ductal carcinoma of the left breast and endosalpingiosis of axillary lymph nodes (Case Rep Pathol 2016;2016:2856358)
- 73 year old woman with ductal carcinoma in situ of the breast and epithelial inclusions in an ipsilateral axillary lymph node (Int J Surg Pathol 2018;26:564)
- Epithelial inclusion in axillary lymph node associated with a breast carcinoma (Pathol Res Pract 1999;195:263)
- Benign inclusion of axillary lymph nodes (Breast J 2009;15:664)
Treatment
- No specific treatment needed, unless associated with another disease
Gross description
- Normal unremarkable lymph nodes
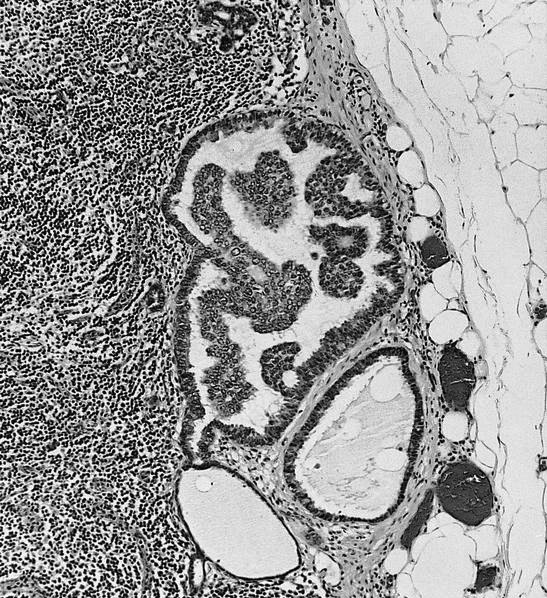
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Reactive follicular hyperplasia
- Well formed epithelial formations, in or near the peripheral sinuses
- Examples include salivary gland, thyroid follicles, breast tissue, respiratory type epithelium, fallopian tube lining or endometrium
- Single or tubules of epithelial cells in subcapsular sinus of draining lymph node after surgical or needle manipulation (Am J Clin Pathol 2000;113:259)
- Also hemosiderin laden macrophages and damaged erythrocytes
Positive stains
- Keratins and specific markers for the cell lineage
Differential diagnosis