Table of Contents
Definition / general | Epidemiology | Terminology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology description | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Molecular / cytogenetics description | Differential diagnosis | Additional referencesCite this page: Wu R. Squamous / glandular / mixed papilloma. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumorsquamouspapilloma.html. Accessed November 27th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Usually occur in large bronchi, often with associated tracheal or laryngeal lesions
- Arises from respiratory epithelium, and has 3 histologic types: squamous, glandular and mixed (squamous and glandular) (Am J Surg Pathol 1998;22:1328)
- Often associated with dysplasia, carcinoma in situ, or invasive squamous cell carcinoma
Epidemiology
- Solitary endobronchial papillomas in adults is rare, < 0.5% of lung tumors
- Squamous papillomas usually occur in middle aged male smokers
Terminology
- Also called squamous cell papilloma, solitary tracheobronchial papilloma
- Termed papillomatosis if multiple lesions present
Clinical features
- Associated with HPV 6 and HPV 11; high risk HPV may be seen in cases associated with carcinoma (Hum Pathol 1994;25:1191)
- Noninvasive but may have dysplasia, recur or develop into squamous cell carcinoma
- Nonspecific lower respiratory tract complaints include hemoptysis, recurrent pneumonia, asthma-like symptoms, dry cough
- Rarely arises in lower bronchial tree, but usually manifests as endobronchial exophytic growth
Diagnosis
- May be difficult on frozen section and small biopsy specimens to distinguish from squamous carcinoma
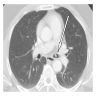
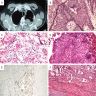
Radiology description
- May be incidental finding on imaging or show symptoms related to obstruction
- Xray: either normal, infiltrative shadow, hilar mass or lobar collapse
- CT: mass shadowing, can be PET avid
Case reports
- 42 year old woman with dry cough (Kyobu Geka 2012;65:808)
- 60 year old man with mixed squamous cell and glandular papilloma (Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014;20:625)
- 70 year old man with spindle and squamous cell carcinoma arising in peripheral mixed squamous and glandular papilloma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2011;135:1353)
- 79 year old woman with HPV 11+ tumor (Intern Med 1999;38:817)
Treatment
- Endoscopic removal, cryotherapy, fulguration
- Surgical resection
Gross description
- Tan-white, friable, pedunculated / polypoid, smooth to verrucoid, glistening
- Wart-like, cauliflower-like
- Generally less than a few centimeters in size
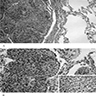
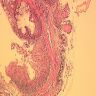
Microscopic (histologic) description
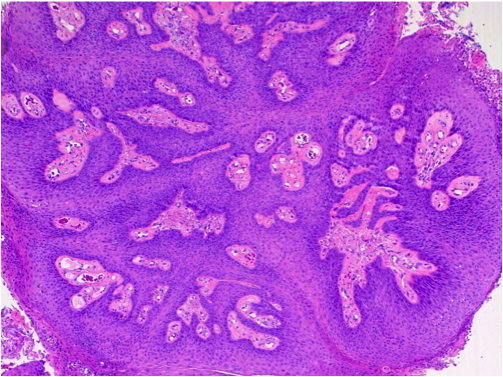
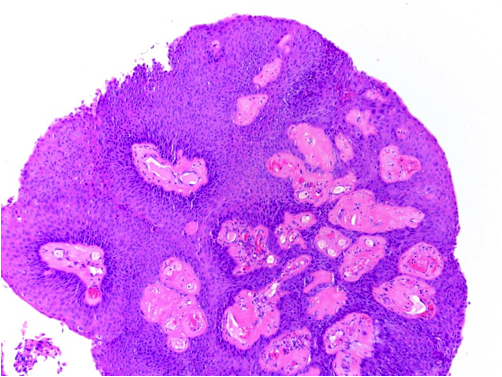
- Usually exophytic, papillary lesion with arborizing fibrovascular cores lined by keratinizing or nonkeratinizing mature squamous epithelium
- Rarely inverted pattern
- Lesion may grow into adjacent alveolar spaces
- May contain areas lined by ciliated or non-ciliated columnar cells with cuboidal cells or mucin-filled cells (mixed squamous and glandular papilloma)
- May exhibit viral cytopathic effect: enlarged hyperchromatic nuclei, nuclear wrinkling, polychromasia, binucleate forms, perinuclear halos
- Mild to moderate stromal inflammation which may be related to airway obstruction
- No mitoses, no necrosis
Microscopic (histologic) images
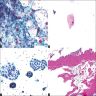
Cytology description
- Moderate cellularity, single and loosely clustered squamous cells
- Cytoplasmic keratinization and dark pyknotic nuclei with variable atypia, may show cells resembling koilocytes
- Background acute inflammation
Positive stains
- p40, CK5/6 (squamous markers)
- Mucicarmine (glandular cells)
- CK7 (mixed papilloma) (Pathol Int 2019;69:104, Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2014;20 Suppl:625)
Molecular / cytogenetics description
- Subset positive for HPV by ISH or PCR
Differential diagnosis
- Inflammatory polyps
- Mucoepidermoid carcinoma: for papillomas with mucus cells
- Papillary squamous cell carcinoma
Additional references