Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Cytology images | Positive stains | Negative stains | Differential diagnosis | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1Cite this page: Wu R. Metastases. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungtumormetastases.html. Accessed December 21st, 2024.
Definition / general
- Lung is a common site of metastases; usually multiple, bilateral, sharply outlined, rapidly growing, more pleomorphic and necrotic than lung primaries
- May appear as multiple discrete nodules in periphery of lung or as lymphangitic carcinomatosis (peribronchial and perivascular patterns via lymphatics)
- Rarely appear as intralymphatic microscopic foci that cause pulmonary hypertension
- Metastases can also be from other lung primaries (Am J Surg Pathol 2009;33:1752)
Essential features
- Lung is a common site of metastatic disease and may be the first or only site of metastatic involvement
- Lung metastases are generally multiple, well circumscribed and tend to grow rapidly
- A history of malignancy is helpful in determining the primary site but a panel of immunohistochemical stains can help support the diagnosis
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- In autopsy studies, 20 - 50% of patients with malignancy had lung metastasis (Cancer 1981;47:2595)
Sites
- Generally peripheral lung but can also be endobronchial
Pathophysiology
- Five year overall survival for all lung metastases is 36% (J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1997;113:37)
Etiology
- Mostly hematogenous or lymphogenous spread from primary site
Clinical features
- Usually asymptomatic or may present with nonspecific cough, chest pain, hemoptysis, spontaneous pneumothorax (J Surg Oncol 2014;109:42)
Diagnosis
- Typically detected by imaging, specifically CT scans
- Confirmation by cytologic or histologic sampling
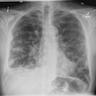
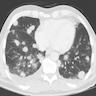
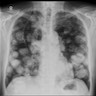
Radiology description
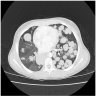
- CT scans are preferred modality
- Single or multiple, peripheral, well circumscribed nodule(s)
- Limited detection of subcentimeter disease
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Clinical variables associated with prolonged survival after lung metastasectomy in colorectal cancer patients
- Prolonged disease free interval between primary tumor and metastasis, normal prethoracotomy carcinoembryonic antigen, absence of thoracic node involvement and single pulmonary lesion (Ann Surg Oncol 2013;20:572)
- Complete resection and longer disease free interval > 6 months associated with better survival (Surg Oncol 2012;21:237)
Case reports
- 48 year old man with lymphangitic spread of hepatocellular carcinoma (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2003;127:e11)
- 50 year old man with ameloblastoma of jaw metastatic to lung (Case of the Week #318)
- 51 year old man with metastatic melanoma showing ground glass opacities (Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2015;191:954)
- 59 year old man with cavitary lung metastasis from urothelial carcinoma, diagnosed by FNA (Can Respir J 2011;18:e46)
- 65 year old woman with parotid gland acinic cell carcinoma metastatic to lung (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2007;131:970)
- 83 year old man with epithelioid tumor of lungs (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2005;129:e7)
Treatment
- Chemotherapy, immunotherapy, other systemic therapy
- Criteria for pulmonary metastasectomy: primary site of disease controlled, complete resection of lung metastasis feasible, patient able to tolerate procedure, no better alternative treatments (J Surg Oncol 2014;109:42)
- Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) may be considered for small, solitary, peripheral tumors
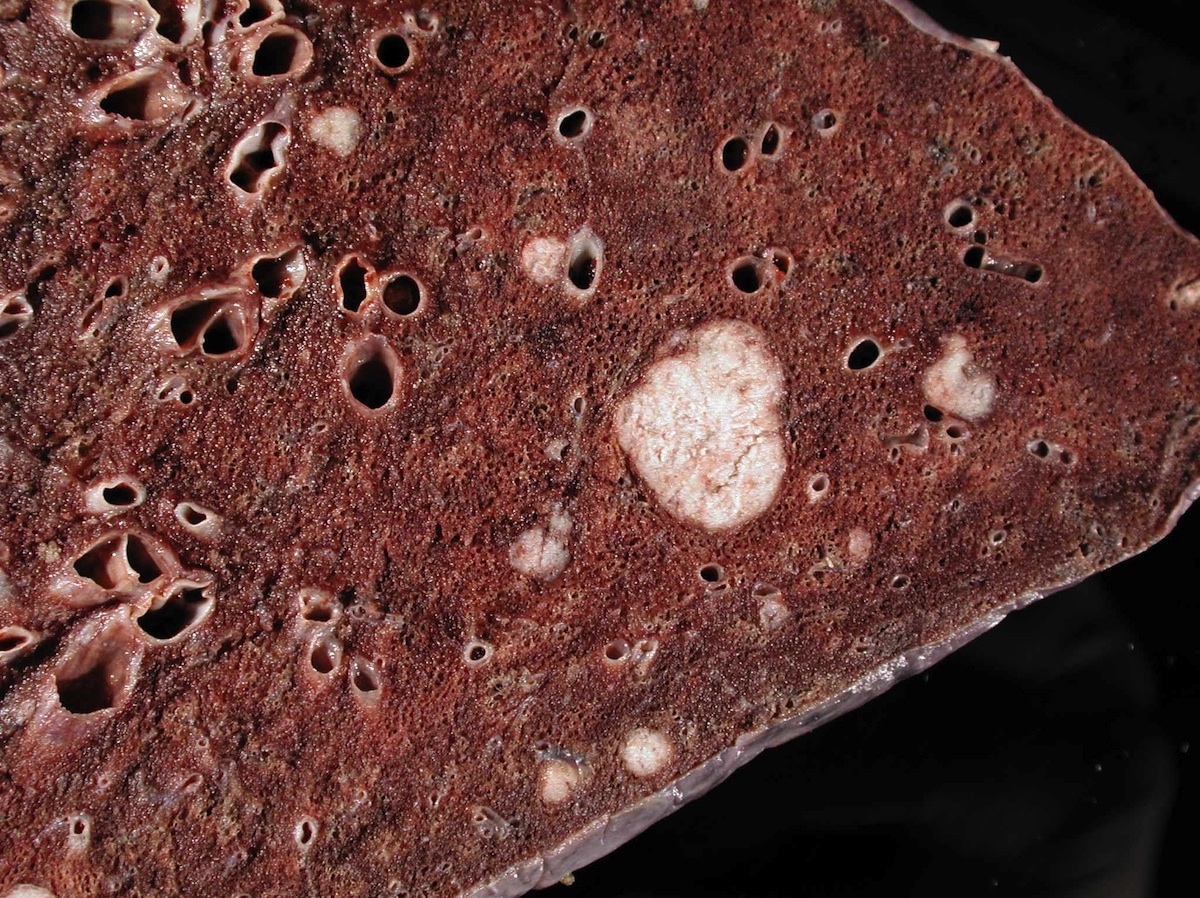
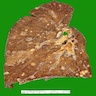
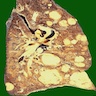
Gross description
-
Patterns associated with specific primaries
- Central cavitation: colonic adenocarcinoma, leiomyosarcoma, squamous cell carcinoma of upper aerodigestive tract
- Intrabronchial masses: breast, colon, kidney
- Lymphangitic carcinomatosis: breast, choriocarcinoma, pancreas, prostate, stomach
- Nodular metastases: breast, GI, kidney, melanoma, sarcoma
- Tumor emboli: breast, choriocarcinoma, liver, stomach
Gross images
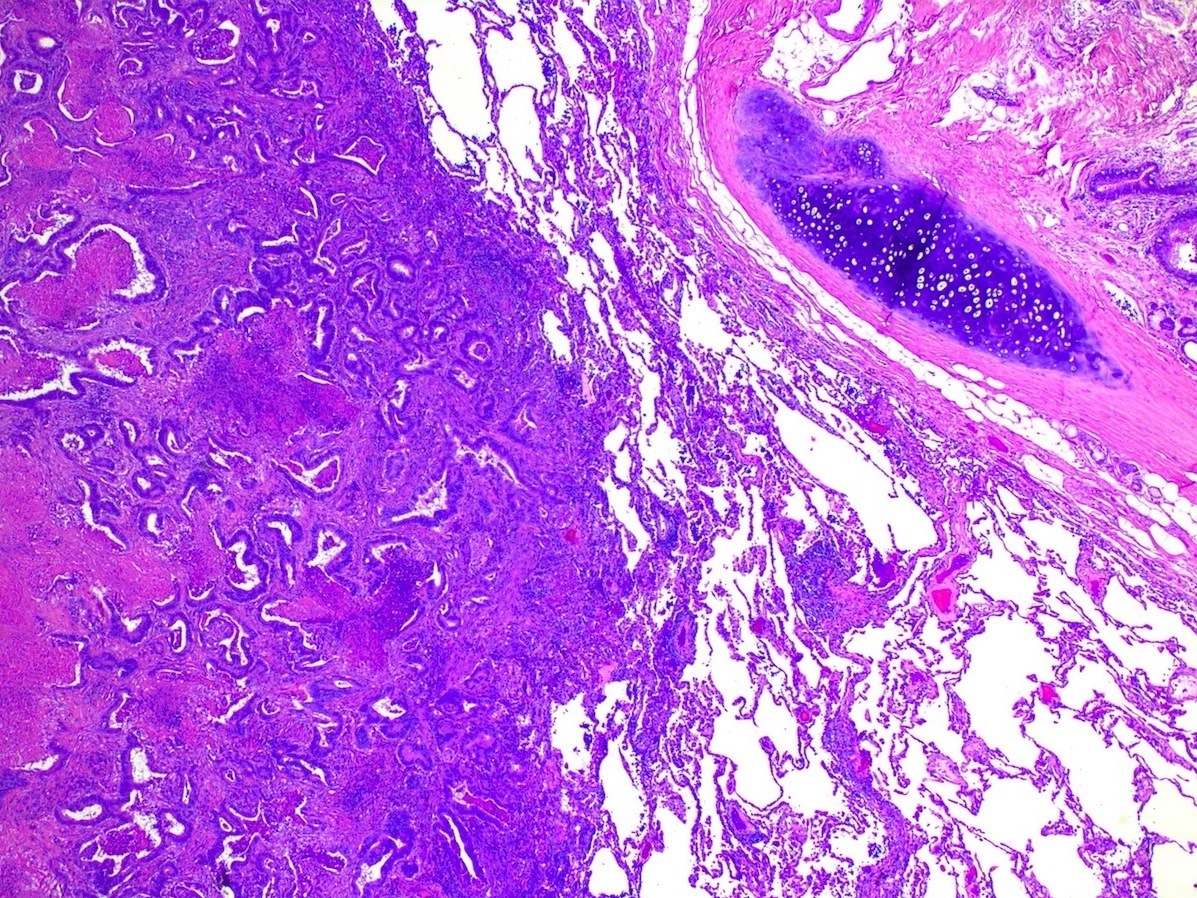
Microscopic (histologic) description
- Dependent on site of origin (colorectal cancer, bone and soft tissue sarcoma, renal cell carcinoma, melanoma, head and neck tumors, germ cell tumors and many others)
- Evidence for breast metastasis over lung primary: comedonecrosis, solid nests, trabecular architecture, cribriform growth pattern (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:122)
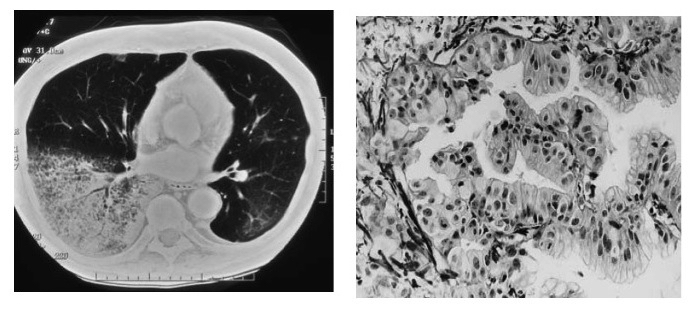
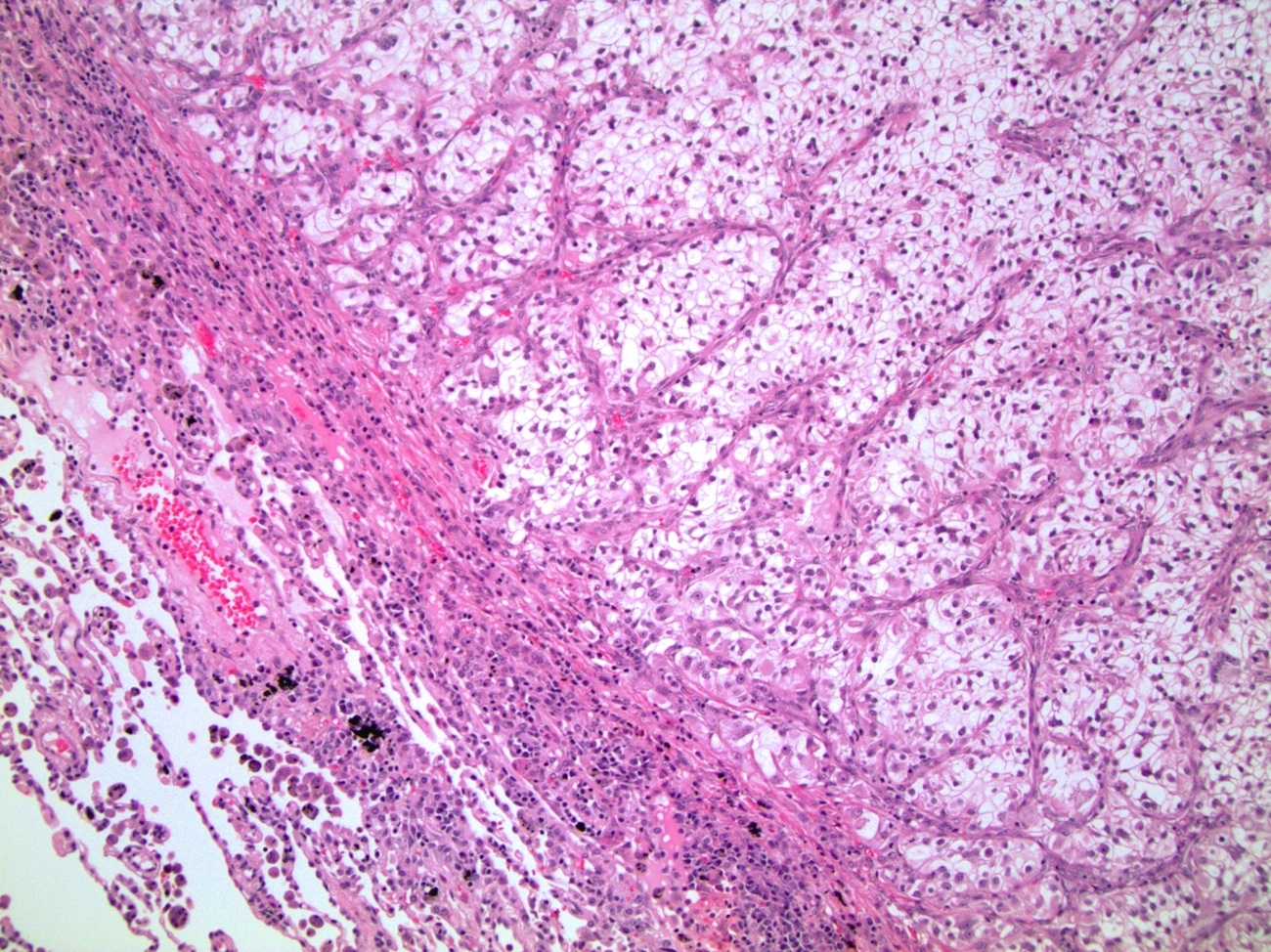
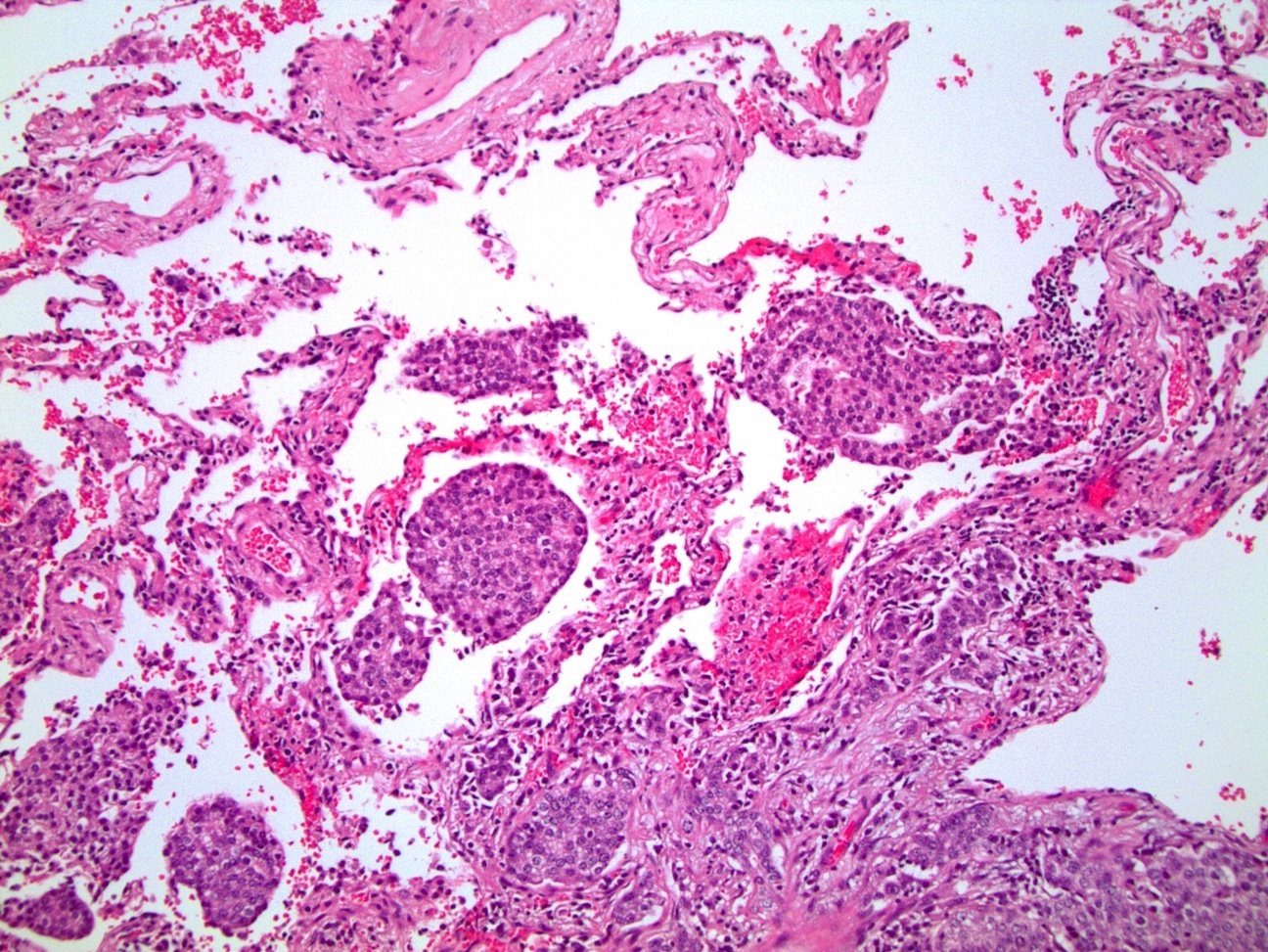
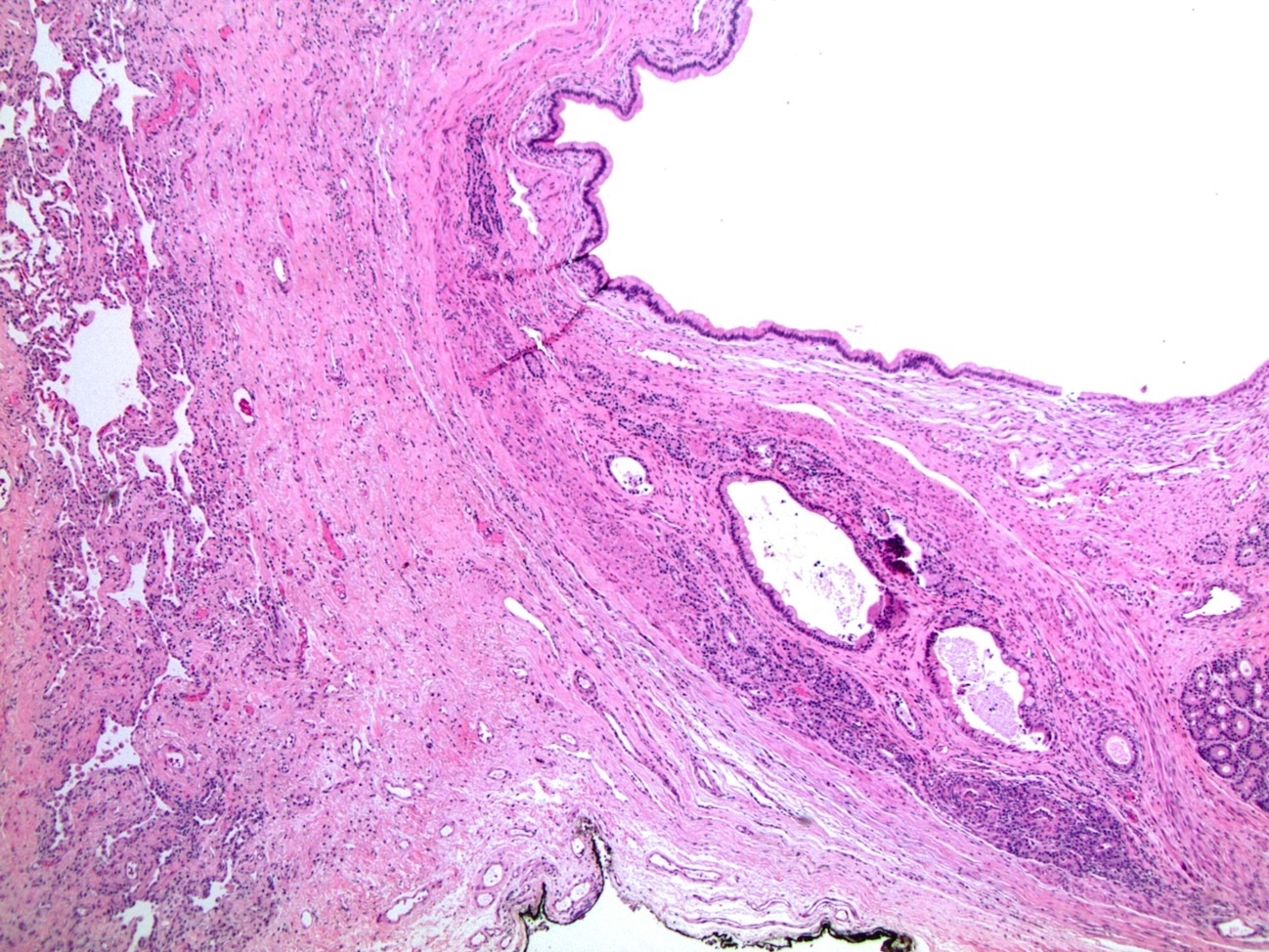
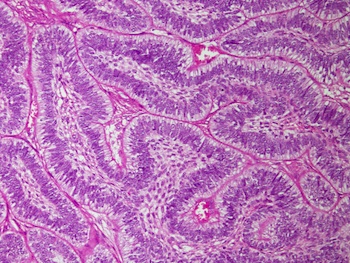
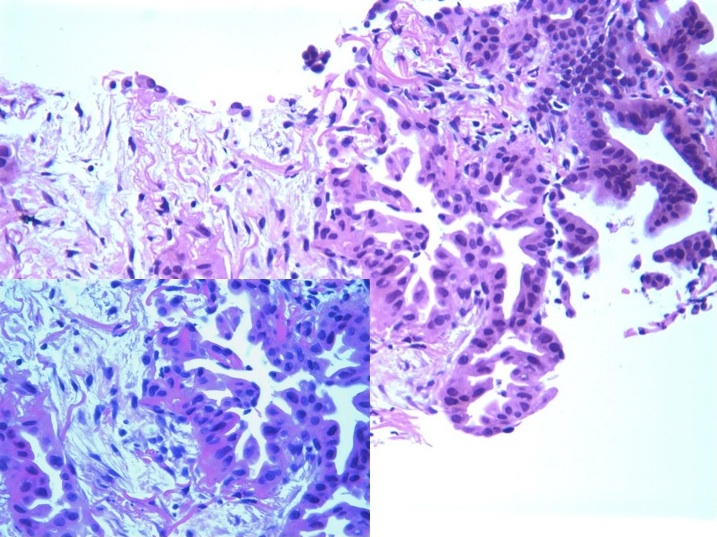
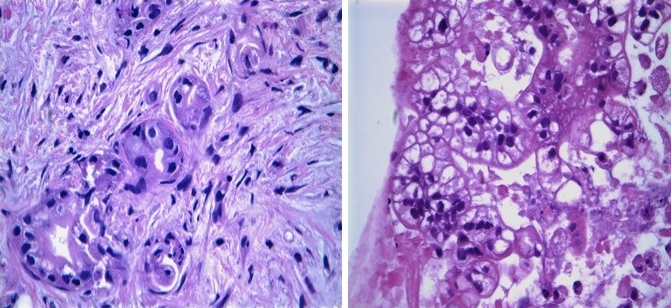
Microscopic (histologic) images
Contributed by Roseann Wu, M.D., M.P.H., Debra Zynger, M.D., Case #318 and Fulvio Lonardo, M.D.
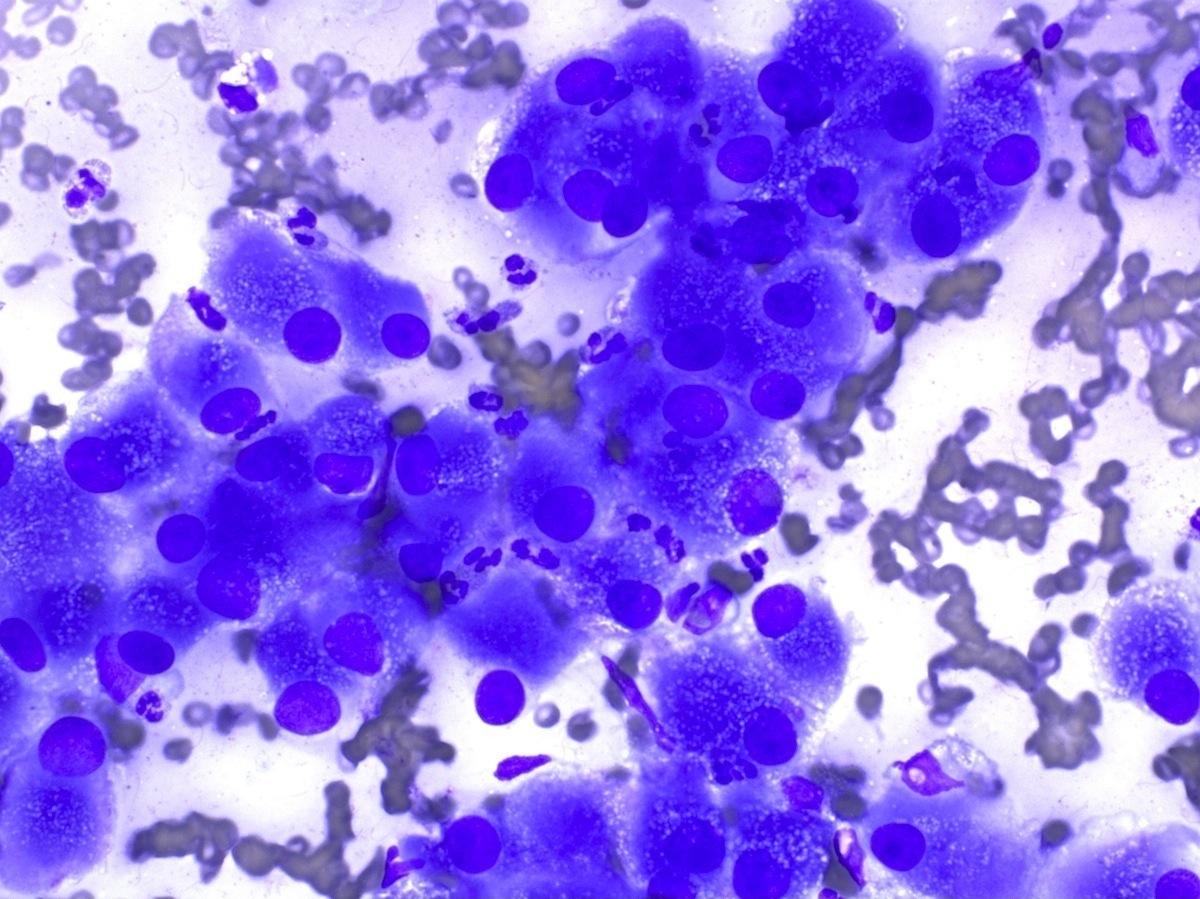
Cytology images
Positive stains
- CDX2 suggests colorectal carcinoma (Am J Surg Pathol 2003;27:141)
- Pankeratin to prove epithelial origin, CK7 / CK20 to help differentiate
- Lineage specific markers variable depending on site of origin, see Table 2 for suggested stains (Arch Pathol Lab Med 2016;140:508)
Differential diagnosis
- Primary lung carcinoma: acini, lepidic growth, nuclear pseudoinclusions, central scar (Am J Clin Pathol 2009;131:122)
- Inflammatory nodule or benign neoplasm
Board review style question #1
- For which malignancy is pulmonary metastasectomy most commonly performed and reported?
- Colorectal cancer
- Germ cell tumors
- Melanoma
- Osteosarcoma
- Renal cell carcinoma
Board review style answer #1