Table of Contents
Definition / general | Essential features | Terminology | ICD coding | Epidemiology | Sites | Pathophysiology | Etiology | Diagrams / tables | Clinical features | Diagnosis | Laboratory | Radiology description | Radiology images | Prognostic factors | Case reports | Treatment | Gross description | Gross images | Microscopic (histologic) description | Microscopic (histologic) images | Virtual slides | Positive stains | Negative stains | Electron microscopy description | Videos | Sample pathology report | Differential diagnosis | Additional references | Board review style question #1 | Board review style answer #1 | Board review style question #2 | Board review style answer #2Cite this page: Yoshikawa A, Bychkov A, Sathirareuangchai S. Organizing pneumonia. PathologyOutlines.com website. https://www.pathologyoutlines.com/topic/lungnontumorBOOP.html. Accessed December 28th, 2024.
Definition / general
- Organizing pneumonia (OP) can be defined as either clinicopathological diagnosis, histological pattern or microscopic findings
- Histologic features include polypoid fibroblastic aggregations, which plug alveolar sacs, ducts and bronchioles
Essential features
- Organizing pneumonia is one of the most commonly seen lung lesions and is associated with a variety of diseases, such as infections and systemic diseases
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is a relatively rare disease but often needs to be considered, since its clinical and radiological manifestations are often varied and nonspecific
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is a diagnosis that is not made by a pathologist; rather, it is a diagnosis of exclusion made by the multidisciplinary care team
- Histologically, both cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and secondary organizing pneumonia are characterized by polypoid fibroblastic aggregations, which plug alveolar sacs, ducts and bronchioles
Terminology
- Organizing pneumonia (OP):
- Can be either clinicopathological diagnosis (cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and secondary organizing pneumonia), histological pattern (organizing pneumonia pattern), or microscopic findings (e.g., Masson body)
- Since 1901, organizing pneumonia has been described with the name bronchiolitis obliterans as an interstitial lung disease with granulation tissue plugs within alveolar ducts and small airways secondary to a variety of causes, including infection, fume exposure, drugs, collagen vascular disease, allergic reactions and obstruction (Chest 1983;83:161)
- Davison et al. (1983) and Epler et al. (1985) reported a series of cases with organizing pneumonia and no evidence of infection or other aetiological agents; after that, the term bronchiolitis obliterans organizing pneumonia (BOOP) was commonly used for a while (Q J Med 1983;52:382, N Engl J Med 1985;312:152)
- Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP):
- Idiopathic form of organizing pneumonia
- In 2002, the American Thoracic Society / European Respiratory Society suggested the term cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (COP) to avoid confusion with airway disease (such as constrictive bronchiolitis obliterans) and categorized cryptogenic organizing pneumonia into acute / subacute interstitial pneumonia (Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2013;188:733)
- Cicatricial organizing pneumonia (ciOP) (Histopathology 2022;80:279):
- Also known as collagenized organizing pneumonia, cicatricial variant of organizing pneumonia, fibrosing organizing pneumonia, scarred organizing pneumonia
- Chronic fibrotic changes of conventional organizing pneumonia with formation of dense collagen fibers within the alveolar space, with no architectural destruction
ICD coding
Epidemiology
- Incidence of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is 6 - 9 per 100,000 (Medicine (Baltimore) 1995;74:201)
- No sex predominance
- Median age at onset is 50 - 60 years old (N Engl J Med 1985;312:152, Chest 2011;139:893, Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2007;11:689)
- No association with smoking history
- Most patients are previously healthy individuals and lack history of lung disease
Sites
- Bilateral or unilateral lobes of the lung
Pathophysiology
- Organizing pneumonia is a repair process (wound healing) of the lung in response to preceding alveolar injury (Thorax 2000;55:318, Eur Respir J 2006;28:422)
- Injury to capillary endothelial cells and alveolar epithelial cells results in the leakage of plasma protein, especially coagulation factors
- Intra-alveolar coagulation of proteins and coagulation factors generate fibrin clotting on alveolar surfaces
- Fibroblasts / myofibroblasts migrate into the damaged area, proliferate and generate loose fibrosis in the form of a small polyp
- IL6, IL8 and TGFβ1 may play an important role in pathogenesis (Adv Exp Med Biol 2016;911:77)
- Galectin 9 and regulatory T cells are increased in the lung with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (Lung 2015;193:683)
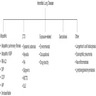
Etiology
- Organizing pneumonia can be a complication or lung manifestation of other diseases (Thorax 2000;55:318, Chest 2011;139:893, Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2007;11:689, J Thorac Imaging 2006;21:22)
- Idiopathic: cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
- Infection: bacterium / fungus / virus / parasite, pneumonia, lung abscess, empyema
- Other interstitial lung disease: nonspecific interstitial pneumonia, hypersensitivity pneumonitis, eosinophilic pneumonia, diffuse alveolar damage
- Autoimmune disease: rheumatoid arthritis, Sjögren syndrome, polymyositis / dermatomyositis, Sweet disease, etc.
- Aspiration
- Drug reaction, fume and toxic exposure
- Radiation
- Inflammatory bowel disease: Crohn's disease, ulcerative colitis
- Neoplasm: primary or metastatic lung cancer, lymphoma / leukemia, myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS)
- Lung infarction
- Secondary organizing pneumonia is much more common than cryptogenic organizing pneumonia; 6.5:1 (Ann Transl Med 2020;8:763)
Diagrams / tables
Clinical features
- Mild and slowly progressive respiratory failure (Chest 2011;139:893, N Engl J Med 1985;312:152, Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2007;11:689)
- Dry cough
- Dyspnea
- Malaise, fatigue and fever
- Duration of symptoms more than 3 months
- Abnormal chest auscultation
- End inspiratory fine crackles in affected lobes
- Restrictive pattern is often observed in pulmonary function tests; however, the abnormality is slight or within the normal range in 30% of cases (Chest 2011;139:893, N Engl J Med 1985;312:152)
- Decreased forced vital capacity (FVC)
- Decreased diffusing capacity of the lung for carbon monoxide (DLCO)
Diagnosis
- Based on clinical features, radiology and histopathology (Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2002;165:277):
- Clinical investigation for a possible cause of the disease is necessary
- Surgical lung biopsy or transbronchial lung biopsy is required to establish a firm diagnosis since the clinical and radiological findings are often not specific
- However, a biopsy may not be necessary if the clinical and radiological features are suggestive enough
Laboratory
- Increased serum surfactant proteins A and D
- Negative serum antibodies of connective tissue diseases and hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- Reference: Respiration 2019;98:534
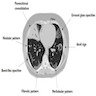
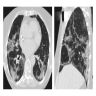
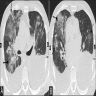
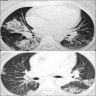
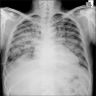
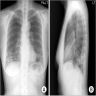
Radiology description
- Simple chest radiography
- Bilateral or unilateral ground glass opacity and consolidation
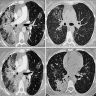
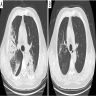
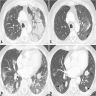
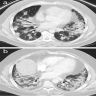
- High resolution computed tomography (Respirology 2016;21:810, Chest 2017;151:1356)
- Typical pattern:
- Patchy ground glass opacity and consolidation with / without air bronchogram
- Often bilateral and asymmetrical
- Often peripheral and migratory
- Size varies from a few centimeters to a whole lobe
- Typical organizing pneumonia sometimes looks similar to eosinophilic pneumonia, pulmonary lymphoma and lepidic adenocarcinoma
- Less common patterns:
- Focal organizing pneumonia: nodular or mass-like consolidation mimicking lung cancer (Int J Clin Exp Pathol 2015;8:511)
- Infiltrative organizing pneumonia: diffuse infiltrative opacity
- Reversed halo sign: central ground glass opacity surrounded by round consolidation
- Crazy paving pattern: areas of ground glass opacities superimposed to focal thickening of pulmonary parenchyma
- Progressive fibrosis pattern: subpleural basal reticulations and architectural distortion, mimicking nonspecific interstitial pneumonia and usual interstitial pneumonia
- Perilobular pattern: curved or arcade-like bands of parenchymal consolidation with blurred borders and thickening of the interlobular septa, resembling a Roman arch
- Linear and band-like opacities: thick radial bands of consolidation containing an air bronchogram or subpleural curvilinear bands, parallel to the pleura
- Typical pattern:
Radiology images
Prognostic factors
- Good prognosis but frequent relapse; 20 - 58% with both cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and secondary organizing pneumonia relapse (Chest 2011;139:893, N Engl J Med 1985;312:152, Int J Tuberc Lung Dis 2007;11:689)
- Relapse predictors (Respiration 2007;74:624, Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2015;78:190, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:571, Chest 1998;114:1599):
- Delay of corticosteroid administration
- Shorter maintenance of corticosteroid dose
- Hypoxemia: lower PaO2, lower PaO2/FiO2 ratio
- Lower serum total protein
- Lower forced vital capacity (FVC)
- Multifocal opacity on radiology
- Relapse predictors (Respiration 2007;74:624, Tuberc Respir Dis (Seoul) 2015;78:190, Am J Respir Crit Care Med 2000;162:571, Chest 1998;114:1599):
- Rarely progresses to severe respiratory failure and death
- Myelodysplastic syndrome (MDS) related organizing pneumonia may be associated with worse prognosis
- Cicatricial form of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is more progressive or persistent and resistant to treatment (Hum Pathol 2017;64:76)
Case reports
- 23 year old woman with organizing pneumonia following influenza B (BMC Infect Dis 2017;17:572)
- 43 year old woman with organizing pneumonia related to trastuzumab (Springerplus 2016;5:1964)
- 57 year old man with severe organizing pneumonia following COVID-19 (Thorax 2021;76:201)
- 64 year old woman with organizing pneumonia related to pembrolizumab (Drug Target Insights 2016;10:9)
- 66 year old man with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and atypical imaging findings (Case Rep Pulmonol 2020;2020:2094625)
- 70 year old man with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia presenting with mass-like lesion (J Int Med Res 2020;48:300060520920068)
- 74 year old woman with rapidly progressive cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (Intern Med 2017;56:1185)
Treatment
- Most with cryptogenic organizing pneumonia and secondary organizing pneumonia completely recover with oral corticosteroids (N Engl J Med 1985;312:152, Chest 2011;139:893)
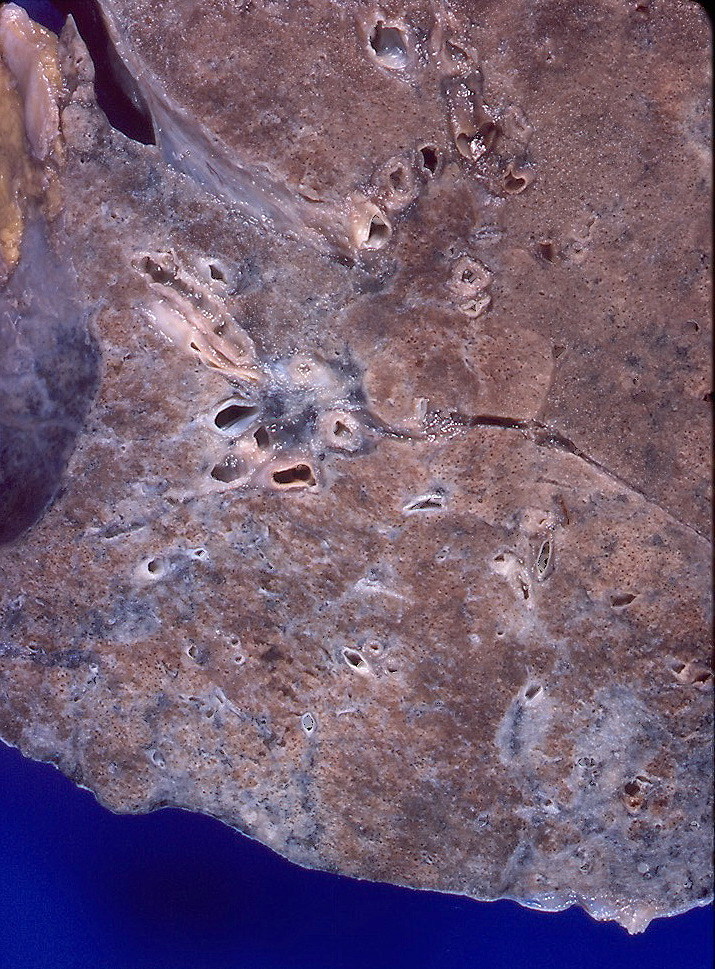
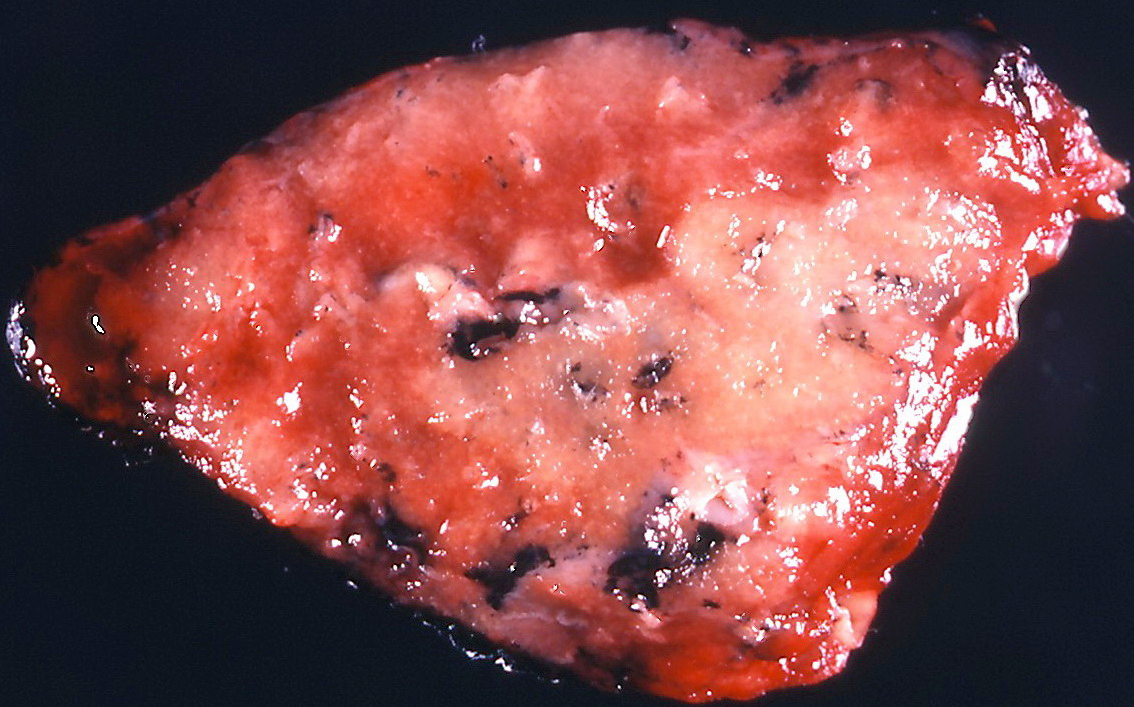
Gross description
- Multiple patchy fibrotic lesions
- Ill defined, soft to firm gray areas
- Volume of the lung is usually normal
- Other changes overlap with secondary organizing pneumonia
Gross images
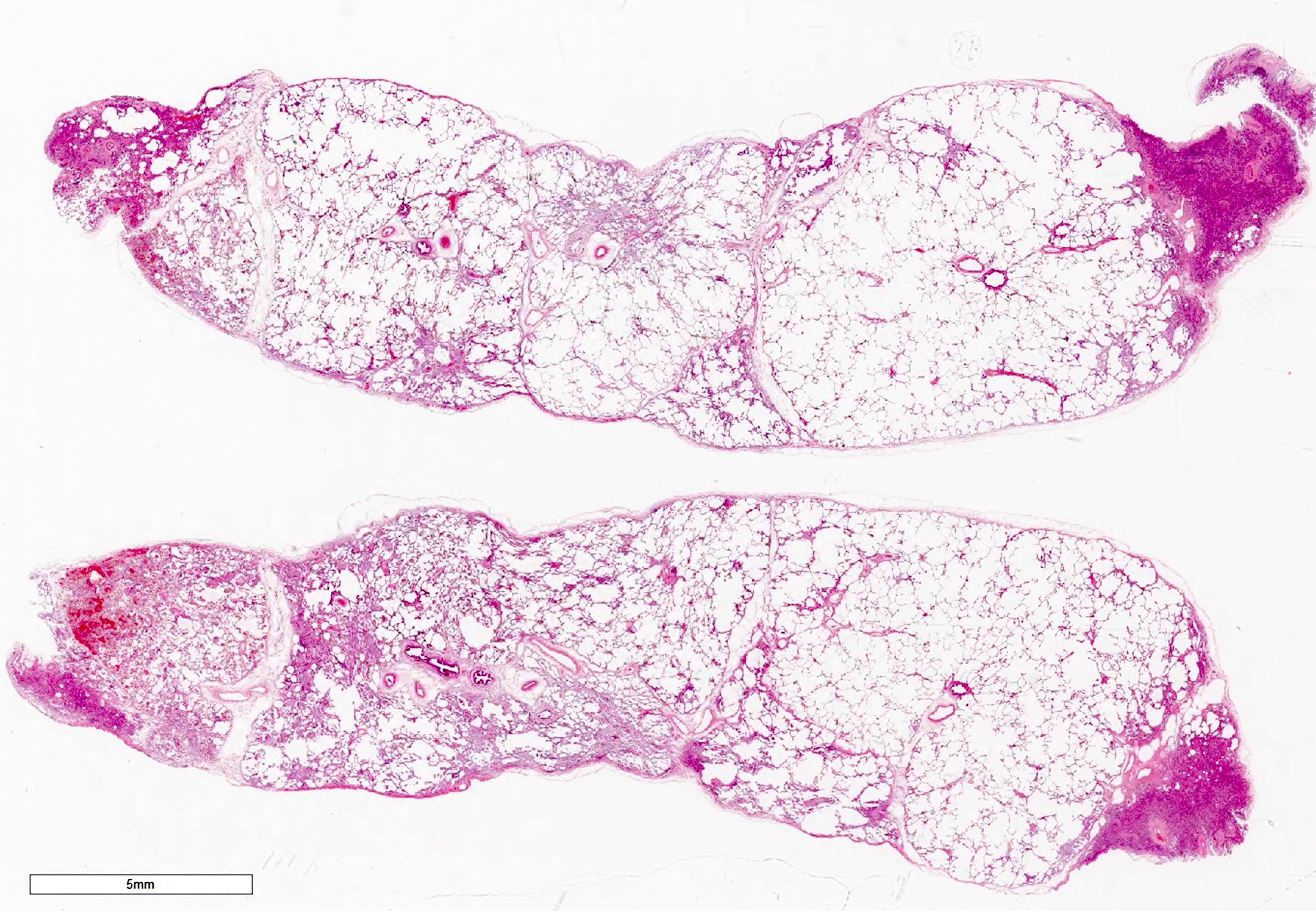
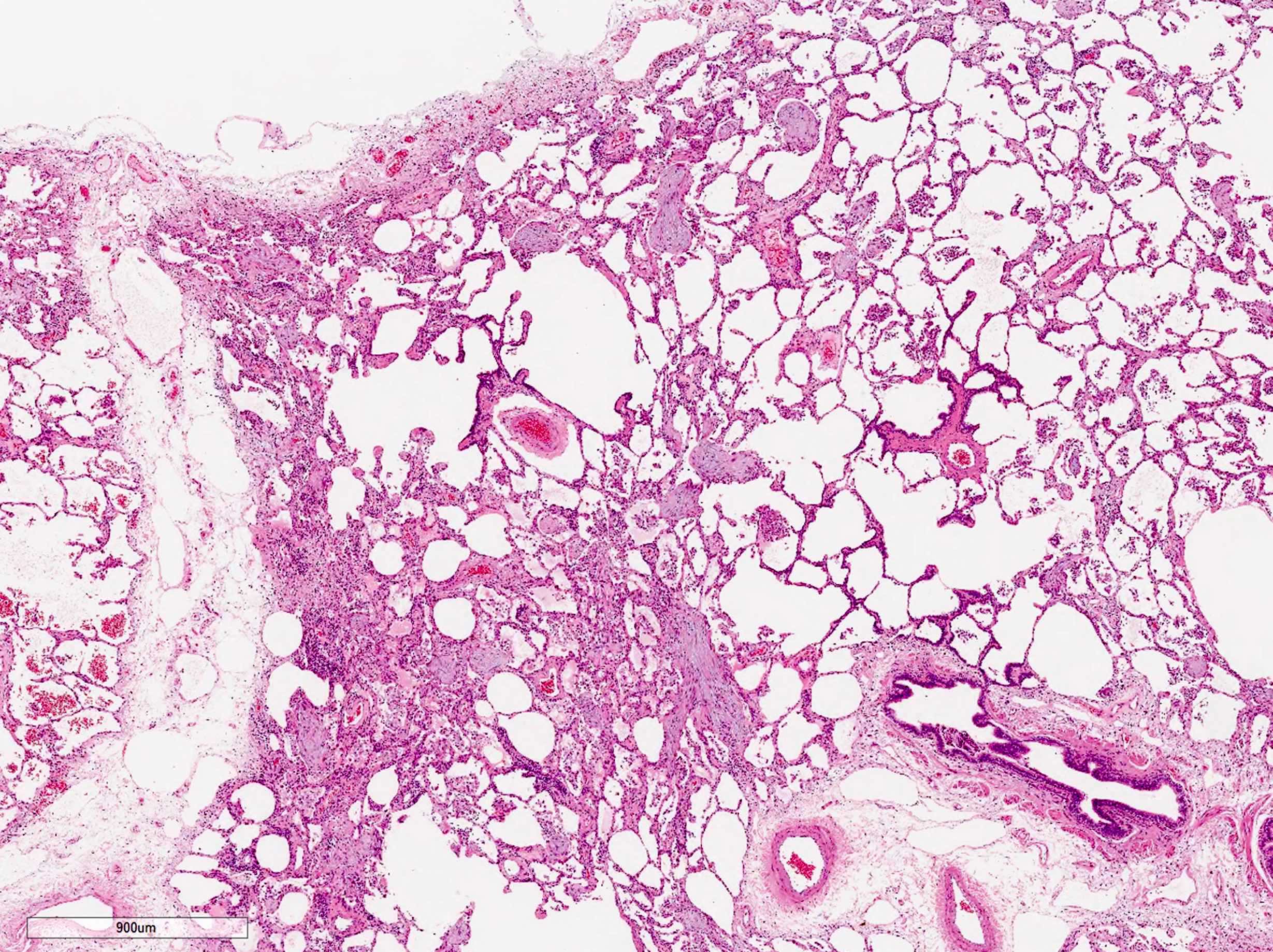
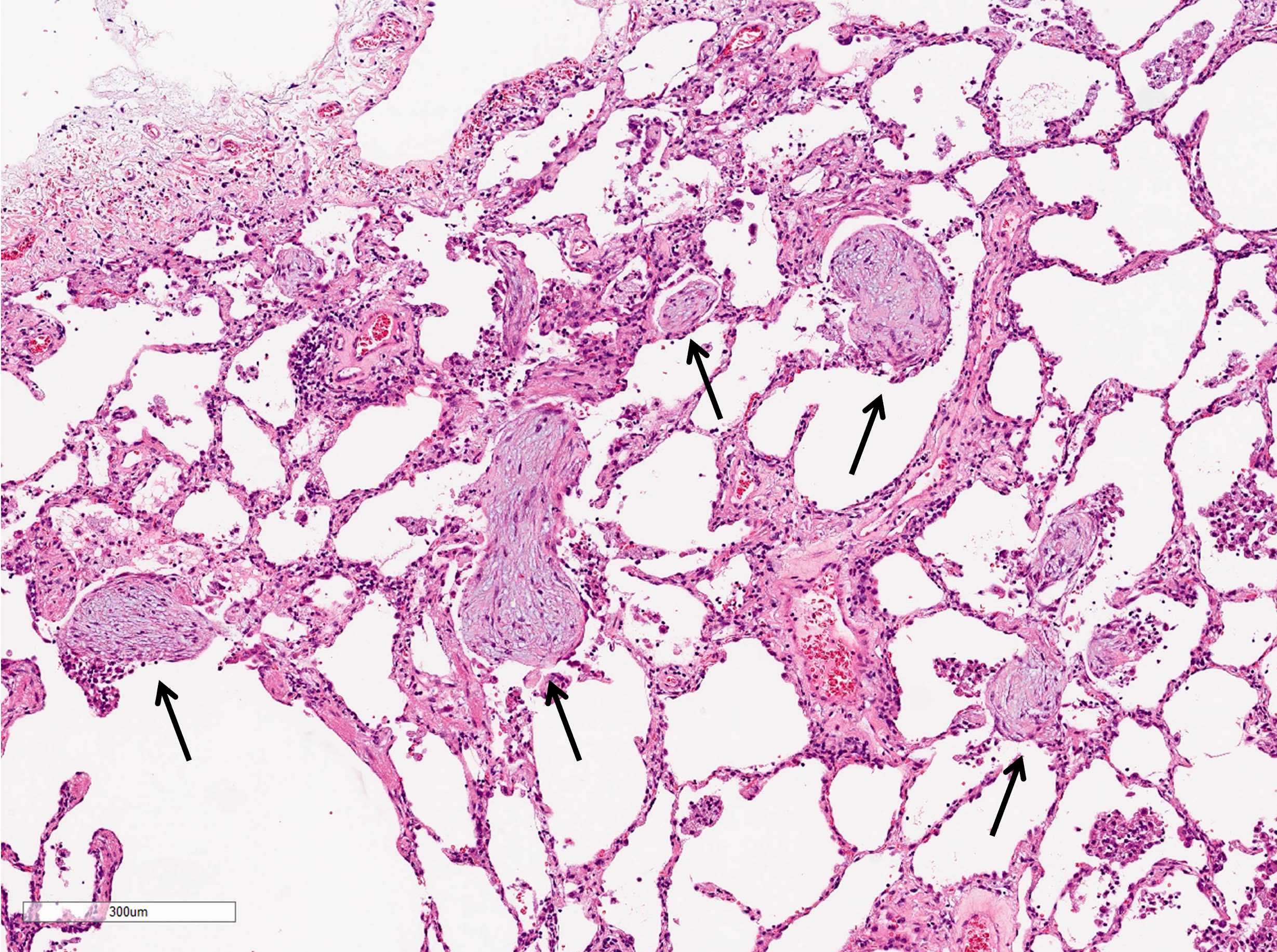
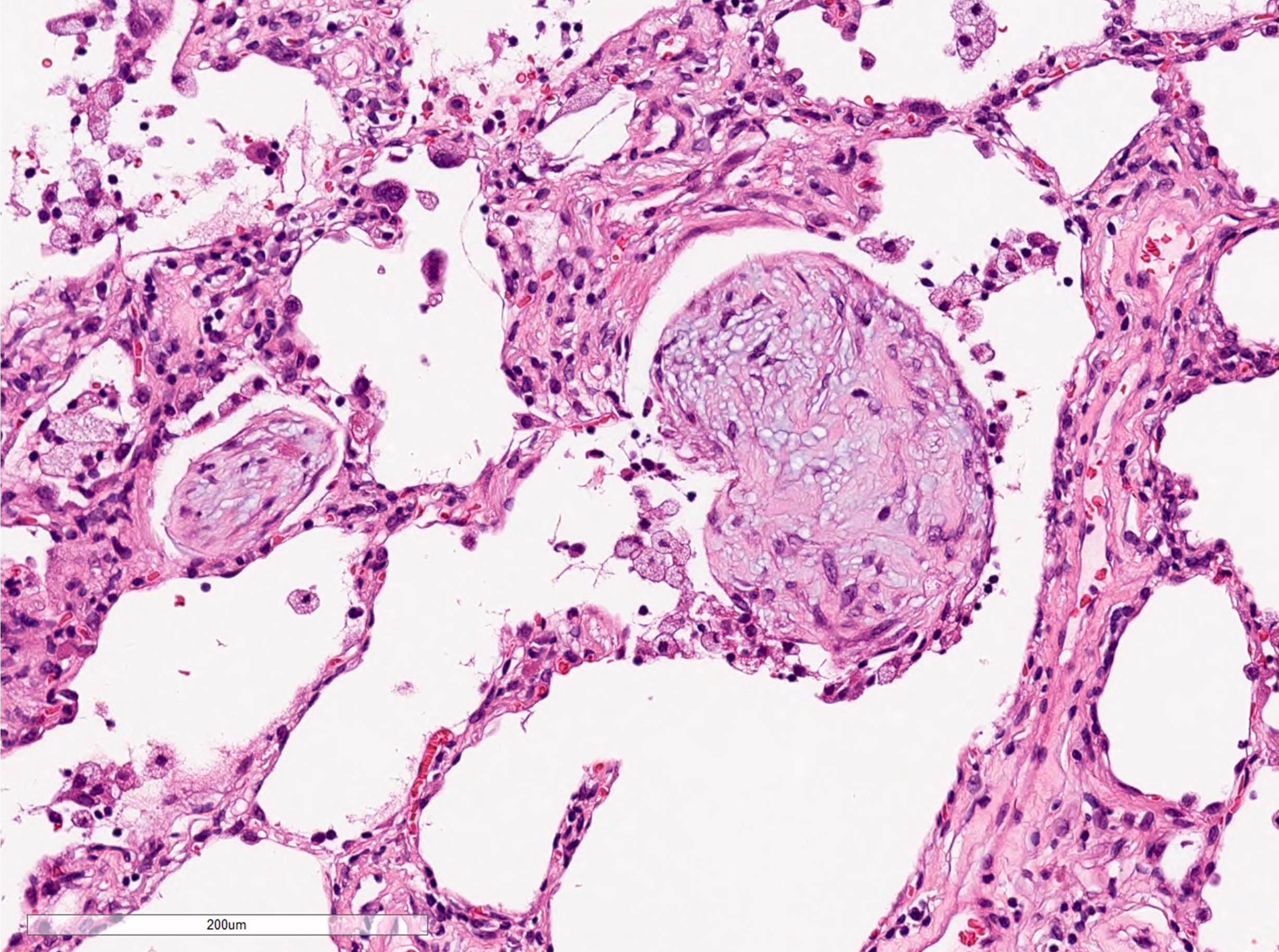
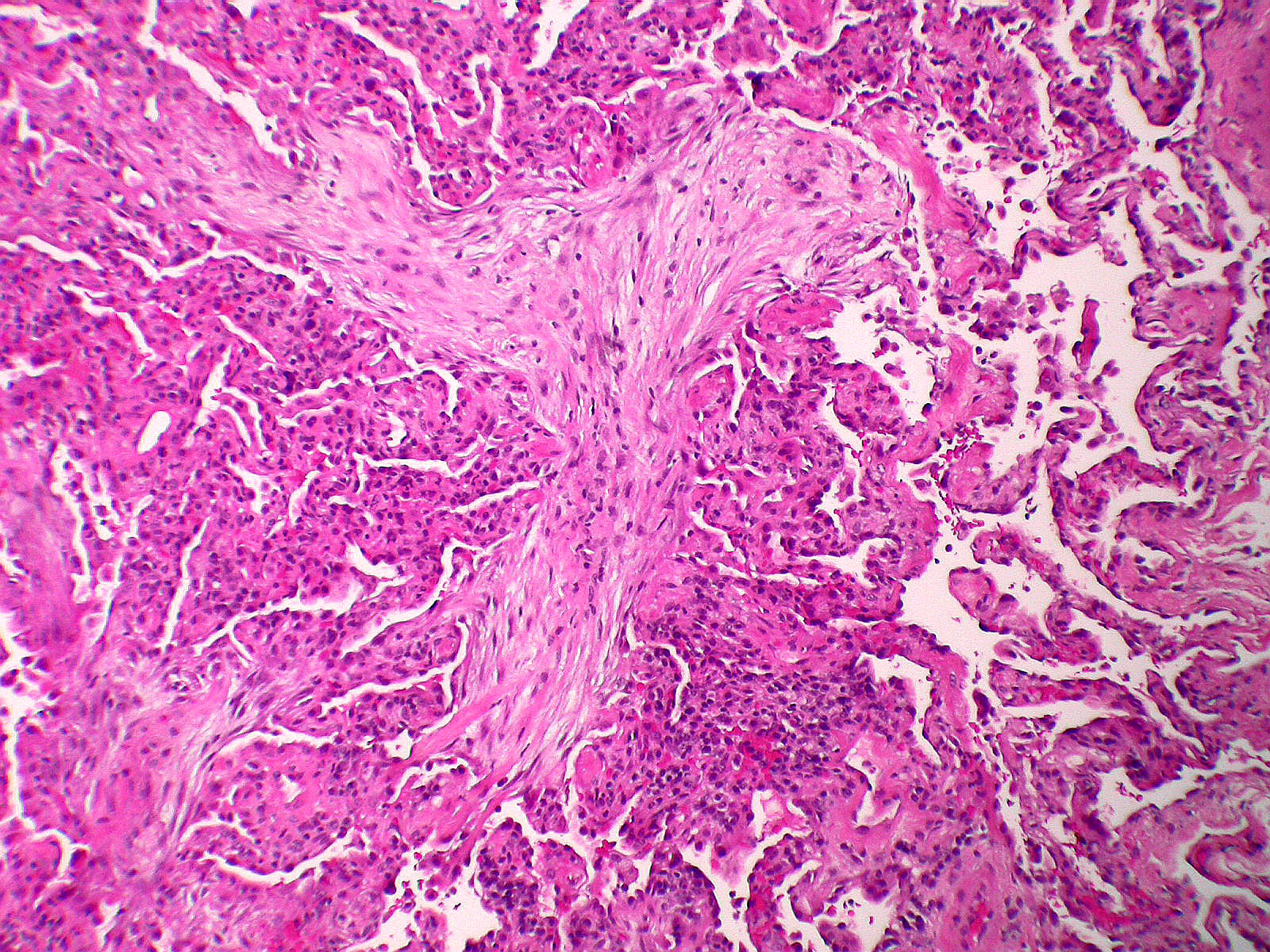
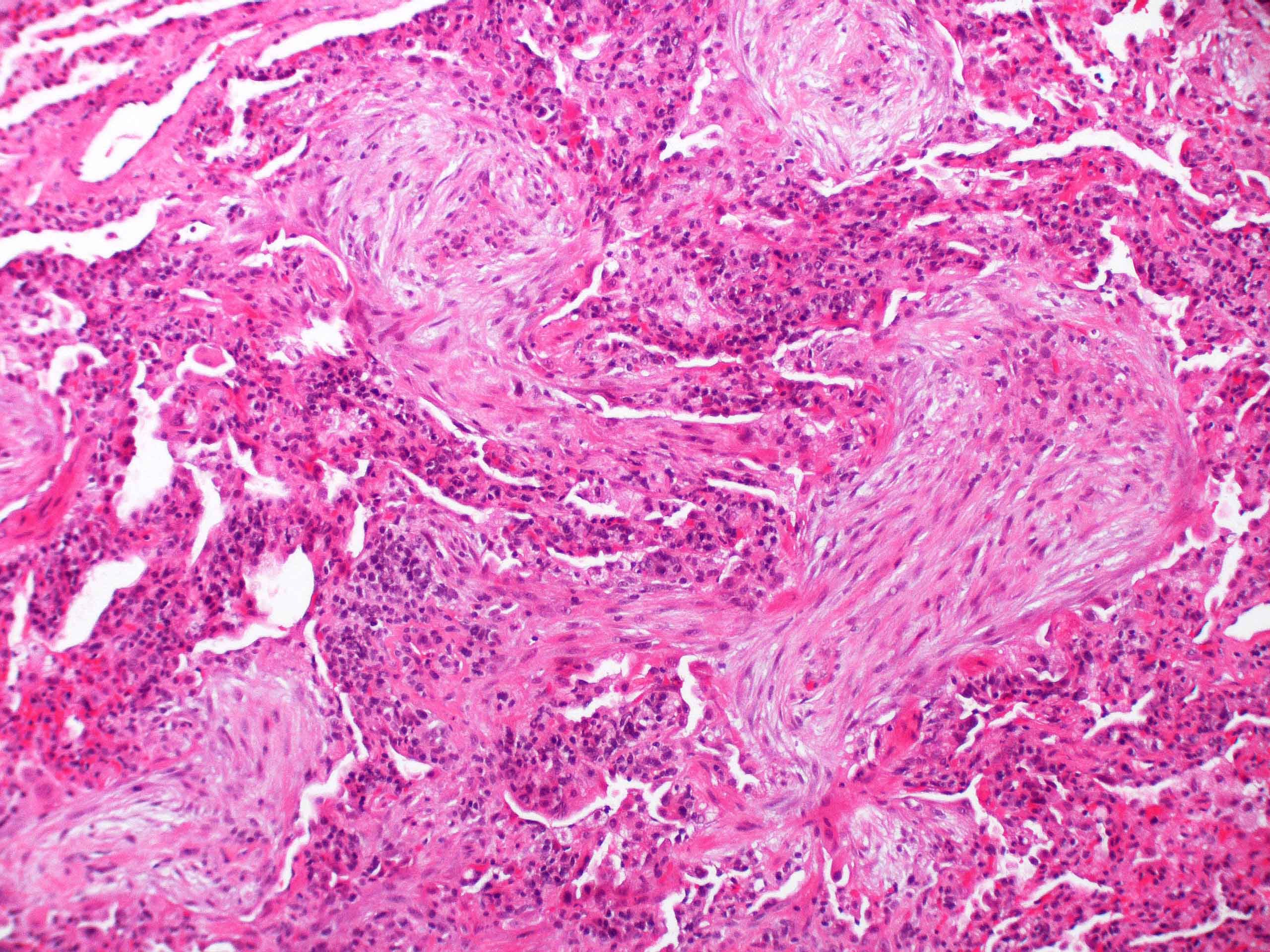
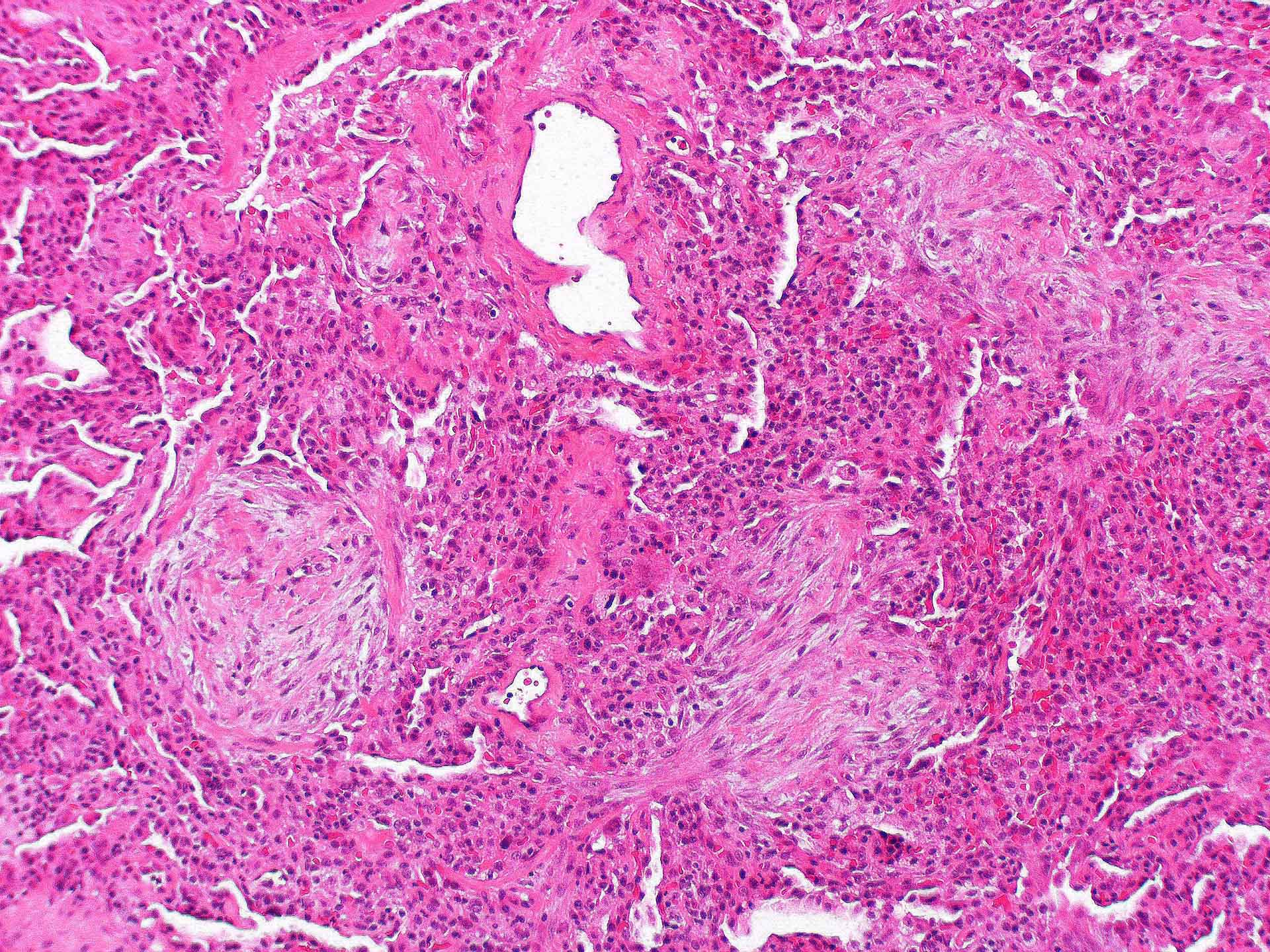
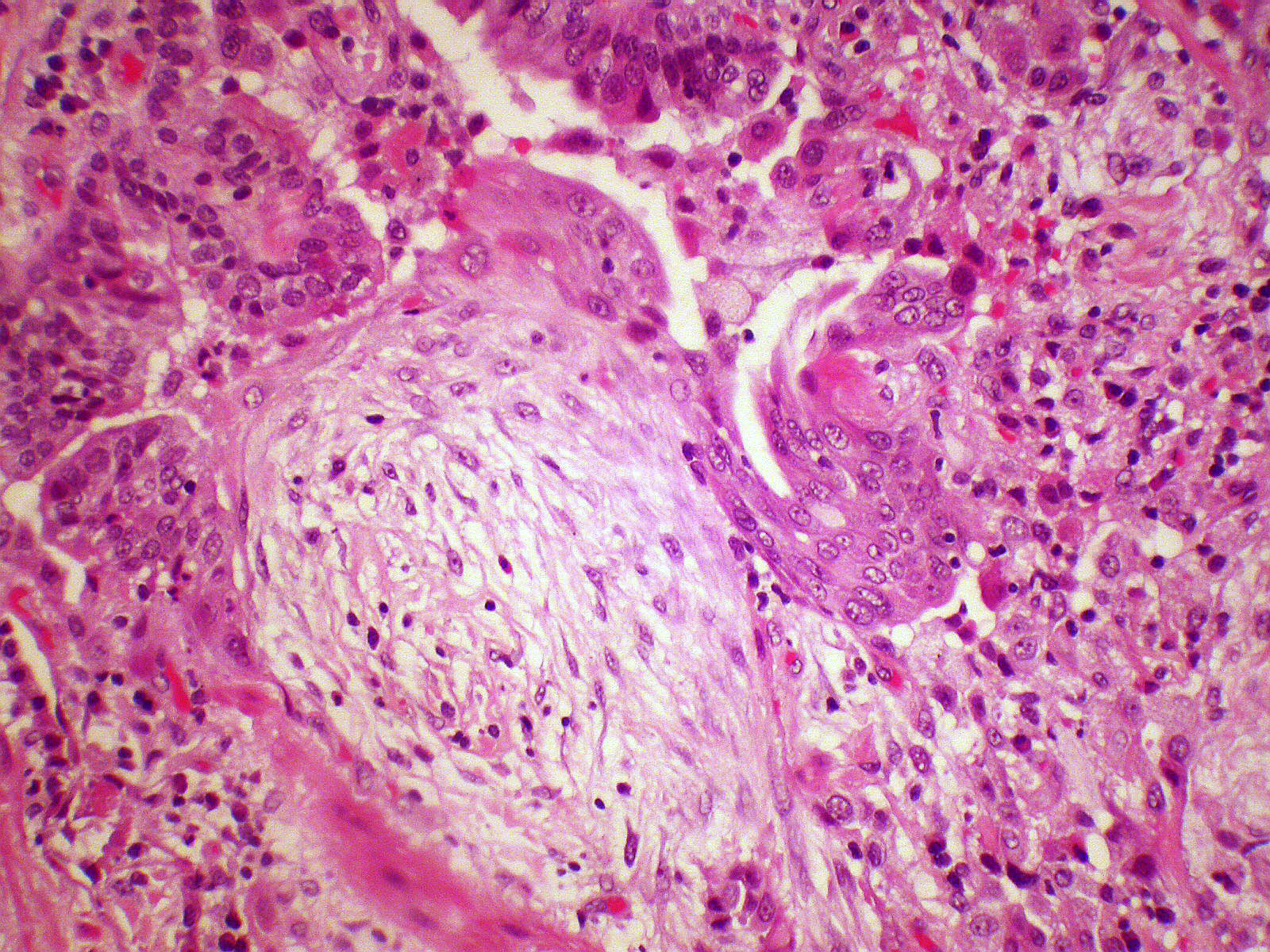
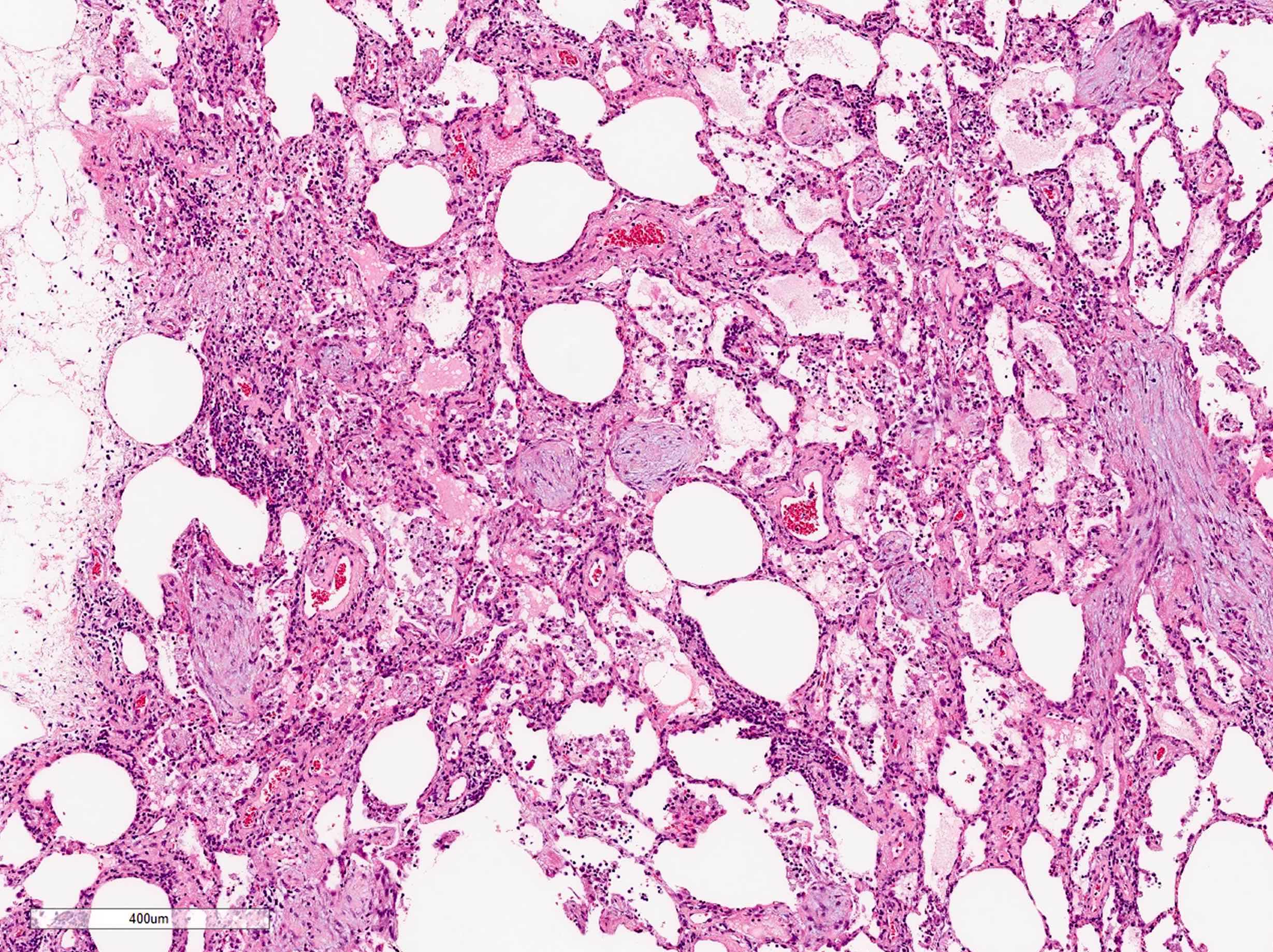
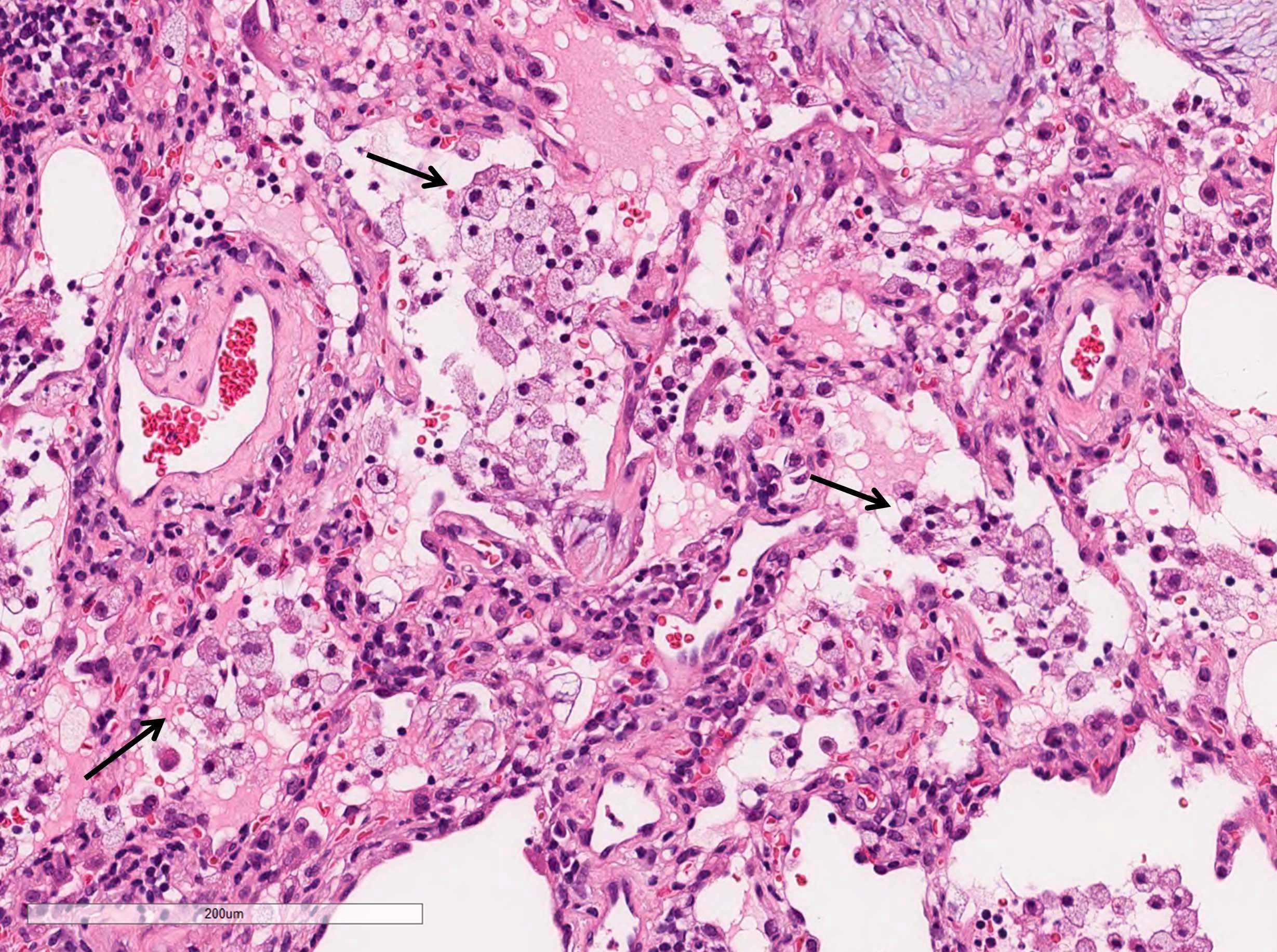
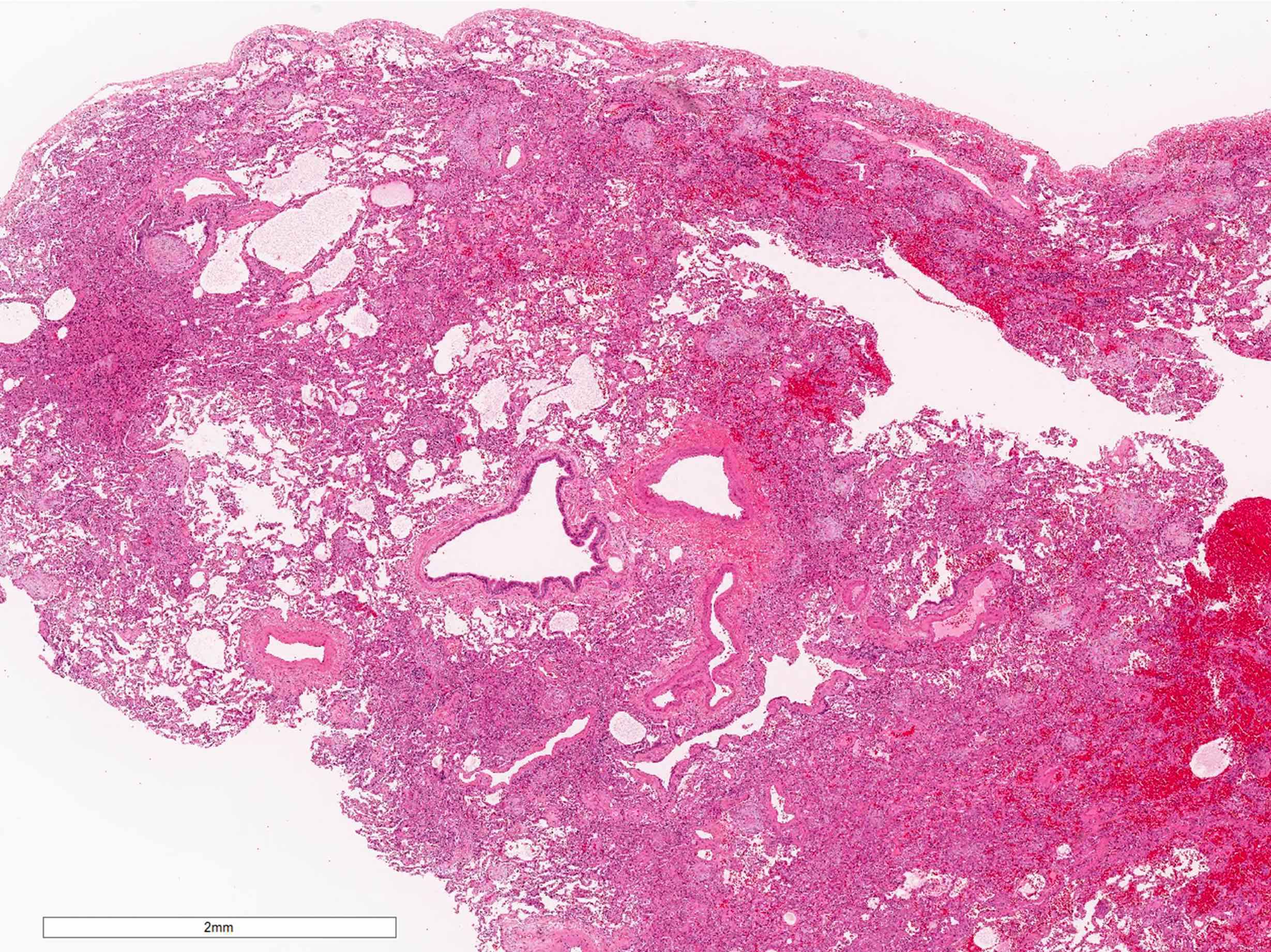
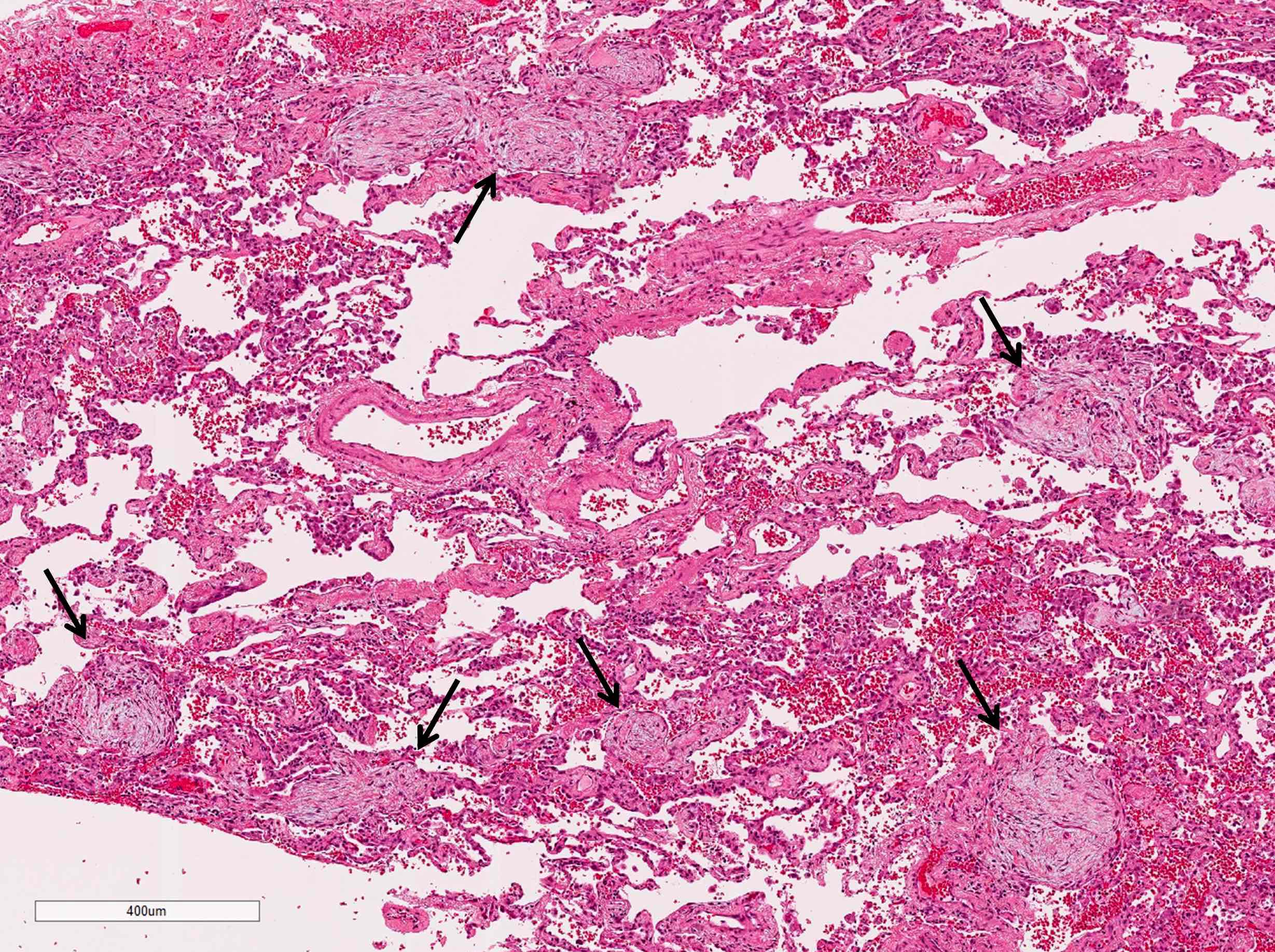
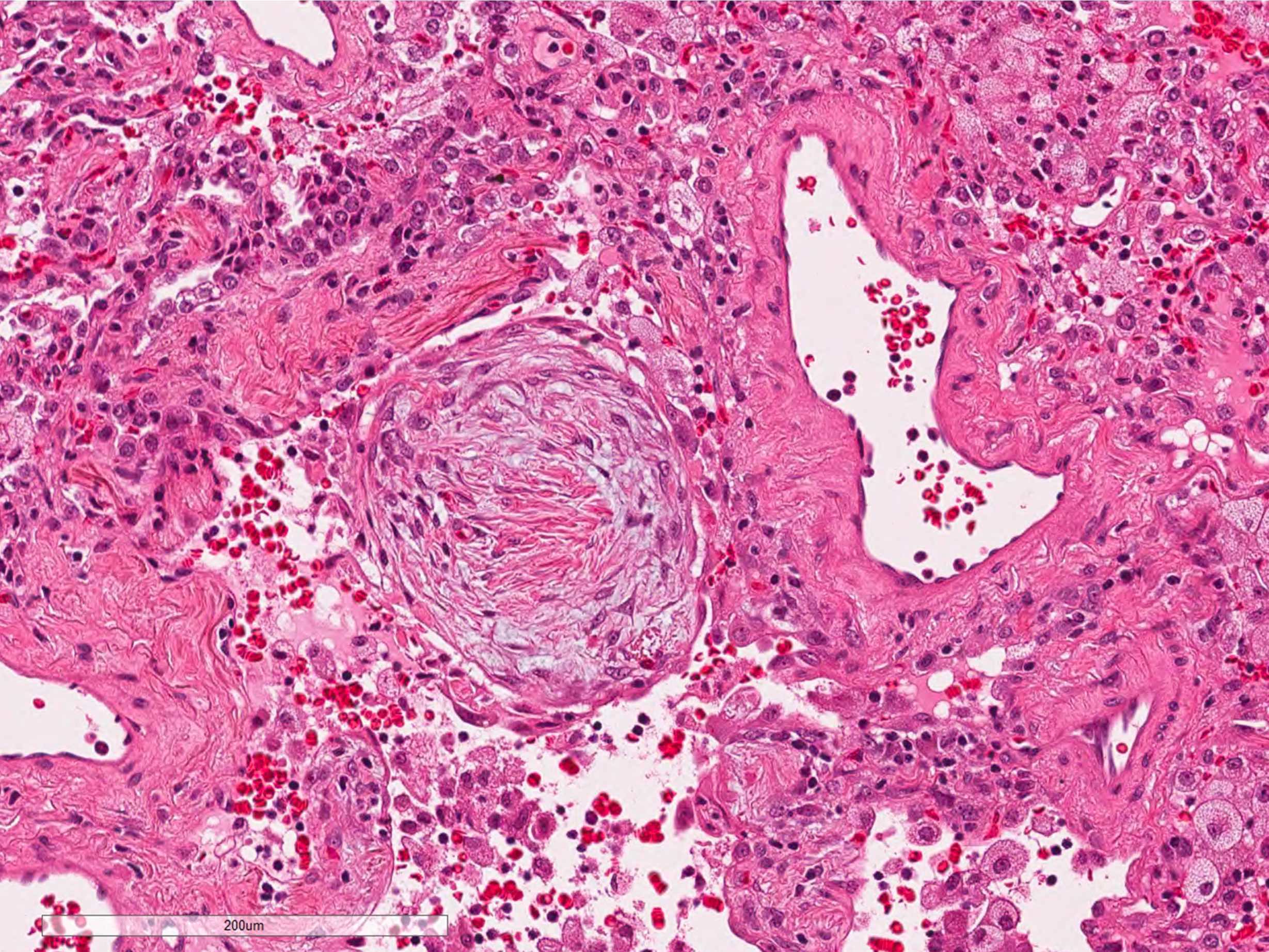
Microscopic (histologic) description
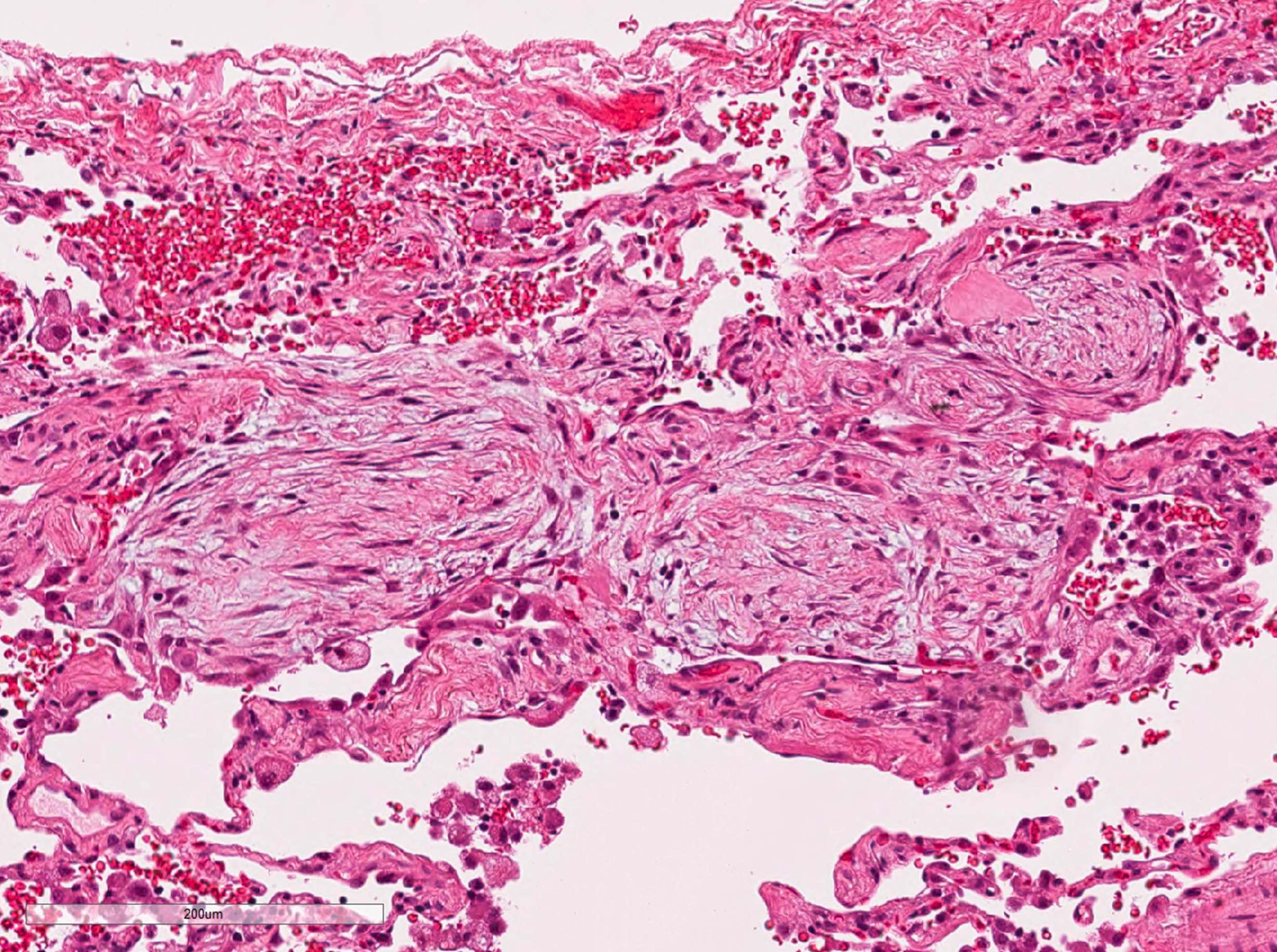
- Organizing pneumonia (Semin Respir Crit Care Med 2012;33:462):
- Fibroblastic plugs in alveolar sacs and ducts (organizing pneumonia) and bronchiolar lumen
- Formed by spindled fibroblasts in pale staining matrix of immature loose collagen with polypoid shape (Masson body) or serpiginous or elongated form
- Organizing pneumonia sometimes extends from one alveolus to the next through interalveolar fenestrae (butterfly pattern)
- Mild to moderate cellular infiltrate in background (Eur Respir J 2006;28:422, Clin Med Insights Circ Respir Pulm Med 2016;9:123):
- Thickened alveolar septa with lymphocytes, plasma cells and histiocytes
- Alveolar architecture is usually preserved in cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
- Because interstitial dense fibrosis, architectural destruction and honeycomb change are not components of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia, the organizing pneumonia lesion is likely to be secondary to other lung disease if these findings are mixed or overlap (J Clin Pathol 2009;62:387)
- Airspace changes (Thorax 2000;55:318):
- Foamy macrophage accumulation in surrounding airspace may be present
- Occasional fibrin deposition
- If prominent, the lesion is more likely to be an infection, eosinophilic pneumonia (especially after corticosteroids), vasculitis (e.g., granulomatosis with polyangiitis) or acute fibrinous organizing pneumonia (AFOP)
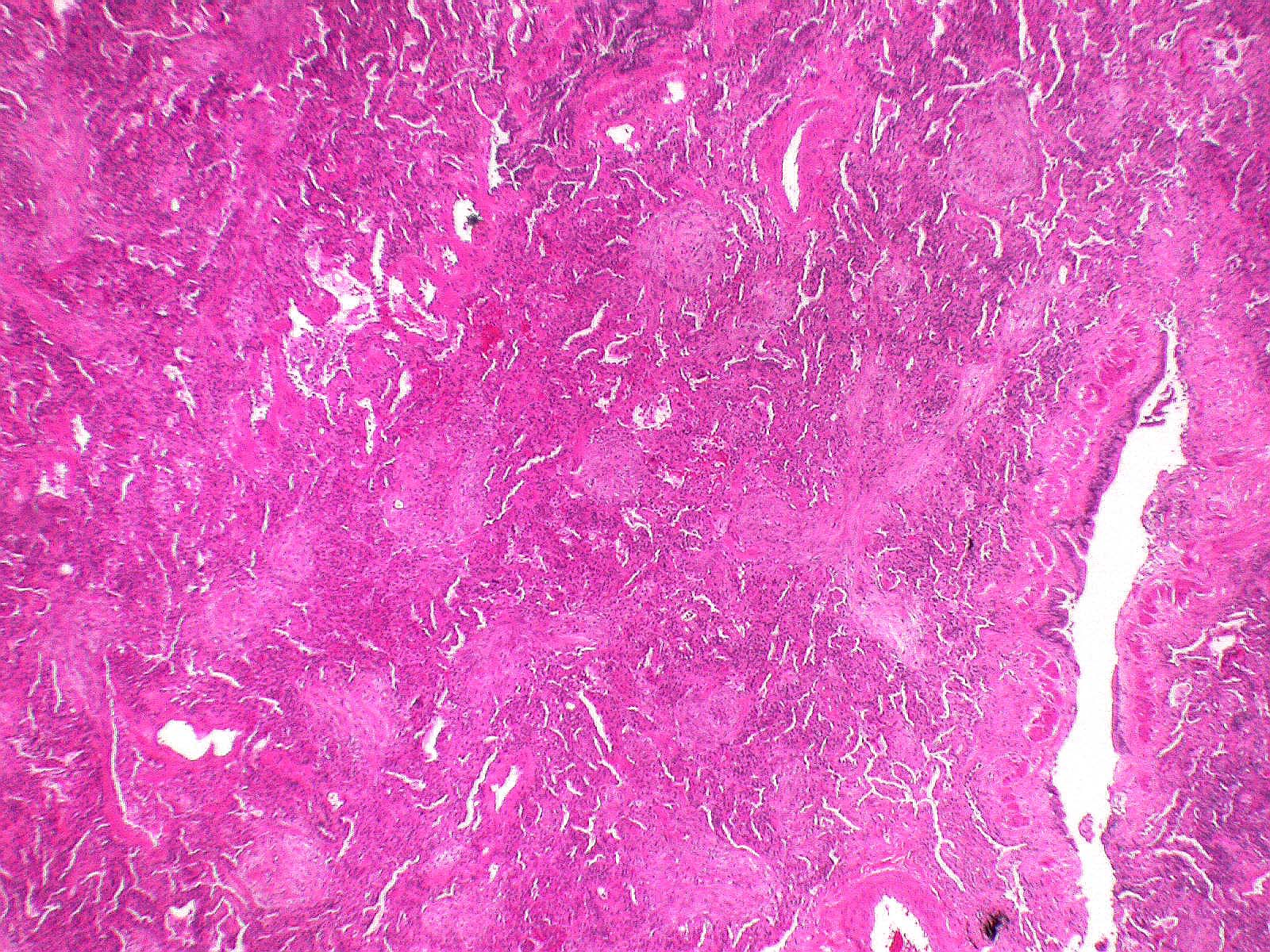
- Cicatricial form of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia (Hum Pathol 2017;64:76):
- Organizing granulation tissue is collagenized or hyalinized and harbors eosinophilic, lamellar and dense fibers
- Airspaces can be filled with collagenized organizing pneumonia but alveolar architecture is mostly preserved
Microscopic (histologic) images
Positive stains
- Elastica van Gieson staining is helpful to evaluate if architecture of alveoli is preserved or not
Negative stains
- Organizing polyps are negative for elastica van Gieson staining except in cicatricial variant
Electron microscopy description
- Type I pneumocyte necrosis in the early phase (Thorax 2000;55:318)
Videos
Cryptogenic organizing pneumonia
Focal organizing pneumonia
Fibrosing organizing pneumonia
Sample pathology report
- Lung, right middle lobe, transbronchial biopsy:
- Organizing pneumonia (see comment)
- Negative for granuloma, vasculitis and malignancy
- Comment: Based on the provided patient information, the diagnosis of cryptogenic organizing pneumonia is favored. However, secondary organizing pneumonia from various causes (infection, drug toxicity, autoimmune disease, malignancy, etc.) needs to be excluded clinically.
Differential diagnosis
- Acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP) / acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS):
- Diffuse alveolar damage (DAD) of AIP or ARDS may have a prominent organizing pneumonia (organizing DAD) radiologic pattern
- If organizing pneumonia is so diffusely distributed that it almost completely occupies the surgical sample, organizing DAD should be favored
- Hyaline membranes, architectural destruction and myofibroblastic aggregation with less extracellular matrix are other clues of DAD pattern
- Eosinophilic pneumonia:
- Intra-alveolar eosinophils
- Pink macrophages (not foamy), more fibrin, frequent type II pneumocyte atypia
- Granulomatosis with polyangiitis:
- Geographic necrosis, hemorrhage, capillaritis
- More eosinophils
- More fibrin deposition
- Inflammatory myofibroblastic tumor:
- Inflammatory pseudotumor (IgG4 related / NOS):
- Nonspecific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP):
- Organizing pneumonia is often seen in NSIP pattern but it does not exceed more than 20% of area
- Interstitial change (cellular or fibrotic) is more predominant
- Spindle cell carcinoma (sarcomatoid carcinoma):
- Nodule / mass of atypical spindle cells
- Usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP):
- Fibroblastic focus in UIP pattern is another type of myofibroblastic aggregation but usually adjacent to dense fibrotic lesion, unlike in organizing pneumonia
- Dense interstitial fibrosis, architectural destruction and honeycomb change are other clues of UIP
Additional references
Board review style question #1
Which of the following findings is against the histologic diagnosis of organizing pneumonia?
- Interstitial mononuclear infiltrate
- Fibrin deposition
- Fibroblastic focus
- Foamy macrophage accumulation
- Masson body
Board review style answer #1
C. Fibroblastic focus. This finding is rather suggestive for usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) pattern.
Comment Here
Reference: Organizing pneumonia
Comment Here
Reference: Organizing pneumonia
Board review style question #2
A 70 year old woman presented with cough, chest tightness and dyspnea. She was a former smoker with 20 pack years. High resolution CT scan of the chest showed bilateral patchy ground glass opacities in the lungs. A transbronchial biopsy was performed. What is the pathologic diagnosis based on the image provided?
- Bronchial asthma
- Desquamative interstitial pneumonia
- Diffuse alveolar damage
- Organizing pneumonia
- Respiratory bronchiolitis
Board review style answer #2
D. Organizing pneumonia. Fibroblast plug is the diagnostic feature for organizing pneumonia.
Comment Here
Reference: Organizing pneumonia
Comment Here
Reference: Organizing pneumonia